Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Data Flow is a fully managed Apache Spark service that enables you to run Spark applications with minimal infrastructure management. However, like any complex system, you might encounter issues with Spark compute pools on OCI Data Flow. This blog post aims to guide you through the process of troubleshooting these issues, ensuring that your data processing pipelines run smoothly. Thanks to Mario Miola for sharing these troubleshooting tips!
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s essential to understand what Spark compute pools are. In OCI Data Flow, a compute pool is a collection of computing resources that are allocated to run Spark jobs. These pools can be tailored to different workloads, providing the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on your requirements. OCI Dataflow Pools are (see documentation for Pools) are ideal for scenarios requiring numerous Spark drivers and executors in a Dataflow cluster for large volumes with minimized startup times. Pools can be used in many Data Flow batch, streaming, session (notebook) workloads by various users at the same time in same tenant.
Pools offer a wide range of functionalities for various use cases, such as:
- Time sensitive large production workloads with many executors which needs faster start up time in seconds.
- Critical production workloads aren’t effected by dynamic development workloads because their resources can be separated into different pools.
- Control cost and usage for development with IAM policy that lets you submit Data Flow runs to specific pools.
- Large number of Data Flow runs need to be processed with less start up time.
- Queueing Data Flow runs in a pool for efficient use of resources and cost control.
- Workloads run only in specific time window of a day that need the automatic start of a pool on a schedule and auto stop when idle.
- Automatic security patching without affecting runs or resources in a pool.
Creating a Pool
You can create pools from the OCI Dataflow Pools section, when you create the pool define the number of executors and also you can define the schedule for when it should be available.
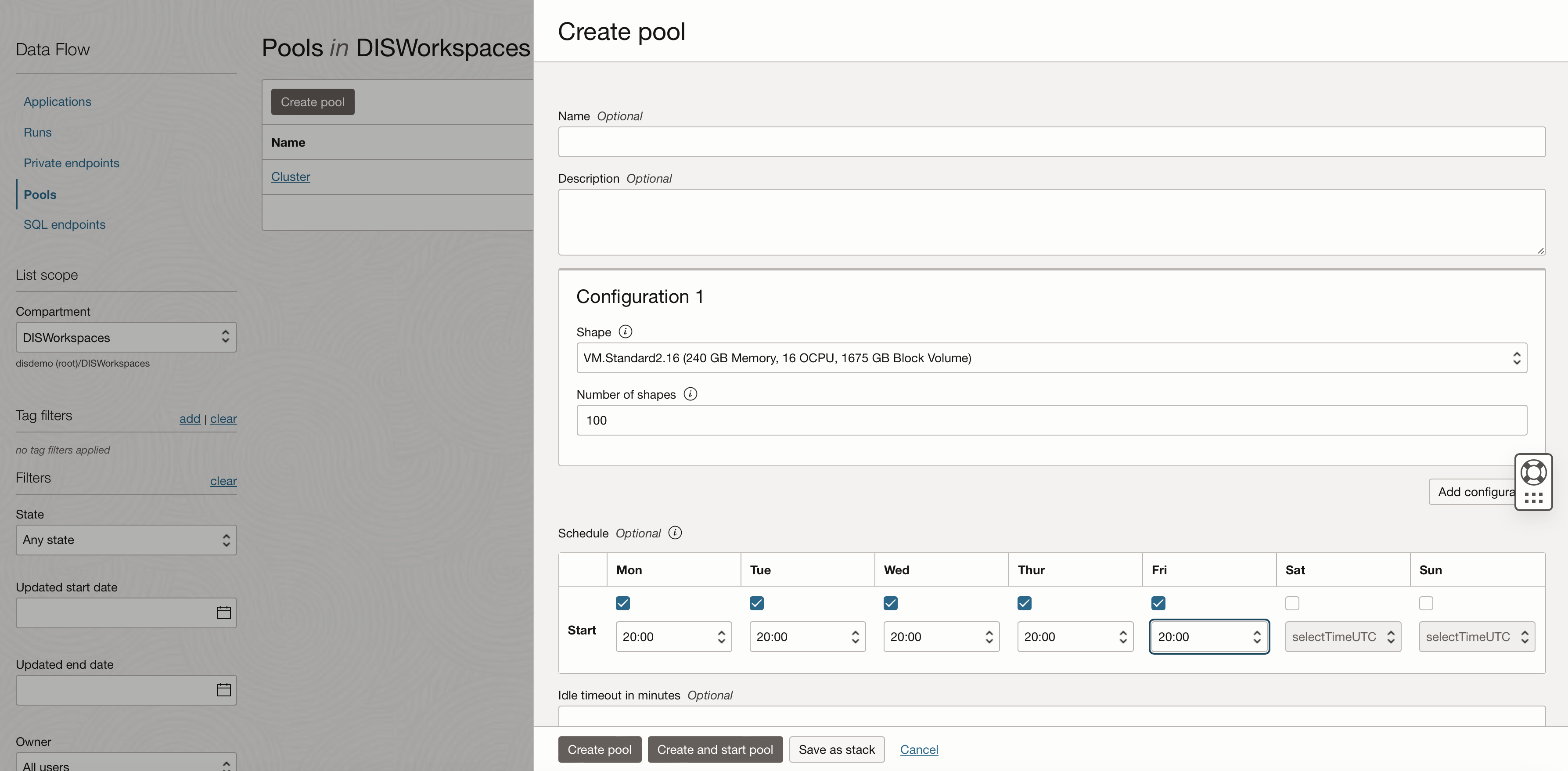
Dataflow Pools support workloads within specific time windows by automatically starting pools on a schedule and stopping them when idle as you can see from above. At the same time, they can queue Data Flow runs to maximize resource utilization and control costs effectively.
Resources allocated to an Application run are not shared with other Applications; hence, the clusters are dedicated to the specific runs.
Common issues
The tabe below illustrates some common issues, the cause and the remediation.
| Message | Cause | Remediation |
|---|---|---|
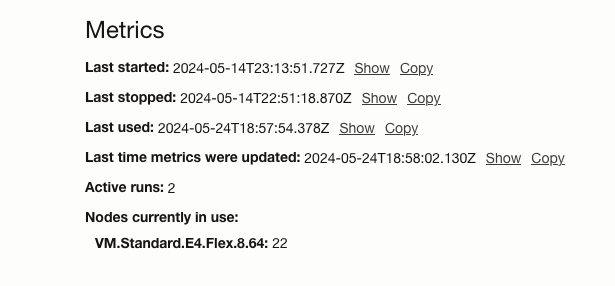
| Pool ocid1.dataflowpool.oc1.iad… does not have enough resources to start your run. You can either increase the pool size or wait for active runs using the pool to be terminated. | There are not enough resources available to start the job execution | Analysis of the resource request:
|
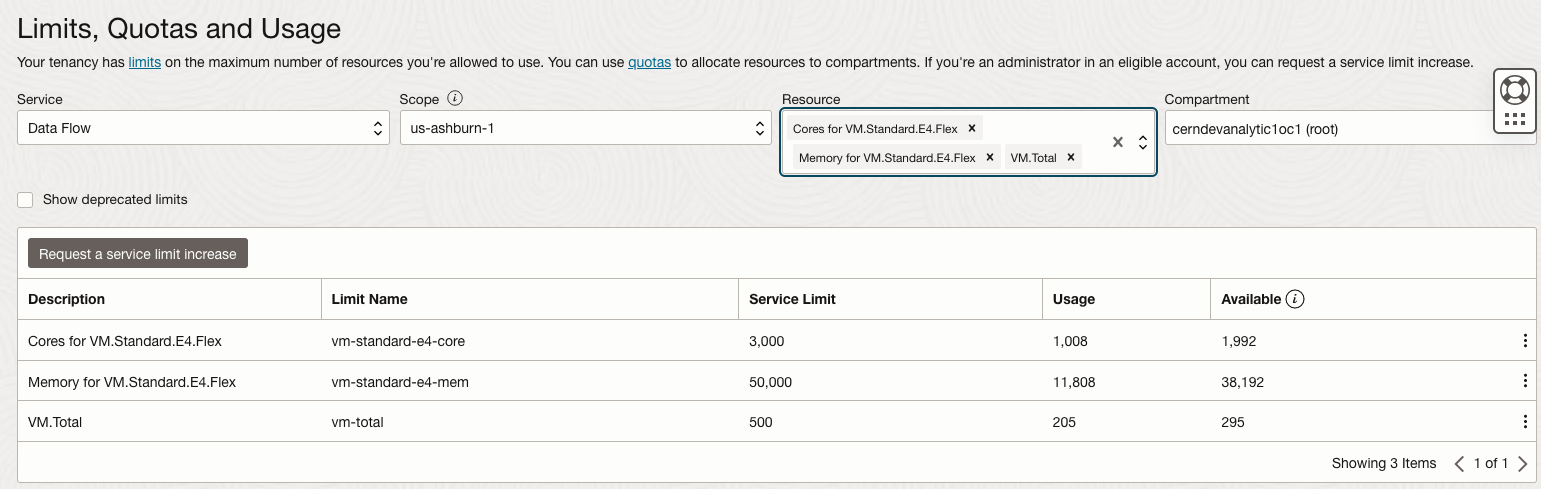
| Provisioning the pool associated with the run. | The pool associated with the run cannot start. | Using the OCI Console under Tenancy Administration, verify the Limits, Quota, and Usage associated with the Dataflow service – for instance.
