Introduction
Exadata patchmgr is a specialized utility that intelligently manages software updates on the Exadata Engineered System, delivering automated updates for Exadata database servers, storage servers, and network fabric switches. It orchestrates complex updates effortlessly and reliably with the simplicity of a single command, minimizing effort. Applying regular software updates is critical for all customers and workloads, ensuring system security, optimizing performance, and maintaining continuous availability. Exadata patchmgr supports online, rolling, and non-rolling updates, giving administrators the flexibility to choose the best patching strategy for their environment. With online and rolling updates, Exadata maintains continuous availability for Oracle RAC databases by applying patches without downtime. For scenarios that require a non-rolling update, patchmgr applies updates in parallel across all target servers, but database downtime is necessary during the process.
Exadata patchmgr Functional Overview
The patchmgr utility is capable of managing automated software updates across multiple database servers. Exadata patchmgr is run on a “driving system”, which is typically a non-Exadata database server, that acts as a central server to update multiple Exadata systems. Comprehensive patchmgr command help is available in the official Exadata documentation.
By default, the appropriate patchmgr distribution is included with the relevant server or switch update. However, it is recommended to always use the latest available version of patchmgr. The patchmgr utility is updated frequently to address known issues and best practices, and to support new hardware.
Let’s now examine the internal architecture and operational workflow of patchmgr.

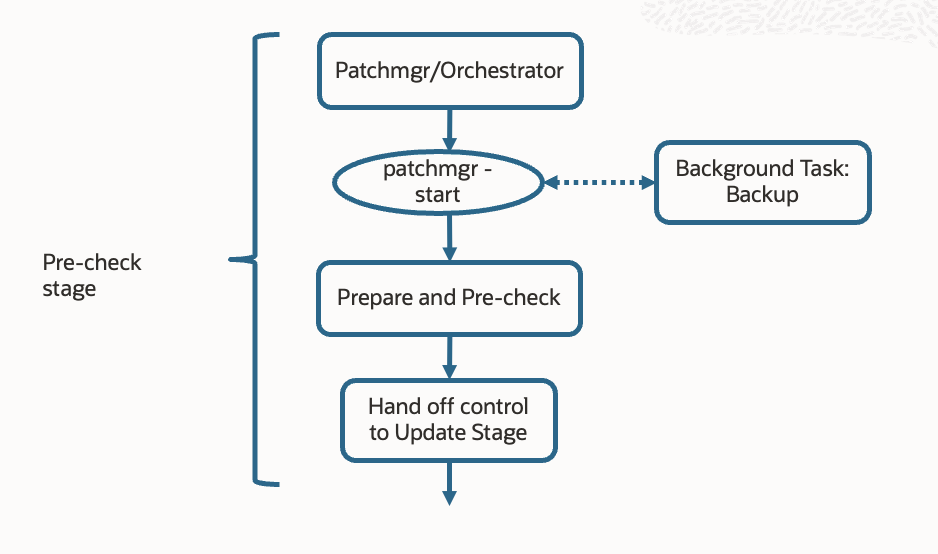 When patchmgr is run on database servers, it begins with a pre-check stage. During this phase, patchmgr uses information provided by the user, such as the desired patch level and target components. The pre-check also validates prerequisites and checks for potential conflicts, ensuring that only the necessary updates are applied and helping prevent errors during the patching process. Next, it stages the necessary software bundles onto the relevant target nodes, verifying integrity and compatibility. patchmgr intelligently validates system readiness by running environment and configuration checks, such as checks of disk space and service status, and also performs checks of applicable patch levels. A successful outcome ensures that all components are ready to be updated. Any blocking issues detected are logged and flagged for resolution, preventing the update from starting under suboptimal conditions. Exadata patchmgr also performs a backup before an update. A recent backup can be used for rollback and will be used for auto-rollback, if necessary.
