We are thrilled to announce the release of the new Pull Request (PR) features with the OCI DevOps Code Repository service! This significant update introduces several critical developer collaboration features, including Pull Requests, Repository Forks, and Repository Insights. Whether you’re developing new application code, enhancing an existing application, or managing Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) repositories, having a workflow that allows teams to review new code changes and enforce code quality controls via mandatory approvals is critical for all enterprise customers.
With this set of feature-rich enhancements, customers can now centrally manage their repository configurations, perform efficient code reviews from the console workflow, enforce compliance best practices via merge checks and code approval criteria, and automate CI pipelines to trigger new pull requests to ensure a successful build run before allowing a code merge. These capabilities are mission-critical for Oracle, with thousands of our developers leveraging them to enable a better code development and collaboration experience. We are excited to extend these benefits to all OCI customers, enabling a more integrated DevOps platform experience to store, develop, build, and deploy software applications using OCI-native developer tooling.
We’ve designed the pull request feature to be an integral part of the DevOps Code Repository service, incorporating all major features expected in a modern developer collaboration platform. Recognizing that developers often face email overload, we’ve introduced personalized notifications, allowing each developer to customize their notification preferences. Unlike some other systems, DevOps admins can configure fine-grained access control measures that determine which user groups have access to specific DevOps resources and the actions these users can perform on them. For instance, admins can configure granular policies that determine which user sub-group is allowed to merge pull requests in a project or repository. Admins can also protect critical code branches using the Branch Protection configuration that helps maintain code integrity and enforces compliance measures that require a pull request review before merging new code changes thereby promoting code quality and collaborative software development. Lastly, repository owners and managers can gain detailed insights on pull request metrics to better analyze and plan their development activities.
Following are some of the key use cases that are enabled by this update:
- Seamless Developer Collaboration: You can seamlessly collaborate on new code changes by raising a PR and adding reviewers who will provide feedback and approval. This process promotes teamwork and ensures code quality.
- Mandatory Code Approvals: You can require mandatory code approvals from someone other than the pull request author. You can set a minimum number of approvals from designated reviewer groups before a Pull Request is allowed to merge, adding an extra layer of scrutiny to ensure high-quality code and helping achieve corporate compliance best practices.
- Automated Build Triggers: You can set up automated triggers in DevOps to start a build pipeline whenever a PR is created, updated, or merged. This ensures that every code change is tested immediately, improving reliability and reducing the toll of manually running or triggering the build process.
- Enforcing Successful Build: You can enforce rules that only allow a Pull Request to be merged if the associated build pipelines have passed. This guarantees that only stable, tested code gets integrated into the main code base thereby reducing the risk of introducing breakages with new code changes.
- Build Pipeline Visibility: You can easily see the status of pipeline runs related to your PRs or commits in one place. This convenience saves time and reduces the hassle of switching between different tools to track progress.
- Configuring Permissible Merge Strategies: You can enable one or more merge strategies such as fast-forward only, squash, rebase and merge, etc for your repository. Repository admins configure permissible merge strategies under Repository Settings to ensure consistency in merging code changes to a target branch.
- Protecting Important Branches: You can enforce several branch protection measures on crucial code branches in your repository. This allows administrators to maintain the integrity of read-only branches and ensure the stability of the code base by mandating developers to require a Pull Request review before merging new code changes.
- Personalized Email Notifications: You can configure your individual preferences at the project, repository, or pull request level to receive personalized updates relevant to your specific needs. You can choose to receive no updates, updates when you are mentioned, or all event updates that occur in the watched resource.
- Repository Forks: You can create copies of a DevOps repository to work on new features or bug fixes without affecting the main code base. Later, you can submit pull requests from your forked repository to the original repository, thereby contributing your changes back to the original project and facilitating collaborative development.
- Repository insights: You can visually analyze data in the form of insights by aggregating it at the repository or project level to help development teams analyze repository activity, track code contributions, and identify bottlenecks in the development process.
Let’s take a deeper look at some of the use cases below.
