Performance Improvements in MySQL 8.0.35
The MySQL team has recently implemented changes that significantly improve the performance of the 8.0.35 version of MySQL Enterprise Edition over the Community Edition.
Benchmarks
sysbench is a tool that is widely used for database benchmarks, especially for MySQL An adaptation of sysbench was used to run various OLTP workloads on a MySQL database. In our setup, four different sysbench tests were executed, each of which captures a specific OLTP workload characteristic.
1. OLTP RO: This is a read only mode, where no UPDATE, DELETE or INSERT queries are performed. The query mix consists of:
* 10 x POINT_SELECT
* 1 x SELECT_SIMPLE_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_SUM_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_ORDER_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_DISTINCT_RANGES
2. POINT_SELECT: This has a number of point select SQL queries.
3. OLTP RW: This is a mix of both read and write SQL queries. The query mix consists of:
* 10 x POINT_SELECT
* 1 x SELECT_SIMPLE_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_SUM_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_ORDER_RANGES
* 1 x SELECT_DISTINCT_RANGES
* 1 x UPDATE_KEY
* 1 x UPDATE_NO_KEY
* 1 x UPDATE_KEY
* 1 x INSERT
* 1 x DELETE
4. UPDATE_KEY: This has a number of SQL queries that update the indexes.
Methodology
- InnoDB buffer pool large enough to hold the entire data set was used.
- sysbench data consisted of 8 tables of 10 million rows each, for a total of 80 million rows. Total data size was 20GB.
- For each scenario, a warmup was run, followed by 5 minutes of sysbench load, repeated 3 times to calculate an average of transactions/second.
- Tests were run with 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024 client connections/threads.
- Hardware consisted of 2-socket servers with Intel E5-2699 v4 CPUs (44 cores @ 2.20 GHz, 88 CPU threads).
- Operating system: Oracle Linux 7.9
Results
OLTP RO
The workload comprises of only SELECT queries – no INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE.
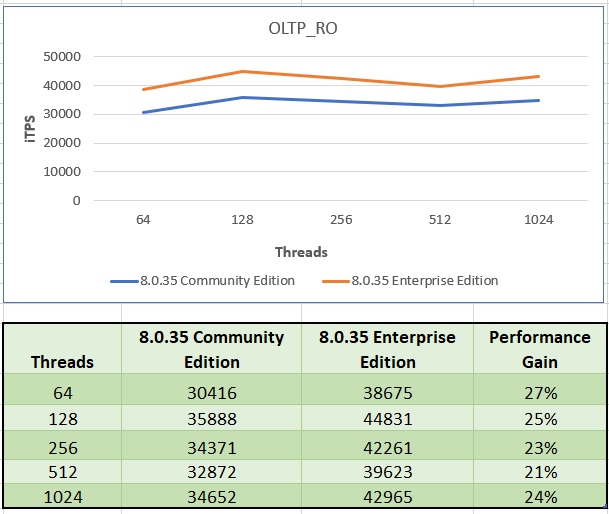
Enterprise Edition has an average gain of 24% across all tested thread configurations.
POINT_SELECT
The workload comprises of only simple point based SELECT queries.
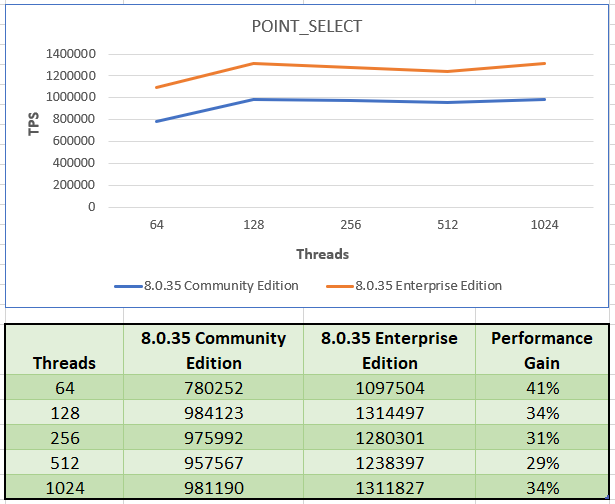
Enterprise Edition has an average gain of 34% across all tested thread configurations.
