In the first part of this series, we introduced Online Redefinition. In this blog post, I will discuss how to start using Online Redefinition sub-programs and walk through an example of using this feature to make online changes without downtime.
DBMS_REDEFINITION- Privileges and Access:
Prior to getting started, users must have the necessary privileges for using DBMS_REDEFINITION procedures. Execute privileges on the DBMS_REDEFINITION package are required to run subprograms in the package. Execute privileges on the DBMS_REDEFINITION package are granted to EXECUTE_CATALOG_ROLE.
If the user needs to redefine the table on their own schema, it is called USER Mode. If the user needs to redefine the table in other schemas, it is called FULL Mode. Here is a breakdown of the privialges and how they can be used:
USER Mode:
- User need to have execute privileges on the DBMS_REDEFINITION package.
- Additional privileges – CREATE TABLE , CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- The CREATE TRIGGER privilege is also required to execute the COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTS procedure.
FULL Mode:
- For a user to redefine a table in other schemas using the package, the user must be granted the following privileges:
- CREATE ANY TABLE ,ALTER ANY TABLE ,DROP ANY TABLE ,LOCK ANY TABLE,SELECT ANY TABLE
- The following additional privileges are required to execute COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTS on tables in other schemas:
- CREATE ANY TRIGGER
- CREATE ANY INDEX
DBMS_REDEFINITION Package and Procedures
To achieve online redefinition, incrementally maintainable local materialized views are used. These logs keep track of the changes to the master tables and are used by the materialized views during refresh synchronization.
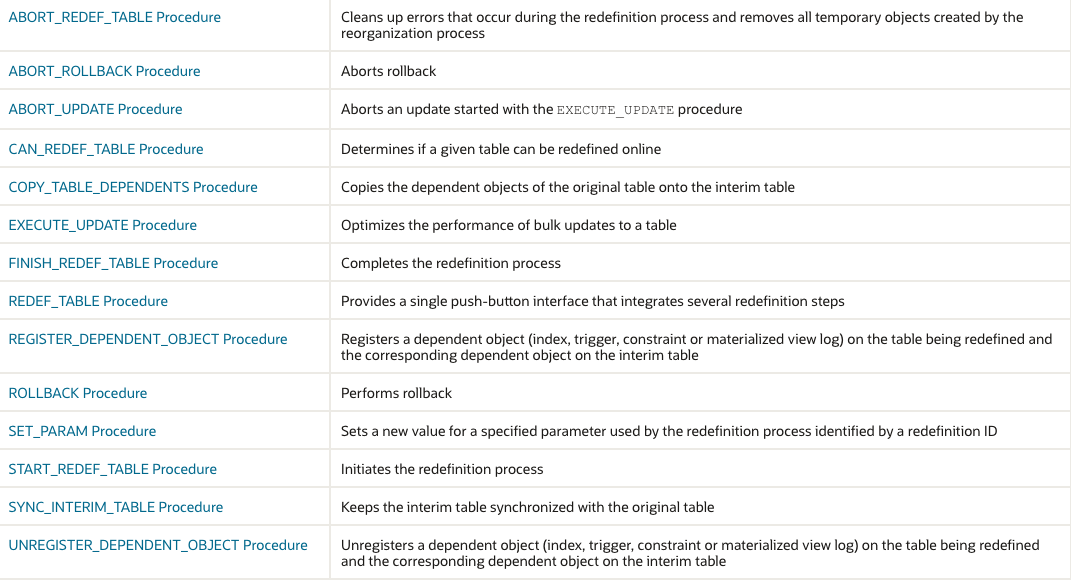
This table lists the DBMS_REDEFINITION subprograms and briefly describes them.
Redefine a table’s storage properties in a single step with the REDEF_TABLE procedure:
In the below example we will perform these changes using the REDEF_TABLE procedure
- Modify the tablespace from data_1 to users
- Table compression type to ‘ROW STORE COMPRESS ADVANCED’
- Index compression type to ‘COMPRESS 1′
- Lob compression type to ‘’COMPRESS HIGH’
Now let see a quick demo of using Online redefinition
CREATE TABLE print_ads
( ad_id NUMBER(6),
ad_text CLOB
);
CREATE INDEX pm.print_ads_ix
ON print_ads (ad_id)
TABLESPACE data_1;
ddl print_ads
CREATE TABLE "PM"."PRINT_ADS"
( "AD_ID" NUMBER(6,0),
"AD_TEXT" CLOB
) SEGMENT CREATION DEFERRED
PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255
NOCOMPRESS LOGGING
TABLESPACE "DATA_1"
LOB ("AD_TEXT") STORE AS SECUREFILE (
TABLESPACE "DATA_1" ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192
NOCACHE LOGGING NOCOMPRESS KEEP_DUPLICATES ) ;
CREATE INDEX "PM"."PRINT_ADS_IX" ON "PM"."PRINT_ADS" ("AD_ID")
PCTFREE 10 INITRANS 2 MAXTRANS 255 COMPUTE STATISTICS
TABLESPACE "DATA_1" ;
BEGIN
DBMS_REDEFINITION.REDEF_TABLE(
uname => 'PM',
tname => 'PRINT_ADS',
table_compression_type => 'ROW STORE COMPRESS ADVANCED',
table_part_tablespace => 'USERS',
index_key_compression_type => 'COMPRESS 1',
index_tablespace => 'USERS',
lob_compression_type => 'COMPRESS HIGH',
lob_tablespace => 'USERS',
lob_store_as => 'SECUREFILE');
END;
/
ddl print_ads
CREATE TABLE "PM"."PRINT_ADS"
( "AD_ID" NUMBER(6,0),
"AD_TEXT" CLOB
) SEGMENT CREATION DEFERRED
PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255
ROW STORE COMPRESS ADVANCED LOGGING
TABLESPACE "USERS"
LOB ("AD_TEXT") STORE AS SECUREFILE (
TABLESPACE "USERS" ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192
NOCACHE LOGGING COMPRESS HIGH KEEP_DUPLICATES ) ;
CREATE INDEX "PM"."PRINT_ADS_IX" ON "PM"."PRINT_ADS" ("AD_ID")
PCTFREE 10 INITRANS 2 MAXTRANS 255 COMPUTE STATISTICS COMPRESS 1
TABLESPACE "USERS" ;
By executing the single command above, all the changes to the tables will be handled using DBMS_REDEFINITON completely online without any downtime.
In the next series of blog post, we will discuss about various aspects of such as how Online Redefinition by popping the hood and looking at how the package functions including some considerations like locking. We will take a look at a more complex example and how DBMS_REDEFINITION can simplify online updates in a control standardized fashion.
Additional resources
Here are some additional resources to help you get started with Online Data Reorganization and Redefinition:
- Online Data Reorganization and Redefinition Product page
- Oracle database 19c- Online Redefinition documentation
Feel free to connect with me directly on Twitter and LinkedIn
