Introduction to Ollama
Omni-Layer Learning Language Acquisition Model (Ollama) is an open source tool that makes large language model (LLM) deployment and integration largely accessible to users. With Ollama, users can independently manage their LLM ecosystems by creating new models, pulling and running pretrained models, copying models, removing models, and duplicating existing models, all from their local machines. The tool was built from a combination of unsupervised learning techniques, deep neural networks, and a multilayered architecture to progressively understand more complex linguistic patterns, allowing it to ultimately learn natural language without direct human intervention or labeling of data.
Ollama offers several key features, of which the following are particularly of note:
- Local execution (no need for cloud resources): Mitigates data risks associated with the cloud and gives users more control and autonomy to run faster models without external reliance.
- Extensive model library: Comes packaged with a wide range of pretrained LLMs (ex: llama, gpt-oss, granite, mistral, etc.) that users can deploy and run from their local machines.
- Customization: Users can create LLMs specific to their use case by editing or adding parameters to existing pretrained models, offering greater autonomy and control.
Compatibility with Oracle Linux
Currently, Ollama is compatible with MacOS, Linux, and Windows operating systems, and can be deployed seamlessly on top of Oracle Linux.
Benefits to running Ollama on Oracle Linux
Running Ollama on Oracle Linux specifically offers users and enterprises several advantages beyond those available through using a generic Linux distribution, including:
- Oracle Ksplice for live kernel patching: Ksplice can uniquely apply critical security and bug patches to the Oracle Linux kernel without interrupting a user’s Ollama workloads or requiring a system reboot.
- Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel (UEK): Ollama can leverage UEK, Oracle Linux’s featured kernel, for GPU acceleration and high throughput workloads in with AI/LLMs, serving forresulting in greater performance and reliability.
- Advanced monitoring with DTrace: Users can take advantage of the Oracle Linux dynamic tracing framework (DTrace) to observe and monitor real-time system behavior and application performance during Ollama installations and deployments.
- Oracle Support: Compatibility or security issues within Oracle Linux environments can be efficiently resolved with Oracle’s world-class enterprise support for both OS and critical libraries.
- Oracle Cloud Native Environment (OCNE) and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE): OCNE and OKE allow Ollama to be deployed in containers, offering advantages such as portability, efficiency, scalability, isolation, and faster development cycles.
Guide to starting Ollama on Oracle Linux
Prerequisites
- Access to an Oracle Linux operating system.
- Ensure that curl is installed:
sudo dnf install -y curl
Download and Run Ollama
- From your Oracle Linux machine, run the following to download the Ollama installation script:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
- After installation, start the Ollama service:
sudo systemctl start ollama
- For Ollama to start automatically on boot:
sudo systemctl enable ollama
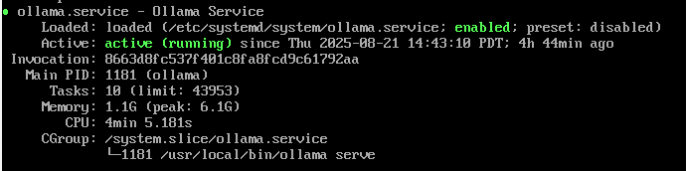
- Verify Ollama is active (running) by checking its status:
sudo systemctl status ollama
- If you want to access Ollama remotely or allow for incoming connections, adjust any firewall settings to allow traffic on the default Ollama port (11434):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=11434/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
- Pull and run a model (make sure you have enough memory space for the model’s requirements):
ollama pull llama3 ollama run llama 3
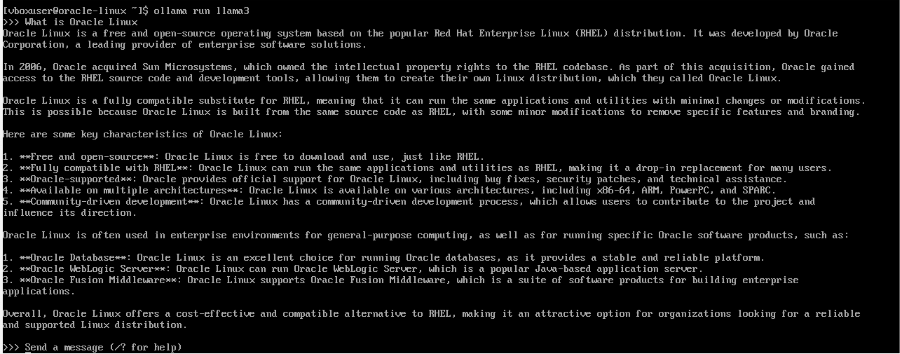
- Interact with the model through the command line and test different prompts:
Ollama’s REST API
Ollama’s REST API allows users to interact locally with LLMs through HTTP requests, so that Ollama’s capabilities to be leveraged by various applications without requiring a CLI or GUI.
