At Oracle CloudWorld last September, we introduced the limited availability of ZeroETL Mirror Pipelines in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) GoldenGate. Today, we are pleased to announce that ZeroETL Mirror Pipelines are now generally available.
What is ZeroETL?
ZeroETL is a modern approach to data integration that removes the complexity of traditional batch-based ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines. Instead of performing separate extraction, transformation, and loading processes, ZeroETL allows data to be instantly loaded from source systems into target databases without requiring manual transformation steps.
With ZeroETL Mirror Pipelines in OCI GoldenGate, you can automate data movement effortlessly into Autonomous Databases. In this article, we will drill down into creating, configuring, and running ZeroETL Mirror pipelines in OCI GoldenGate.
Getting Started with ZeroETL Mirror Pipelines
To create a ZeroETL Mirror Pipeline in OCI GoldenGate, follow these simple steps:
Create a ZeroETL Mirror Pipeline
In the Console navigation menu, click Oracle Database, and then select GoldenGate to access its Overview page.
First, create the Connections required for your source and target databases. On the Connections page, click Create Connection and create two Connections: one for your source and another for your target database.
Note: ZeroETL Mirror pipelines support Autonomous Databases as sources and targets. Ensure that connections use dedicated endpoints as their traffic routing method.
On the Pipelines page, click Create Pipeline to open the Create ZeroETL Mirror pipeline panel. When you create a ZeroETL Mirror pipeline, many tasks are automated:
- An OCI GoldenGate Data replication deployment is created with 1 OCPU and auto-scaling enabled.
- The connections you previously set up are assigned to this deployment.
- The initial load process is configured.
- GoldenGate Capture and Apply processes required for the ongoing data replication are created.
- The transition from the initial load to the ongoing replication is handled transparently.
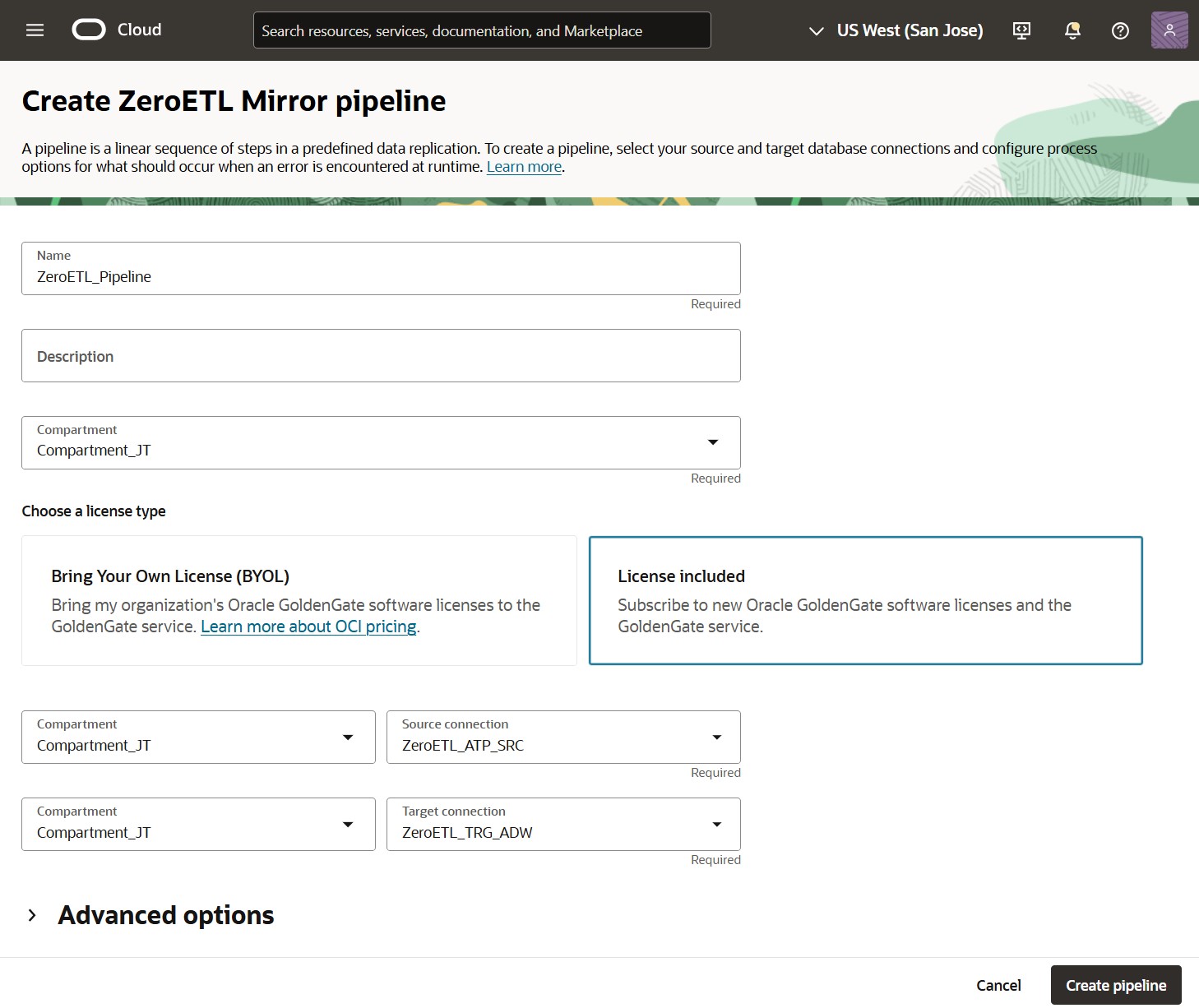
Enter a Name, select your Compartment, pick the license type (License included or BYOL), and select your Source and Target connections.