When patchmgr is run on database servers, it begins with a pre-check stage. During this phase, patchmgr uses information provided by the user, such as the desired patch level and target components. The pre-check also validates prerequisites and checks for potential conflicts, ensuring that only the necessary updates are applied and helping prevent errors during the patching process. Next, it stages the necessary software bundles onto the relevant target nodes, verifying integrity and compatibility. patchmgr intelligently validates system readiness by running environment and configuration checks, such as checks of disk space and service status, and also performs checks of applicable patch levels. A successful outcome ensures that all components are ready to be updated. Any blocking issues detected are logged and flagged for resolution, preventing the update from starting under suboptimal conditions. Exadata patchmgr also performs a backup before an update. A recent backup can be used for rollback and will be used for auto-rollback, if necessary.
The patchmgr log contains information about the Exadata system software update process, including details about database server reachability, any errors encountered, and the progress of the update. A subset of the log is presented here.
|
<timestamp> :INFO : Hosts Reachable: [test_machine] <timestamp> :INFO : All hosts are reachable via ICMP/ping <timestamp> :Working: Verify SSH equivalence for the root user to test_machine <timestamp> :SUCCESS: Verify SSH equivalence for the root user to test_machine <timestamp> :INFO : Preparing nodes: test_machine <timestamp> :Working: Check for enough free space on test_machine to transfer and unzip files. <timestamp> :SUCCESS: Check for enough free space on test_machine to transfer and unzip files. |
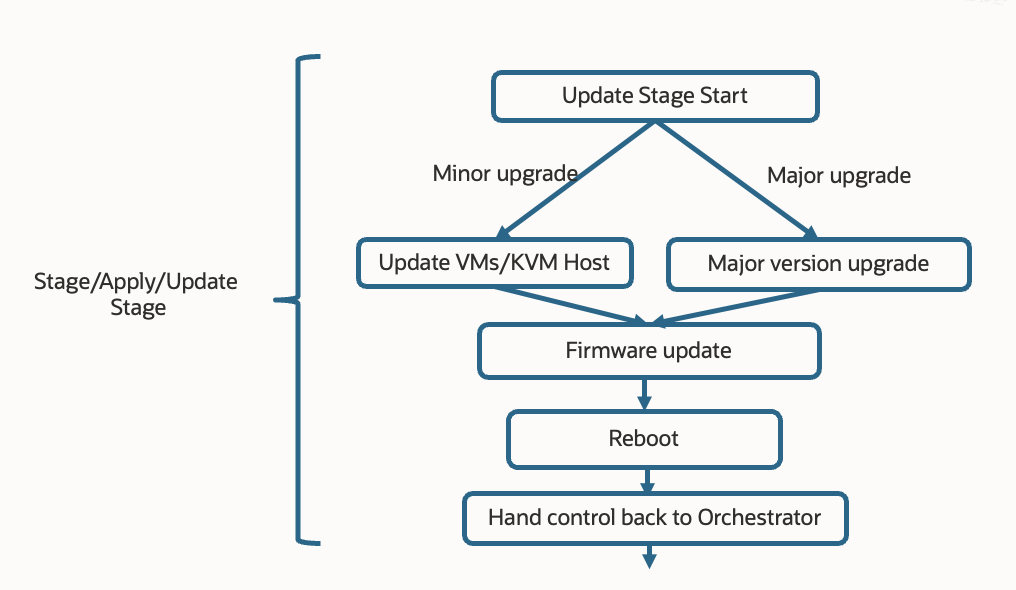 Once the pre-check stage completes successfully on a database server, the patchmgr moves to the Stage/Apply/Update stage and initiates the update process. patchmgr automation intelligence coordinates multiple sub-utilities to manage the update. The automation then orchestrates the update using yum or dnf, applying the designated RPMs to the database node stack. yum is used for updates on Oracle Linux 7, while dnf (dandified yum) is used for updates on systems that run Oracle Linux 8 and later. The update is carefully checked and sequenced to ensure that dependencies are honored, and rollback options are available in case of failure. Updates, including those involving firmware, may require multiple reboots.
