Using MySQL Autopilot to improve price performance for OLTP workloads
MySQL HeatWave is a fully managed database service with an integrated query accelerator which enables organizations to efficiently run transaction processing, real-time analytics and machine learning on data stored inside MySQL database or in the object store.
MySQL Autopilot is a feature of MySQL HeatWave which provides workload-aware, machine learning-based automation of various aspects of the application lifecycle, including provisioning, data management, query execution, and failure handling. It improves performance of the application reduces cost by predicting the optimal configuration to run a workload, and automates many database administration tasks. MySQL HeatWave leverages MySQL Autopilot to achieve high performance and scalability for OLTP, OLAP and workloads on object store.
MySQL Autopilot recently added a new capability Auto Shape Prediction that automatically collects the most recent OLTP query execution metrics and uses advanced machine learning models to predict the MySQL database instance shape for optimal OLTP transaction performance. Auto Shape Prediction continuously monitors running workloads to provide suggestions that adapt to your evolving workload patterns, allowing you to maintain the best OLTP price performance.
Challenges to get the right hardware configuration for OLTP workloads
To determine the right hardware configuration, you need to know the characteristics of your OLTP workload. This is not an easy task especially with today’s continuously dynamic changes of users demands.
Running on a compute shape that does not meet the requirements of a workload has no direct impact on the server functionality, however it has a significant impact on performance and/or cost. On one hand, using a server shape with inadequate memory or CPU leads to significantly degraded performance due to frequent buffer pool misses (long IO) and/or overutilization of CPU. On the other hand, over-provisioning server shape is a waste of server (DRAM, CPU) resources and would incur additional costs. Right sizing the server shape requires analyzing the workload in production as the workloads dictate the ideal size (read/write ratio, file size, access patterns). Moreover, the workloads might evolve over time, therefore, continuous monitoring and assessment of the workload are needed.
Automating workload prediction with MySQL Autopilot
Auto Shape Prediction estimates the minimum buffer pool size for a healthy runtime via continuous workload monitoring and advanced ML techniques. The feature suggests users to upsize/downsize their MySQL shape based on the required DRAM sizes for their workload. By doing so, the workload buffer pool misses are mitigated to maintain the best performance for a given amount of DRAM capacity.
How does MySQL Autopilot predict the right buffer pool size?
Figure 1 depicts the high-level architecture of MySQL Autopilot – Auto Shape Prediction for MySQL HeatWave that analyses the workload and assesses the suitability of your current shape.
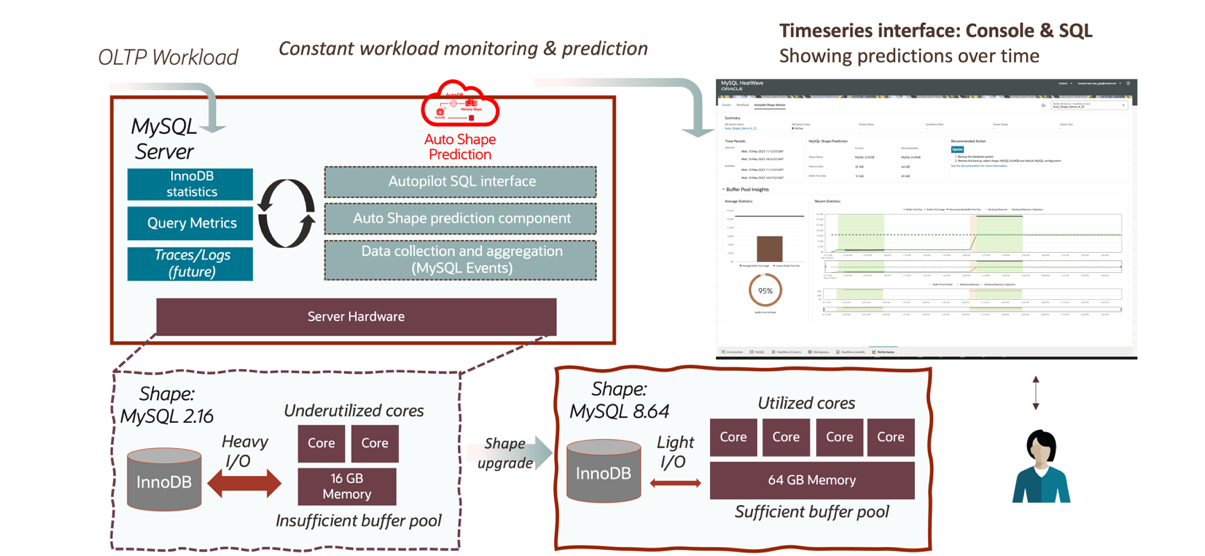

Figure 1 Auto Shape Prediction high-level architecture and user flow
Auto Shape Prediction continuously collects MySQL statistics reflecting your current workload. Statistics are collected at varying intervals, and Auto Shape Prediction creates a prediction every few minutes. If there is insufficient or no activity in each interval, or if buffer pool usage is growing, Auto Shape Prediction postpones making a prediction for that interval.