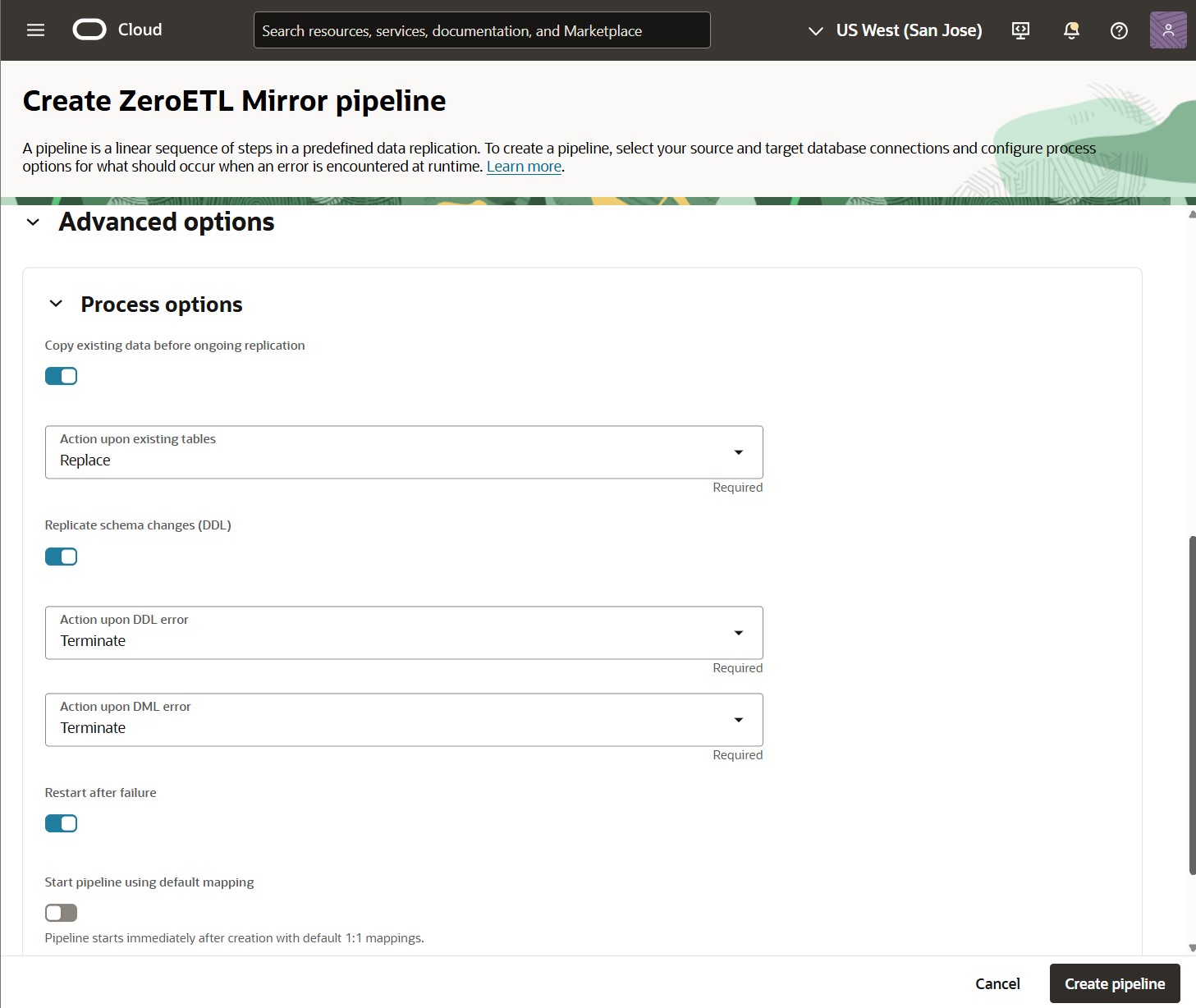
Optionally, review the Advanced options:
- Copy existing data before ongoing replication: Performs an initial load from the source database into the target database before ongoing synchronization.
- Action upon existing tables: Determines the pipeline behavior if the target schema is not empty. Valid values are Replace, Truncate, Append, and Skip. Applicable only if ‘Copy existing data before ongoing replication’ is enabled.
- Replicate schema changes (DDL): Controls if the ZeroETL Mirror pipeline replicates DDL changes.
- Action upon DDL error and Action upon DML error: Manage the behavior of the pipeline if DDL or DML errors occur at runtime. Valid values are Terminate, Discard, and Ignore. Discarded records can be accessed using Collect Diagnostics on the ZeroETL Mirror pipeline details page.
Action upon DDL error is applicable only if ‘Replicate schema changes (DDL)’ is enabled. - Restart after failure: Sets the pipeline to restart its runtime processes automatically if any failure occurs.
- Start pipeline using default mapping: Controls whether the ZeroETL Mirror pipeline starts immediately after creation with the default 1:1 mapping rules (*.* into *.*).
All these options are enabled by default except ‘Start pipeline using default mapping’.
Click Create pipeline to start the pipeline creation job. Review Create pipelines for more information.
Configure a ZeroETL Mirror Pipeline
Once the ZeroETL Mirror pipeline is created, you can access its details page and review its information.
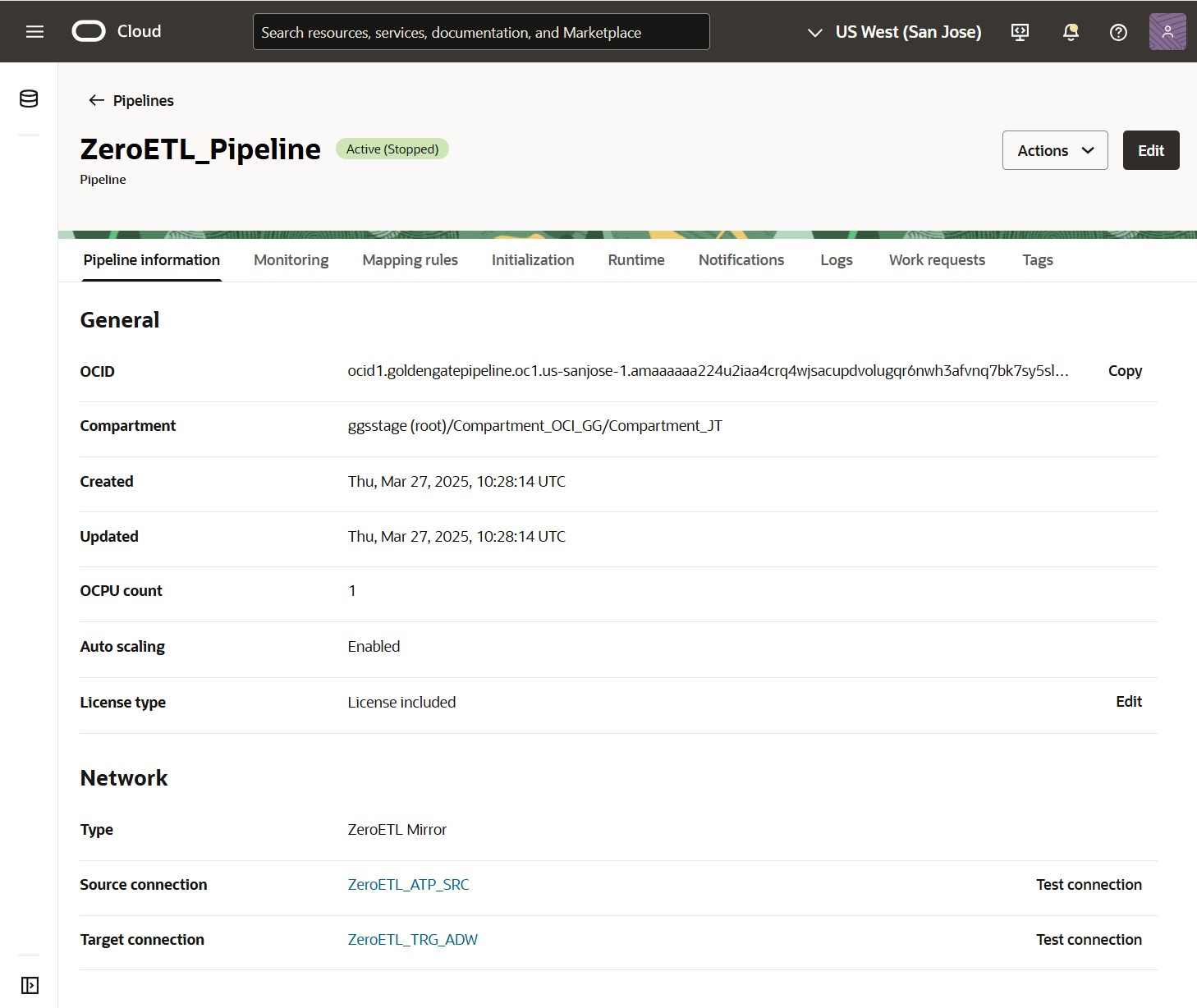
Click Test connection next to the Source and Target connection on the Pipeline information page to validate connectivity before applying any configuration changes.
