MySQL HeatWave is an extremely powerful Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) engine for MySQL on OCI. Analytic SQL queries that would normally takes hours can be executed in minutes and therefore MySQL HeatWave can help to save a lot of time, processing power and cost.
Wouldn’t it be great if a developer of an OLAP application could directly access and work with MySQL HeatWave instances right from VS Code – the preferred development environment of many MySQL developers?
MySQL Shell for VS Code – our new, upcoming VS Code Extension – offers the extensive feature set of MySQL Shell embedded inside VS Code and has full support for MySQL HeatWave built into it.
In this blog post I am going to demonstrate how easy it is to start using MySQL Shell for VS Code to develop analytic SQL queries running against MySQL HeatWave.
Connecting to a MySQL HeatWave instance on OCI
Before we can get started, we have to setup a DB Connection to the MySQL HeatWave instance on the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
This only needs to be done once since MySQL Shell for VS Code will store all registered DB Connections. To create a DB Connection, follow the instructions below or watch the screen recording following it.
Let’s start by logging into OCI and generating a new API key. This key will be used by MySQL Shell for VS Code to access the resources on OCI.
- Click the user icon, top right and select User Settings.
- Click API Keys on the bottom left and click Add API Key.
- Click Download Private Key and store the API Key in a .oci folder inside your user’s home directory. Then click Add.
- Copy the configuration file text and switch to VS Code.
- In VS Code, select the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension and click on the configuration icon right to the ORACLE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE view.
- Paste the configuration file text into the config file that has opened. Rename the top section from DEFAULT to the name of the tenancy.
- Type the path to the stored Private Key file as indicated in the text. Close the file and reload the ORACLE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE view.
Now MySQL Shell for VS Code is configured and you can browse the resources of your OCI tenancy. Next we are going to create the DB Connection inside MySQL Shell for VS Code.
- Browse to the MySQL HeatWave instance and click the right mouse button.
- Select Create Connection with Bastion Service, the DB Connection dialog will show. It might ask whether to create a new Bastion, if so, confirm.
- Enter the MySQL user name and click Store Password to enter the MySQL password.
- Click OK to create the connection.
Now you can connect by clicking the DB Connection tile or by pressing the > button next to the name of the DB Connection in the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view.