Once the pre-check stage completes successfully on a database server, the patchmgr moves to the Stage/Apply/Update stage and initiates the update process. patchmgr automation intelligence coordinates multiple sub-utilities to manage the update. The automation then orchestrates the update using yum or dnf, applying the designated RPMs to the database node stack. yum is used for updates on Oracle Linux 7, while dnf (dandified yum) is used for updates on systems that run Oracle Linux 8 and later. The update is carefully checked and sequenced to ensure that dependencies are honored, and rollback options are available in case of failure. Updates, including those involving firmware, may require multiple reboots.
|
<timestamp> :INFO : Current image version on dbnode(s) is: <timestamp> :INFO : test_machine: 25.1.5.0.0.250517 <timestamp> :INFO : For details, check the following files in /u01/patchmgr/dbserver_patch_250517: <timestamp> :INFO : - <dbnode_name>_dbnodeupdate.log <timestamp> :INFO : - patchmgr.log <timestamp> :INFO : - patchmgr.trc <timestamp> :INFO : Exit status:0 <timestamp> :INFO : Exiting. |
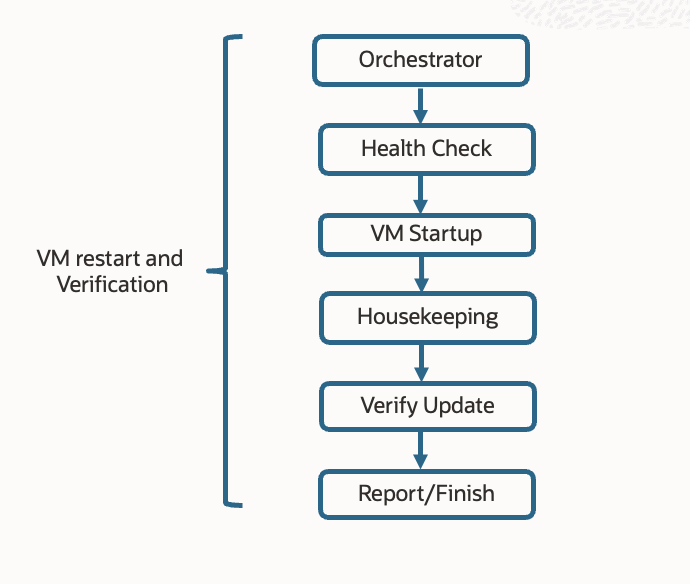 After the update is applied and the node is brought back online, key services are validated before control is handed back. The patchmgr then confirms update completion, logs the update status, and continues to the next node or component in the patching plan.
After the update is applied and the node is brought back online, key services are validated before control is handed back. The patchmgr then confirms update completion, logs the update status, and continues to the next node or component in the patching plan.
With the introduction of Exadata Live Update, patchmgr can now apply updates, such as security patches, to the running kernel and user-space libraries, without requiring a reboot. Using industry-standard utilities such as Ksplice and RPM, Live Update enables customers to update their database servers – bare metal, VM Hosts, and VM Guests, and, more specifically, kernel/system packages, firmware, user space packages, and Exadata packages – online! With Live Update, the target system remains available and does not need to be restarted for changes to take effect. These interruption-free and online software updates on Exadata database servers can be run frequently and, because they apply security fixes, help organizations meet security compliance requirements.
If the update requires a restart, patchmgr monitors the restart process, ensuring that all expected services come up cleanly. Health checks are automatically performed to validate critical components. It is also verified that the patched software components are running the updated versions and that system resources are functioning within expected thresholds. Additional housekeeping tasks, such as cleanup of temporary files and logging, are completed to maintain a clean state. Once all nodes or VMs have been successfully restarted and validated, patchmgr logs the results and generates a comprehensive report summarizing the patch status, including any warnings, and reports the final system health. This ensures traceability and gives administrators a clear view of the update outcome.
|
<timestamp> :SUCCESS: Completed run of command: ./patchmgr --dbnodes dbs_group --upgrade --repo /u01/patches/dbnode/p37471649_241000_Linux-x86-64.zip --target_version 25.1.5.0.0.250517 <timestamp> :INFO : Upgrade performed on dbnode(s) in file dbs_group: [test_machine] <timestamp> :INFO : Current image version on dbnode(s) is: <timestamp> :INFO : test_machine: 24.1.5.0.0.250517 <timestamp> :INFO : For details, check the following files in /u01/patchmgr/dbserver_patch_250517 <timestamp> :INFO : - <dbnode_name>_dbnodeupdate.log <timestamp> :INFO : - patchmgr.log <timestamp> :INFO : - patchmgr.trc <timestamp> :INFO : Exit status:0 <timestamp> :INFO : Exiting. |
And that’s all there is to it. The update step is managed with a single command. With patchmgr, updates to database servers aren’t just easy. They’re effortless, automated, reliable, and intelligent.