Note: If test connection is unsuccessful, you may need to rerun it.
Next, go to Mapping rules. ZeroETL Mirror pipelines use a default 1:1 mapping rule that moves all the schemas and tables from the source database into the target database. You can add or remove mapping rules, but at least one Include mapping rule must always be defined. See Add mapping rules for more information.
Click Preview to list the tables and schemas that will be replicated into the target based on your Mapping rules.
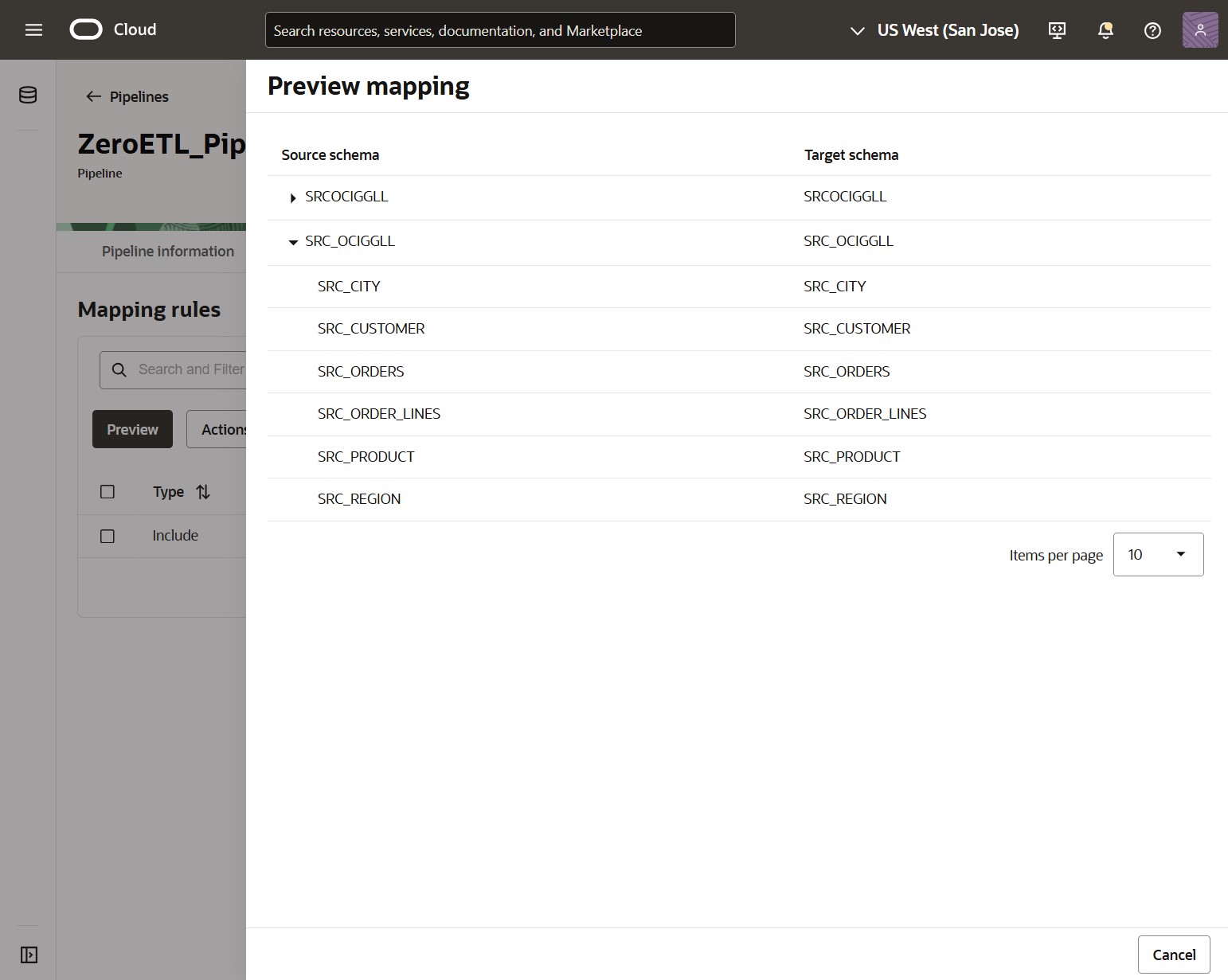
Click Actions and Add rule to add Include or Exclude rules.