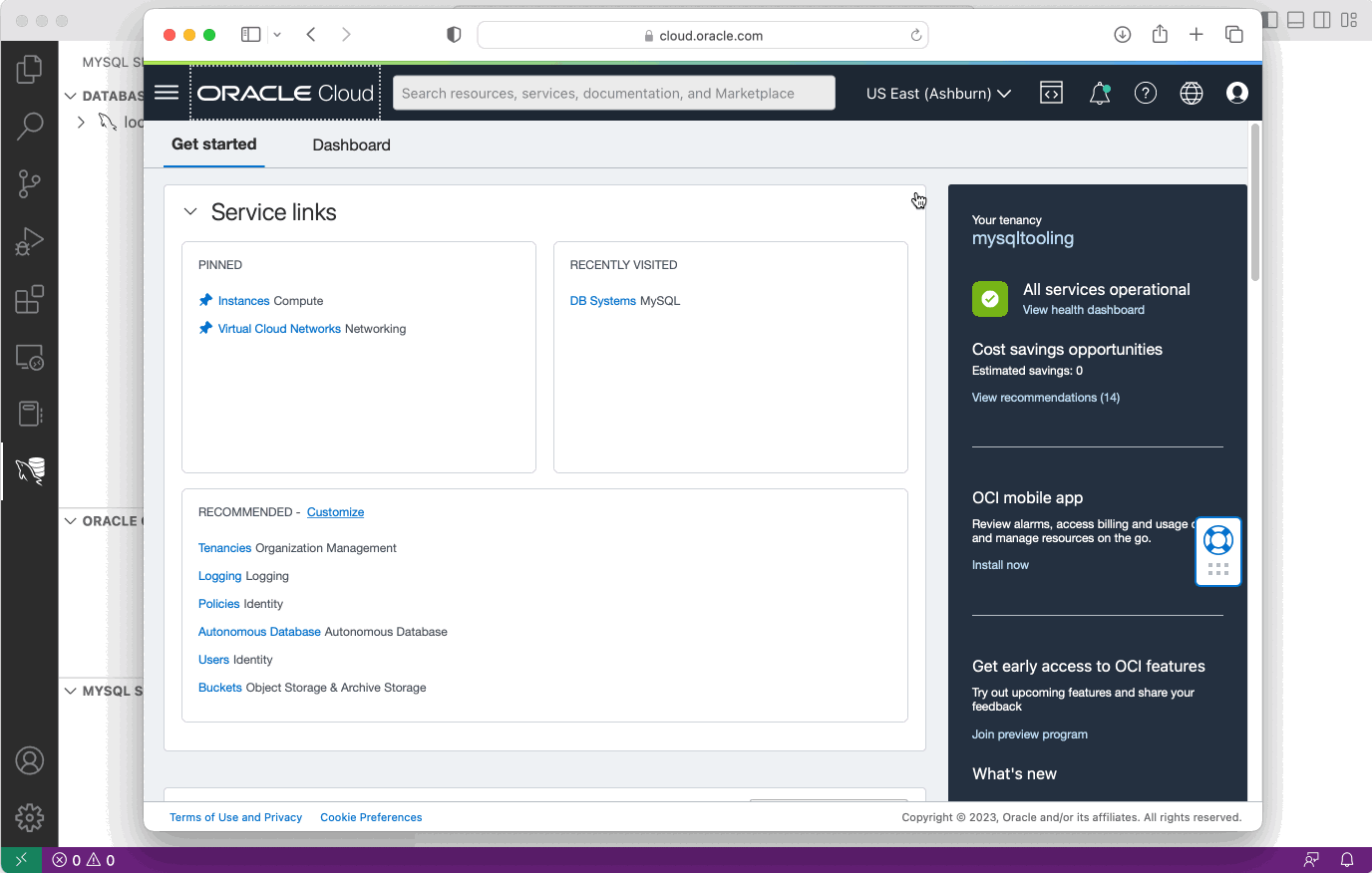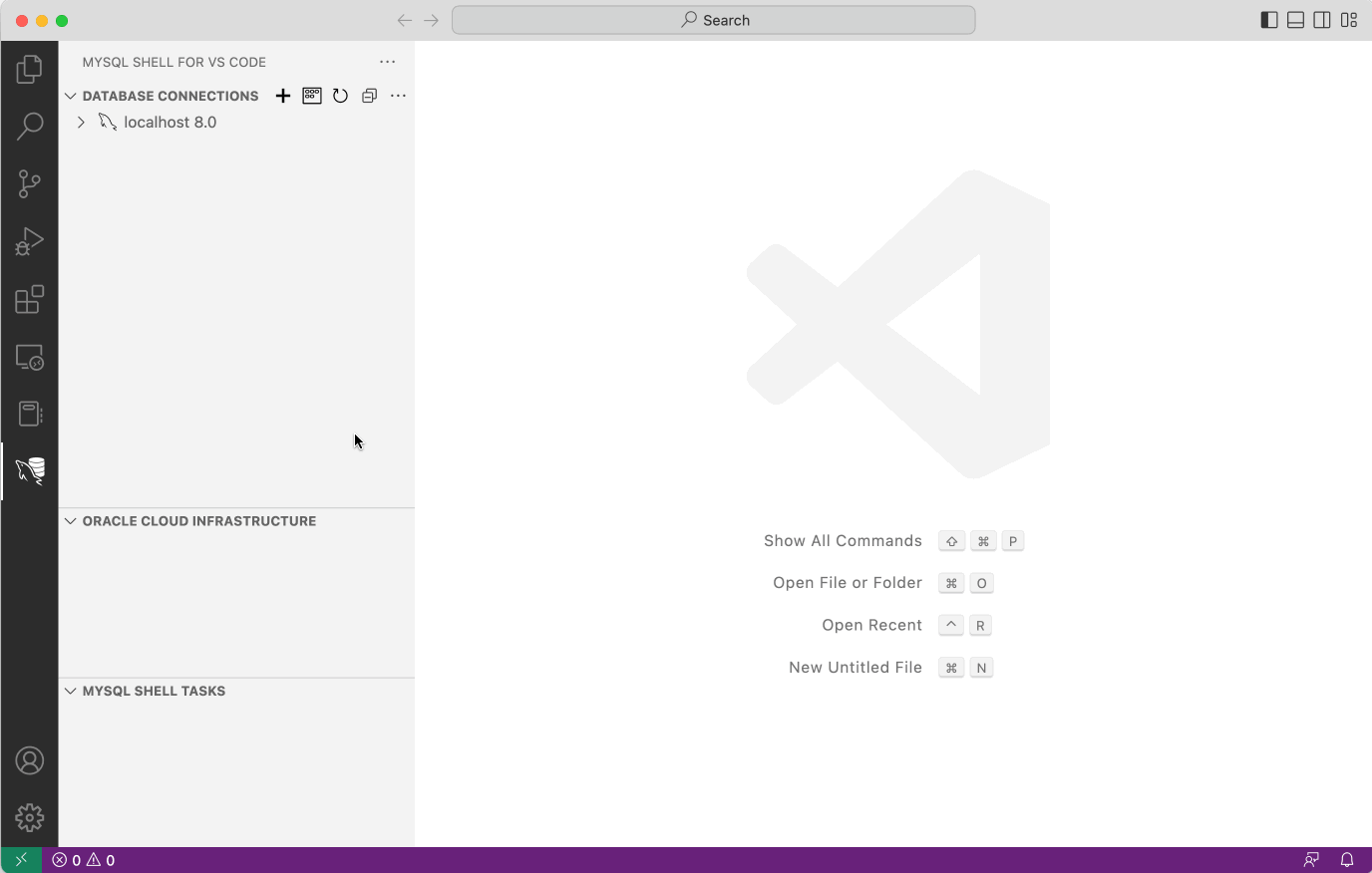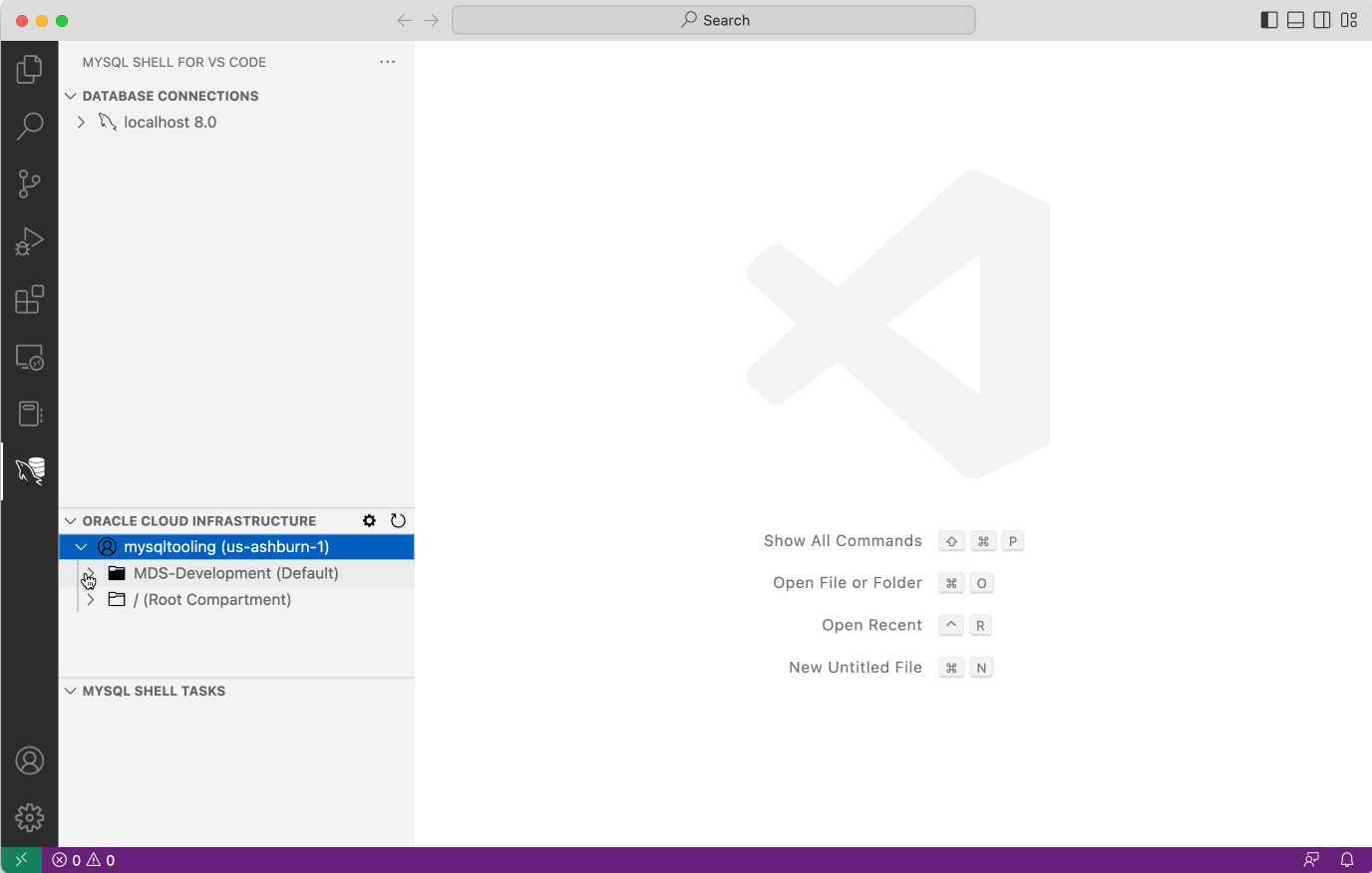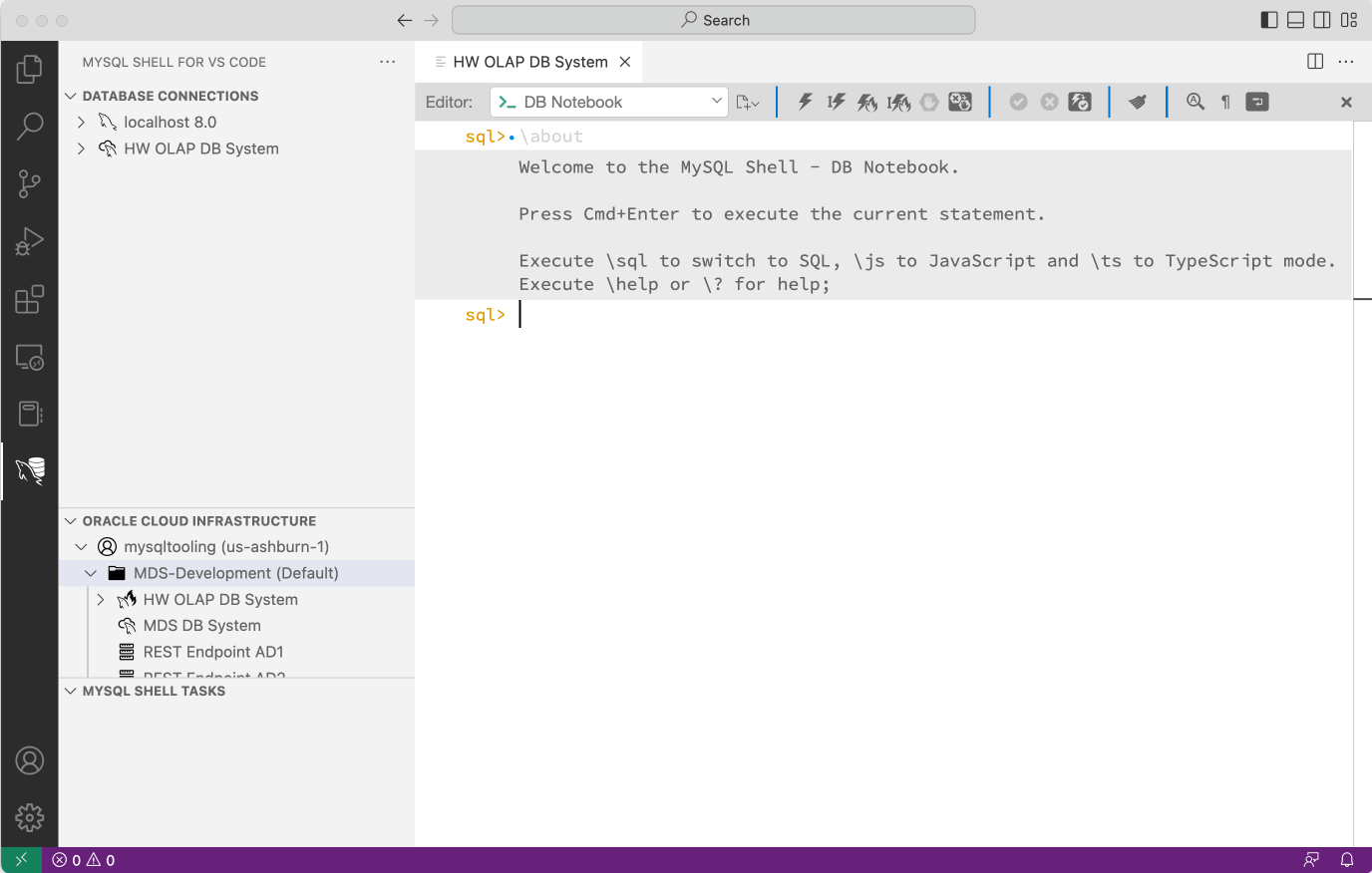
Once connected to the MySQL HeatWave instance, you can execute any SQL Query.
Rescaling and Managing the MySQL HeatWave Cluster
MySQL Shell for VS Code allows developers to manage the MySQL HeatWave instance right from the IDE. It supports basic operations like Start/Stop/Restart but also more advanced features like rescaling the MySQL HeatWave Cluster.
Rescaling the HeatWave Cluster is usually done to increase the amount of data that can be accessed in analytic queries. Since the MySQL HeatWave Cluster is a memory based engine, the full data set of a query needs to fit in the total memory of all the cluster instances.
- Adding a HeatWave Cluster
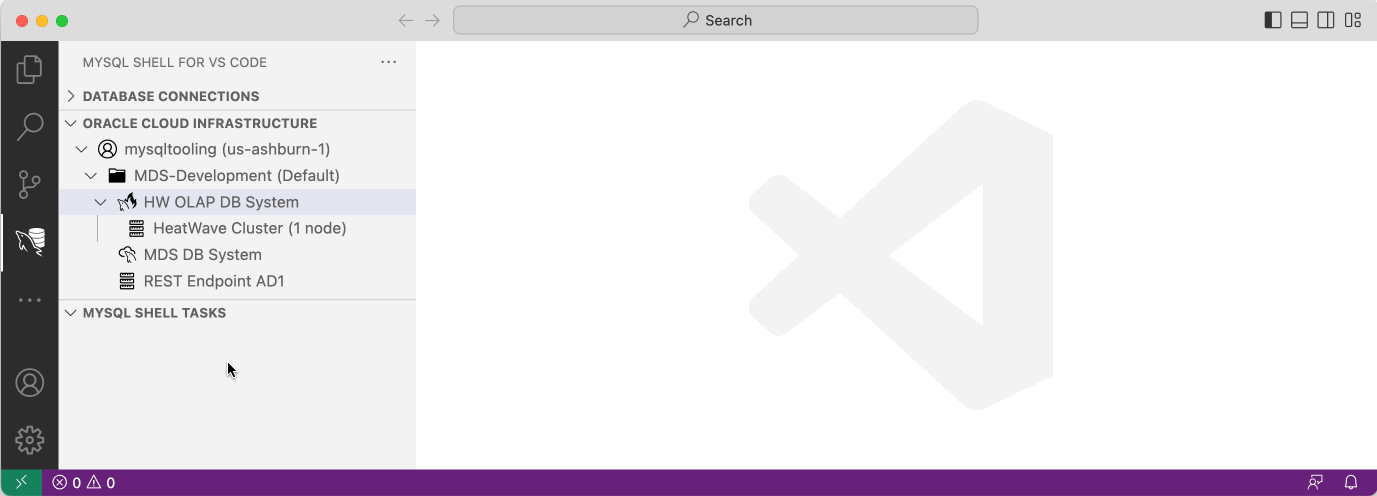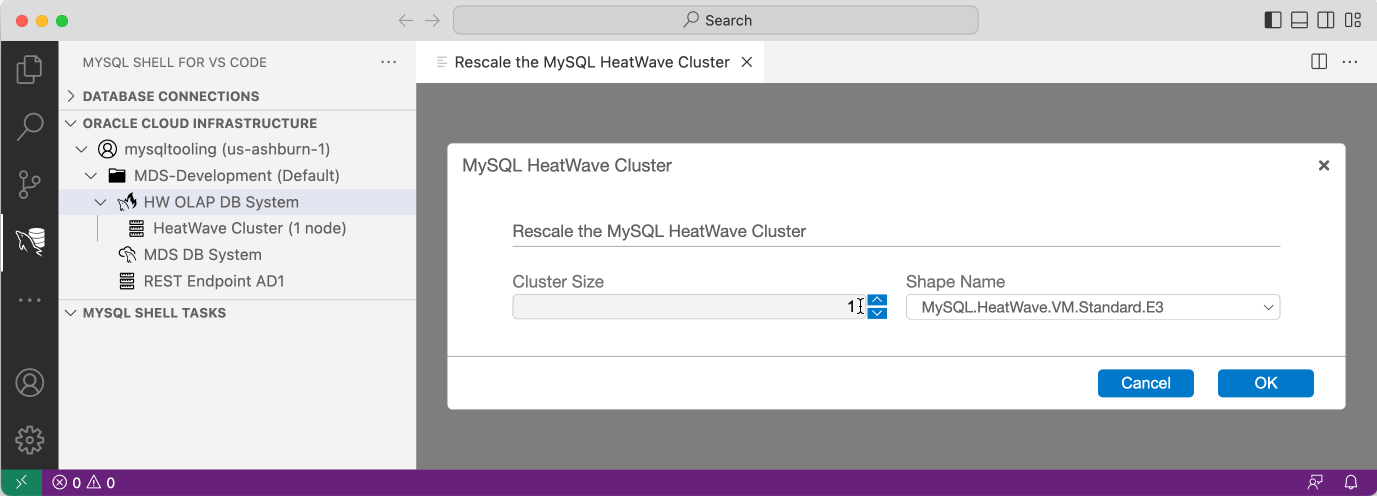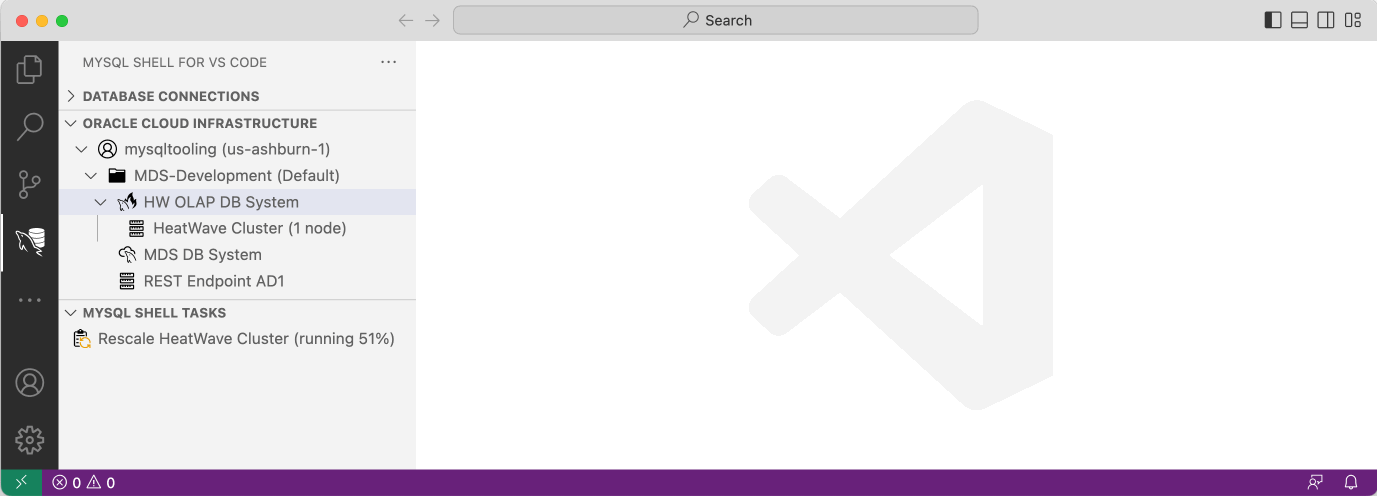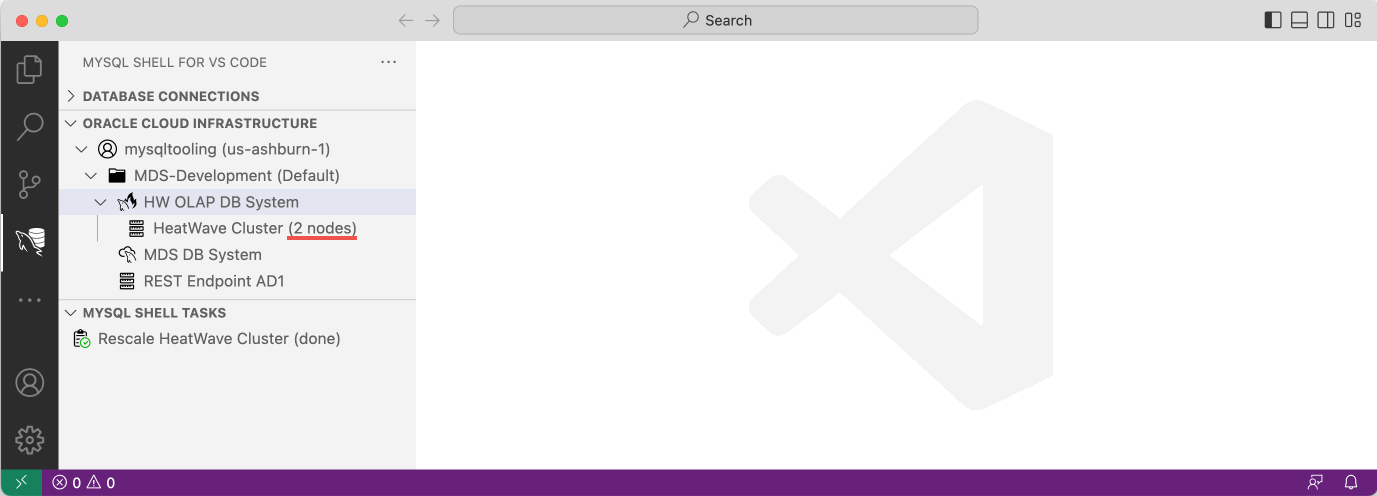
- If no HeatWave Cluster has been added yet, right click on the desired MySQL DB System tree node in the ORACLE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE view and select Add HeatWave Cluster. Enter the Cluster Size and choose the VM Shape Name and click OK to add a HeatWave Cluster.
- Start / Stop / Restart / Delete a HeatWave Cluster
- Expand the MySQL DB System tree node in the ORACLE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE view and right click on the HeatWave Cluster. Then choose the right operation from the popup menu.
- Rescaling a HeatWave Cluster
- When working with a larger data set it is often required to rescale the HeatWave Cluster. Expand the MySQL DB System tree node in the ORACLE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE view and right click on the HeatWave Cluster. Then choose Rescale the HeatWave Cluster from the popup menu.
The following screen recording shows how to perform a rescale operation of a HeatWave Cluster. The progress of the rescaling operation can be monitored in the MYSQL SHELL TASKS view.
Please note that this recoding was sped up since the rescale operation can take a considerable amount of time.
Uploading Database Schemas to the MySQL HeatWave Cluster
Before running analytic SQL queries, the data set used by the query needs to be uploaded to the HeatWave Cluster. This operation can be performed right from the MySQL for VS Code Extension.
- Expand the DB Connection tree item in the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view and select the database schemas that should be uploaded. Hold the Cmd key on macOS (Control Key on Linux/Windows) to select multiple database schemas.
- Right click on one of the selected database schemas and select Load Data to HeatWave Cluster from the popup menu.
- Set all required options on the MySQL HeatWave Cluster loading dialog and click OK.
- Monitor the progress until the database schemas have been uploaded.
