Introduction
Securing Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) integrations often relies on OAuth 2.0, a widely used authentication method. When using OAuth as the security policy for OIC triggers, the standard practice involves creating trusted or confidential applications in the Identity Domain of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Console. This setup is crucial for ensuring that only authenticated and authorized entities can access your integration processes.
For those looking to delve deeper, Oracle’s documentation provides detailed instructions on OAuth authentication in OIC, including the process of creating trusted applications within the OCI Identity service.
Usecase
When setting up a Customer Managed Disaster Recovery (DR) solution for an OIC instance, a secondary instance is typically created in a different cloud region as a replica of the primary (production) instance. The detailed configuration and architecture of this DR solution for OIC are provided in Oracle’s documentation.
Since trusted or confidential applications in OAuth are generally tied to specific OIC instance resources, supporting OAuth-based integrations in a DR scenario requires careful planning. Here are two possible approaches:
- Create a New Trusted/Confidential Application for the DR Instance
- In this approach, a new trusted/confidential application is created within the OCI Identity service specifically for the secondary (DR) instance. End systems that consume OIC services would need to use this new application to generate authentication tokens for accessing the DR instance. This ensures that the secondary instance is secured with a distinct OAuth configuration.
- Update the Existing Trusted/Confidential Application to Include DR Instance Resources
- Alternatively, the existing trusted/confidential application associated with the primary (production) instance can be updated to include the resource scope of the secondary (DR) instance. This allows end systems to continue using the same trusted application as they do with the production instance but switch the resource scope to target the DR instance. This way, they can generate an authentication token that authorizes requests to the DR instance without creating a new application.
Both approaches impact the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) for the DR solution, as they require updates from the end systems that interact with the OIC services using OAuth.
Solution
In this blog, we’ll discuss the approach that minimizes configuration changes while setting up the DR solution, avoiding modifications to end systems and ensuring no impact on the Recovery Time Objective (RTO). The steps involved are as follows.
- Update the Cloud Service Application of the Primary (Production) Instance
- Expand the Scope of the Trusted/Confidential Application
- Configure the Secondary (DR) Instance Cloud Service Application roles.
- Generate and Test Authentication Token for both Primary and Secondary instances.
Update the Cloud Service Application of the Primary (Production) Instance
Modify the Cloud Service Application configuration of the primary (production) instance to include URLs for the secondary (DR) instance. This ensures that both instances are recognized within the same application setup.
Navigate to the Oracle Cloud Services section, under Identity Domain from the OCI console. Select the Primary instance.
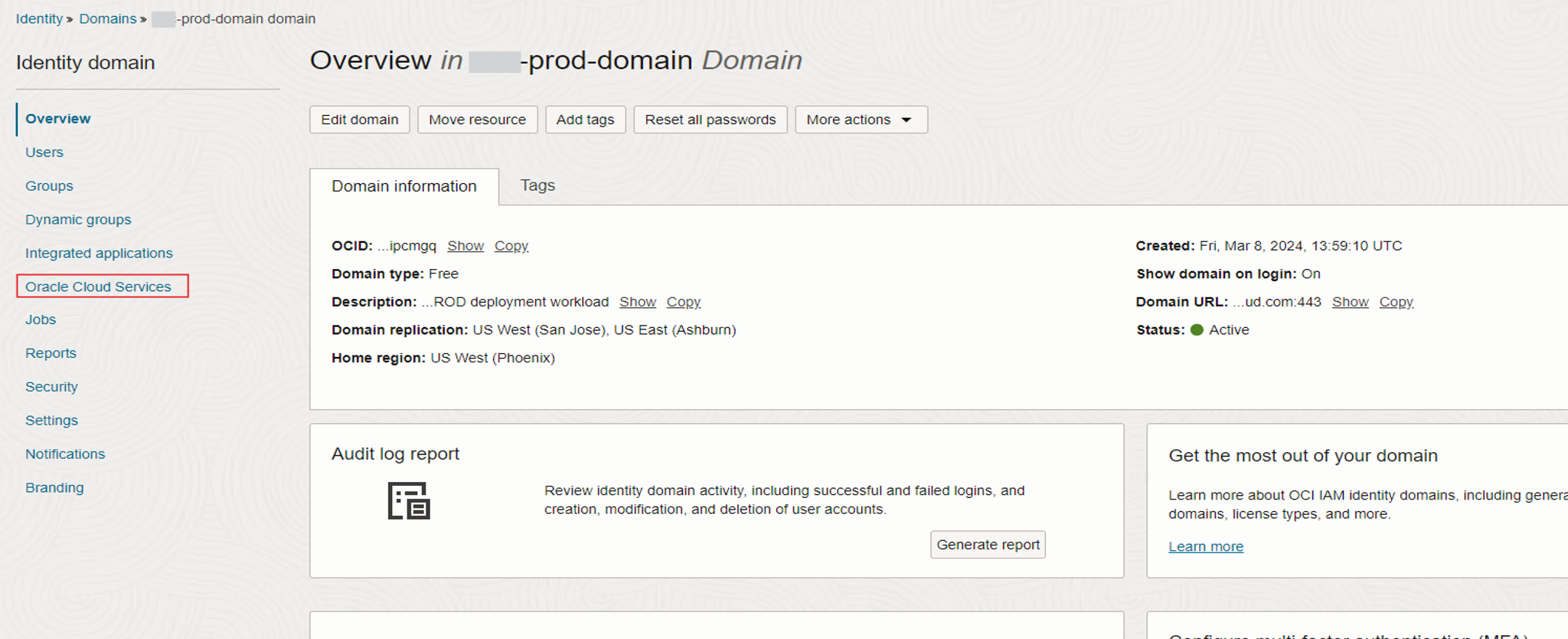
Open the Oracle Cloud Service for the primary instance.
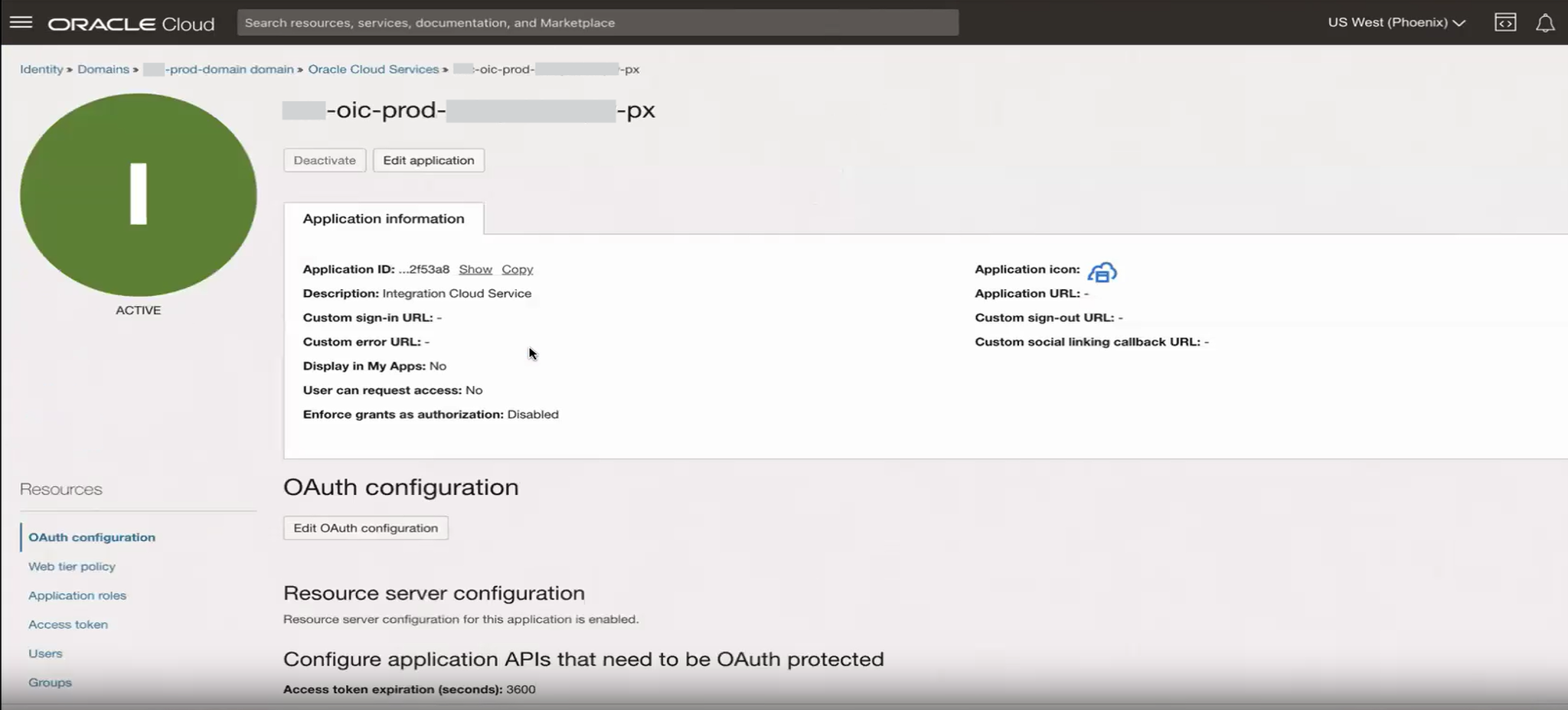
Edit the OAuth configuration to add entries for the secondary audience.