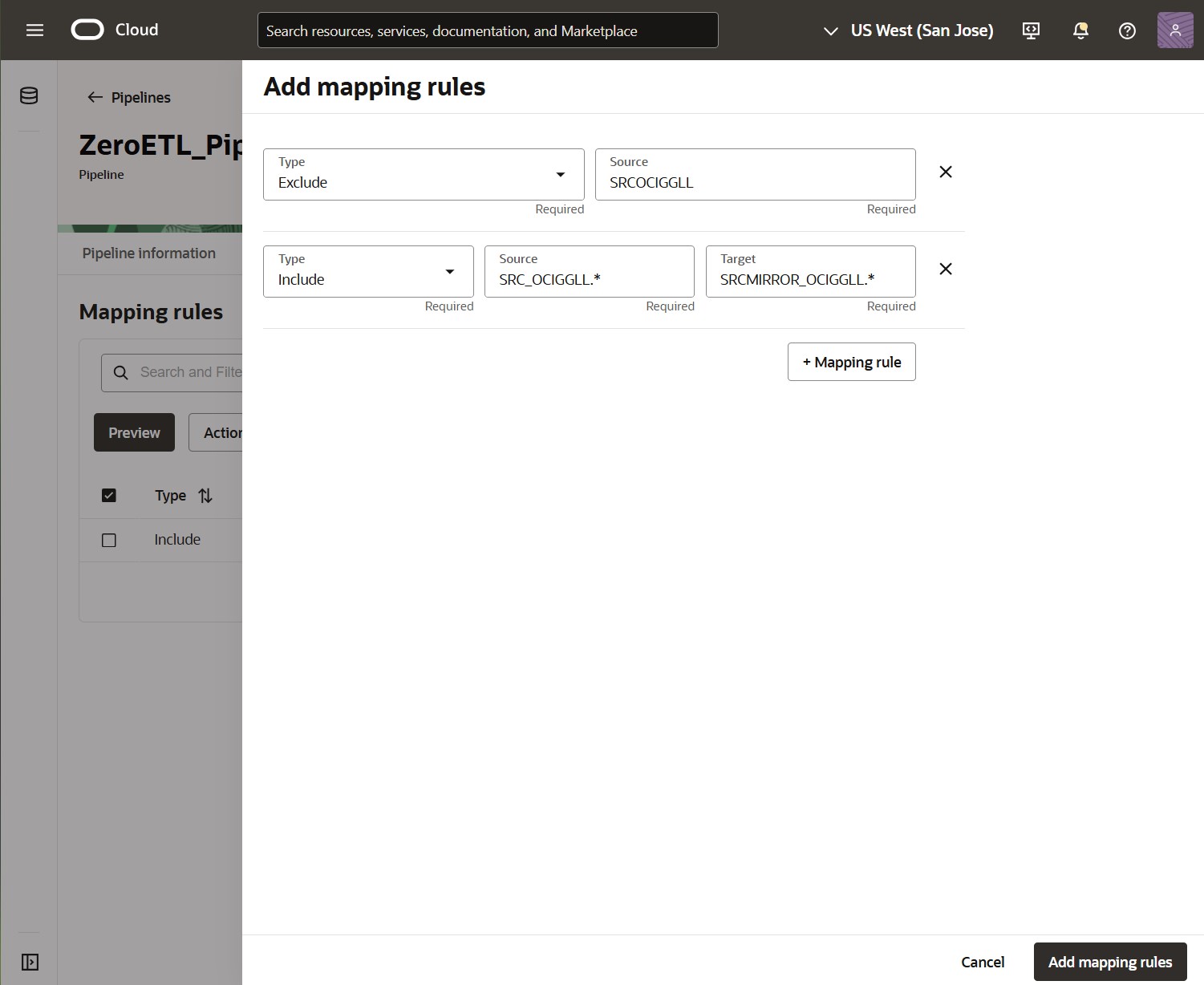
Exclude rules will remove schemas or tables from the list of objects to be moved, while Include rules will add new objects.
You can also remove or edit Mapping rules from the list.
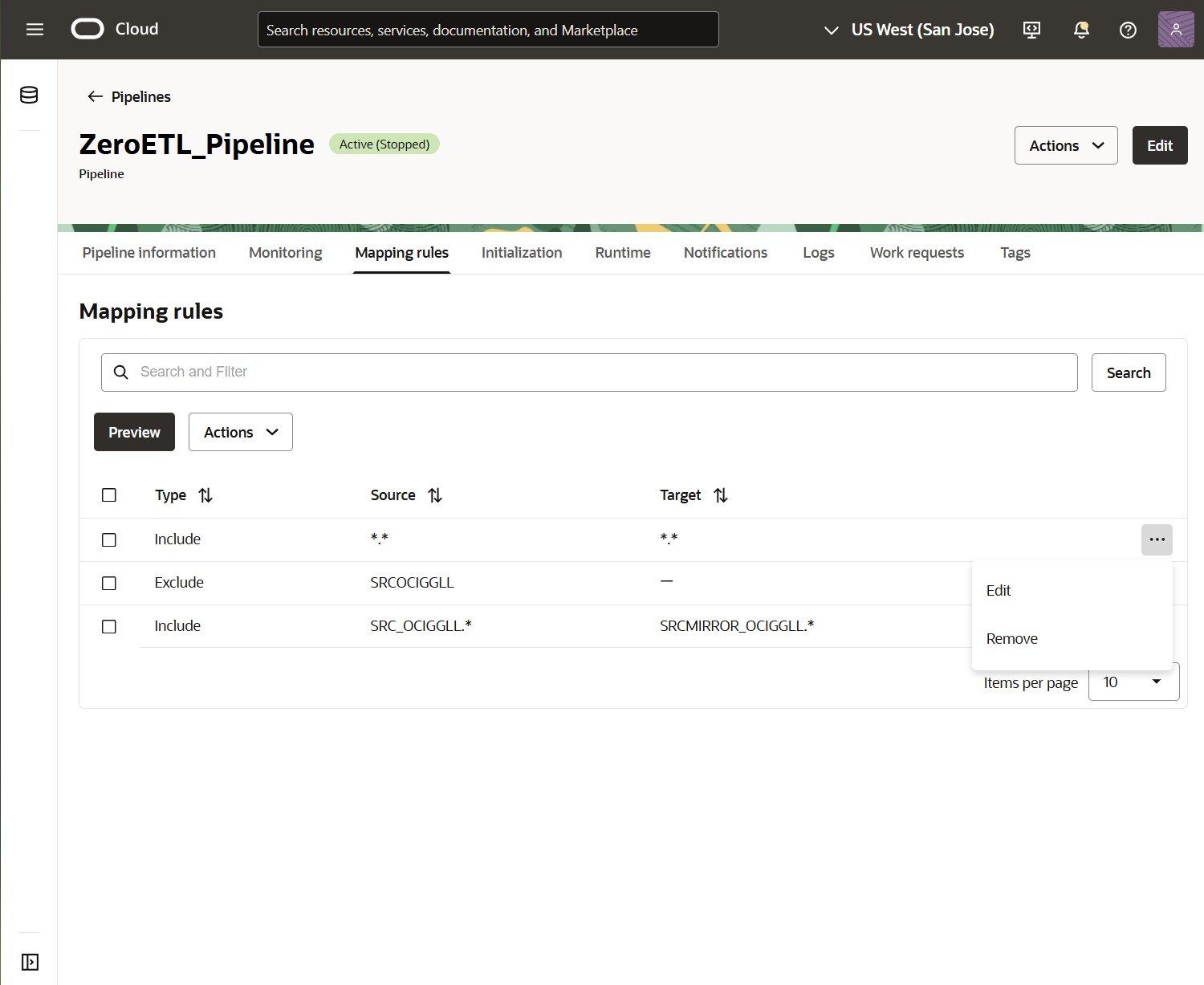
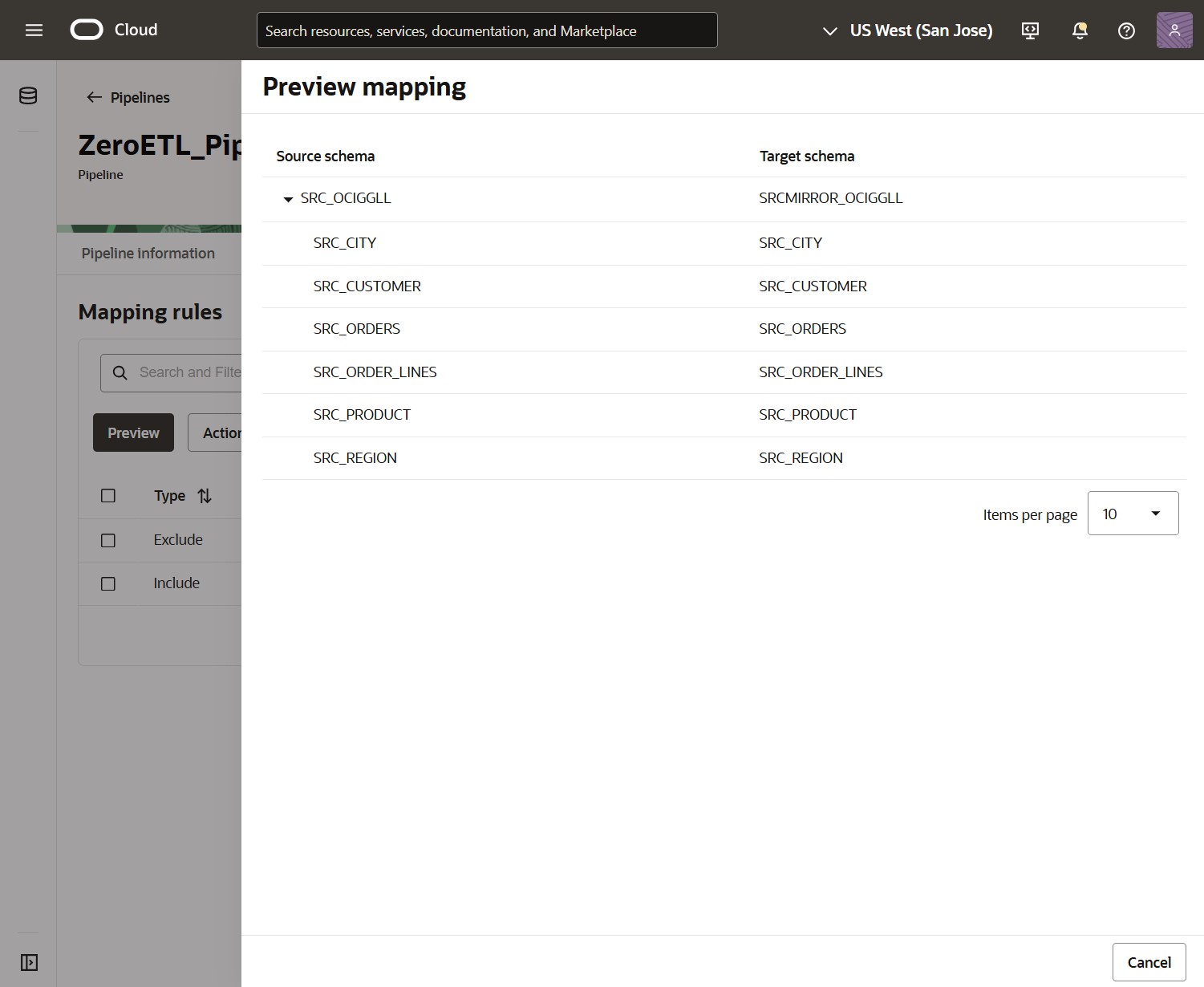
