Oracle announced the availability of Oracle Database 23ai in the Oracle Cloud on May 2nd, 2024. With this release, which contains over 300+ features, we enter a new era of the Oracle Database with huge advancements spanning leaps forward in supporting mission-critical data combined with AI and a slew of features for developers, DBAs, and just about anyone who interacts with data in the technology world. Hopefully, many are already kicking the tires of Oracle Database 23ai in the cloud and getting a taste of these features.
I know everyone is excited about some fantastic AI features like AI Vector Search and is likely to start exploring the new version with a focus on that particular product area. In this blog, I am going to take a sidestep and focus on a bit more finite set of key 23ai features and how they may impact the many customers that take advantage of our Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) Gold Tier, which provides extremely low downtime (i.e. single digit seconds to under a minute, depending on the type of failure with Application Continuity masking the downtime as a brown out if enabled) for unexpected outages with zero data loss protection (i.e. SYNC option) as well as seamless rolling patching and upgrades which eliminates or minimizes data time depending on the configuration.
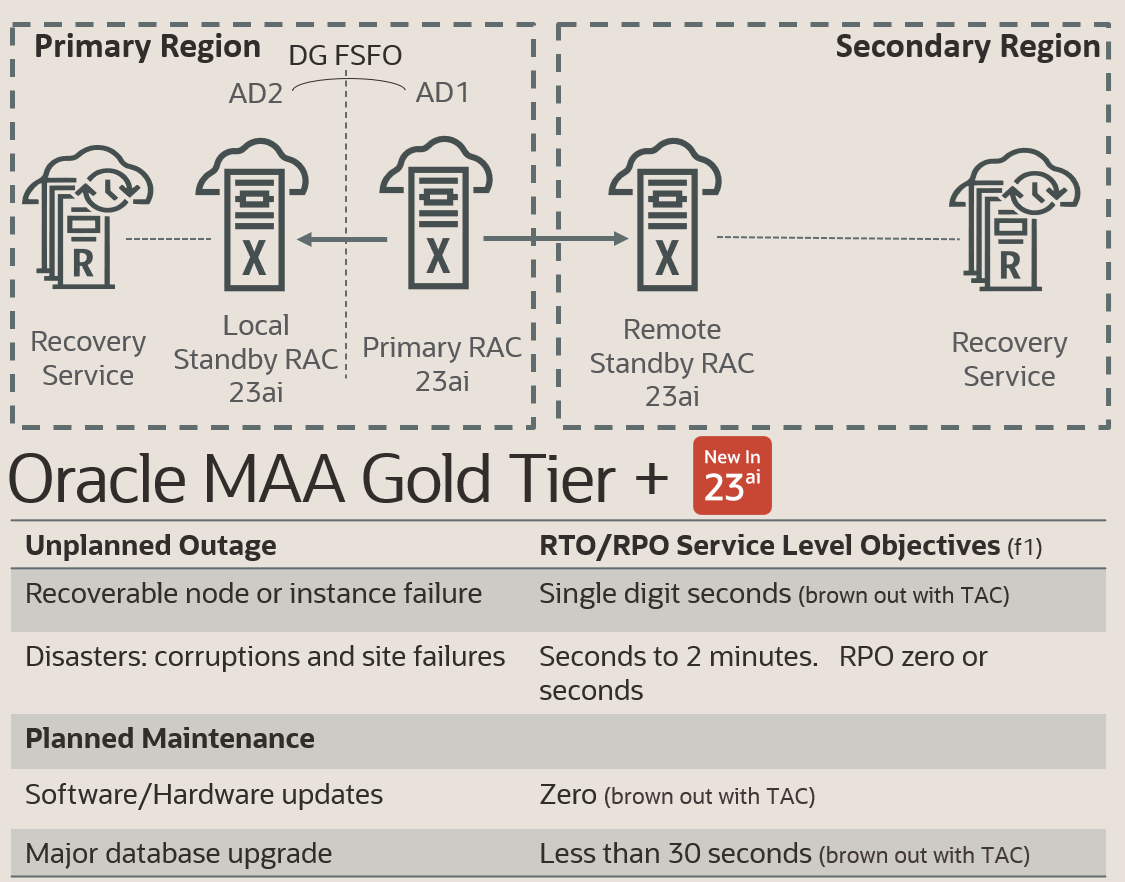
This is the MAA tier (reflected in the simplified diagram and outage matrix below) that most are looking for when you are talking about a mission-critical application that should ideally be up and serving your business 24/7, 365 days a year. Downtime is measured from the point of loss of availability until that availability is restored in relation to the Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Potential data loss is measured against the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) backward from the point of impact to the last valid backup or replica of the data.