By default, the Ollama server is set to run at http://localhost:11434/api . This functions as the base URL for all the API endpoints. Ollama offers the following two primary endpoints:
- /api/generate: generate a text response for a specific prompt with a provided model
- /api/chat: allows for conversations by keeping track of a history of messages
More details about the accepted parameters can be found in the official Ollama REST API documentation.
Use the Ollama REST API to run and manage models
- The Ollama server runs at http://localhost:11434 by default. You can check if it is running by confirming that the following outputs a response:
curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags

- Interact with the API using curl (for CLI), Python (with the requests library), or any tool/language that supports HTTP.
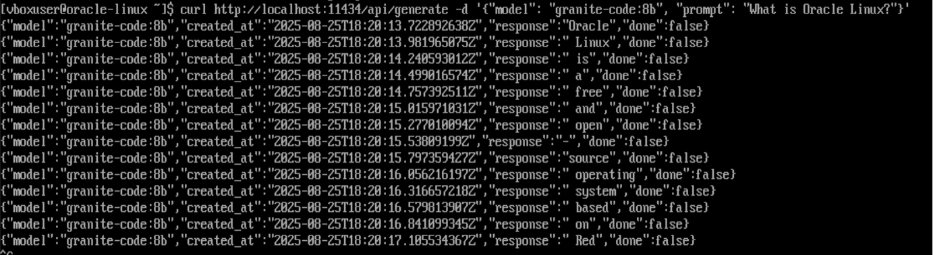
E.g.: generate text from model (streaming)
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate -d '{
"model": "granite-code:8b",
"prompt": "What is Oracle Linux?"
}'
Returns a stream of JSON objects
E.g.: generate text from model (no streaming):
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate -d '{
"model": "granite-code:8b",
"prompt": "What is Oracle Linux?",
"stream": false
}'
Returns response without streaming

E.g.: basic example with python
import requests
url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"
data = {
"model": "granite-code:8b",
"prompt": "What is Oracle Linux?"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
print(response.txt)
Modelfiles
Modelfiles are configuration files used by Ollama to create a custom version of AI models that start from a pretrained public base model and are then finetuned based on a user’s specific needs. This feature of Ollama allows for the following:
-
Defining a model’s persona or behavior
-
Finetuning parameters (to specify creativity, response length, response format, etc.)
-
Formatting input/output through templates
-
Packaging behavioral and parameter changes into a reusable model
Using Modelfiles to create a customized version of LLMs
Modelfiles can be used to build upon pretrained LLMs and fine-tune them for specific use cases. For instance, an Oracle Linux bot can be built seamlessly on top of an existing LLM like llama3 that is set to assist a user with questions about Oracle Linux and maintain certain predefined parameters when responding. All the available parameters can be found in official Ollama documentation, and some are outlined in the example below.