Once you finished configuring your Mapping rules, click Preview to validate the list of objects before starting the pipeline execution.
Next, click Logs and Enable log next to Critical Events, and then provide the required information to activate it.
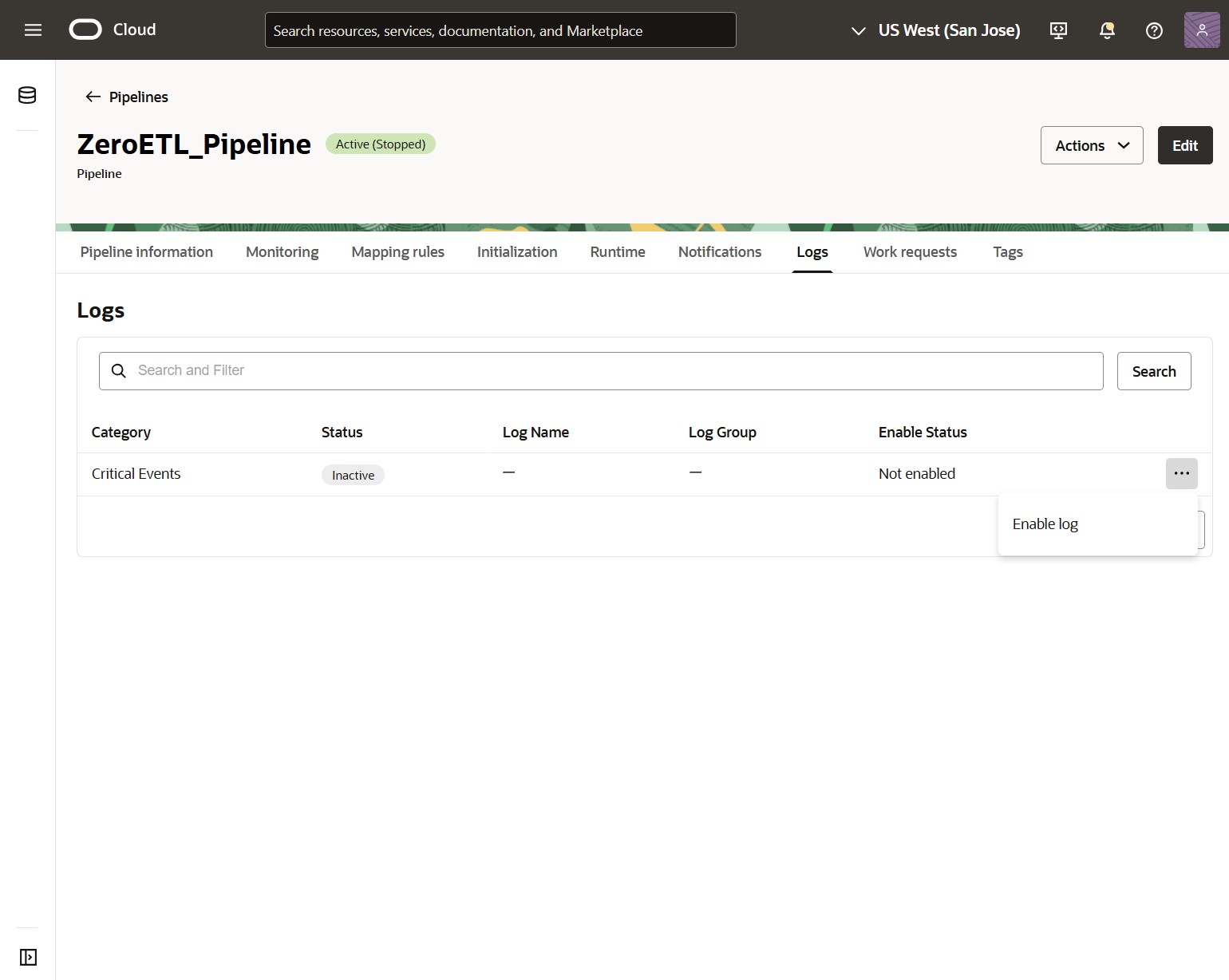