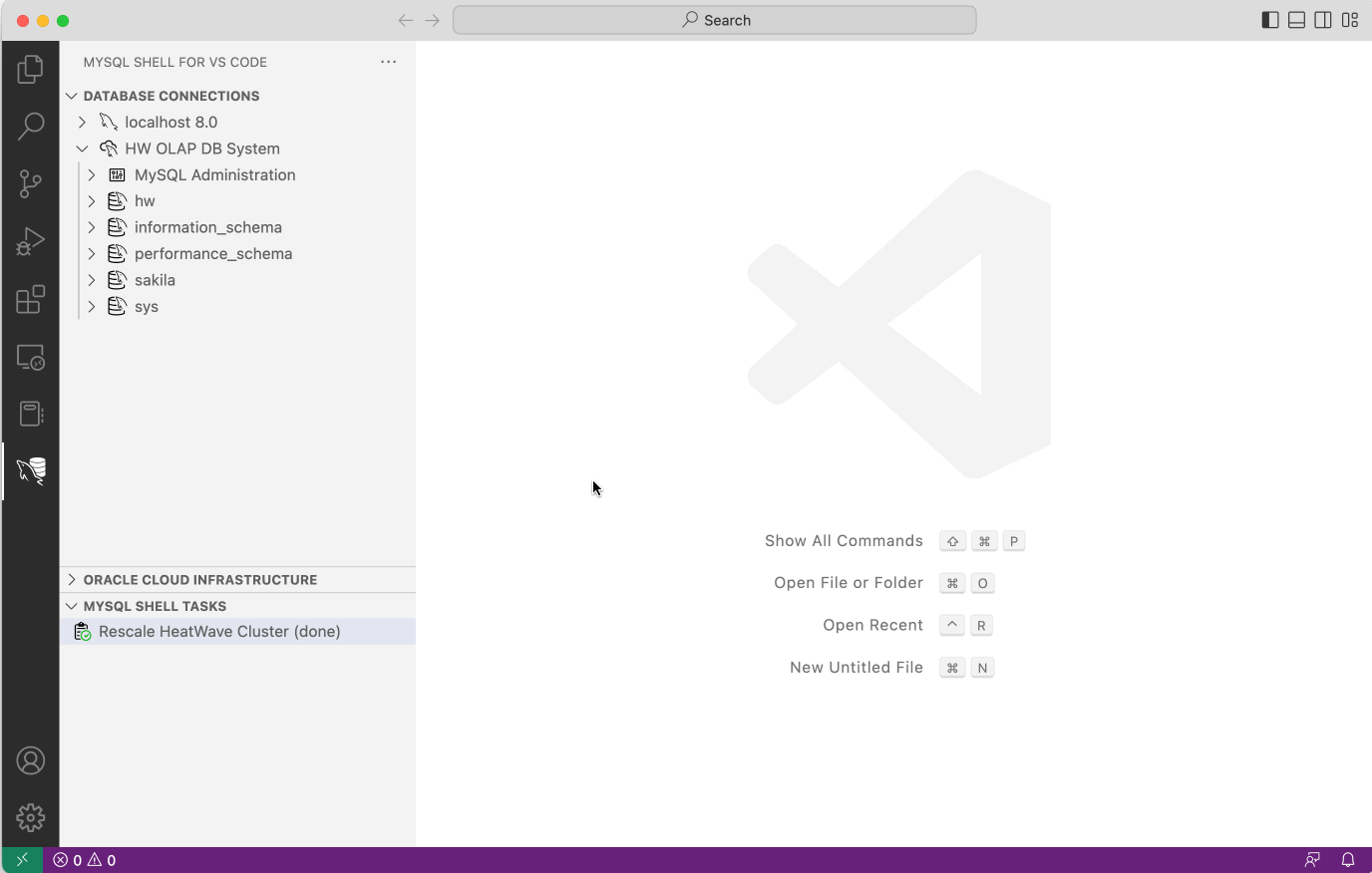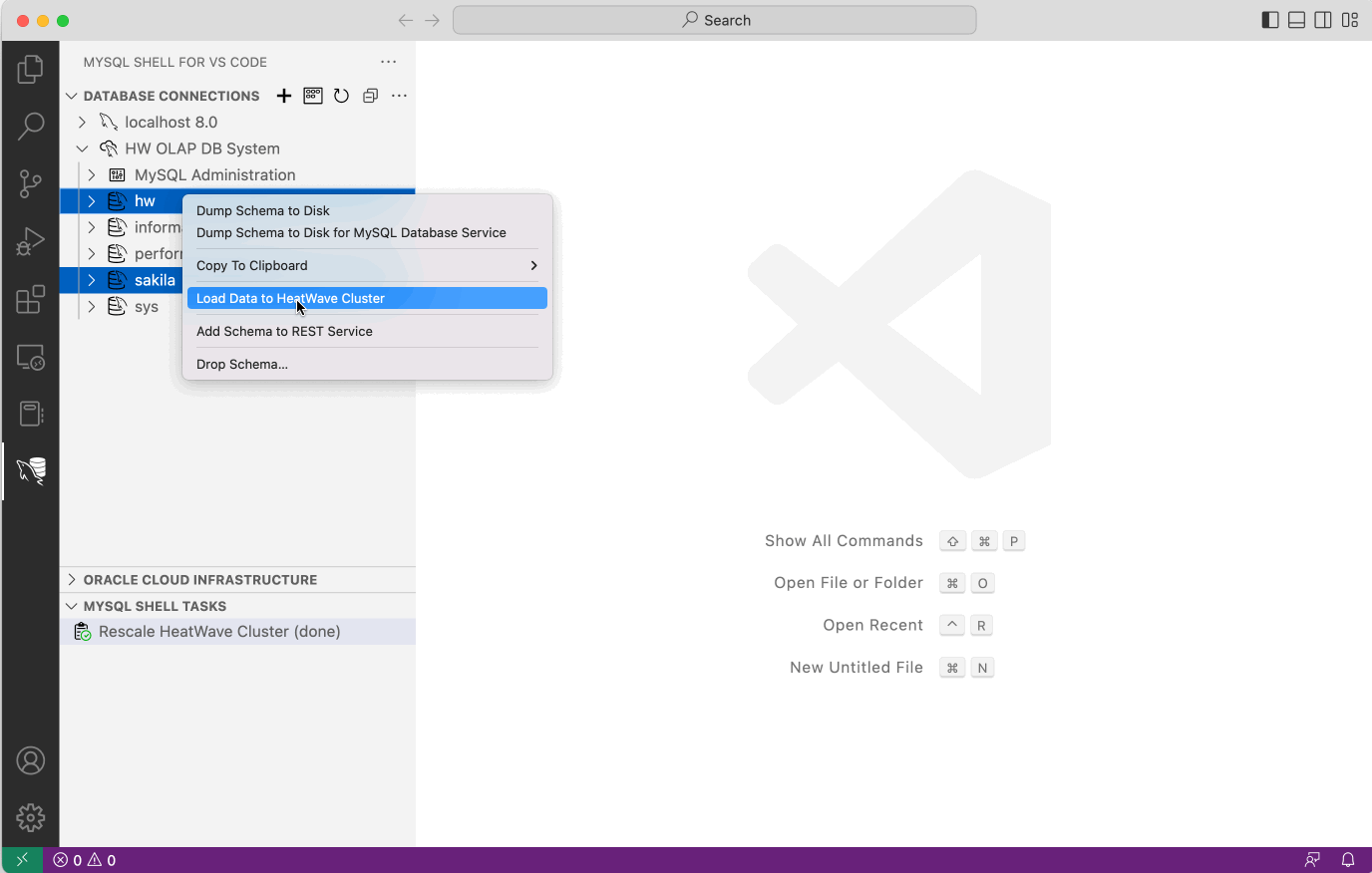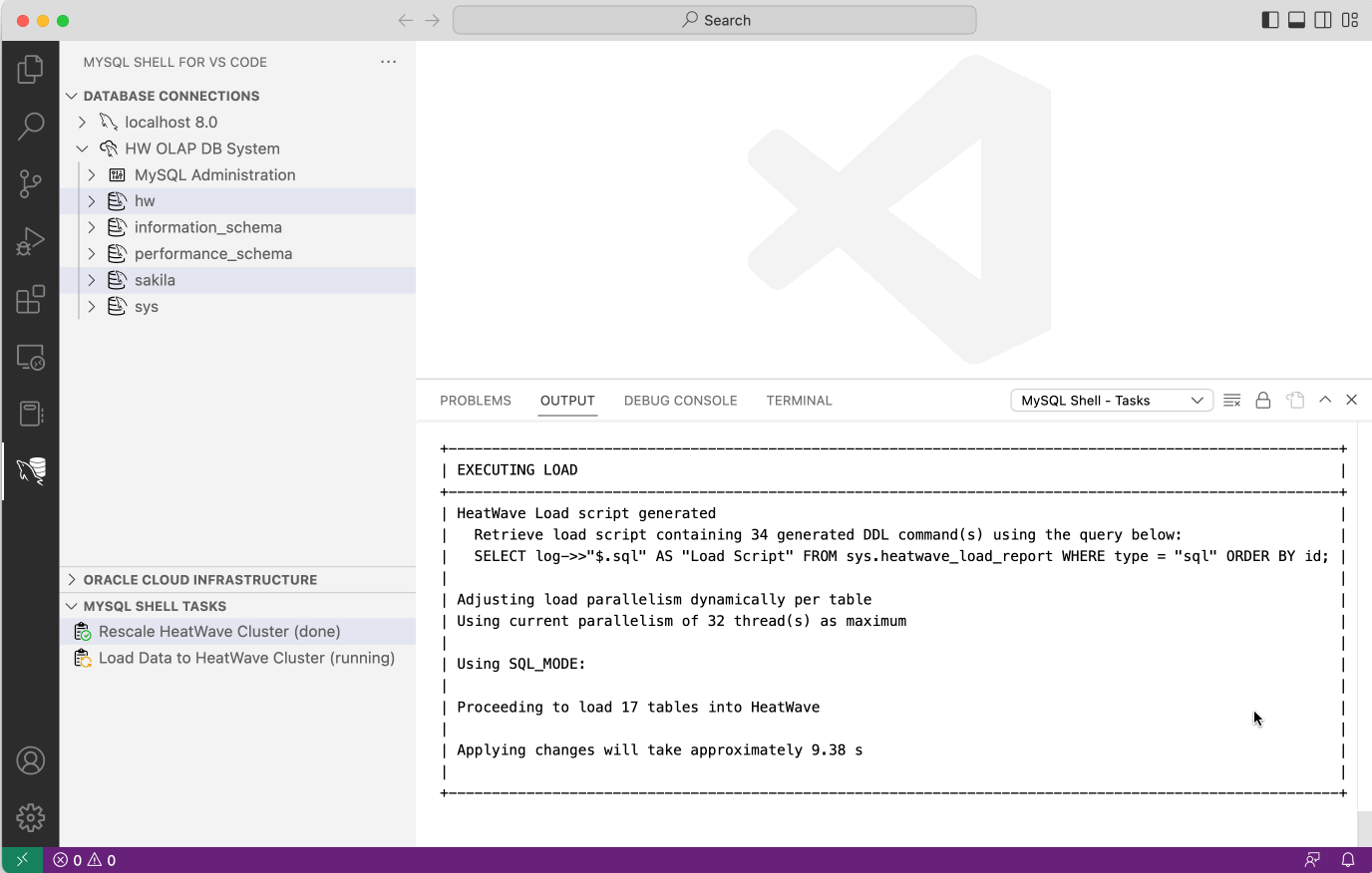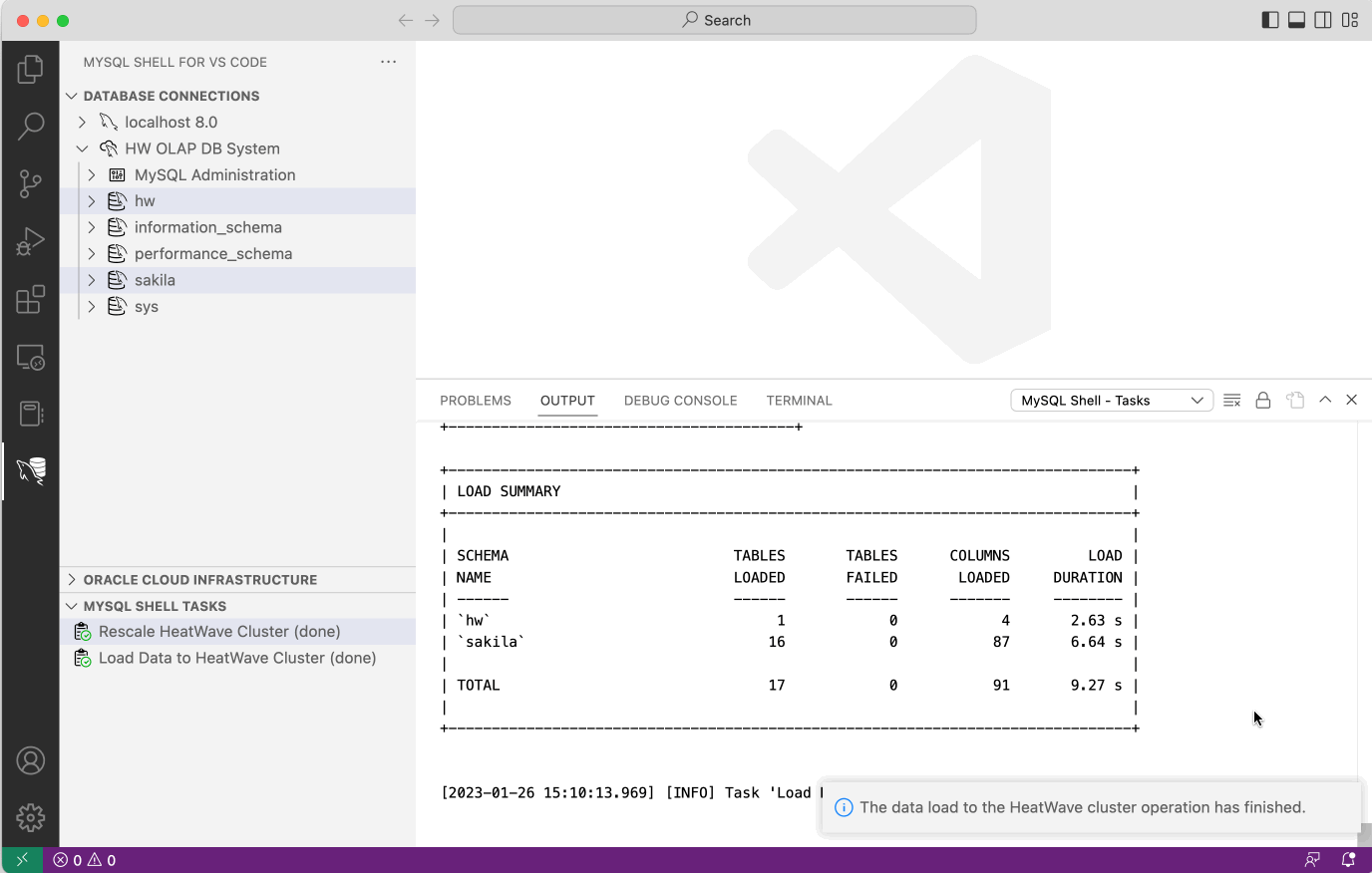
Depending on the size of the data set the upload can take a considerable amount of time. You can continue to work while the upload takes place, open a DB Connection and perform other tasks. To check the progress of the upload operation, click the Load Data to HeatWave Cluster entry in the MYSQL SHELL TASKS view.
Executing Analytic Queries against the HeatWave Cluster Engine
Once the data set has been uploaded, the SQL queries can be composed and executed. The MySQL HeatWave instance will automatically detect if a SQL query can be accelerated by offloading the execution to the HeatWave Cluster. If the SQL query cannot be offloaded, the regular MySQL engine will be used which can lead to slow execution times of analytic queries.
For this reason, MySQL Shell for VS Code will automatically show two special execution buttons in the DB Notebook toolbar when connected to a MySQL HeatWave instance.
These HeatWave execution buttons will force the execution of the SQL query on the HeatWave Cluster and show any issues in the case a SQL query cannot be executed there.
