Welcome Everyone….
In this blog we would setup OCI Goldengate Service data replication to migrate a MySQL RDS from AWS to OCI.
We can have any target as Oracle GoldenGate is a comprehensive software for enabling the replication of data in heterogeneous data environments.
In this blog, we are using OCI Autonomous database as a target.
Architecture:
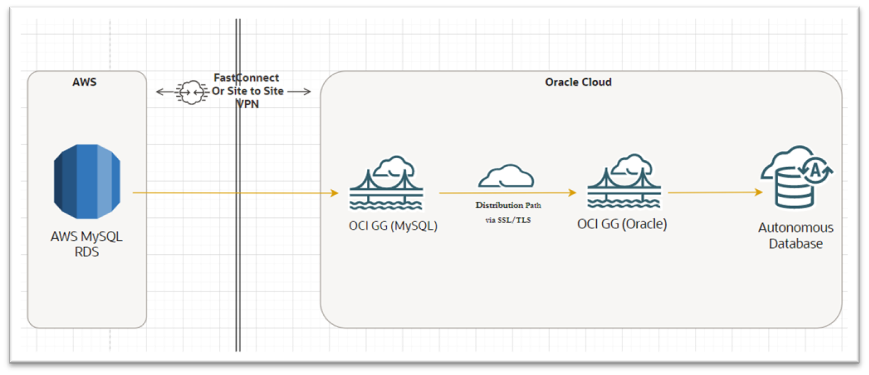
Requirements:
- MySQL 5.7, 8.0 version instance running on AWS RDS
- Oracle Autonomous database on OCI
- OCI Goldengate deployment for MySQL
- OCI Goldengate deployment for Oracle
- Low Latency network connection between AWS and OCI (Private VPN or Fast Connect is preferred)
Important: All the supported technologies and versions by OCI GG is listed here – What’s supported
Steps to follow for migration:
- Configure Change data capture extract in GG MySQL. Which will start capturing the any changes that would happen on the MySQL DB.
- Configure Initial load extract and get all the initial data from AWD MySQL RDS
- Configure a replicat to load initial load data into target ADB
- Configure CDC replicat which will apply the changes after the initial load is done (we might have to take care of duplicates with HANDLECOLLISIONS)
AWS RDS MySQL Setup before configuring the Goldengate:
Important Note: All the steps performed here are using Amazon RDS MySQL 8.0, but you can also use Amazon RDS MariaDB 10.5 with little to no change in these steps.
- Create a parameter group and assign it to AWS MySQL RDS with below parameters and reboot the AWS MySQL RDS instance
- show VARIABLES LIKE ‘binlog_format’; à ROW
- show VARIABLES LIKE ‘binlog_row_image’; à FULL
- show VARIABLES LIKE ‘binlog_row_metadata’; à FULL
- Need to change the retention period of binlog to at least 24hr , so that if there is a network error then extract can endure the failure
call mysql.rds_set_configuration(‘binlog retention hours’, 24);
- For MariaDB version 10.2 and later, Oracle GoldenGate works in the same way as for MySQL, but a new variable needs to be configured.
The variable that needs to be added is “binlog-annotate-row-events=OFF“.
Restart MariaDB after configuring this variable and then start the Extract process
- For remote capture to work , Grant access permissions to the Oracle GoldenGate remote capture user. Or you can use the admin user created while creating the RDS.