Exadata update of Storage Servers
Updates to Exadata Storage Servers can be applied independently from the updates to Exadata database servers and RDMA switches. As with database servers, the patchmgr utility allows running the storage server update in a rolling or non-rolling fashion.
A non-rolling update of storage servers involves coordinated downtime. During this process, all databases and cluster services are stopped. This ensures system and data consistency and simplifies the update path. All storage servers (cells) are then updated in parallel. With the databases and cluster-ready services offline, all updates can be applied simultaneously. This approach minimizes total update time while requiring a planned maintenance window.
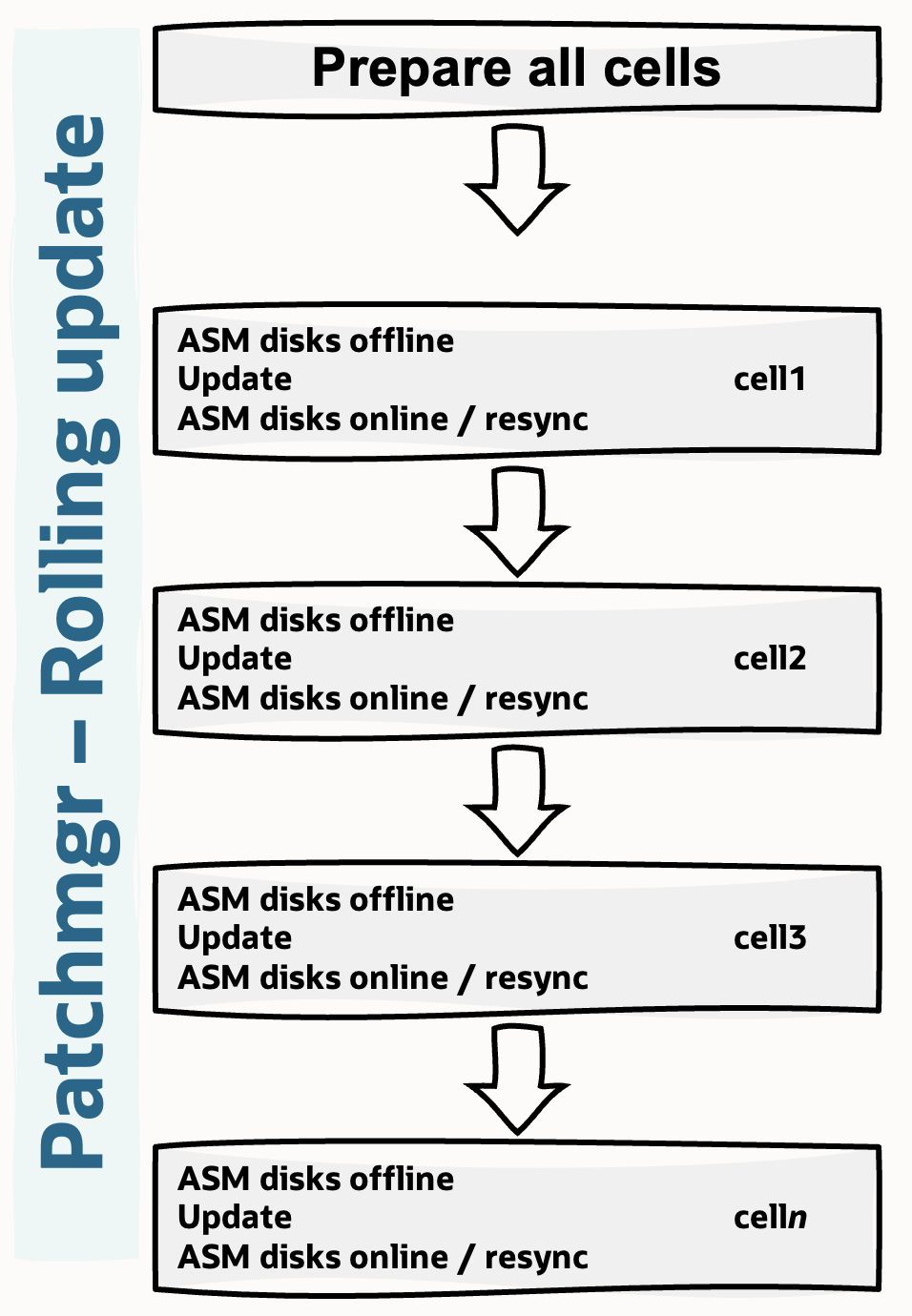
Alternatively, a rolling update of Exadata Storage Servers allows continuous database availability. Databases and cluster services remain online throughout the process. patchmgr updates one storage server at a time, first taking all grid disks and ASM disks offline, subsequently applying the update to the server, and finally bringing all ASM disks and grid disks back online. After each storage server is updated, patchmgr ensures that ASM disk groups or storage pools are fully resynced and rebalanced before moving to update the next server. This automated sequencing and monitoring is orchestrated by patchmgr, and it is done with no service disruption.