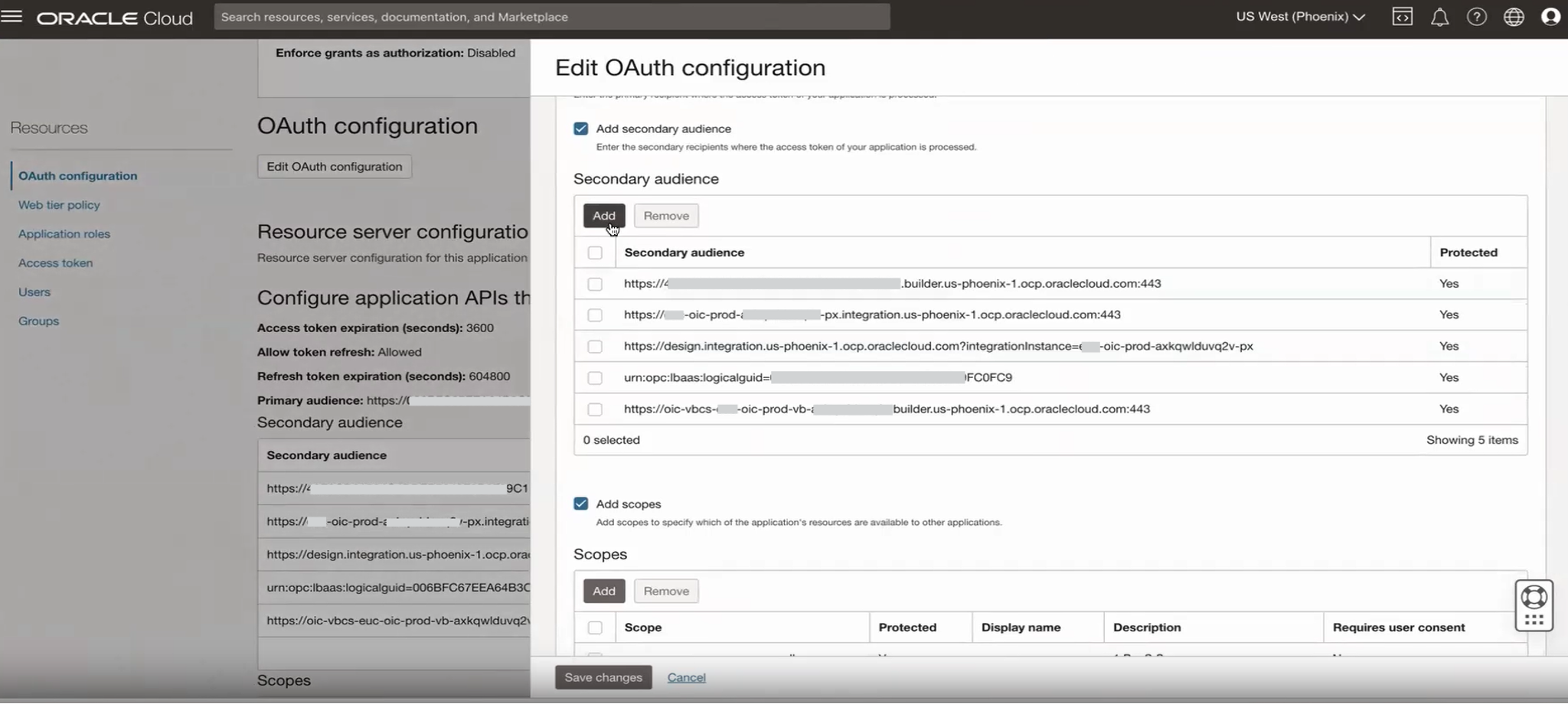
Add the Runtime and Design time URL of the secondary OIC instance in the Oracle Services app of the primary instance.
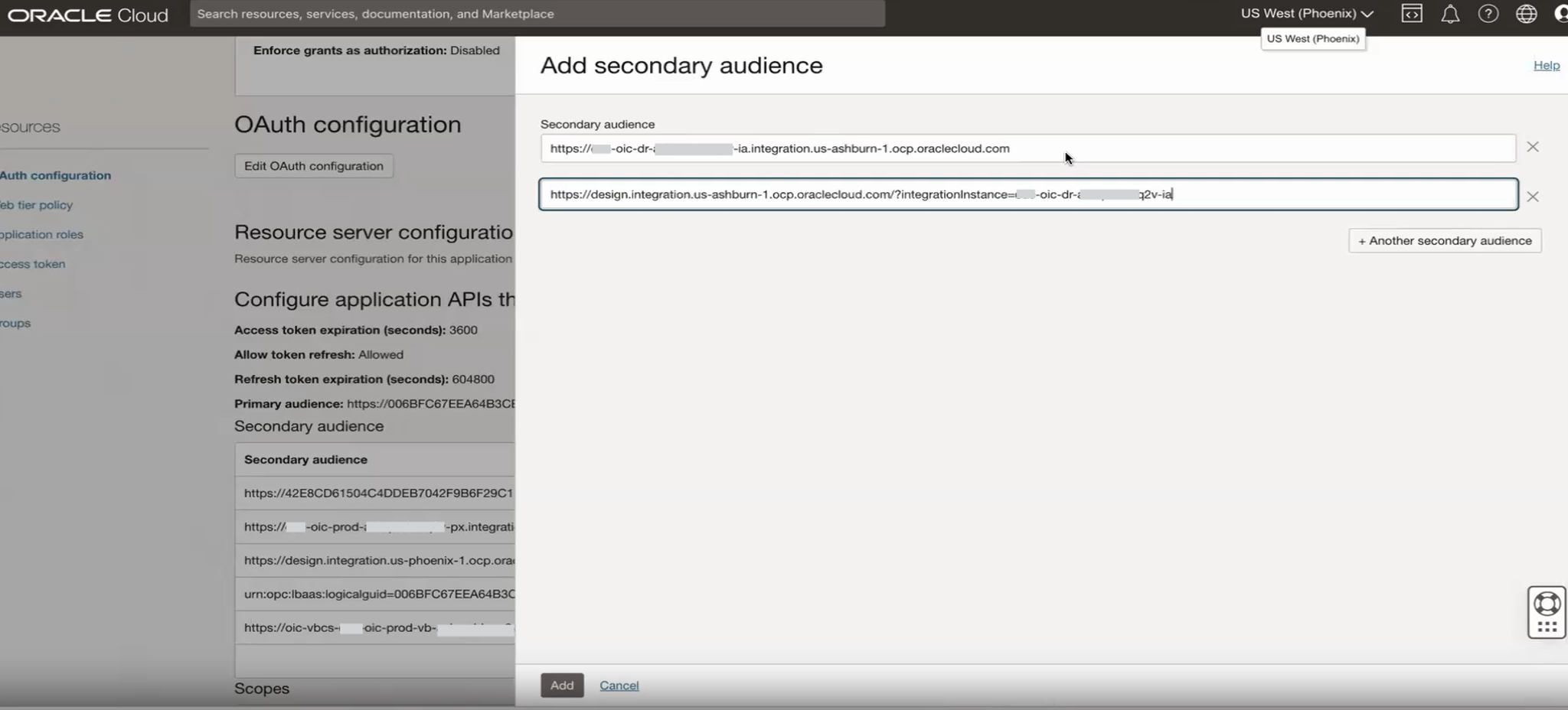
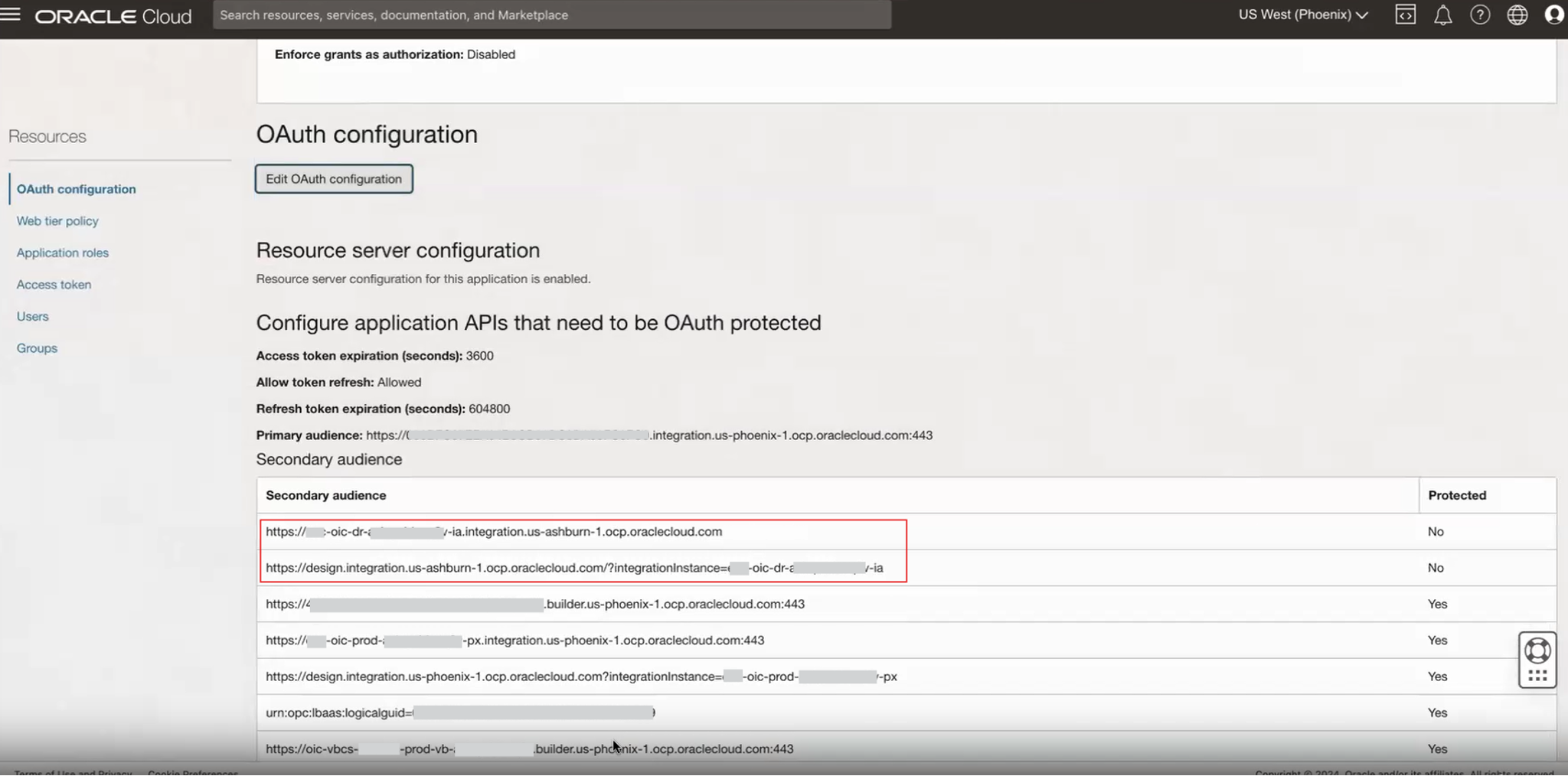
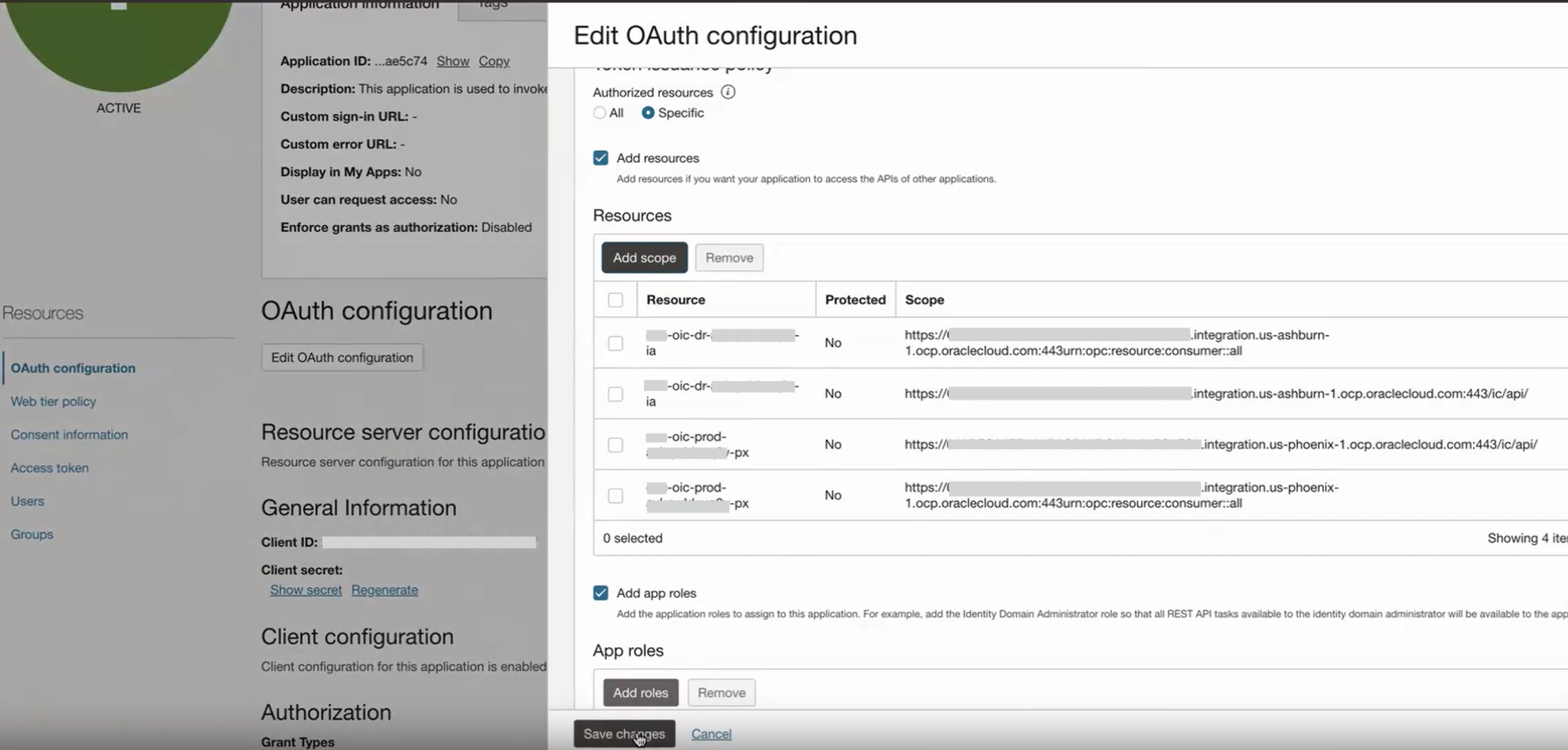
Expand the Scope of the Trusted/Confidential Application(s)
Update the trusted or confidential application associated with the primary (production) instance to include the resource scope of the secondary (DR) instance. This adjustment allows the same OAuth application to handle requests for both the production and DR instances.