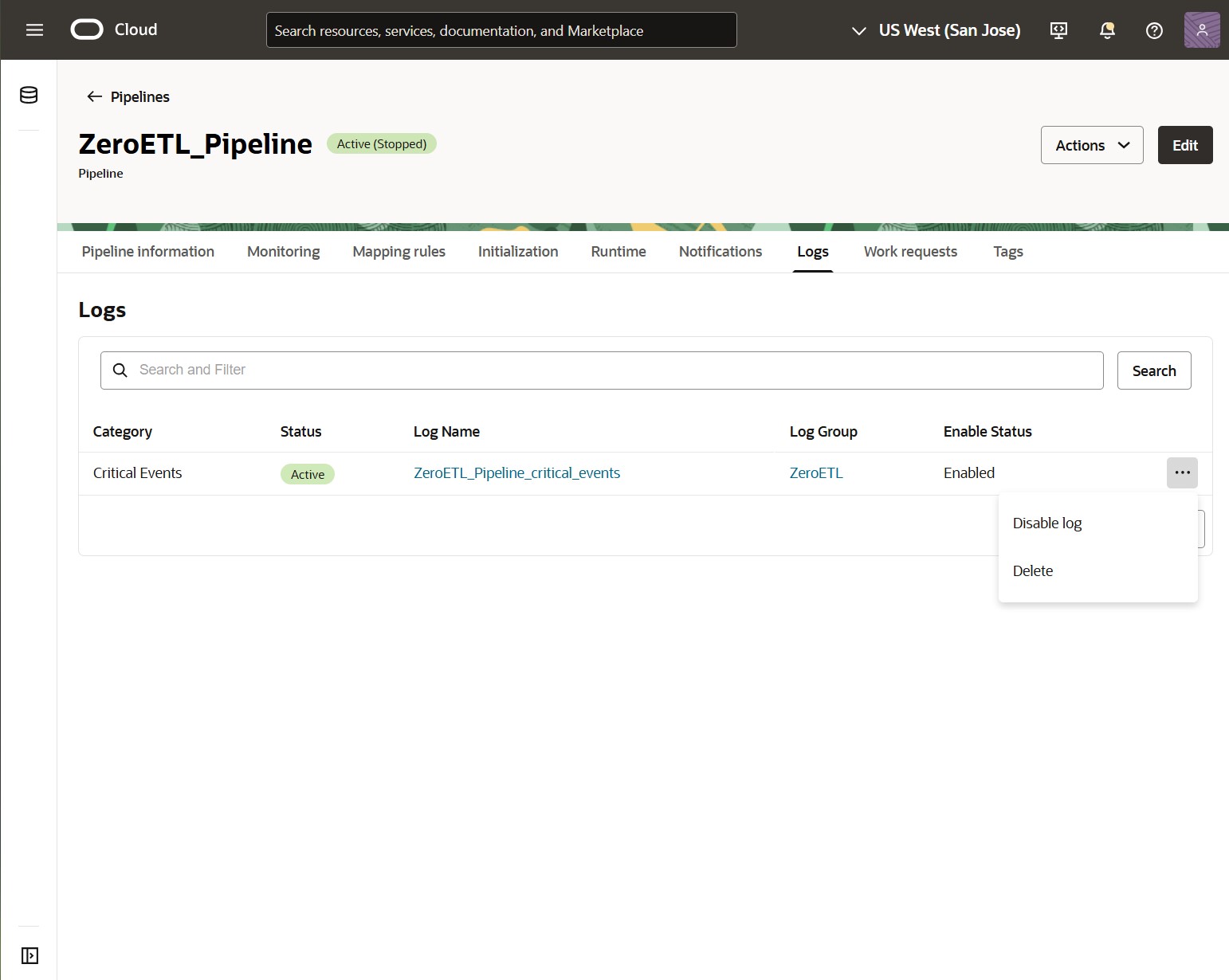
Once enabled, click the Log Name to review critical events and set up notifications in OCI Logging.
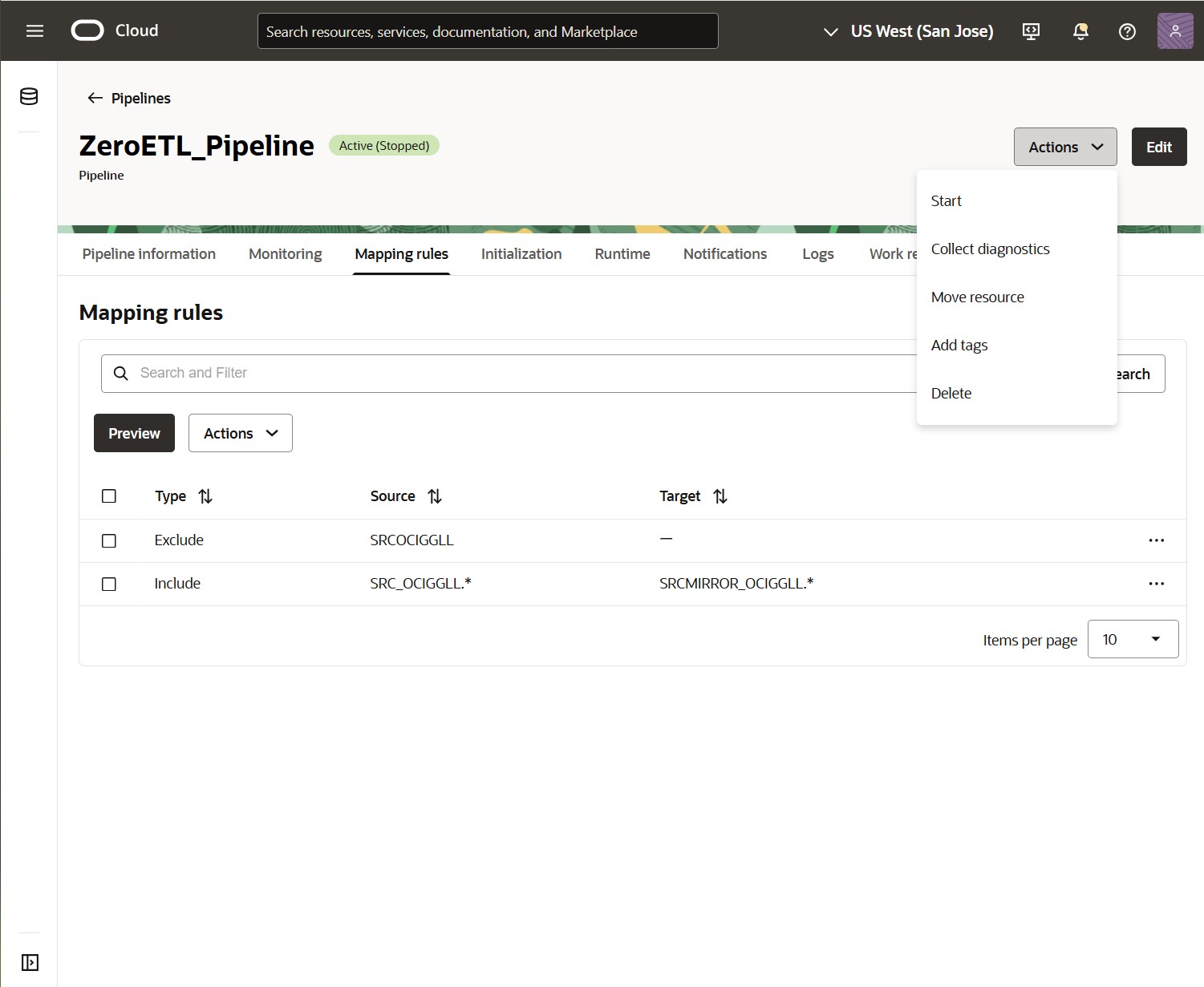
Run a ZeroETL Mirror Pipeline
Click Actions on any of the ZeroETL Mirror pipeline pages and click Start to initiate the pipeline execution.
