Introduction
Oracle Goldengate is a software tool that replicates and transforms data between databases. It can be used to perform data migrations with minimal downtime. Oracle Goldengate is available as a native service in OCI and available as an on-premises solution.
Oracle Data Transforms is used to build ETL pipelines using graphical data transformations in the form of data flows and workflows to move and transform data between different systems.
OCI Goldengate has data transforms as a part of its service.
In this blog, let’s explore how we can use Goldengate and data transforms to achieve the near real time replication with heavy transformations on data.
Use Case
It is observed that many times customers look for near-real time replication without any interruption to source OLTP systems. At the same time, they want to perform heavy transformations like joins, lookups etc on the source data and load it to the data warehouse tables.
We will try to understand the use case with an employee table which we want to join with department table to load the data into final target table.
Design
The data from source database can be extracted using Oracle Goldengate and it is loaded into a stage schema in the target database. Oracle Goldengate also adds the last modified date field to the stage table which will be used in data transforms to capture the incremental loads.
The data in the stage schema is then transformed using Oracle Data transforms and the final data is loaded into the target table.
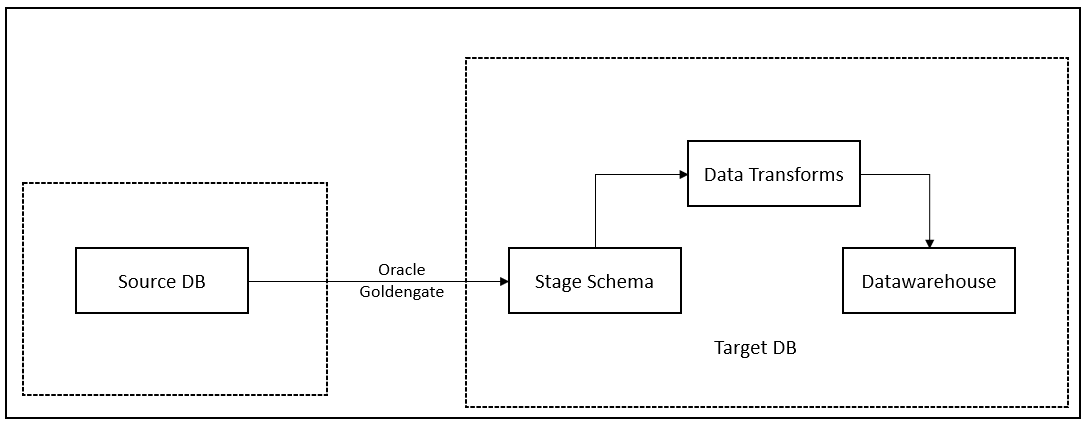
Implementation
Below is the flow that we will use to capture the data from employee table and load it into target table.
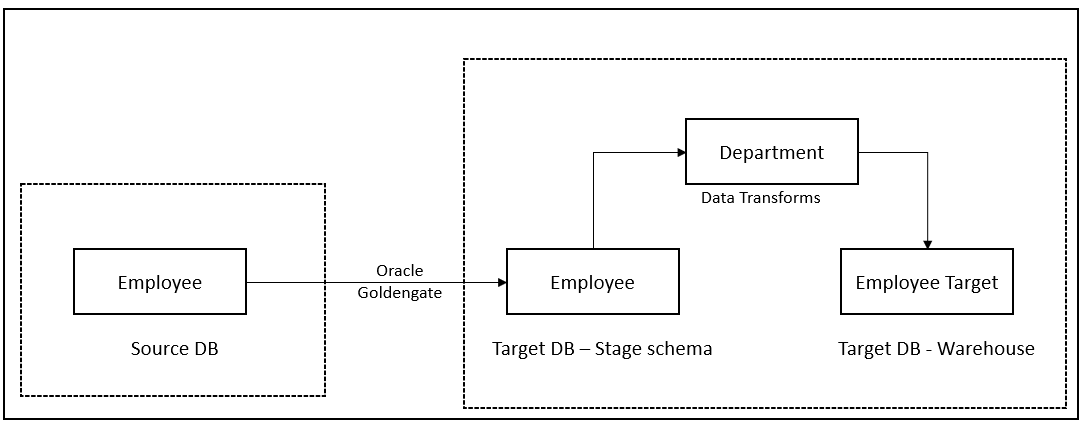
The DDL for the source, stage and target tables are given below.
CREATE TABLE SOURCE.EMPLOYEE (EMP_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, EMP_NAME VARCHAR2(100), DEPT_ID VARCHAR2(10), LOCATION_ID VARCHAR2(10), EMP_SALARY NUMBER);
CREATE TABLE STAGE.EMPLOYEE (EMP_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, EMP_NAME VARCHAR2(100), DEPT_ID VARCHAR2(10), LOCATION_ID VARCHAR2(10), EMP_SALARY NUMBER, LAST_MODIFIED_DATE TIMESTAMP);
CREATE TABLE TARGET.DEPARTMENT(DEPT_ID VARCHAR2(10) PRIMARY KEY, DEPT_NAME VARCHAR2(50));
CREATE TABLE TARGET.EMPLOYEE_TARGET (EMP_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, EMP_NAME VARCHAR2(100), LOCATION_ID VARCHAR2(10), EMP_SALARY NUMBER, DEPT_NAME VARCHAR2(50));
Stage employee table has an additional field last_modified_date. The data in this column is loaded using Oracle Goldengate.