CREATE USER ‘ggadmin’@’%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘<password>’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘ggadmin’@’%’ WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- The server_id value of the remote MySQL server should be greater than 0. This value can be verified by issuing the following statement on the MySQL remote server:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘server_id’;
Deploy OCI GG and Create Connections for Both Source AWS RDS MYSQL and OCI ADB:
- Deploy OCI Goldengate for MySQL in OCI
You will find OCI Goldengate in Oracle Database section of OCI Menu
Go to deployments and create a deployment
Select the technology as MySQL and create the deployment
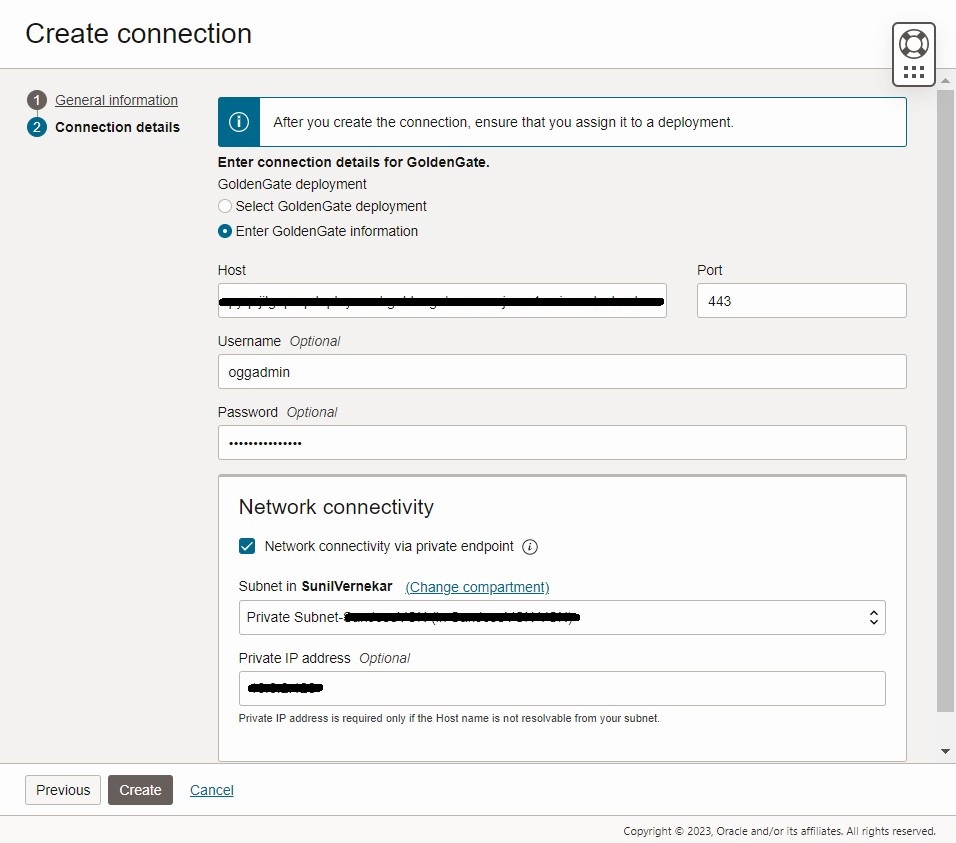
- Once the deployment is ready , create the connection to AWS MySQL RDS in OCI
You need to use ‘Network connectivity via private endpoint’ and provide private ip and subnet if you have a VPN or Fast Connect.Assign the connection to the MySQL deployment
Once assigned it would show up in Goldengate console , you can try connecting
- Create a deployment for OCI Goldengate for Oracle and connection to Autonomous database.
OCI Autonomous database already has a Goldengate as ‘ggadmin’ unlock the user and you should be able to connect
alter user ggadmin identified by <password> account unlock;
ALTER USER ggadmin QUOTA unlimited ON data;
GRANT UNLIMITED TABLESPACE TO ggadmin;
Set up Goldengate capture and apply processes both Initial Load and CDC:
Before configuring the Goldengate you should have the MySQL table structures created in target database. In our case it would be OCI Autonomous database. As Goldengate will only get the data and tables creation needs to be done before hand
Assuming we already have table structures on target DB –
- Start CDC extract and generate trails. Do not start replicat to consume these trail files.