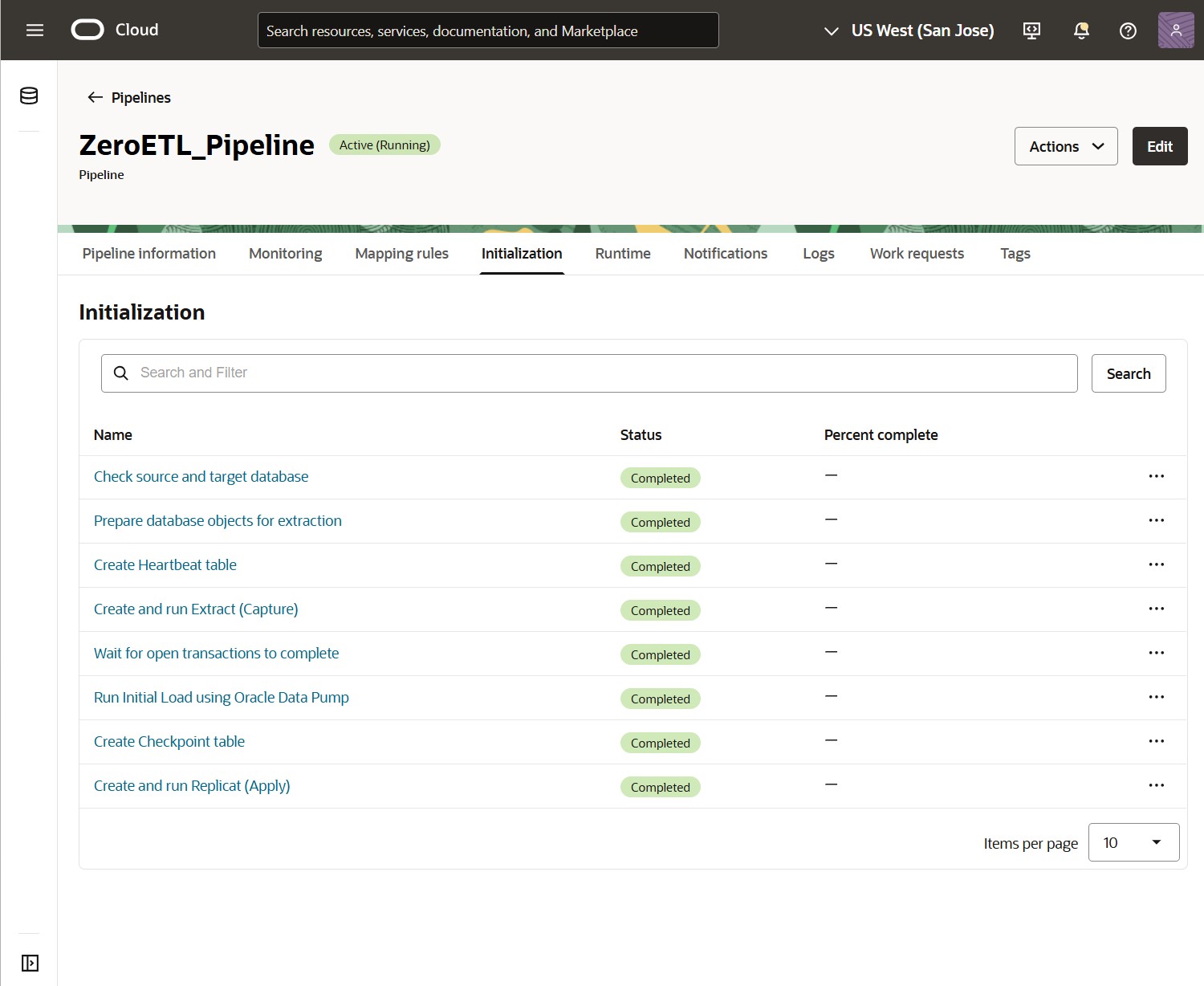
The pipeline will first start initializing. You can follow the steps on the Initialization tab and review their details.