Goldengate function datenow() can be used in that replicat parameter file to load the data in last_modified_date column.
last_modified_Datacolumn=@datenow()
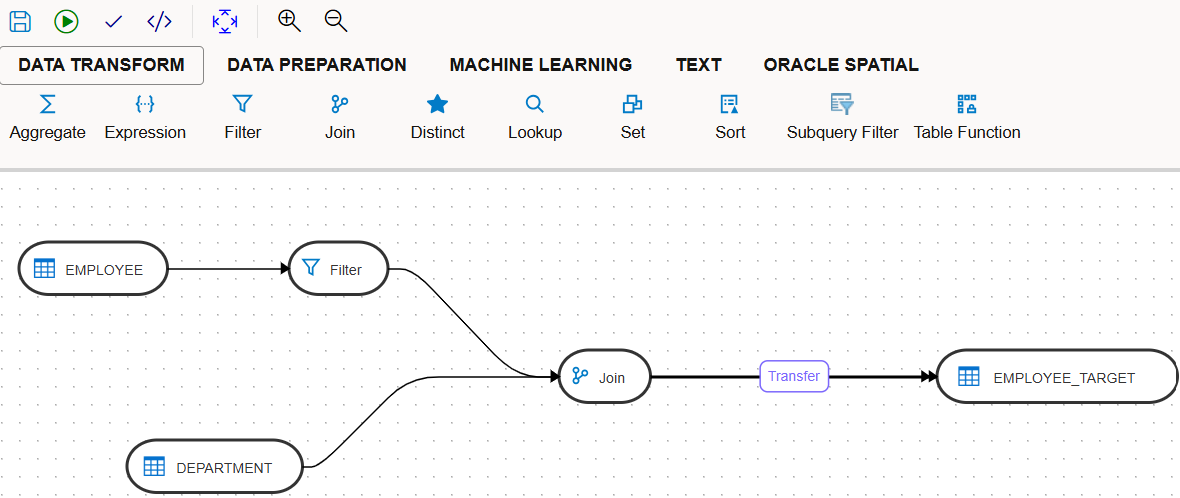
The max date to last modified date is captured using the variables in Data transforms and it is used to get the changed records from the employee table. This data is then combined with department table and loaded into the employee_target table.
Below is a screenshot of data transforms mapping and the workflow.
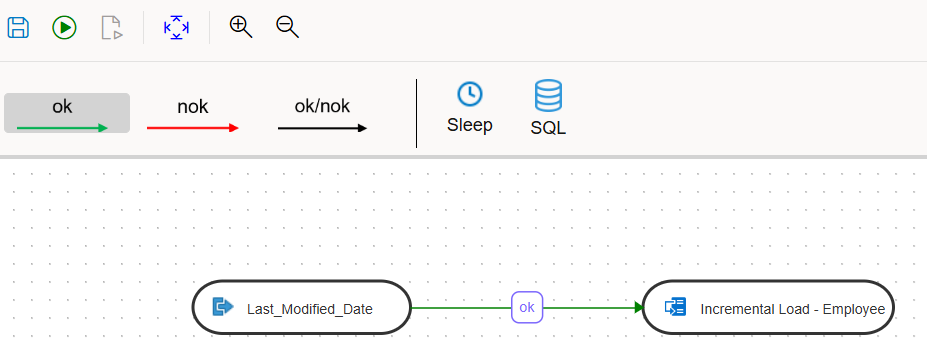
The last modified date is refreshed in the workflow to capture the lastest records.
Last modified date: select max(LAST_MODIFIED_DATE) from target.employee_target
The Data transforms workflow can be scheduled to run periodically to load the data into target table.
Below is the sample data in the final target table.
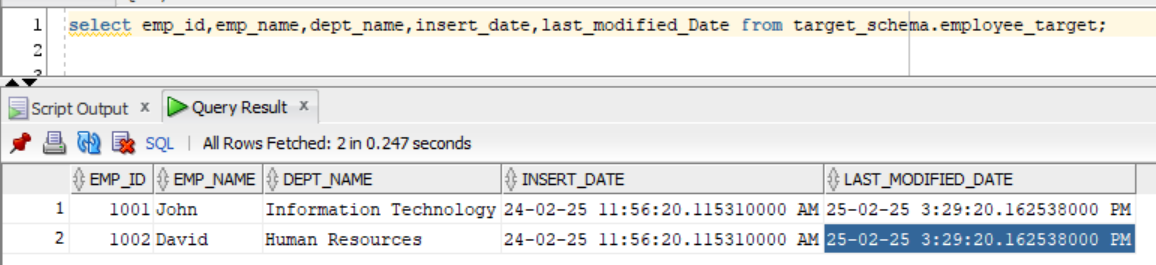
Conclusion
In this blog, we learnt an approach to achieve the near real time replication and heavy transformations using Oracle Goldengate and data transforms.
References
https://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/tutorials/obe/fmw/odi/odi_11g/odi_gg_integration/odi_gg_integration.htm