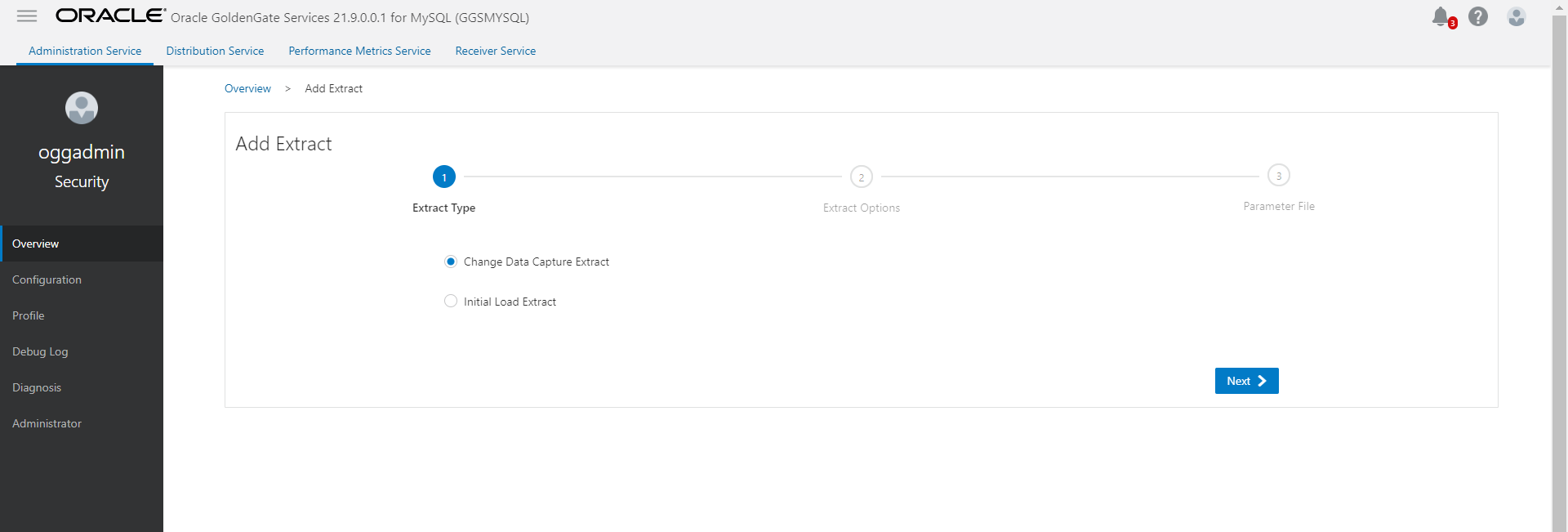
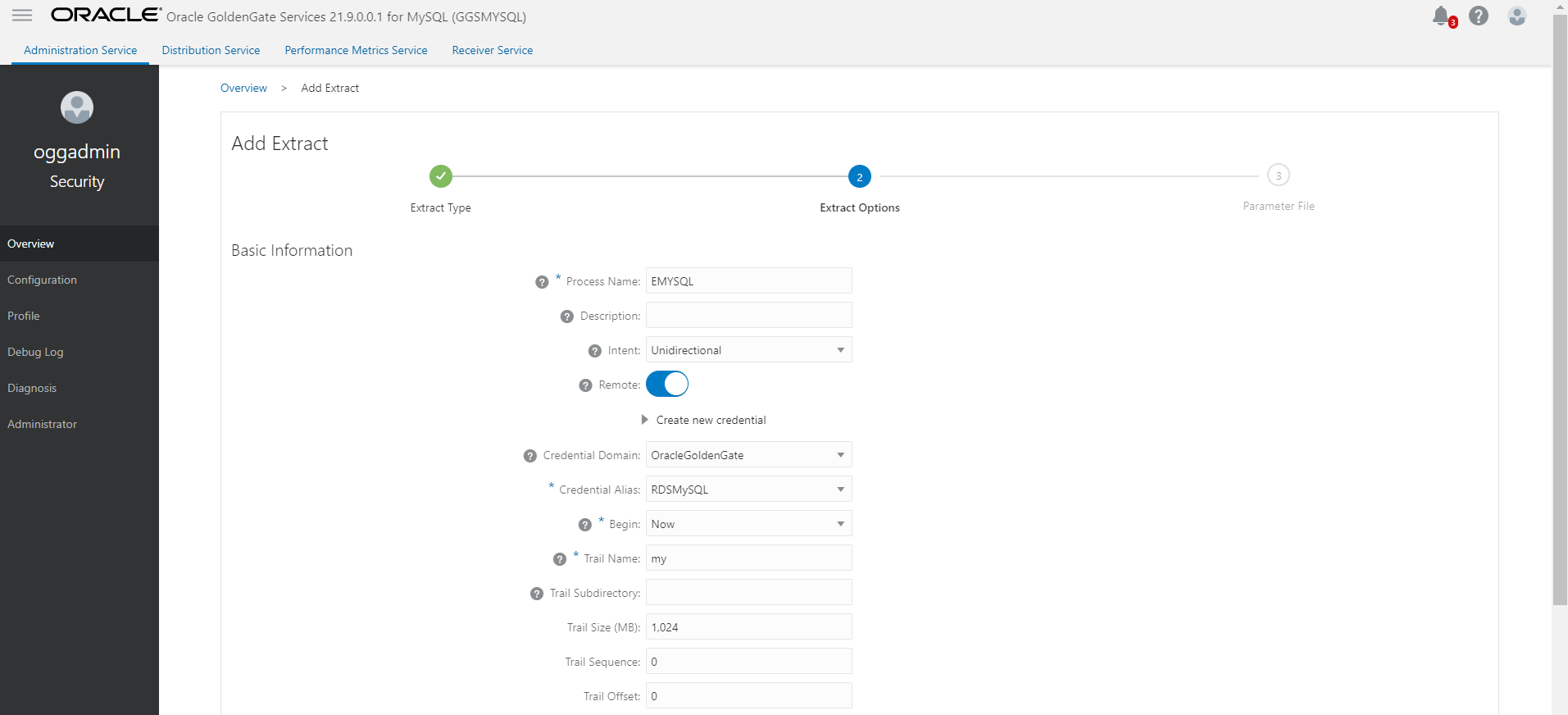