Navigate to the Integrated applications section, under Identity Domain from the OCI console.
Open the Confidential application for the OAuth to the primary instance.
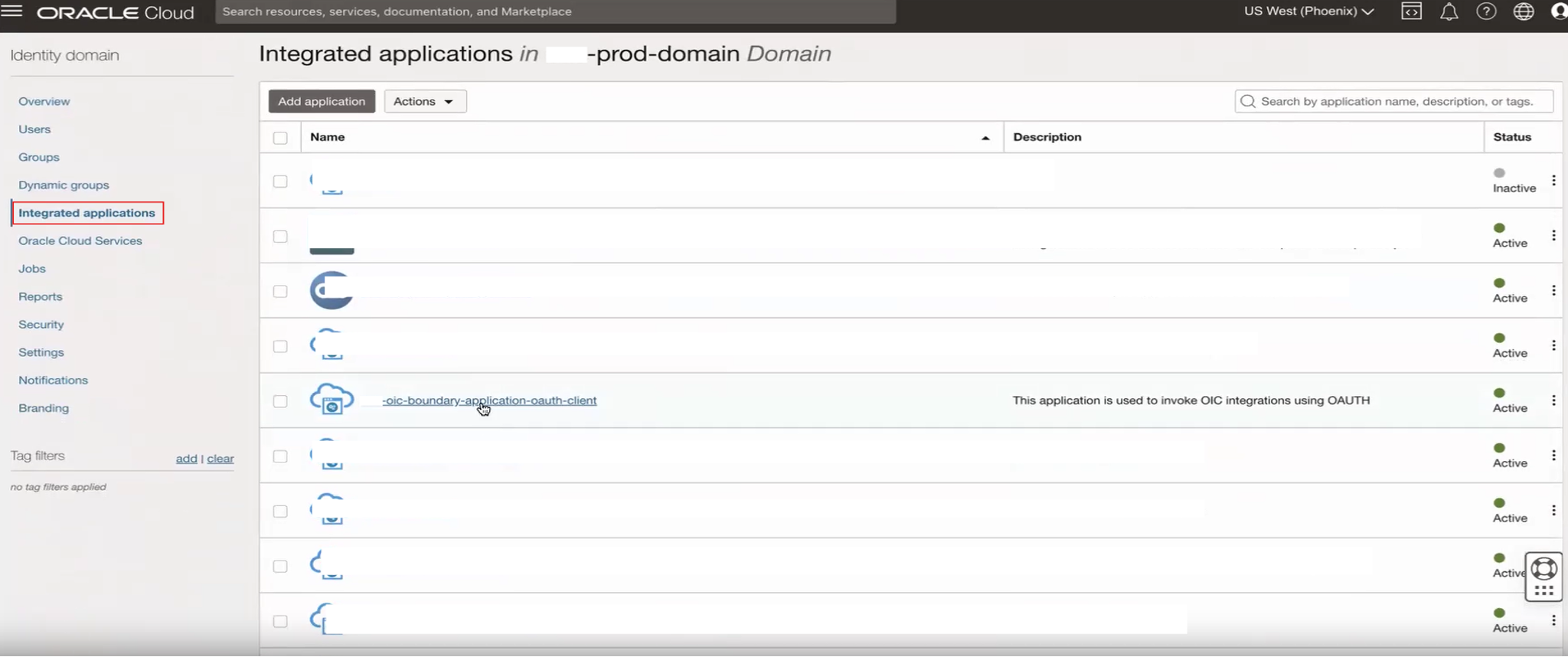
Edit the OAuth configuration of the selected application.
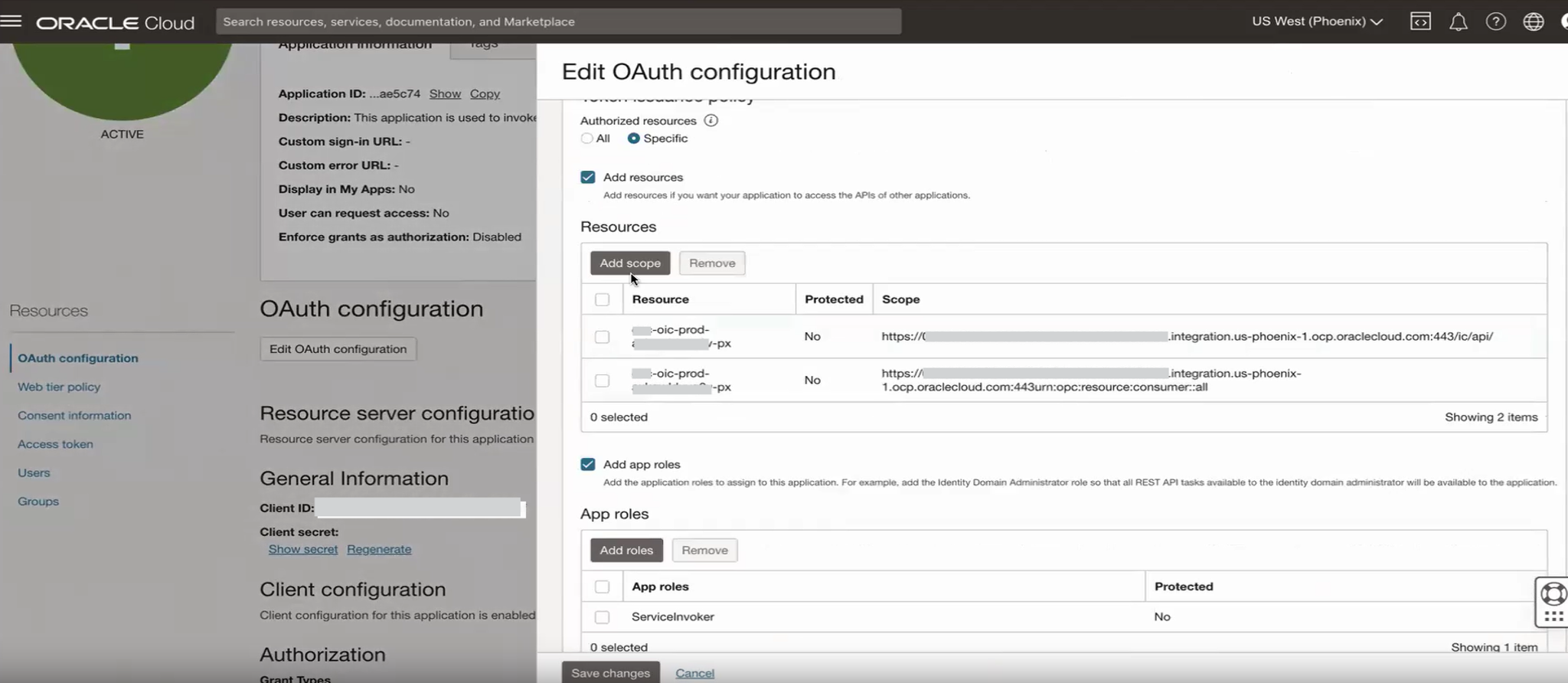
Add the secondary instance scope to the application under the scope section.