OLTP RW
The workload comprises of both read and write queries i.e SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE.
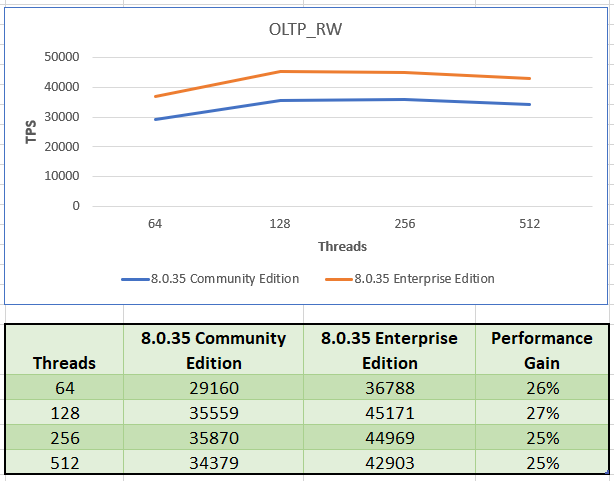
Enterprise Edition has an average gain of 26% across all tested thread configurations.
UPDATE_KEY
The workload comprises of queries that UPDATE the indexes.
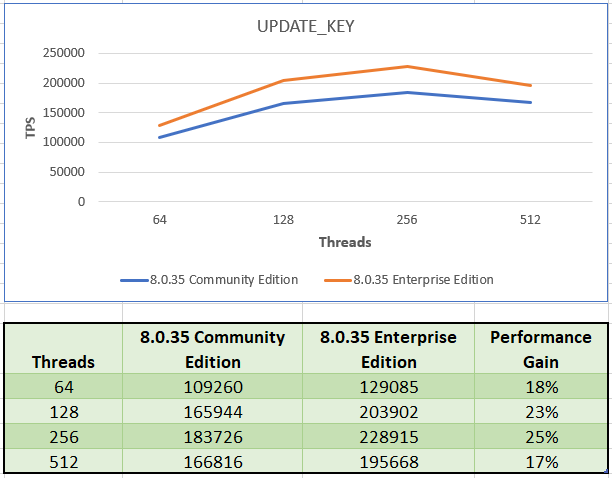
Enterprise Edition has an average gain of 21% across all tested thread configurations.
Summary
In summary, these benchmark results show that MySQL Enterprise Edition, 8.0.35 has significant performance gains over the Community Edition, across all the four types of workloads that were tested.
Disclaimer: Actual observed improvements depend upon the specific user load, data, configuration, hardware, and operating system employed. This means that the improvements discussed here are specific to the setup used, and this may not correspond exactly to results observed elsewhere.
Configuration Details
Data Set
Sysbench load. 8 tables, 10 million rows each. Total 80 million rows
Data Size 20GB. Data is fully cached in buffer pool.
Hardware
Oracle Linux server release 7.9
Kernel 5.4.17-2012.201.3.el7uek,x86_64
Memory 515.91GB
Intel® xoen® CPU E5-2699 v4 @2.20ghz
2 sockets, 44 cores, 88 CPU threads
MySQL Configuration
All configs are defaults, except those listed below.
[mysqld]
## Server ##
back_log=0
disable-log-bin
max_connections=1200
max_prepared_stmt_count=100000
log_error_verbosity=3
thread_cache_size=1200
## Innodb ##
innodb_buffer_pool_instances=16
innodb_buffer_pool_size=128G
innodb-change-buffering=none
innodb_io_capacity_max=12000
innodb_io_capacity=10000
innodb_log_files_in_group=16
innodb_log_file_size=1G
innodb_numa_interleave=ON
innodb_page_cleaners=16
innodb_read_io_threads=16
innodb_write_io_threads=4
innodb_undo_log_truncate=OFF
range_alloc_block_size=16384
Toolkit
sysbench-bmk