Auto Shape Prediction looks at the overall buffer pool usage, workload activity, and access patterns, and uses various ML models to predict the right MySQL shape. You can then decide to follow the recommendation that accommodates the buffer pool size needed for the workload. Not following the recommendation does not affect MySQL functionality, however, in the case where the current MySQL buffer pool size is too small, the performance of the DB System will suffer through excessive disk I/O.
How to use the Auto Shape Prediction feature?
Auto Shape Prediction is enabled by default on every DB system in MySQL HeatWave on AWS. You can access the recommendation details via the MySQL HeatWave Console or SQL interface.
Accessing Auto Shape Prediction via MySQL HeatWave console
The screenshot in Figure 2 shows the MySQL Autopilot Shape Advisor on the MySQL HeatWave on AWS console. This interactive console allows users to easily see the suggested shape recommendation. It also provides insights on usage and prediction trends where users can see the historical predictions (roughly over a week) and relevant metrics such as buffer pool hit ratio and buffer pool utilization factor to better understand their workload.
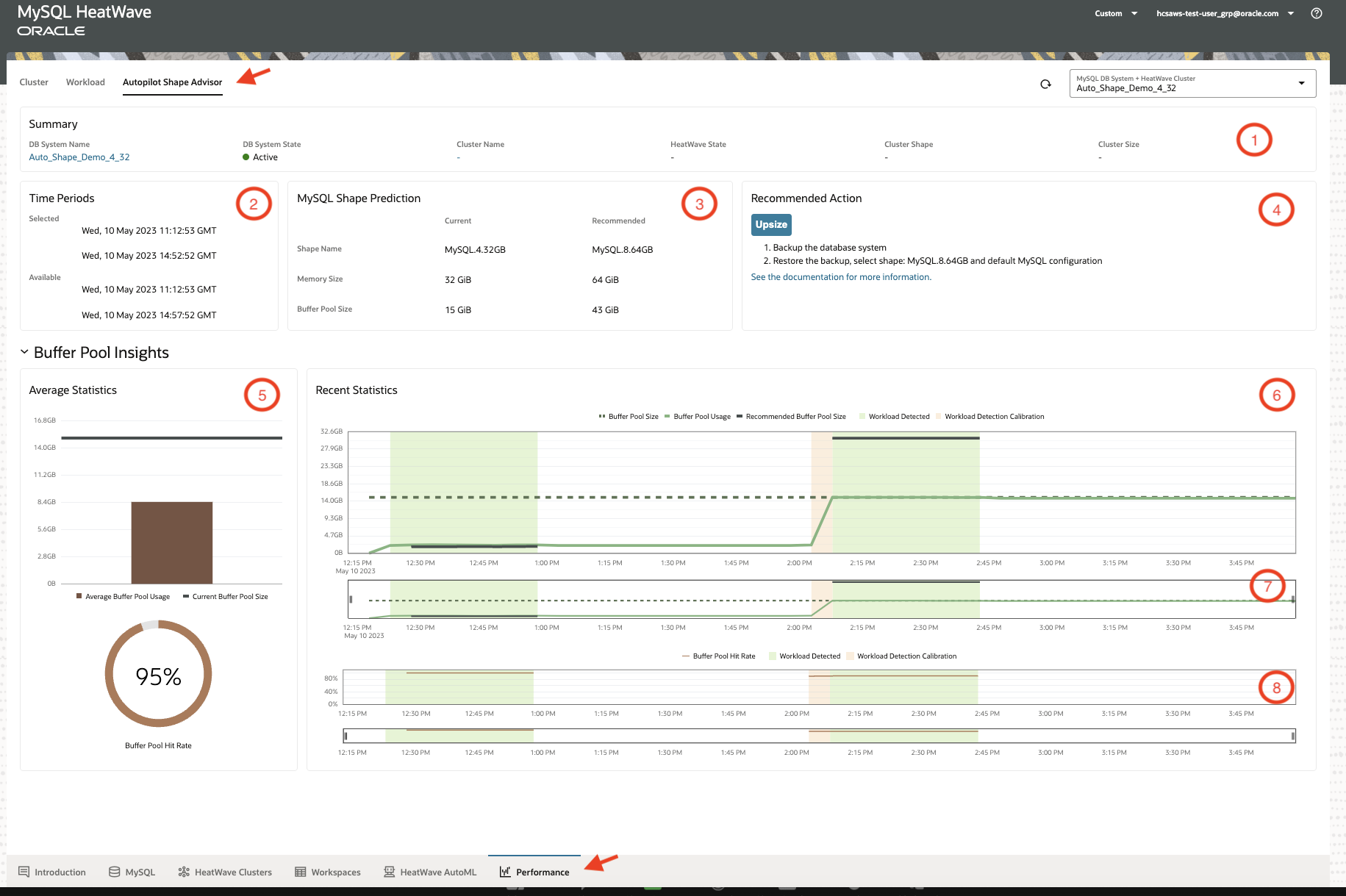
Figure 2: Auto Shape Prediction interactive console UI
To access MySQL Autopilot Shape Advisor on the console, navigate to the Performance tab and select a DB System and HeatWave Cluster from the drop-down. Then click on the Autopilot Shape Advisor tab, as shown in arrows in Figure 2.