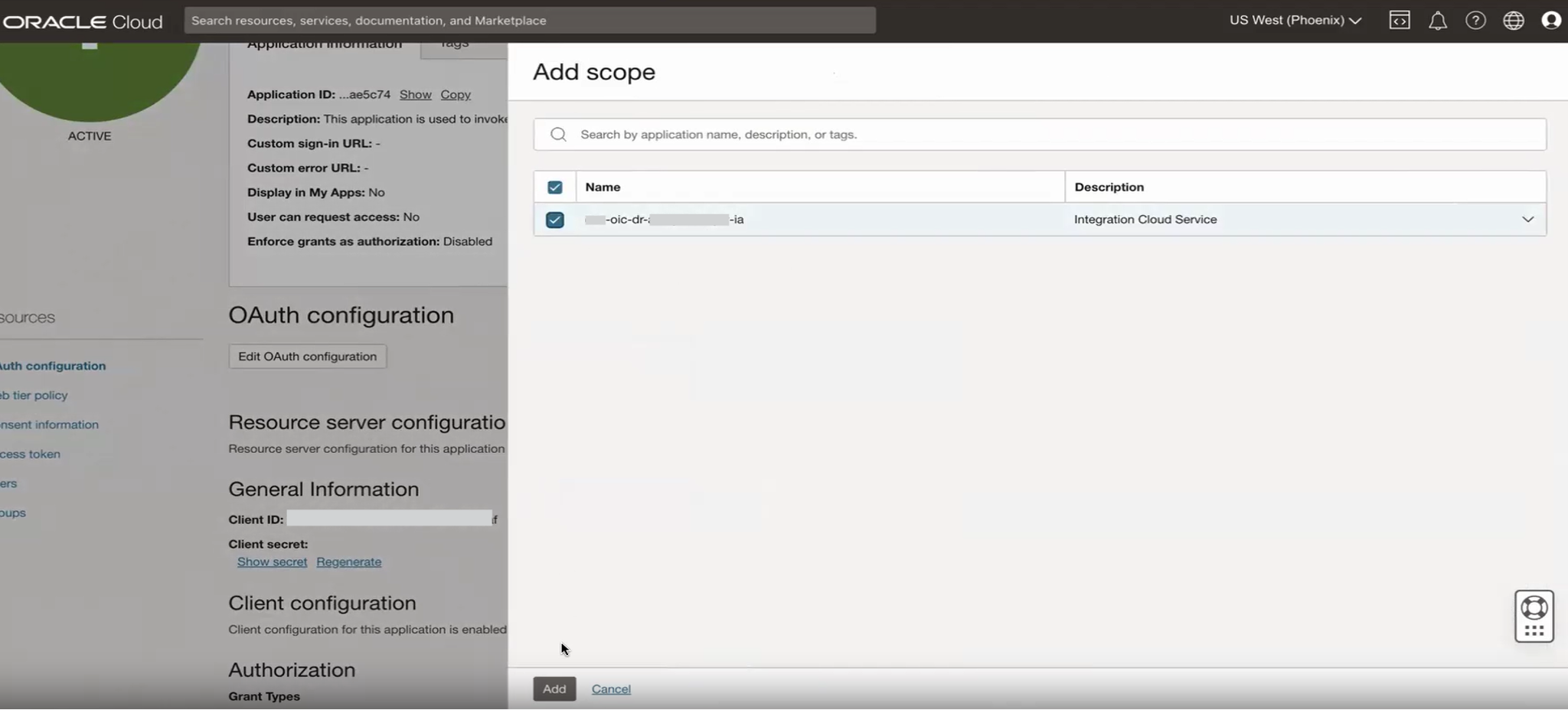
Save changes once the scope is added successfully.
Configure the Secondary (DR) Instance Cloud Service Application roles.
Update roles and permissions to integrate with the trusted/confidential applications configured in the above step. This ensures that the DR instance aligns with the primary instance’s OAuth settings.