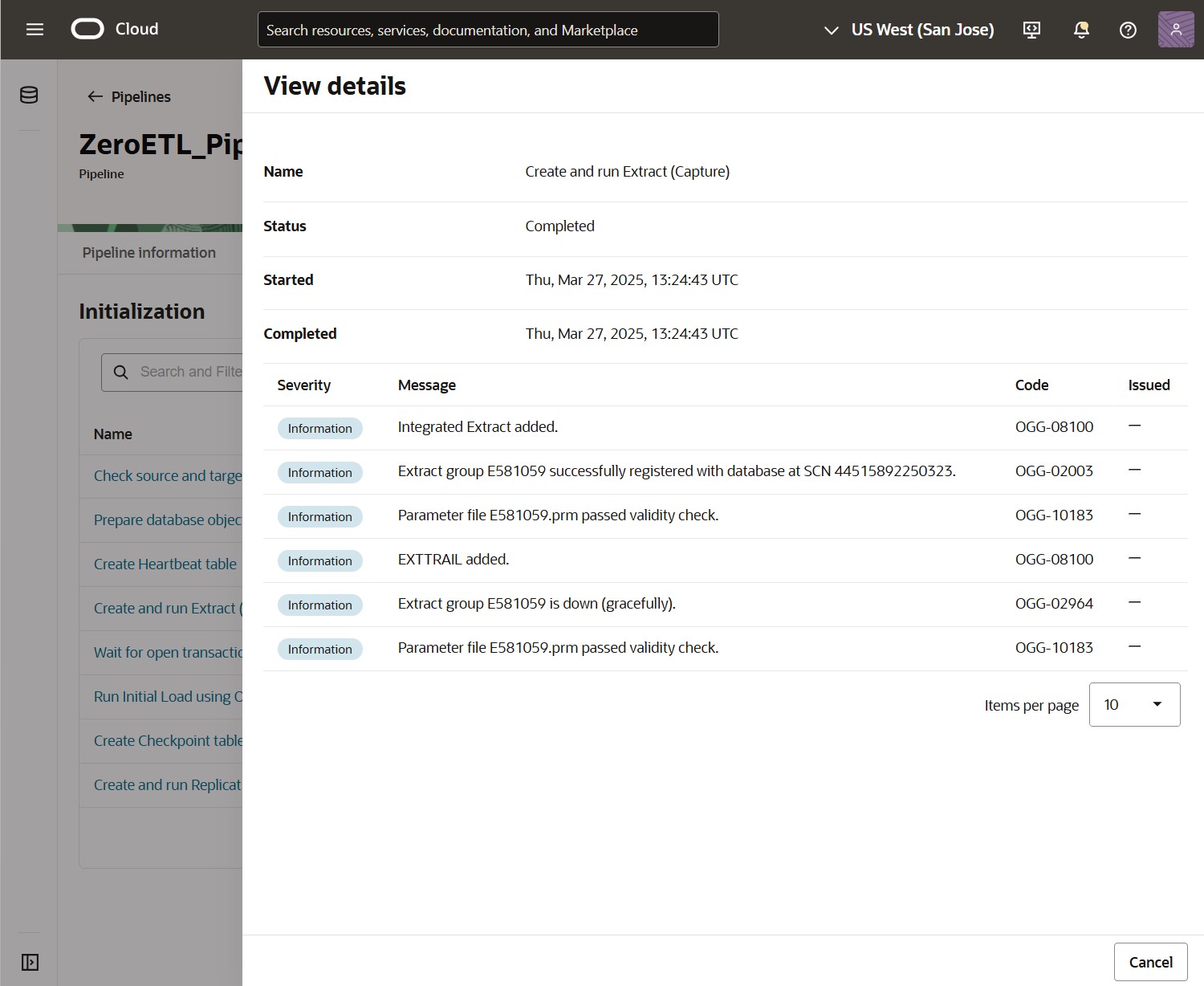
Once the Initialization phase ends, you can find the Capture and Apply processes on the Runtime tab. The list includes process names, state, current latency, and when their information was last updated.
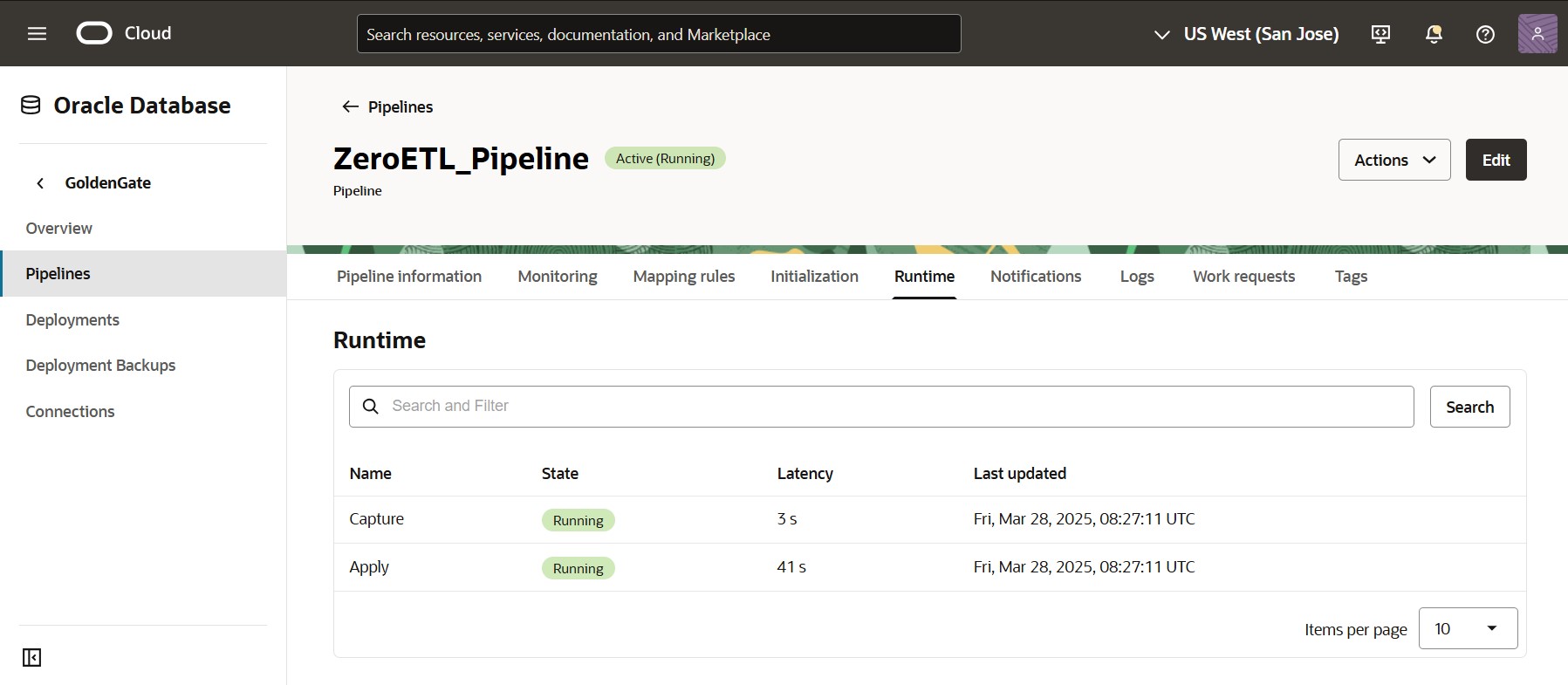
The ZeroETL Mirror pipeline is now running and will continuously move data between the source and target systems based on the Mapping rules. You can monitor its execution using the Runtime tab, review metrics on the Monitoring tab, set up notifications using the Notifications tab, and review any warnings or error messages using the Logs page and OCI Logging.
Additional Resources