Following describes each of the sections (numbered in Figure 2):
The top sections provide an overview of the DB system and the recommendations:
- The Summary section shows current status of the chosen DB System and HeatWave cluster if HeatWave is enabled.
- The Time Periods section displays the time period that Auto Shape Prediction data is available, and it shows that what time period has been selected in order to be used in the shape prediction process. You can select the time periods by using the horizontal scrolls (left and right slider controls) in the section marked by the number 7. Autopilot Shape Advisor data is kept for approximately seven days.
- The MySQL Shape Prediction section shows the shape recommendation for the selected time period. This recommendation includes the memory, and buffer pool size predicted and the corresponding MySQL shape.
- The Recommended Action section shows the actions needed to change to the recommended shape. There are five possible action recommendations:
- Upsize: Change the DB System to a larger MySQL shape.
- Downsize: Change the DB System to a smaller MySQL shape.
- No Change: No need to change the MySQL shape.
- Not Enough Data: There is not enough workload activity, or Auto Shape Prediction cannot make a prediction.
- Prediction Data Not Available: Auto Shape Prediction is disabled, or it is enabled but has not produced the first prediction, or the MySQL HeatWave Console data has not been refreshed within the last 5 minutes.
The lower sections under Buffer Pool Insights provide information about the buffer pool in the selected time period (you can adjust the time period by moving the slider on the graphs):
- The Average Statistics section provides average metrics over the chosen time period:
- Buffer Pool – A graph that shows Average Buffer Pool Usage and Current Buffer Pool Size. This uses the selected time period.
- Buffer Pool Hit Rate – A percentage value calculated between the selected time period.
- The Recent Statistics section provides trends over the chosen time period:
- Buffer Pool (marked by 7) – A detailed graph that shows Buffer Pool Size, Buffer Pool Usage, and Recommended Buffer Pool Size.
- Buffer Pool Hit Rate (marked by 8) – A detailed graph that shows the Buffer Pool Hit Rate between the selected time periods.
Workload markers (highlights) on the two time series graphs indicate recent activity:
- Green markers: The workload is running and stable. Good predictions.
- Orange markers: The workload is running, but it is not stable. Difficult to predict.
- No markers: No recent activity, and no predictions.
Continuous Monitoring
As previously stated, you can modify the time periods by utilizing the left and right slider controls. When the selected time intervals vary, predictions and other insights displayed in the Autopilot Shape Advisor change as well. Given that various workload could be continuously running over long periods of time, the predictions will change over time, and Autopilot Shape Advisor chooses the largest shape available during the selected time period.