 When you start thinking about disaster recovery, the possible causes seem almost endless. It could be something as simple as a regional power outage or other natural disaster that impacts production data centers or something as elusive as a cyberattack. Even if you have a monster attacking your data center, the goal is the same: to protect your data and keep your application up and running regardless of what happens. The Oracle Database has always shined in this level of resiliency as we focus on ensuring our technology can handle and protect mission-critical applications. The MAA Gold tier was designed to allow people to build out application architectures that will enable minimal downtime during planned maintenance activities and withstand all different types of unexpected outages, including human error and corruption.
When you start thinking about disaster recovery, the possible causes seem almost endless. It could be something as simple as a regional power outage or other natural disaster that impacts production data centers or something as elusive as a cyberattack. Even if you have a monster attacking your data center, the goal is the same: to protect your data and keep your application up and running regardless of what happens. The Oracle Database has always shined in this level of resiliency as we focus on ensuring our technology can handle and protect mission-critical applications. The MAA Gold tier was designed to allow people to build out application architectures that will enable minimal downtime during planned maintenance activities and withstand all different types of unexpected outages, including human error and corruption.
With Oracle Database 23ai, how has MAA Gold been enhanced?
We have a lot of features and enhancements in Oracle Database 23ai, many of which empower mission-critical data workloads for applications, including the growing number of AI-focused applications, but which of those specifically tie in with MAA Gold? The answer spans MAA’s focus on reducing downtime during planned maintenance and unexpected outages. Let’s start by looking at some of the planned maintenance features of Real Application Clusters (RAC) and Active Data Guard, which are core technologies in our MAA Gold reference architecture.
-
Rolling Patching for Complex Changes: Rolling Patching has long been the answer to reducing maintenance-related downtime for the database, which is critical from the MAA perspective. Unfortunately, some patches cannot be applied via rolling patching in just one operation. For those “complex changes,” Oracle Database 23ai has introduced two features allowing for the application of otherwise non-rolling patches in stages. Oracle RAC Two Stage Rolling Updates and Deferred SQL Patching enable the application of the patch (software update) and the activation via SQL at different times of the rolling patch application process, thereby enabling patches to be patched in a rolling fashion.
-
DBMS_ROLLING with Transparent Application Continuity: DBMS_ROLLING enables the automated rolling application of version-changing upgrades and patch sets. Transparent Application Continuity hides database downtime from users by assisting in draining sessions up to a set timeout and then replaying the remaining sessions after the role transition. Together, Transparent Application Continuity and DBMS_ROLLING hide the final switchover needed at the end of the automated process. This feature allows applications requiring MAA Gold Tier RTOs to experience a brownout instead of a blackout during the server reboot interval of the upgrade process, with the resulting downtime surfacing in the application as a performance blip.
-
RAC Fast Pluggable Database Open: Open PDBs in an RAC database up to 2x faster by performing an open operation in parallel with DLM reconfiguration, another critical enhancement tied to multitenant activities in an MAA Gold Tier deployment. This feature is especially vital given that all Oracle Database installations from 21c onward utilize Multitenant architecture.
Excellent, you say, but what about the Oracle Database 23ai features that impact MAA Gold for unexpected outages? Oracle Database 23ai includes many new features that greatly enhance high availability, scalability, and disaster recovery from that perspective, including a couple in the security category, keeping in mind that security breaches can and often do significantly impact availability. The key features and enhancements below tackle many unexpected downtime scenarios, including performance issues related to scalability problems that can impact your data and application.