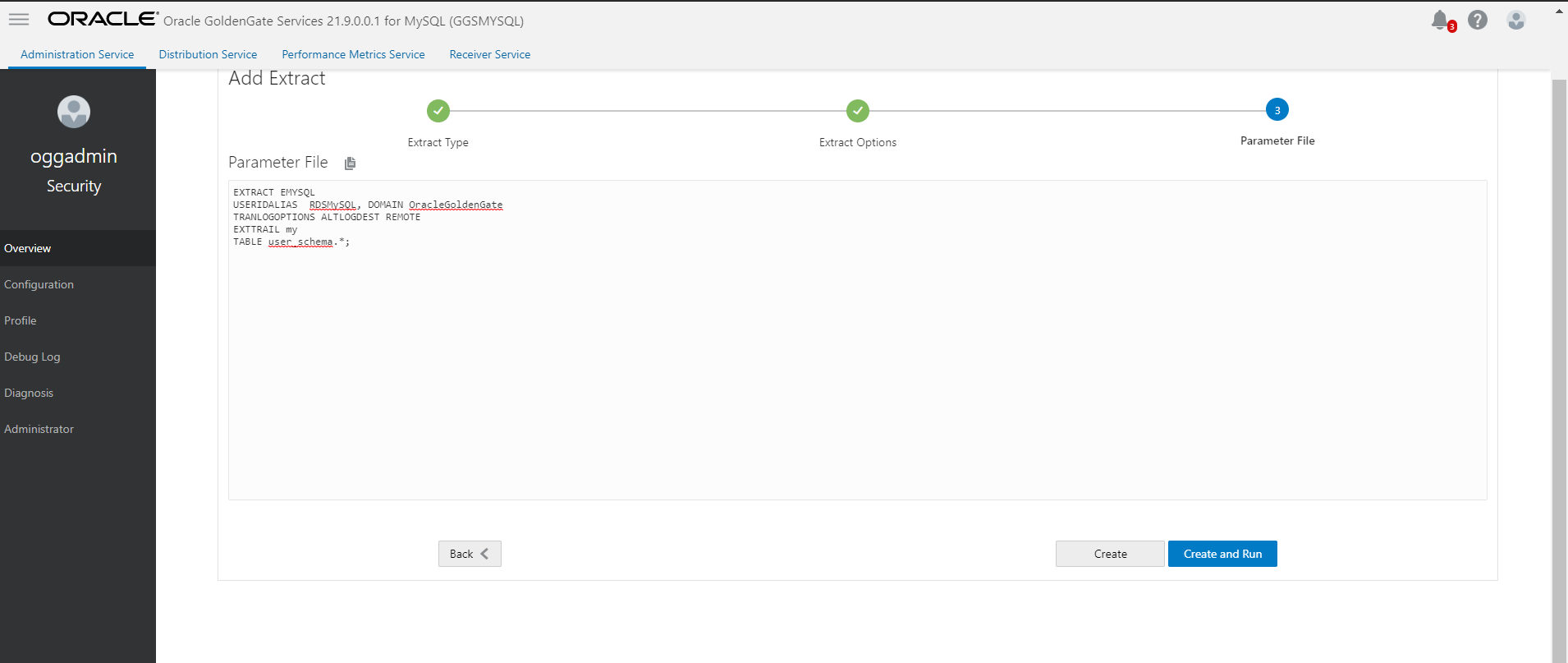
- Start Initial load extract and wait for initial load to complete.