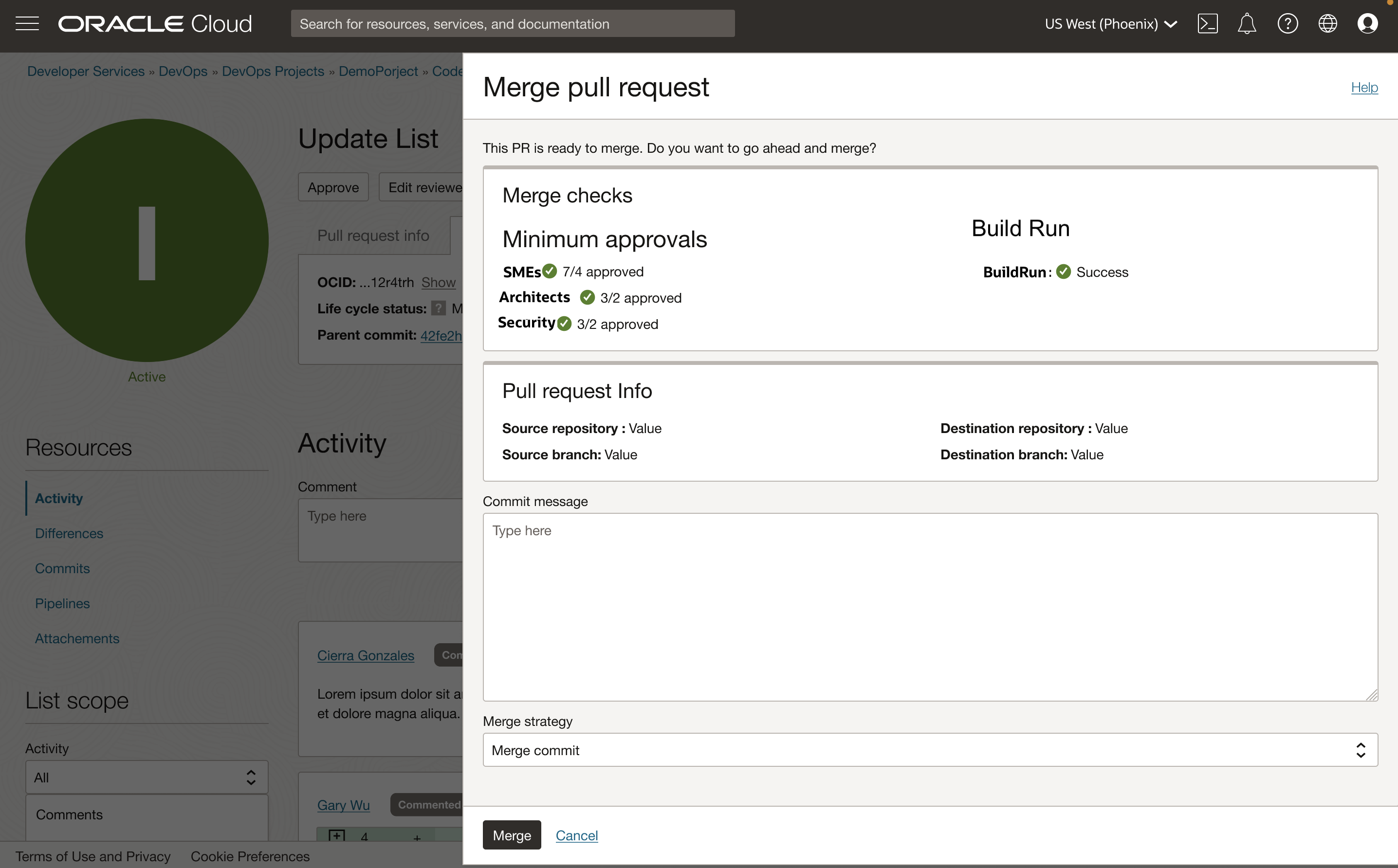
Mandatory code approvals
You can configure Approval rules to ensure that pull requests are reviewed by designated users defined by the repository admins. This process enables better code quality by having peers review and approve new code changes, thereby catching potential issues early in the development cycle. You can configure approval rules at the project or repository level. These rules are additive, and the system will ensure that approvals rules defined at both the project and repository level get enforced. For each level, you can one or more approval groups and define a minimum approval count for each group. Once these groups are defined, the system enforces that all new pull requests cannot be merged until it receives the required number of approvals defined by the approval rules.