Navigate to the Oracle Cloud Services section, under Identity Domain from the OCI console.
Select the Secondary instance.
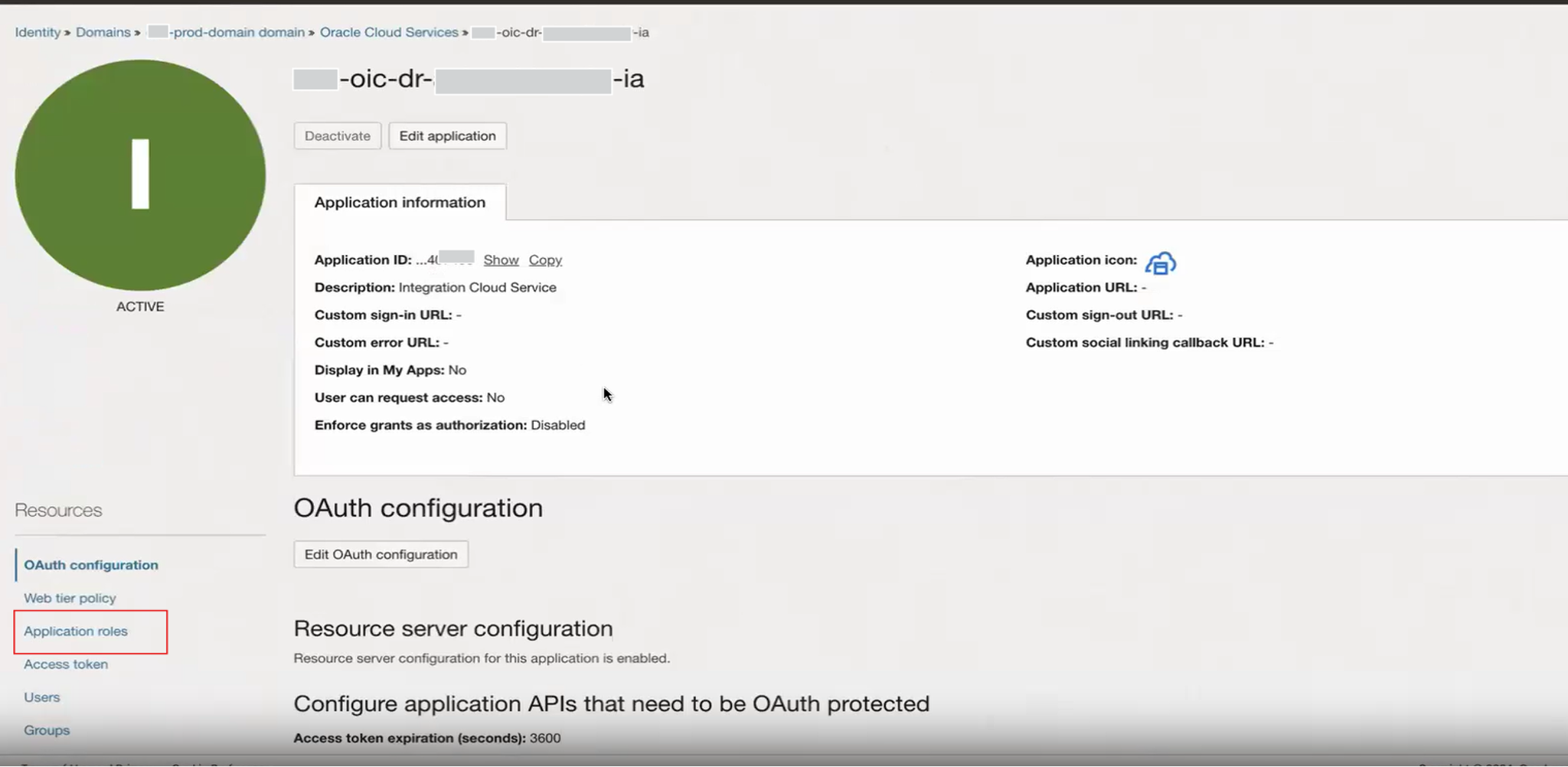
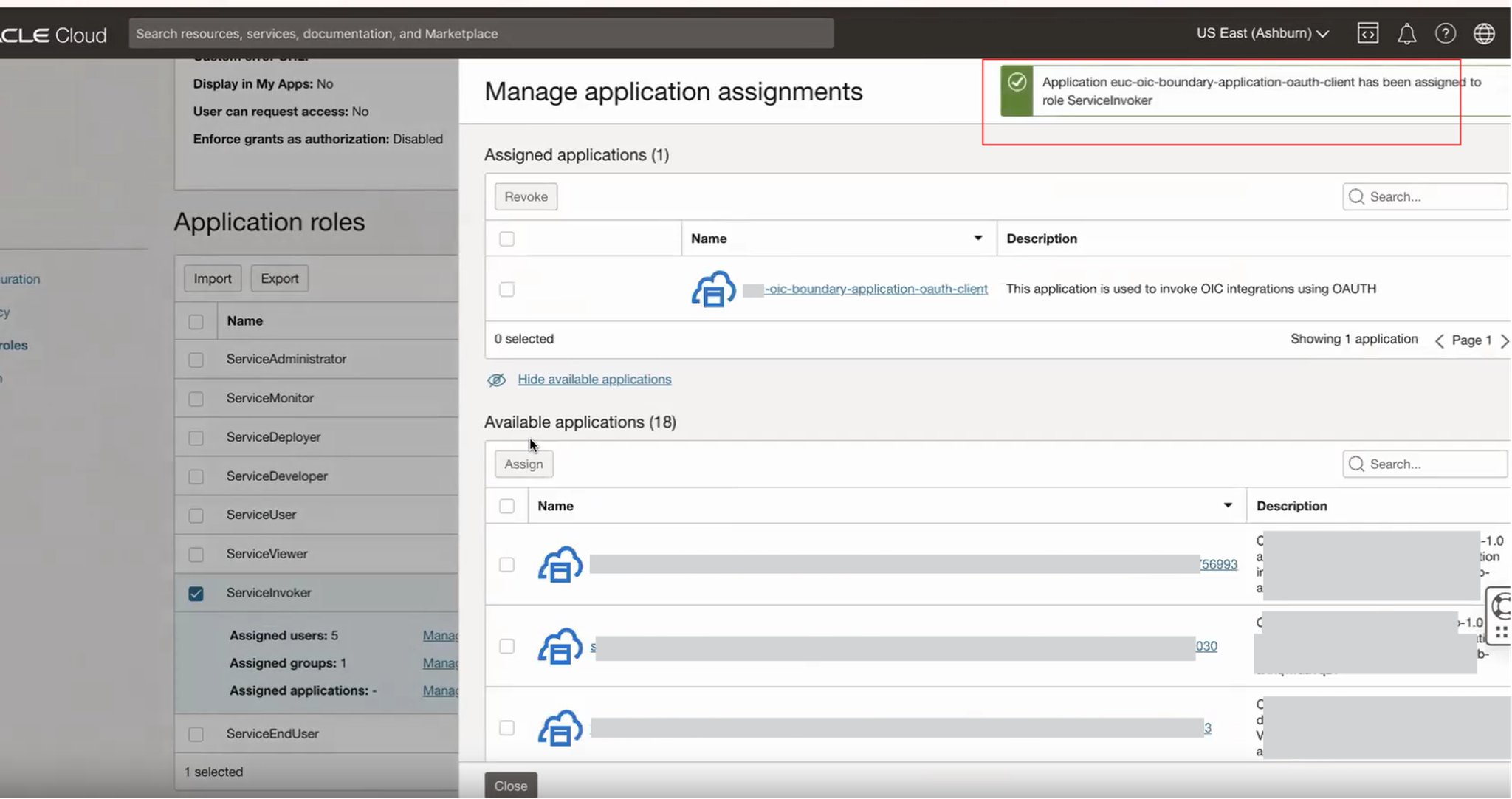
Click on the application roles from the resources. Expand the desired role and click Manage
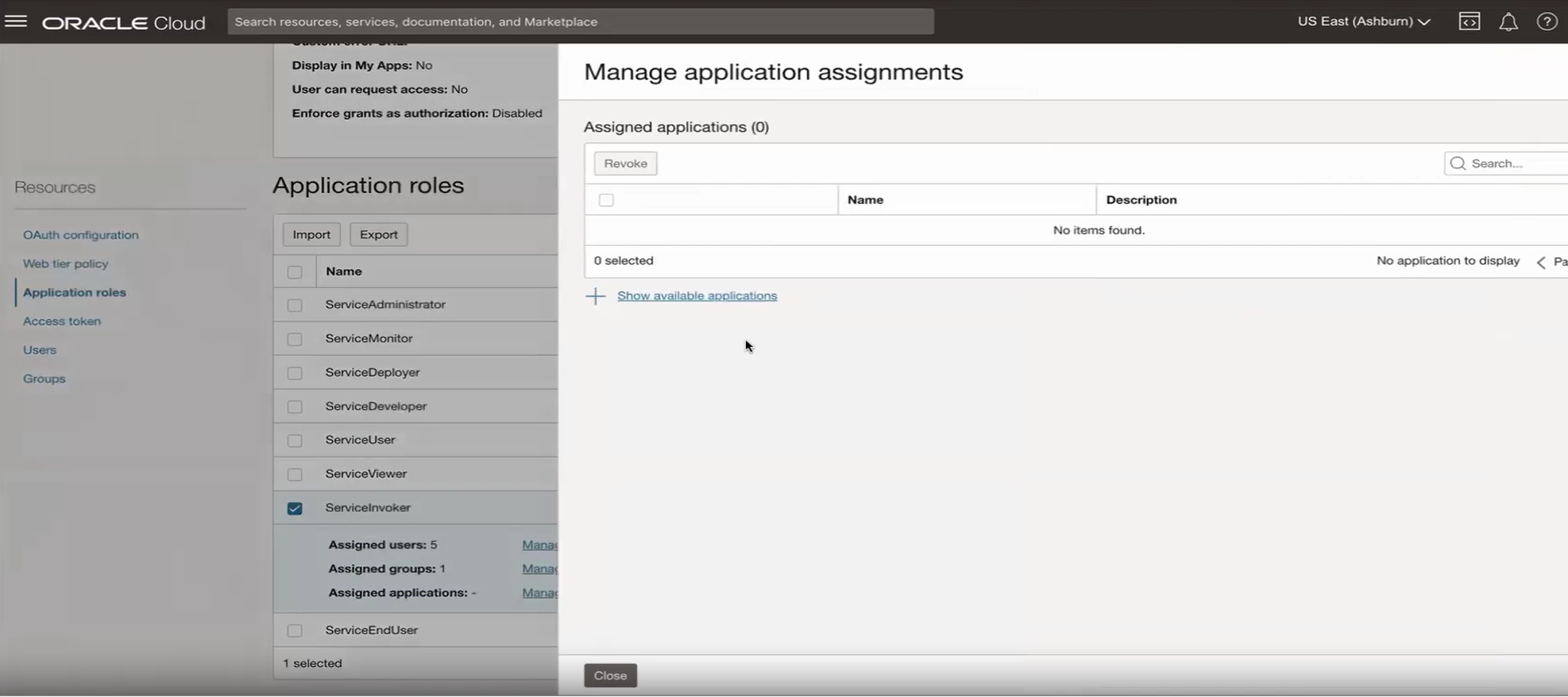
Select the trusted/confidential application and assign it with the appropriate role.