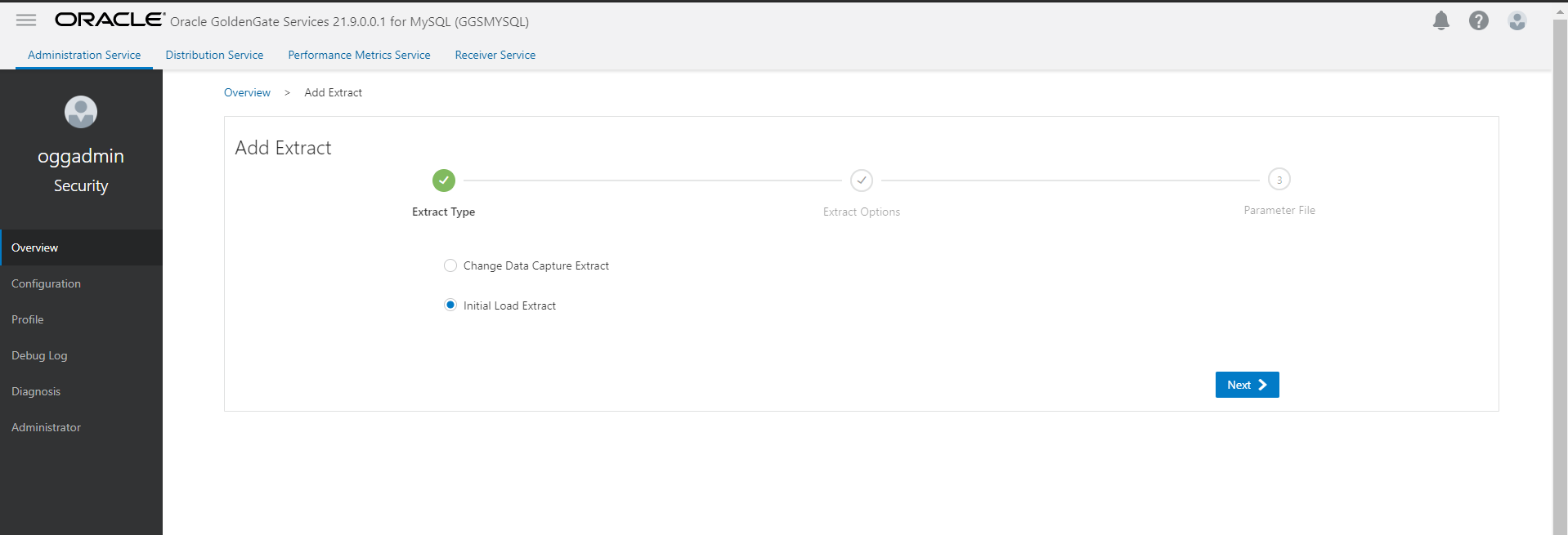
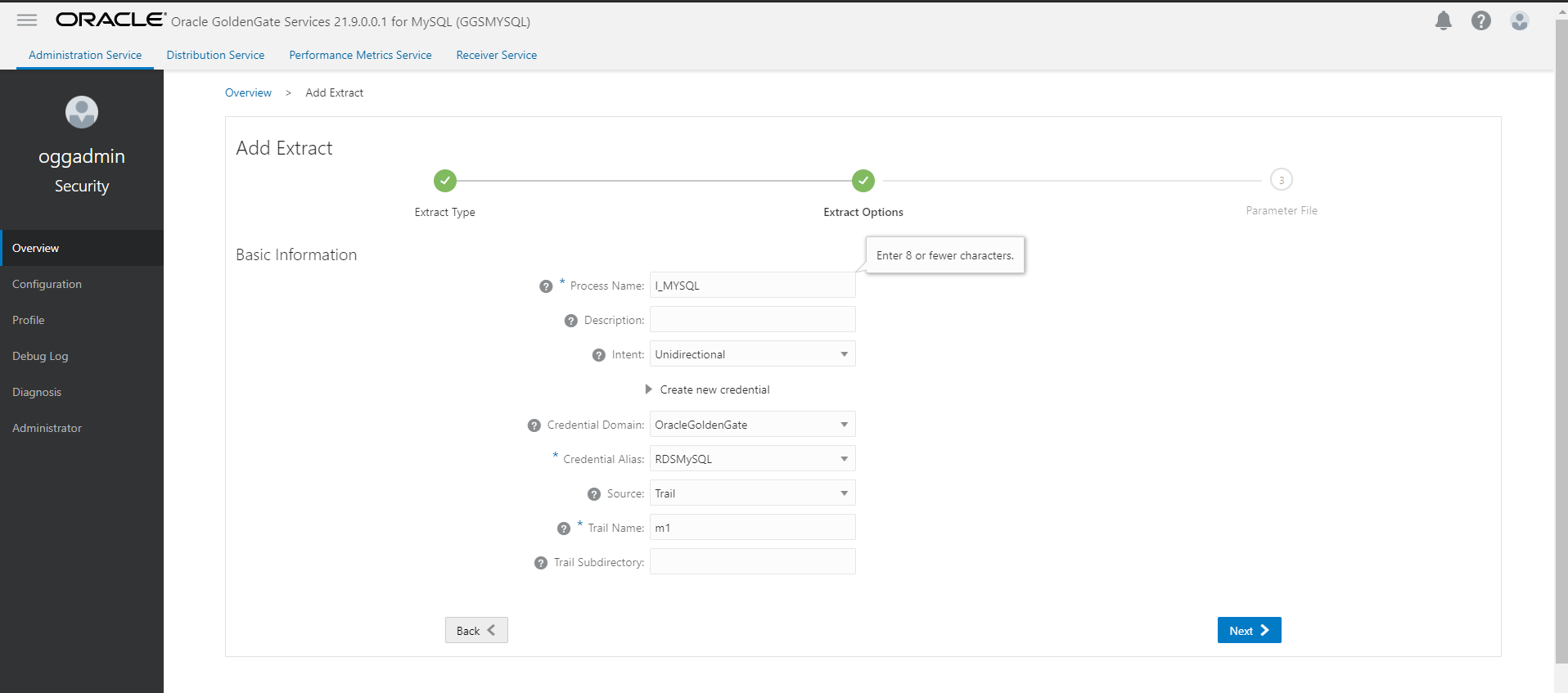
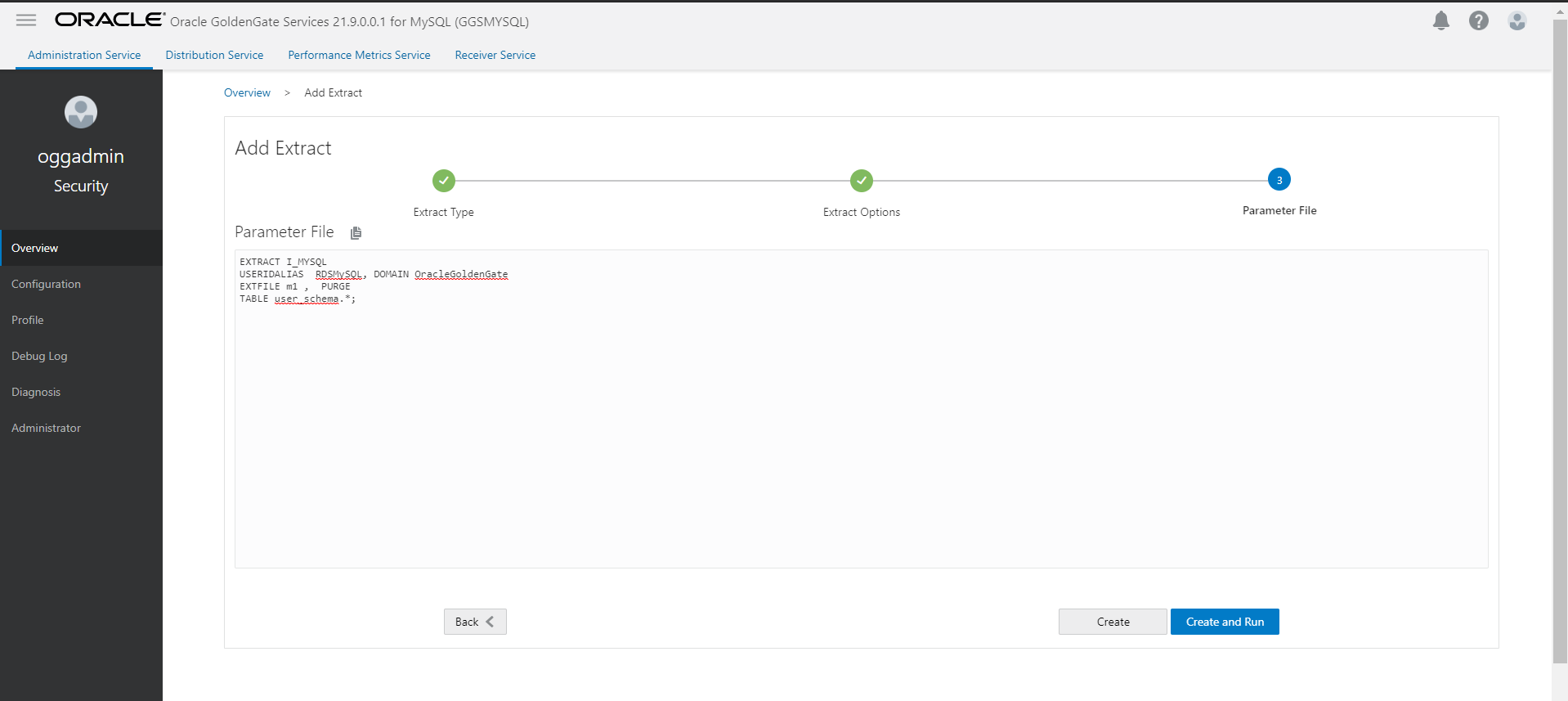