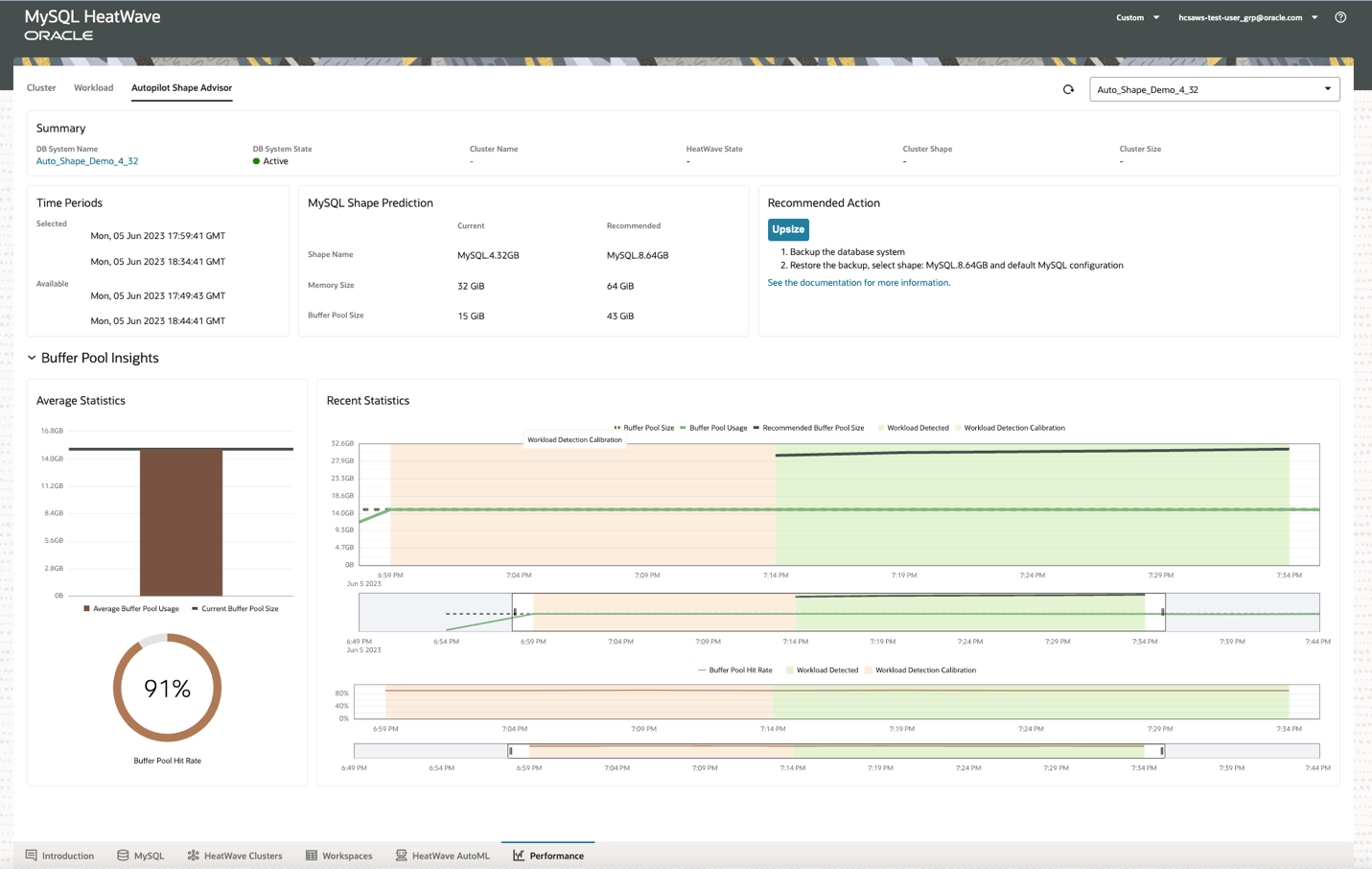
Figure 3: Auto Shape Prediction interactive console UI with an UPSIZE example
Figure 3 depicts a Benchbase Twitter benchmark conducted on MySQL.4.32GB with a scale factor of 9000. The benchmark data is around 36GB in size. And the MySQL.4.32GB machine is set up with a 15GB buffer pool.
Auto Shape Prediction recommends to UPSIZE the current MySQL shape. It predicts a buffer pool usage of 30GB is needed for the workload, which can be accommodated by a MySQL.8.64GB shape with 43GB buffer pool size.
To understand the prediction, you can use the provided buffer pool hit ratio and buffer pool utilization. In this example, throughout the active periods of the workload, the buffer pool was fully utilized (100%), and the buffer pool hit ratio was high (91%). This indicates that the workload encountered high buffer pool misses and needs a larger buffer pool.
After analyzing the graphs and explanations, you can follow the instructions in the “Recommended Actions” panel to change your MySQL instance to the suggested shape. The larger shape mitigates the performance hits because of buffer pool misses, improving the overall performance of the OLTP workload.
Summary
Right sizing the compute shape for the ever-changing demands for OLTP workloads is a time-consuming and challenging task. MySQL Autopilot – Auto Shape Prediction automatically and continuously monitor the workload and use advanced machine learning techniques to provide optimal shape recommendation for the best price performance. It also provides explanations for the predictions with insights on MySQL usage.
To learn more about MySQL Autopilot, click here
Addition Resources
