Everyone understands the value in secure, expedient access to data. As business-critical analytics data is spread out across cloud vendors, expediency becomes the challenge.
Cross-cloud vendor zero copy data sharing doesn’t need to be complicated. In your Autonomous Database you can easily set up secure data sharing with your Salesforce CRM Data Stream in seconds. Using the Salesforce CRM data connector type, you can access your Salesforce CRM data from your Autonomous Database by simply defining the necessary credentials and creating secure database link access. This blog walks you through those steps and demonstrates on-the-fly access to the Salesforce CRM Sales Cloud dataset.
Salesforce requirements:
User login credentials
User security token
organization hostname – fully qualified domain name
Salesforce Data Streams configured with Salesforce CRM Data Connector Type
Salesforce Data Stream Status is ACTIVE
Standard User access and Profile privilege to access and read the data
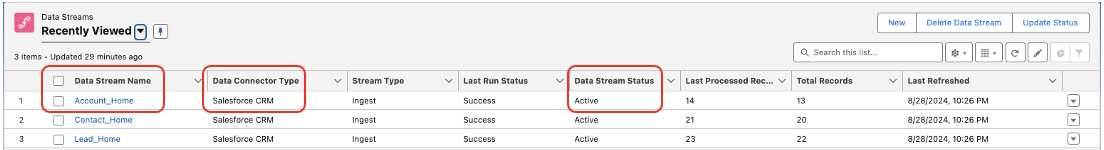 Figure1. On the Data Streams Dashboard confirm the Data Stream Name, Data Connector Type and Data Stream Status
Figure1. On the Data Streams Dashboard confirm the Data Stream Name, Data Connector Type and Data Stream Status
In your Autonomous database instance:
Create your credential:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => ‘<your credential name>',
username => ‘<your salesforce log-in id>’
password => ‘<your salesforce password');
END;
/
Create your database link:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.CREATE_DATABASE_LINK(
db_link_name => '<your database link name>',
hostname => ‘<your host>.my.salesforce.com',
port => '19937',
service_name => 'salesforce',
ssl_server_cert_dn => NULL,
credential_name => ‘<your credential name>’,
gateway_params => JSON_OBJECT(
'db_type' value 'salesforce',
'security_token' value '<your security token>'));
END;
/
The requirements for credential and database link definitions for cloud vendor, external database types are available in the HETEROGENEOUS_CONNECTIVITY_INFO view. For example,
select database_type, required_port, sample_usage from heterogeneous_connectivity_info where database_type = 'salesforce';
reports:
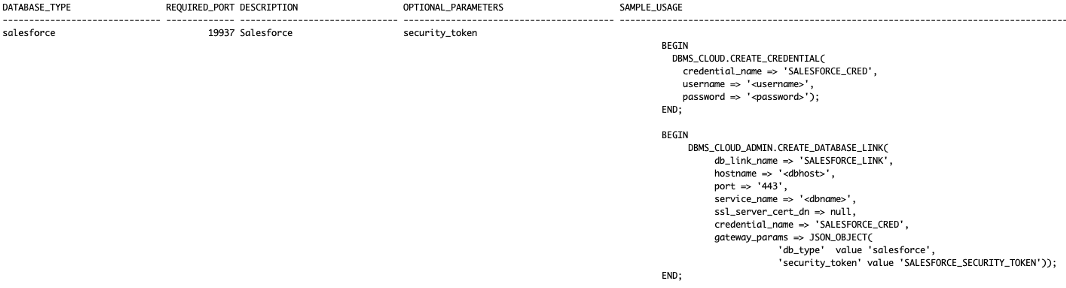
Figure2. Select output from the heterogeneous_connectivity_view
See Create Database Links to Non-Oracle Databases with Oracle-Managed Heterogeneous Connectivity
Now, let’s walk through a demonstration. The following uses the Salesforce CRM Connector to establish our connection to your Salesforce CRM organization. This demonstration uses the Salesforce Data Cloud Sales synthetic data in the Account_Home Data Stream. First, we confirm our data stream is using the Salesforce CRM Data Connector Type and that the data stream is in ACTIVE status. Using the Data Cloud Data Explorer we validate the data.
We then connect to our Autonomous Database in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and launch SQLPLUS. Using SQLPLUS we check the HETEROGENEOUS_CONNECTIVITY_INFO view for the Salesforce database type. We issue a SELECT statement on our Salesforce CRM Account_Home Data Lake object, which fails to connect as the credentials and necessary database link have not been configured.
We now set up connectivity. On-the-fly, using DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure, we create the necessary credentials to connect to our salesforce org using our Salesforce log in credentials. We then use DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.CREATE_DATABASE_LINK procedure to create the database link to our Salesforce CRM database. Once the credentials and database link are configured we issue the select statement against the ACCOUNT data and examine the results.