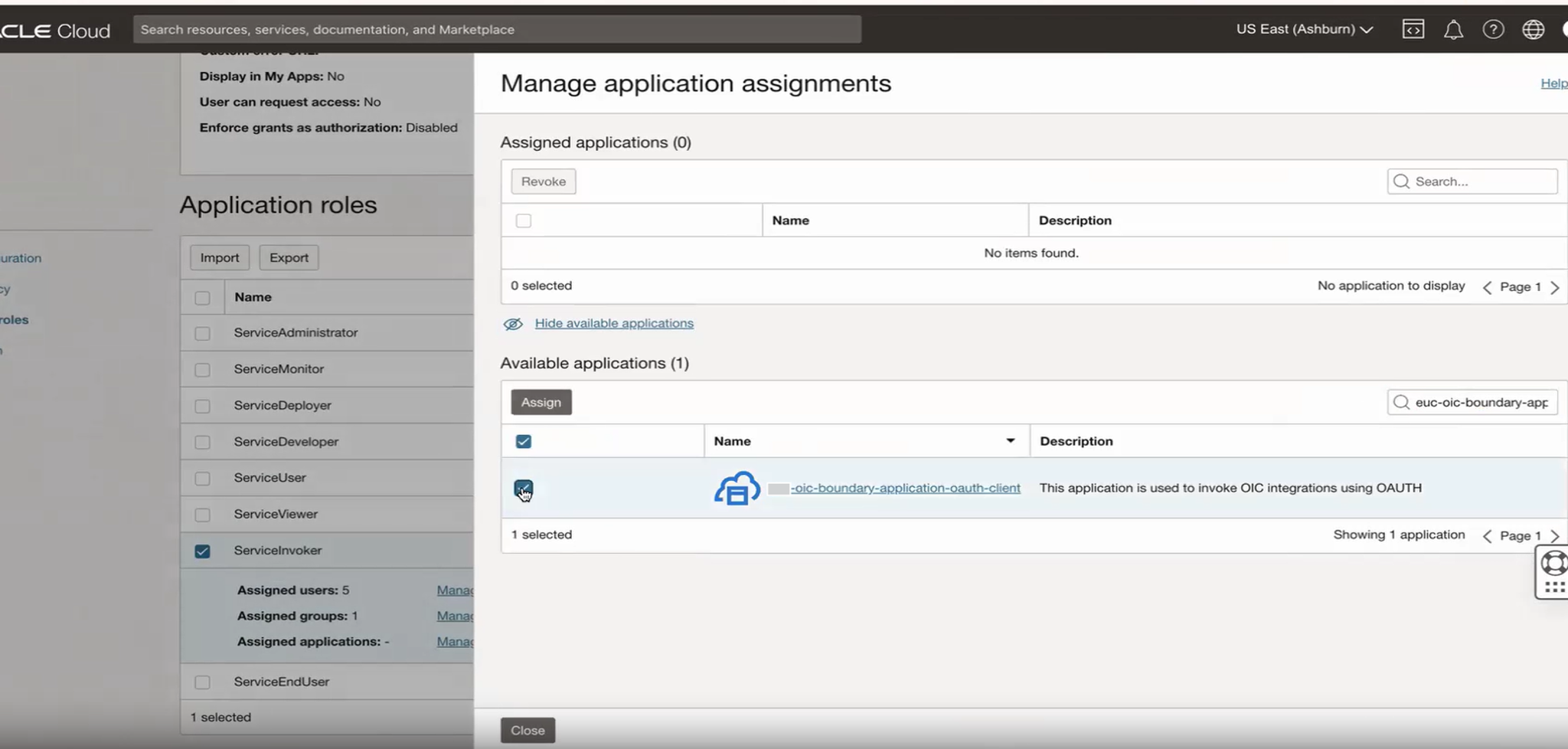
Assign the selected application to the role.
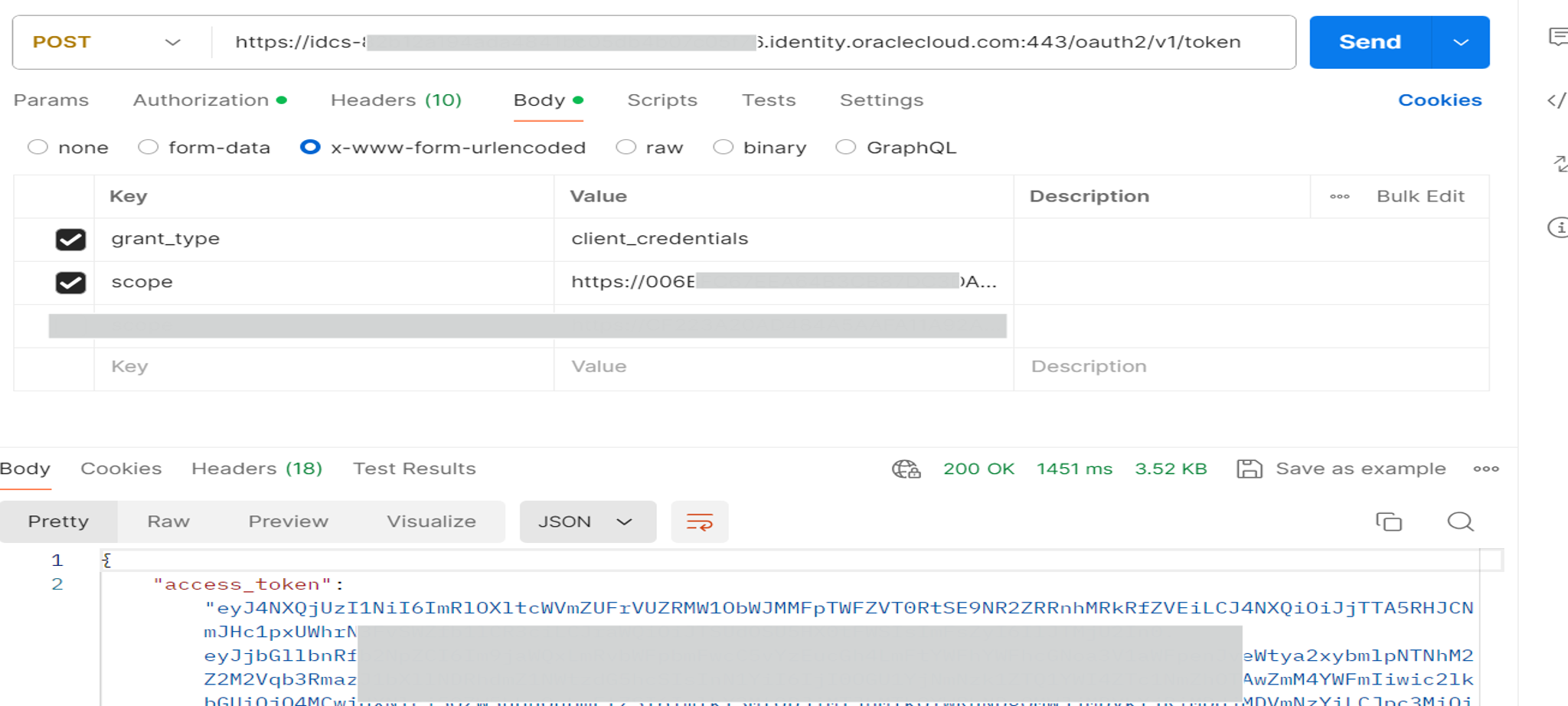
Generate and Test Authentication Token for both Primary and Secondary instances.
To test the solution, generate the OAuth token for the trusted/confidential application using the scope of primary application.