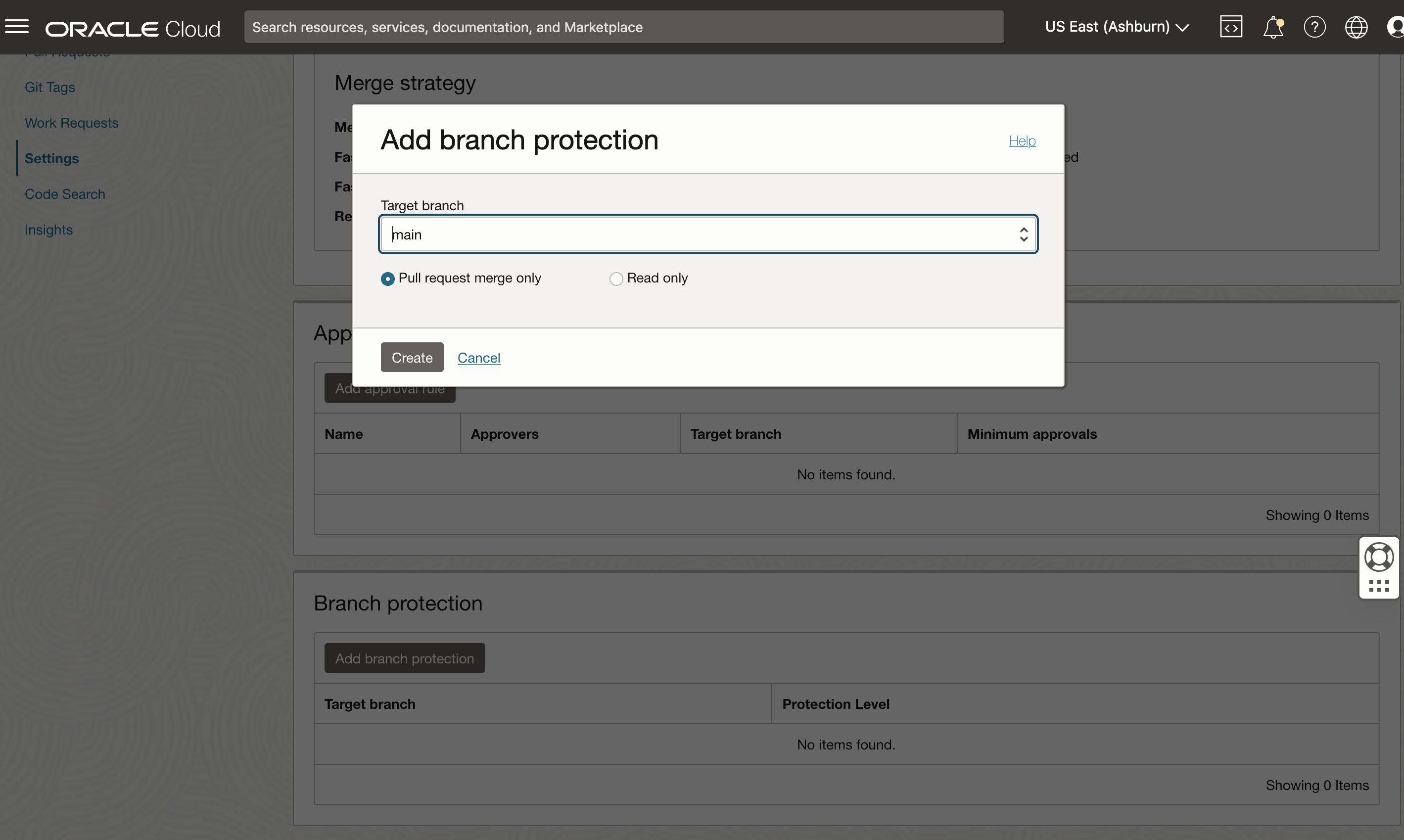
Branch protection for important code branches
You can define branch protection rules to enforce restrictions on your critical code branches. Using the combined power of branch protection rules and DevOps IAM policies you can protect code repositories from several patterns such as unwanted branch deletion, accidental commits to a read-only branch, and direct push-commits to a branch where review and approval via a Pull Request is required. This feature enables your teams to collaboratively develop software more securely while ensuring that the quality and integrity of the code base is preserved throughout the development lifecycle.