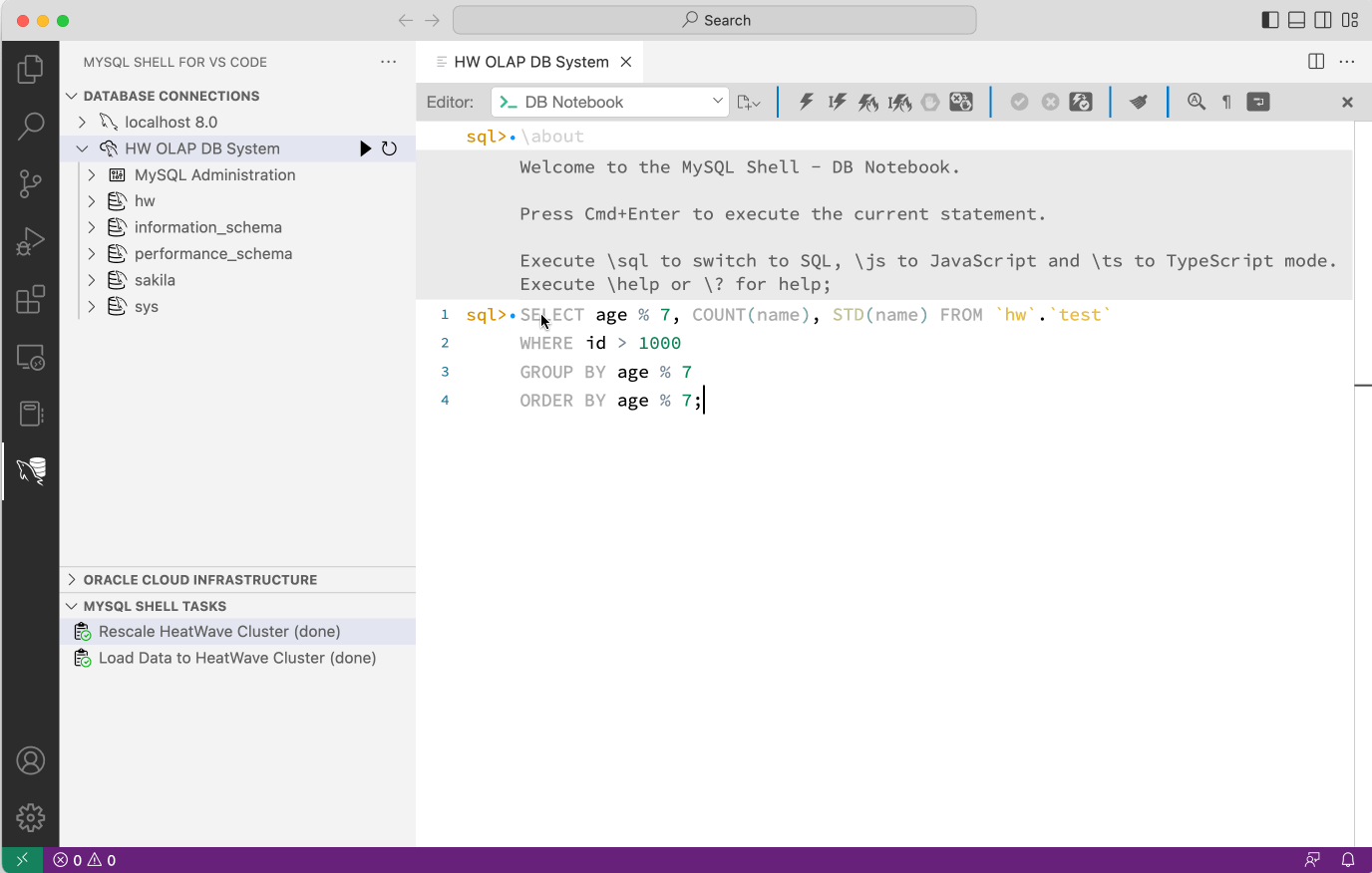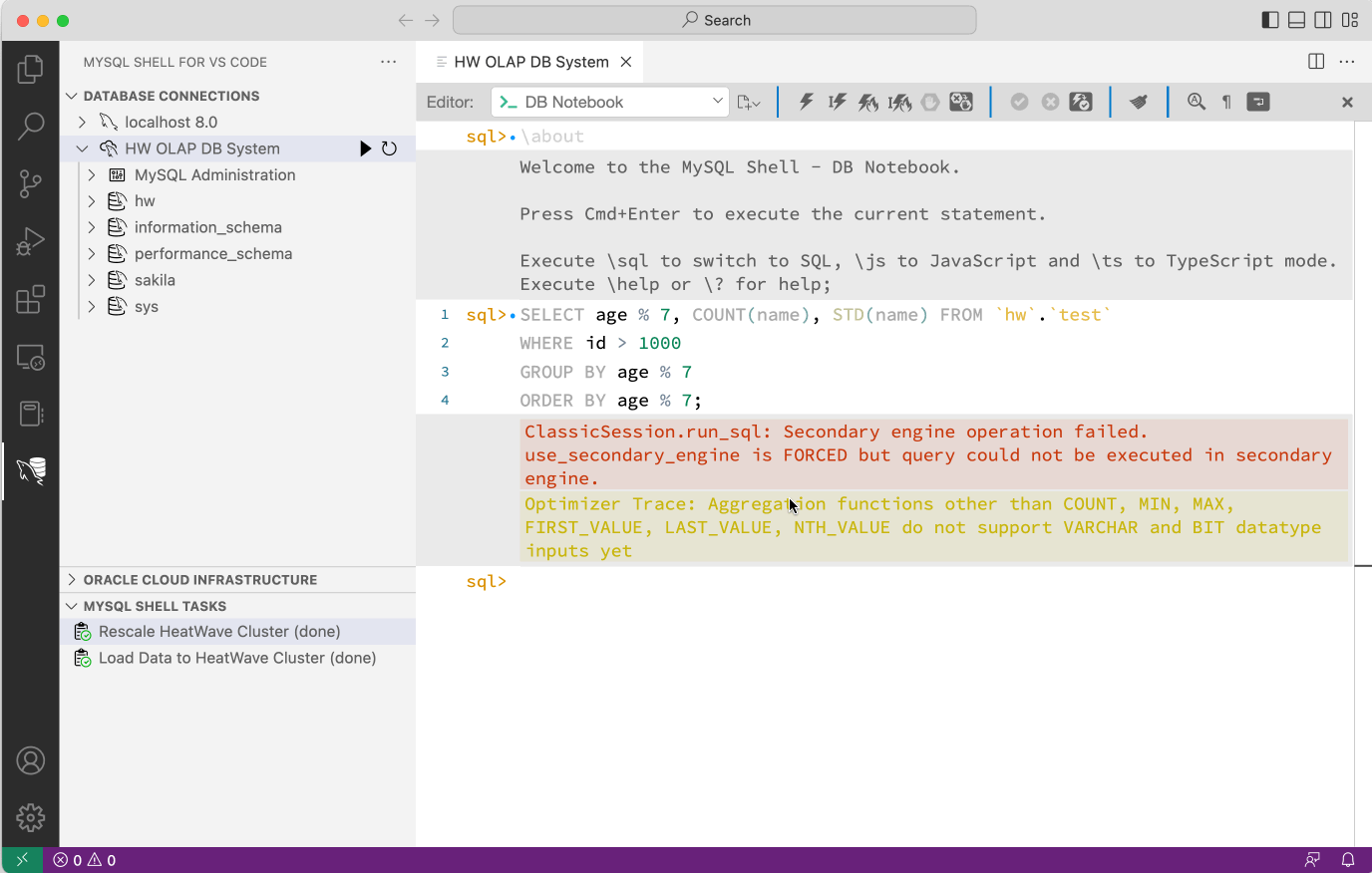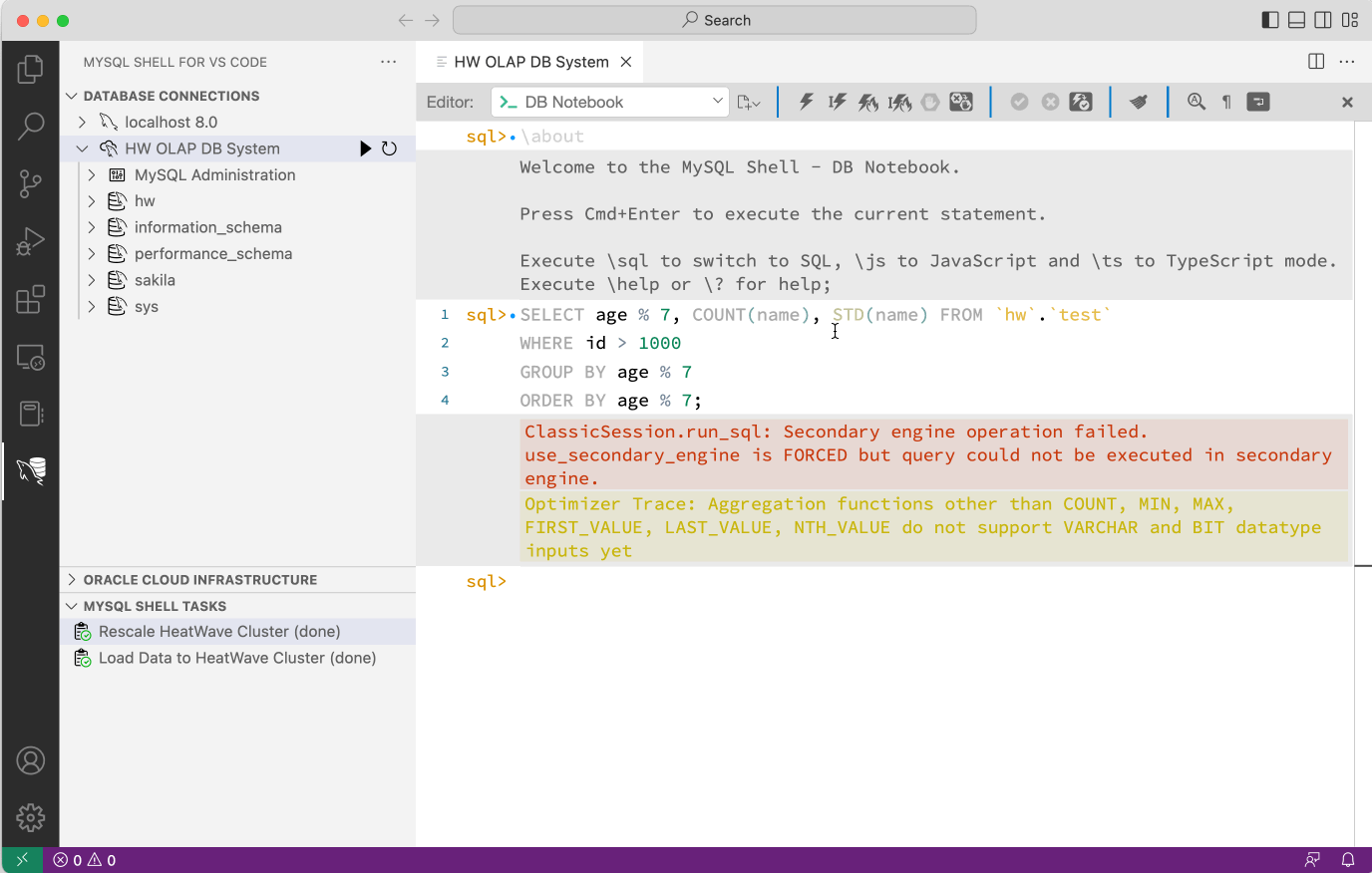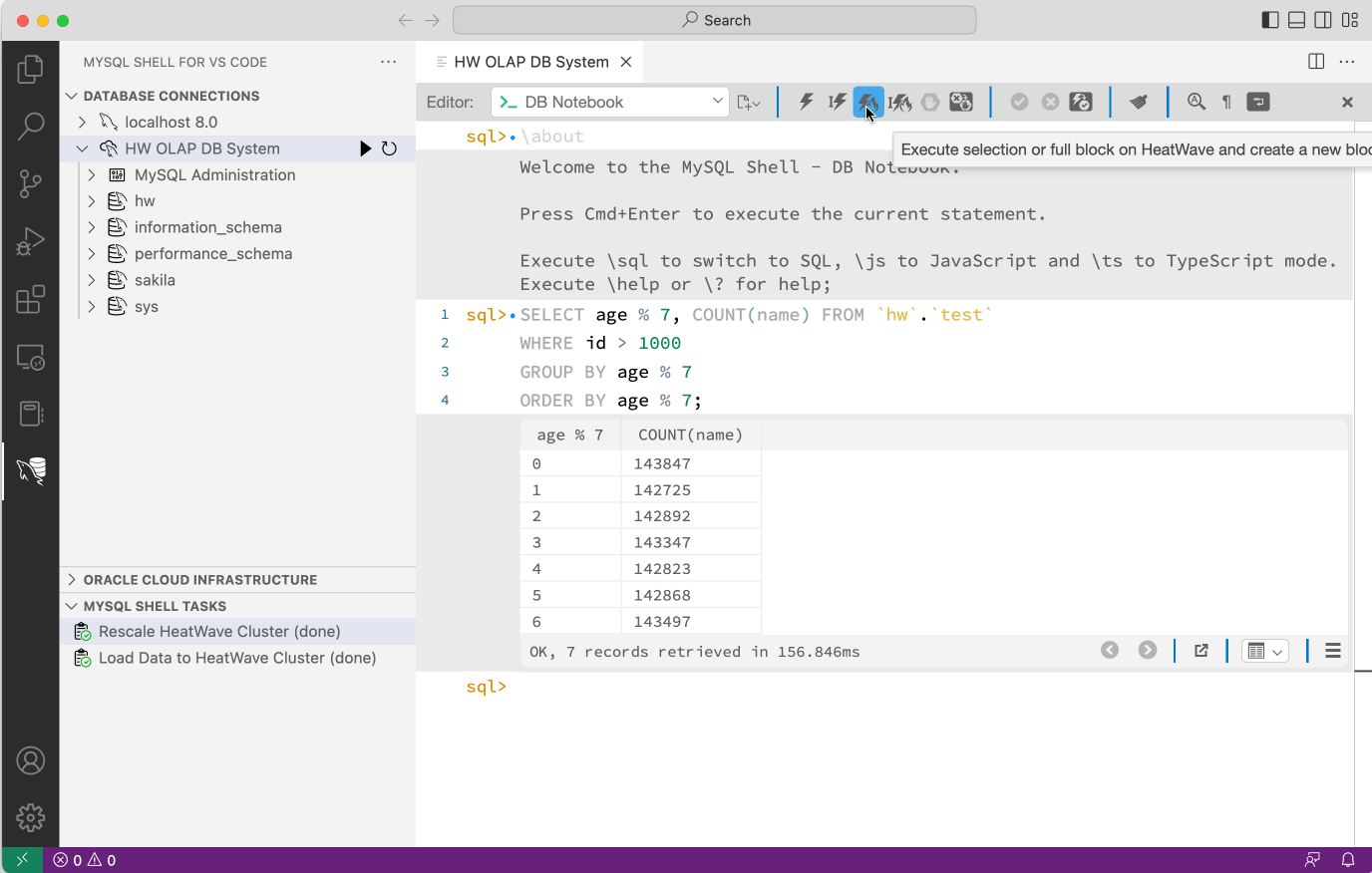
In the case below, the screen recording shows an error when trying to execute the SQL query. It also shows the MySQL optimizer trace that explains why the upload fails. In this case the usage of the STD() aggregation functions is not yet supported by the HeatWave engine. The SQL query can than be modified in order to work around the issue.
Summary
The MySQL Shell for VS Code Extension makes it very easy for developers to connect, manage and work with MySQL HeatWave instances right from within VS Code. It hides a lot of the complexity and helps users focus on the powerful analytic features of MySQL HeatWave.