Figure3. Zero Copy Data Share Demo
Now that we have zero data share access to the Salesforce CRM Data Lake ACCOUNT object, let’s see what we can do with this data.
We would like identify the local account representative for Pyramid Construction Inc. To find the local account rep., We will need to cross-cloud join on the Salesforce CRM ACCOUNT shared object and a local ACCOUNT_REPS table:
select a.emp_last_name, a.emp_first_name, a.emp_region, b.id, b.name, b.accountnumber, b.ownership, b.industry from account_reps a, Account@mysalesforcelinkjpm b where a.emp_region = b.billingcountry and b.name like '%Pyramid Construction%';
Let’s see what that looks like:
Figure4. Zero Copy Data Share cross-cloud local and remote join
Let’s say we would like a local copy of the Salesforce CRM ACCOUNT Data Lake object. We can issue a simple Create Table As Select (CTAS) statement to create the object locally:
create table sfcrm_account_local
as select
ID,
NAME,
TYPE,
BILLINGSTREET,
BILLINGCITY,
BILLINGSTATE,
BILLINGPOSTALCODE,
BILLINGCOUNTRY,
SHIPPINGSTREET,
SHIPPINGCITY,
SHIPPINGSTATE,
SHIPPINGPOSTALCODE,
SHIPPINGCOUNTRY,
PHONE,
FAX,
ACCOUNTNUMBER,
INDUSTRY,
NUMBEROFEMPLOYEES,
OWNERSHIP,
RATING
from account@mysalesforcelinkjpm;
And let’s see what that looks like:
Figure5. Create Table as Select on remote data source
Lastly, we may want to keep a local version of the Salesforce CRM ACCOUNT Data Lake object in sync with the master, defining object but not create a table locally. We can do this by creating a cross-cloud MATERIALIZED VIEW on the master, defining object – the Salesforce CRM ACCOUNT object. In the demo below, we create a BUILD IMMEDIATE, REFRESH FORCE, ON DEMAND synchronous refreshable cross-cloud MATERIALIZED VIEW locally so that we can track Accounts rated as WARM for possible sales lead follow up.
create materialized view sfcrm_account_local_mv
build immediate
refresh force
on demand
as select
ID,
ISDELETED,
MASTERRECORDID,
NAME,
TYPE,
PARENTID,
BILLINGSTREET,
BILLINGCITY,
BILLINGSTATE,
BILLINGPOSTALCODE,
BILLINGCOUNTRY,
BILLINGLATITUDE,
BILLINGLONGITUDE,
BILLINGGEOCODEACCURACY,
SHIPPINGSTREET,
SHIPPINGCITY,
SHIPPINGSTATE,
SHIPPINGPOSTALCODE,
SHIPPINGCOUNTRY,
SHIPPINGLATITUDE,
SHIPPINGLONGITUDE,
SHIPPINGGEOCODEACCURACY,
PHONE,
FAX,
ACCOUNTNUMBER,
WEBSITE,
PHOTOURL,
SIC,
INDUSTRY,
ANNUALREVENUE,
NUMBEROFEMPLOYEES,
OWNERSHIP,
TICKERSYMBOL,
RATING,
SITE,
OWNERID,
CREATEDDATE,
CREATEDBYID,
LASTMODIFIEDDATE,
LASTMODIFIEDBYID,
SYSTEMMODSTAMP,
LASTACTIVITYDATE,
LASTVIEWEDDATE,
LASTREFERENCEDDATE,
JIGSAW,
JIGSAWCOMPANYID,
CLEANSTATUS,
ACCOUNTSOURCE,
DUNSNUMBER,
TRADESTYLE,
NAICSCODE,
NAICSDESC,
YEARSTARTED,
SICDESC,
DANDBCOMPANYID,
OPERATINGHOURSID,
CUSTOMERPRIORITY__C,
SLA__C,
ACTIVE__C,
NUMBEROFLOCATIONS__C,
UPSELLOPPORTUNITY__C,
SLASERIALNUMBER__C,
SLAEXPIRATIONDATE__C
from account@mysalesforcelinkjpm;
Figure6. Create cross-cloud materialized view on remote zero copy data share Salesforce CRM data set.
Conclusion
As demonstrated, secure, multi-cloud zero data copy access does not have to be complicated. You get on-the-fly, cross-cloud, local or cross-region, access by executing two, fast and simple steps to expedite secure zero copy data share access to your Salesforce CRM data. This removes the cost and overhead of cumbersome ETL operations and pipeline builds and gives you immediate access to your business-critical data.