E.g.: Using a Modelfile to create an Oracle Linux Bot to assist users with FAQs
FROM llama3 SYSTEM "You are an Oracle Linux Bot, an expert on Oracle Linux. Use only information from official Oracle Linux public documentation, FAQs, and support articles found at oracle.com/linux. If the user asks about something not covered or you don't know the answer, respond with: 'I'm sorry, I can only answer questions based on the official Oracle Linux public documentation at oracle.com/linux.' Do not provide speculative or unofficial guidance." # Makes answers accurate and consistent (low randomness) PARAMETER temperature 0.15 # Encourages diversity in word choice to some extent PARAMETER top_p 0.8 # Makes responses more robust but not too lengthy PARAMETER num_predict 300
- From the directory with the Modelfile, run
ollama create oracle-linux-bot -f ModelFile
- To start the customized model, run
ollama run oracle-linux-bot

Deploying a User-Friendly Interface through Open WebUI
What is Open WebUI
Open WebUI is an open source web interface that provides a graphical web interface to interact with LLMs and other AI models completely offline. It supports Ollama and OpenAI-compatible APIs and includes local Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) integration, web browsing capability, image generation integration, code interpretation, and more. It provides a way to interact with an Ollama instance through a user interface.
Installing Open WebUI
- Install Open WebUI using pip as follows
pip install open-webui
- Start Open WebuUI by running
open-webui serve
- Then, the Open WebUI server will start and can be accessed at http://localhost:8080. Ensure that no other processes are using ports 5050 or 5173.
Note: If using a virtualization software like Oracle VirtualBox, set up port forwarding from Host Port 8080 to Guest Port 8080 to access the server through your host machine (alternatively, open a web browser through the VM directly).
- Click the Get Started button and register your admin account or log in if you have an existing account.
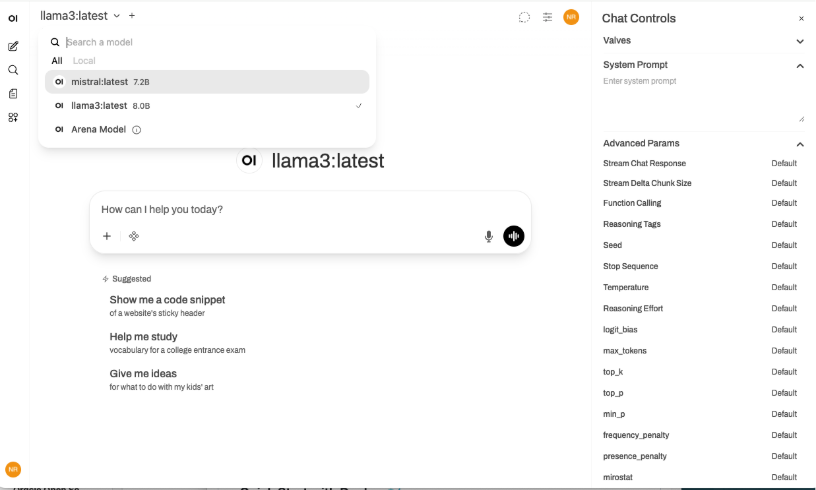
- Interact with the Open WebUI through the chat interface and toggle between models previously installed through Ollama. The Chat Controls allow for customization of various model parameters and configuration of system prompts. Additional administrative features can be changed and set through the Settings panel.
Try it yourself!
Deploying Ollama on top of Oracle Linux combines the security and performance of an enterprise-grade operating system with cutting-edge AI tools. Features such as Ksplice, UEK, and DTrace, along with world-class Oracle Support, make Oracle Linux an ideal choice for deploying efficient, scalable AI workflows.
Download Oracle Linux sources, binaries, ISOs, and errata through the Oracle Linux yum server and download Ollama through the Ollama downloads page to get started today.
Resources
- Ollama Explained: Transforming AI Accessibility and Language Processing
- Ollama Features and Deployment
- Ollama GitHub
- Oracle DTrace
- Supported Oracle Linux Containers
- Exploring Ollama REST API Endpoints
- Ollama Documentation
- Ollama Parameters and Values
- Using Ollama with Open WebUI
- Open WebUI GitHub