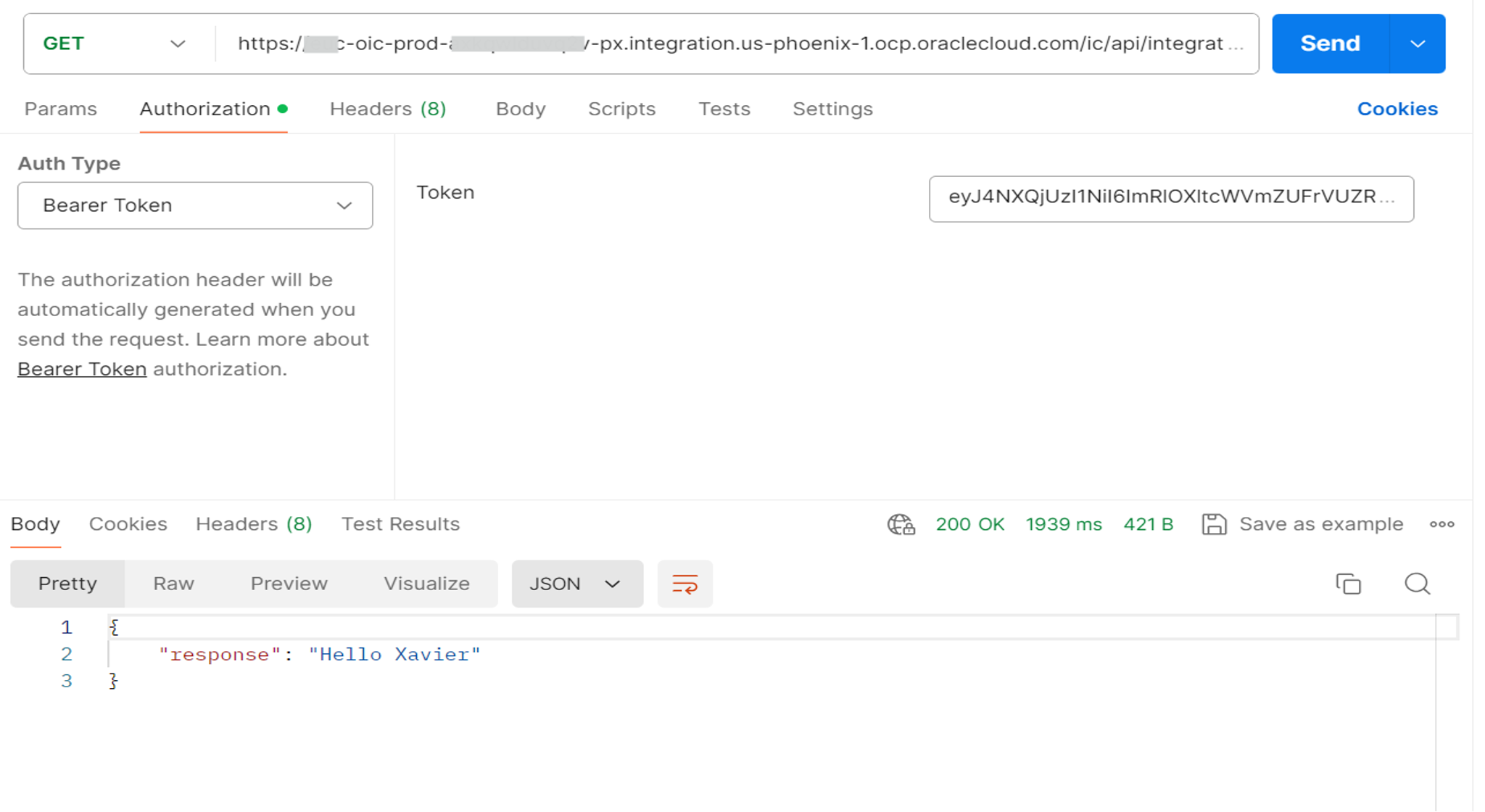
Test the integration on the Primary (Prod) instance using the access token.
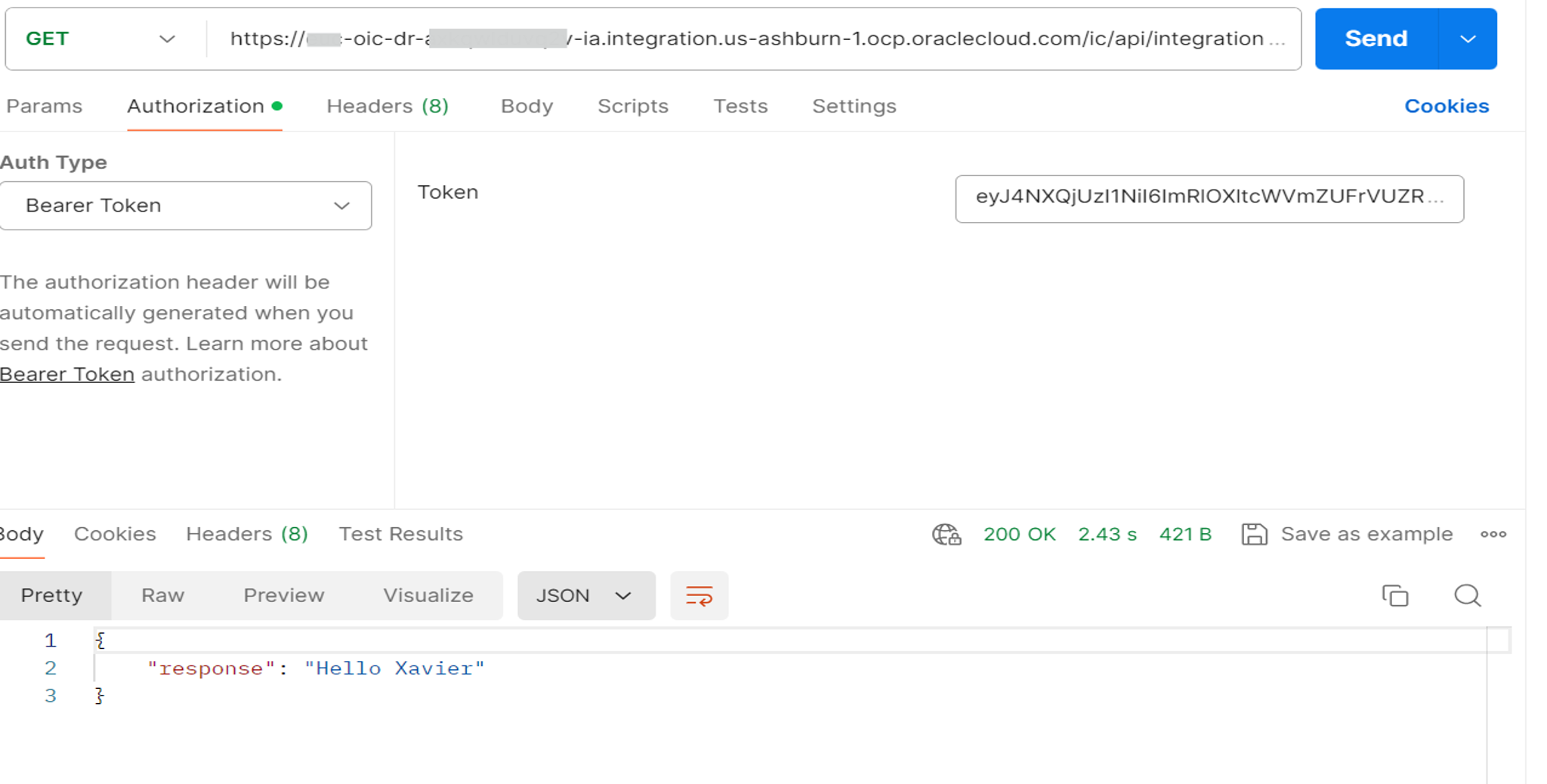
Test the integration on the secondary (DR) instance using the access token.
Conclusion
Implementing a Disaster Recovery (DR) solution for Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) while maintaining seamless OAuth integration is crucial for ensuring business continuity. By following the outlined approach, you can streamline the DR setup with minimal configuration changes, no impact on end systems, and without compromising the Recovery Time Objective (RTO). This method ensures that your DR instance is ready to take over seamlessly in the event of a failure, providing robust and reliable continuity for your critical integrations.
Learn more about why Oracle Integration is right for you at oracle.com/integration.