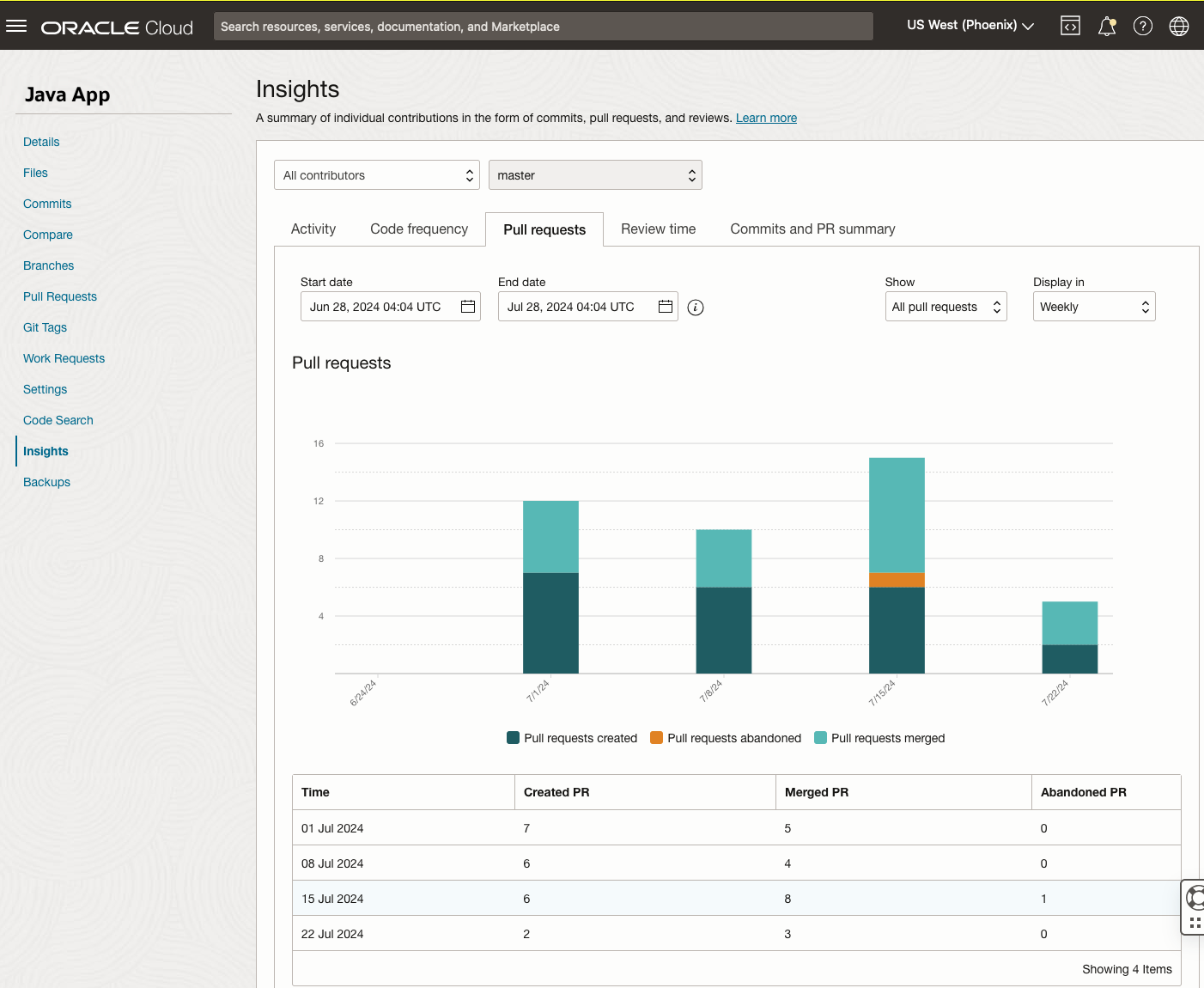
Pull Request Insights
You can gain valuable insights into your code development activities using the Repository Insights feature in DevOps. This feature enables you to visualize your repository activity, code commit frequencies, pull request throughput and review times, and summaries of team member contributions. By capturing and evaluating this data, you can effectively analyze your code activity, identify process bottlenecks, and measure developer contributions across repositories within a project.
These enhancements elevate your software development experience, ensuring robust collaboration, stringent code quality, and streamlined workflows within the OCI DevOps platform.
For more information on these enhancements, see the following resources:
- Managing Pull Requests: https://docs.public.content.oci.oraclecloud.com/en-us/iaas/Content/devops/using/manage_pullrequest.htm
- Forking a Code Repository: https://docs.public.content.oci.oraclecloud.com/en-us/iaas/Content/devops/using/fork_repo.htm
- Defining Approval rules and Branch Protection settings: https://docs.public.content.oci.oraclecloud.com/en-us/iaas/Content/devops/using/reposettings.htm
- Code Repository Insights: https://docs.public.content.oci.oraclecloud.com/en-us/iaas/Content/devops/using/coderepo_insights.htm