To update Exadata storage servers, you’ll use just a few steps to prepare, execute, and monitor the update process. The key commands and options used to perform the pre-check and the update efficiently are presented here. Exachk is a comprehensive health-check tool for Exadata systems that validates hardware, software configurations, and best practices to ensure system stability and compliance. Running Exachk before a server update identifies and highlights pre-existing issues (e.g., configuration errors or software mismatches) that could disrupt the patching process, while post-update execution confirms the update’s success and verifies system health. The update step is managed with a single command.
|
Simple Storage Server Update Steps
1. Exachk Health Check
2. Perform a pre-update validation
# patchmgr
--cells cell_host_file
: cell_host_file
: The cell_host_file is a text file containing the host names
: of the storage servers to update. The file contains one
: storage server host name or IP address per line. The
: storage server patching will fail if the list file is
: not specified.
--patch_check_prereq [--rolling]
: patch_check_prereq
: Runs a prerequisite check on all the storage servers to determine
: if the patch can be applied to the storage servers.
: --rolling Specifies that the update is done in a rolling fashion.
: If not specified, the update is done in a non-rolling fashion.
3. Update all storage servers
# patchmgr
--cells cell_host_file
--patch [--rolling]
: Apply the patch, including firmware updates,
: wherever possible (BIOS, Disk Controller and disk drives)
: to all storage servers in the cell host list file.
4. Exachk Health Check
: Verify that the system operational status is normal |
Updates of RoCE (RDMA) and Management Network Switches
Exadata patchmgr can also manage updates of Exadata Management switches and RoCE/RDMA network switches. Infiniband switches in older Exadata systems can also be updated. With built-in pre-checks and the ability to update firmware and configurations through a single command, patchmgr automates and streamlines the entire update process, ensuring all switch updates are performed safely and consistently. Updating switches is as simple as executing a single patchmgr command, making the process fast, reliable, and effortless.
Power of Exadata patchmgr
By automating complex update workflows and ensuring consistency across the stack, patchmgr significantly reduces operational risk and administrative overhead in Exadata updates. For organizations that rely on Exadata, patchmgr is an indispensable tool that keeps the systems secure, performant, and fully updated. Oracle Fleet Patching and Provisioning (FPP) is a powerful solution that centralizes and automates Exadata updates in large-scale enterprise environments, and it too seamlessly integrates with patchmgr to deliver automated, streamlined maintenance across the fleet.
Regular updates are critical for Exadata to ensure database availability, integrity, and system integrity by applying the latest product and security fixes, protecting data, and maintaining compliance with security best practices. Software updates also address vulnerabilities and potential issues before they can impact operations, supporting continuous and reliable business service. Exadata patchmgr orchestrates and automates complex, multi-component software updates across database servers, storage servers, and network switches, each done with a single command.
Acknowledgments
This article benefits from the discussions that the author had with Alex Blyth, Rene Kundersma, and Doug Utzig.