|
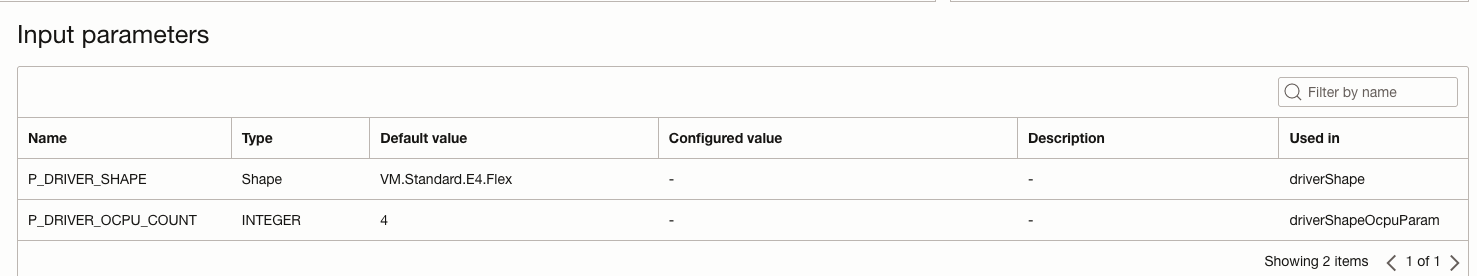
| CreateRun operation in DataFlow service.(400, InvalidParameter, false) Driver/Executor shape configuration not found in pool. | The pool associated with the OCI Dataflow Application does not contain the shape requested for this execution run | Check the shape associated with the execution run request.
Check the Dataflow Application pool and the associated pool configurations. Make the appropriate changes to the shape requested (in this case, the OCPU value should be set to 8).
|
Some best practices include;
- Regularly review and plan the resource requirements for your Spark jobs. Ensure that your compute pools have sufficient capacity to handle peak loads.
- Set up monitoring and alerts to track the health and performance of your compute pools. OCI Monitoring and Logging can help you stay proactive in identifying and resolving issues.
- Maintain consistent and optimized Spark configurations. Regularly review and update these settings based on the changing needs of your workloads.
- Keep detailed documentation of your Spark jobs, including configurations, dependencies, and troubleshooting steps. This will help in quicker resolution of issues and smoother handovers between team members.
Summary
Troubleshooting Spark compute pools on OCI Data Flow involves a combination of understanding the underlying infrastructure, analyzing logs and configurations, and monitoring resource utilization. By following the steps outlined in this guide and adopting best practices, you can effectively manage and resolve issues, ensuring that your data processing tasks run efficiently and reliably.
Remember, OCI Data Flow provides powerful tools and features to help you manage your Spark jobs. Leveraging these capabilities and staying proactive in monitoring and optimization will go a long way in maintaining a robust data processing environment.
Check out the documentation and tutorials linked below, comment and share the blog and reach out on LinkedIn, would love to hear from you.
- https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/data-flow/using/pools.htm
- https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/data-flow/data-flow-tutorial/getting-started/dfs_tut_get_started.htm
- https://blogs.oracle.com/dataintegration/post/notebooks-big-data-and-spark-jobs-in-oci