-
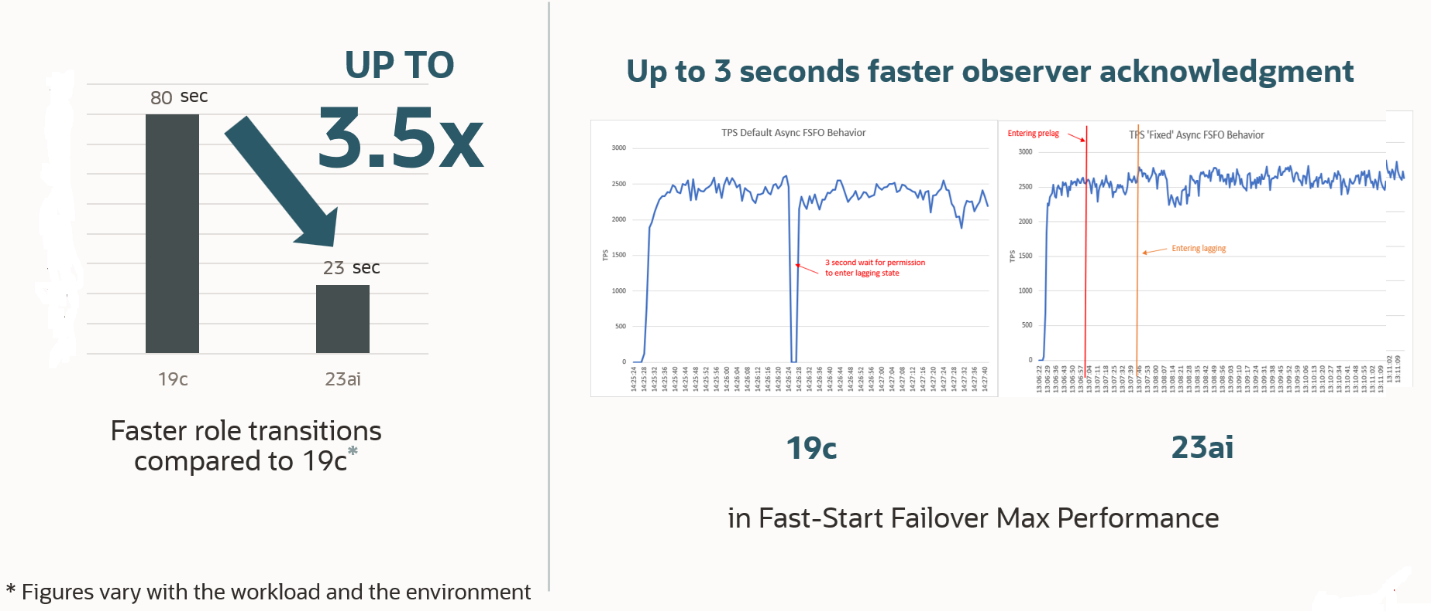
Faster Oracle Data Guard Role Transitions: Oracle Data Guard 23ai provides Lower RTO through various role transition optimizations, such as introducing additional pre-emptive actions to prevent stalls. The team’s internal MAA testing showed role transitions approximately 3.5x faster than 19c using maximum performance protection mode with fast-start failover (an essential RTO requirement for the MAA Gold tier).
-
Data Guard Redo Decryption for Hybrid DR Configurations: Oracle Data Guard now provides the capability to decrypt redo operations in hybrid cloud disaster recovery configurations where the cloud database is encrypted with Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) and the on-premises database is not. This feature provides more flexibility regarding the requirement to encrypt the on-premises databases for those that may not have adequate on-premises data centers to meet the MAA Gold RTO and RPO goals. It should be noted that encrypting both the on-premises and cloud environments is highly recommended for security reasons. However, depending on the environment and resources, we know that is not always an option. Therefore, this feature aims to lower the requirements for those who are quickly trying to get their DR configuration in place and may have challenges around the encryption requirements of the cloud.
-
Real-time Query for PDB Standby: In Oracle Database 21c, Oracle Data Guard per Pluggable Database (DGPDB) was introduced, expanding DR configurations to allow for them to be enabled at either the PDB or CDB (default) level of granularity. This means that a single PDB could be independently failed over between two “primary” CDBs. While this flexibility allowed a lot more freedom in how Data Guard was deployed, many features available for CDB-level Data Guard configurations were not initially available for a PDB-level Data Guard configuration, including many of the Active Data Guard features. With Oracle Database 23ai, a key Active Data Guard feature allowing queries to be offloaded to standby PDB databases is now available, allowing for more scalability when using DGPDB, which makes use of all the resources available.
