Introduction
What is the Accounting Hub?
The Fusion Accounting Hub offers accounting services to upstream applications. It consists of accounting rules, an accounting engine and results in the form of journals and balances. The accounting engine combines accounting rules, enterprise structure definitions and source system transactions to generate one or more complete sets of accounting known as accounting representations. It constitutes a single source of financial data for downstream financial reporting and management analytics. For more details, see the ERP-ACE blog post: What is the Fusion Accounting Hub?
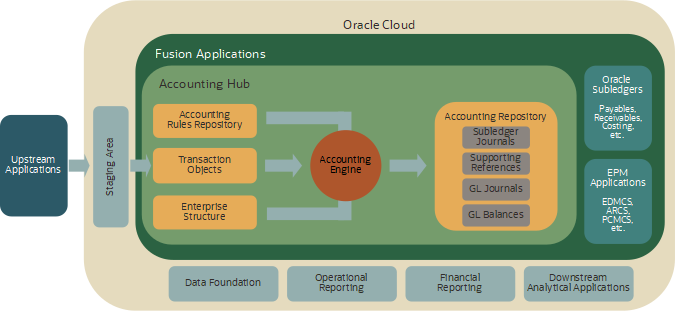
What is Pass-through Accounting?
Pass-through accounting takes place when an upstream application sends balanced journal entries to the Accounting Hub. The upstream application has applied its own accounting rules to the source system transactions or balances to generate balanced journal entries.
The Accounting Hub ingests the pass-through journals without modifying journal transaction currency amounts. It may, however, calculate ledger currency amounts and map chart of accounts (COA) in the primary, secondary and reporting currency ledgers.
What is Event-based Accounting?
The upstream application sends raw transaction data to the Accounting Hub which applies accounting rules to transform them into balanced journal entries. Transaction attributes combined with Accounting Hub rules govern every aspect of the resulting journal entry: accounting date, debits, credits, account combinations, descriptions, etc.
What are the Advantages of Event-based Accounting?
Event-based accounting centralizes the definition and execution of accounting rules in a business user orientated application. Accounting logic is no longer distributed across source systems, interface programs and, in many cases, spreadsheets. Accounting rules can be shared across source systems and, as requirements evolve, modified centrally in the Accounting Hub.
A centralized application for accounting rule configuration provides users with visibility and control. All user communities share a single source of truth for creation, maintenance and audit of accounting rules.
Why Implement Pass-through Accounting?
Most financial institutions recognize the business value of event-based accounting. Hence, the target state of finance transformation initiatives is usually event-based accounting in the Accounting Hub. However, converting existing systems to event-based accounting may necessitate changes interfaces and staging areas.
For upstream applications that are currently generating complete and valid accounting, the short term effort to implement event-based accounting in the Accounting Hub may exceed that for pass-through. Conversely, upstream applications that generate incomplete or incorrect accounting and hence, represent an audit and compliance risk, may benefit from going directly to event-based.
Why Implement the Accounting Hub for Pass-through Accounting?
Some financial service institutions question the business value of implementing the Accounting Hub for pass-through accounting. They ask, why not send the journals directly to Cloud General Ledger?
Here’s why…
Multiple Accounting Representations
Multiple accounting representations address requirements to generate accounting according to different accounting standards and / or accounting currencies.
The Accounting Hub applies multiple sets of accounting rules (accounting methods) to source system transactions in parallel. For each accounting representation, it generates a detailed journal entry based directly on the data passed to the Accounting Hub.
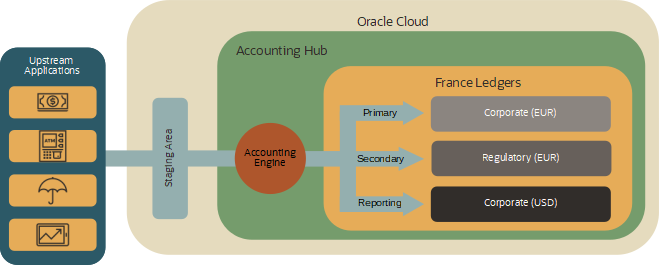
The Accounting Hub improves on applications or manual procedures that duplicate and modify journals and balances:
- Complete: the Accounting Hub generates multiple representations in parallel to ensure each one is complete and valid.
- Reconciliation: the Accounting Hub strongly links the journal entries generated across accounting representations. You can demonstrate, for example, how transactions are accounted according to different accounting standards and currencies.
- Consistent: the Accounting Hub shares reference data such as enterprise structures, exchange rates, chart of accounts, etc. with General Ledger. It is impossible for inconsistencies to arise between the Accounting Hub and General Ledger.
- Flexible: Accounting Hub rules and mapping sets support complex conditional mappings, wildcards, overlays, etc.
Note also that implementers can configure Enterprise Data Management (EDMCS) to centrally maintain the mapping sets used by the Accounting Hub to convert from one chart of accounts (COA) to another.
Streamline Financial COA
The objectives of finance transformation initiatives often include:
- Streamline purely financial processing by using a stripped down COA.
- Free financial close from dependencies on operational processing and adjustments.
- Ensure consistency between financial and operational reporting.
The Accounting Hub’s supporting references assist by “extending” the financial COA with source system specific dimensions such as trading desk or location. Supporting references are stored on Accounting Hub journal lines or balances but are not transferred to GL. They represent a bridge between detailed contract level and highly summarized GL balances. These features:
- ease reconciliation between source systems and financial accounting.
- liberate GL from operational detail. Financial processing is streamlined.
- insulate GL from frequent operational changes and adjustments.
Enrichment
Upstream applications journals usually balance pass-through journals in the source system’s transaction currency. But they may not be able calculate ledger currency amounts using appropriate exchange rates. Implementers can configure the Accounting Hub to calculate amounts for multiple ledger currencies using centrally defined rates.
Similarly, implementers can configure modifications to the account combinations derived by the upstream application, when necessary, without recourse to upstream application administrators or developers.
Future Changes in Accounting Policies
The Accounting Hub treats event-based and pass-through feeds in exactly the same way. If, and when, accounting policies change, new or modified accounting rules can be applied to both of them.
Centralizing accounting rule changes in the Accounting Hub removes the need to coordinate changes across multiple upstream applications.
Business users can manage account derivation rule changes based on mapping sets in the Accounting Hub or EDMCS without recourse to developers.
In summary, storing both event-based and pass-through accounting in the Accounting Hub prepares you for future changes.
Accounting Repository
By sending pass-though and event based transactions to the Accounting Hub you store a consistent set of detailed accounting entries across all upstream applications. Accounting Hub journals and balances constitute a single source for extracts to downstream reporting and analytical applications.
Smooth Transition to Event-based Accounting
The Accounting Hub insulates GL and other downstream applications from the transition from pass-through to event based accounting. Interface controllers and other users will avoid dealing with a switch from GL interface to the Accounting Hub.
Note that the Accounting Hub strongly partitions accounting rules by subledger application. Converting a subledger application’s accounting from pass-through to event-based will not provoke issues in other application’s accounting rules.
Other Considerations
Using the Accounting Hub to Account to Suspense
Upstream applications do not always generate complete and valid pass-through journals. Examples of one-sided journals or invalid account combinations flowing into the Accounting Hub are quite common.
Rather than investigate, correct and re-submit errors, the requirement is to post them to suspense. Users will review them to determine the appropriate corrective action / adjustments during normal working hours.
The Accounting Hub never creates invalid journal entries. But it does offer features to support straight through processing either through posting to suspense or by automatically correcting disabled accounts. Since, the Accounting Hub retains an audit trail of how accounting rules were applied to transactions, auditability is guaranteed.
Unbalanced Journals
Implementers can configure Accounting Hub accounting rules to automatically balance journals using the suspense account of their choice. For more details, see the ERP/ACE blog posts Mapping defaults versus subledger suspense accounting and Subledger accounting balancing demystified. The last section of the post: Explicit balancing rules details how to configure accounting rules to address the requirement.
Invalid Account Combinations
Invalid account combinations occur when, for example, a segment value has not been defined in Cloud ERP or a cross validation rule is violated.
When the Create Accounting program encounters an invalid account combination, the pass-through journal’s status is set to “Invalid”. To implement straight through processing of these errors, re-launch the Create Accounting program with the Process Events parameter set to Invalid Accounts. For more details, see the Review and Correct Accounting Exceptions section of the Using Subledger Accounting Book. You can orchestrate re-processing of invalid account errors using web services.
End Dated Account Combinations
As enterprises evolve, the definition of what constitutes a valid account combination changes. For example, a trading desk or location closes and hence, the associated segment value and account combinations end dated. Historical entries and balances remain valid but no new accounting should flow in from upstream systems. Unfortunately, inflight transactions and retroactive source system adjustments mean pass-through journals using the old accounts often flow in from upstream applications long after the end date.
Rather than posting these invalid combinations to suspense, the alternate account feature stores a replacement account combination. When Create Accounting encounters a disabled combination it uses the alternate account instead. For more details, see the ERP-ACE blog post Use Alternate Account for Straight-Through Accounting.
Accounting Foundation Cloud Service (AFCS) and Accounting Hub
AFCS and Accounting Hub work together to a comprehensive and performant solution for financial services.
AFCS stores source system raw transactions or pass-through journals in its staging tables. It validates and summarizes them before propagating them to the Accounting Hub.
The Accounting Hub applies accounting rules to the transactions and pass-through journals to generate one or more accounting representations.
- Its financial balances are fed into downstream financial consolidation and reporting applications offered by external applications or Enterprise Performance Management (EPM).
- Its detailed journals are passed to AFCS which calculates instrument grain account balances using its decomposition feature.
The AFCS management ledger stores instrument grain account balances, financial balances and source transactions and makes them available for reporting and downstream processing.
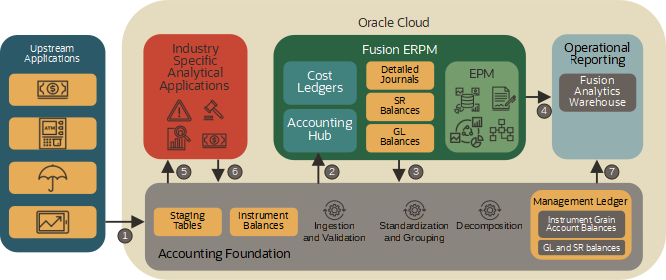
For more details, see the Accounting Hub Financial Services Reference Architectures and Best Practices white paper available from the Customer Connect’s Subledger Accounting and Accounting Hub forum. For more details on AFCS, See Oracle Financial Services Accounting Foundation Cloud Service on Oracle.com
Conclusion
Even if you plan to send pass-through journals from upstream applications to Oracle Cloud Applications, processing them in the Accounting Hub offers clear business benefits.