-
Globally Distributed Database (formerly known as Sharding) with RAFT: Raft Replication enables rapid failover within seconds and zero data loss during node or data center outages, facilitating an active-active-active symmetric distributed sharded database architecture that enhances availability, simplifies management, and optimizes resource utilization globally. This synchronous technology provides another flexible option for the MAA solution, depending on the configuration.
-
Clusterware Resiliency: Oracle Clusterware 23ai, the basis for Oracle RAC and used as a standalone cluster solution, has been enhanced to be more resilient to internal errors, providing more core availability to Oracle MAA Gold (and Silver) tier deployments. Previously fatal Cluster Synchronization Service (CSS) conditions can now be overcome by splitting CSS into restartable client-side and server-side daemons that can tolerate failures independently. In addition, proactive detection and correction of certain error conditions are performed, such as restarting ASM instances to remount an OCR disk group if no OCR diskgroup is mounted or moving the ASM listener if not co-located with the ASM instance.
-
Oracle RAC Fast Start Reconfiguration: Instead of pausing work for reconfiguration and instance recovery after an instance crash, Oracle RAC 23ai Fast Start Reconfiguration allows work to start on clean blocks immediately, leading to work resuming 6x faster compared to Oracle Database 19c. This enhancement significantly benefits MAA Silver, Gold, and Platinum tier deployments.
-
RDMA-based Exadata RAC Scaling: It is no secret that Exadata is the ideal hardware platform for Gold (as well as any tier above silver) MAA deployments of the Oracle Database, given the integrated hardware/software benefits (see Exadata MAA blog series here for more details). With Oracle Database 23ai, Oracle RAC performance on Exadata has made yet another leap forward by reducing the load on the LMS process with RDMA for commit propagation. The result is an application that can scale and maintain availability from the performance perspective, even under extreme peak workloads.
-
In-Database Firewall: A new feature of Oracle Database Vault, SQL Firewall is built directly into Oracle Database. SQL Firewall inspects all incoming SQL statements and ensures that only explicitly authorized SQL are run. Because SQL Firewall is embedded in the Oracle database, it cannot be bypassed. All SQL statements are inspected, whether local or network or encrypted or clear text. It examines top-level SQL, stored procedures, and the related database objects. Maximum Security Architecture (MSA) goes hand in hand with MAA, given that security issues can quickly deteriorate into full-blown and often long-term application outages. Thus, this feature is essential from the perspective of availability as well.
-
True Cache: True Cache is an in-memory, consistent, and automatically managed cache for Oracle Database. It operates similarly to an Active Data Guard reader farm, except True Cache is mostly diskless and designed for performance and scalability, as opposed to disaster recovery. An application can connect to True Cache directly for read-only workloads, significantly improving both scalability and performance, which in turn ensures application availability as workloads peak.
The features listed above are just some of the highlighted MAA features that tie in with Gold Tier RTO and RPO levels in Oracle Database 23ai that are certainly worth trying out on your own. Although I chose to highlight the features that I feel align most with the MAA Gold tier, many other Oracle Database 23ai enhancements impact the usability, flexibility, and overall capabilities of the technologies under the MAA umbrella, including Oracle RAC and Active Data Guard as well as other closely related technologies like GoldenGate 23ai. It should be noted that some of the new features above are still undergoing rigorous validation and testing via the MAA team’s Chaos Engineering methodology to determine their fit into the MAA tiers based on the multitude of planned maintenance and outage events and conditions. This type of validation never ends as the team constantly works hard to evolve our MAA architecture as the modern world continues towards technical advancement (AI being the latest).
Please stay tuned for more Oracle Database 23ai MAA guidelines, as I will be diving deeper into some of these 23ai features in the near future. In the meantime, you can check out the resources below for more information on Maximum Availability Architecture and Oracle Database 23ai.
- AI and Converged Data: Oracle’s Strategy for Data Management (Video with Larry Ellison and Juan Loaiza)
- Oracle Database 23ai Documentation
- Oracle MAA 23ai Documentation
- Oracle Data Guard 23ai MAA Best Practices