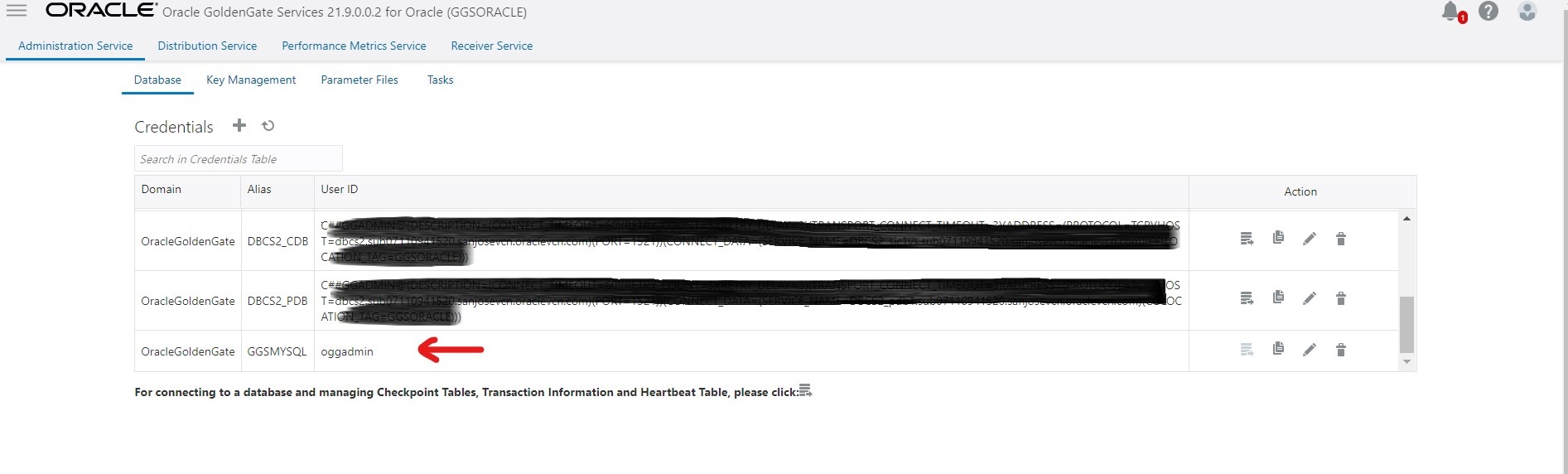
- We need to send the trail files from MySQL deployment to Oracle deployment. For that we create a Goldengate type connection of MySQL Deployment and assign it to Oracle deployment
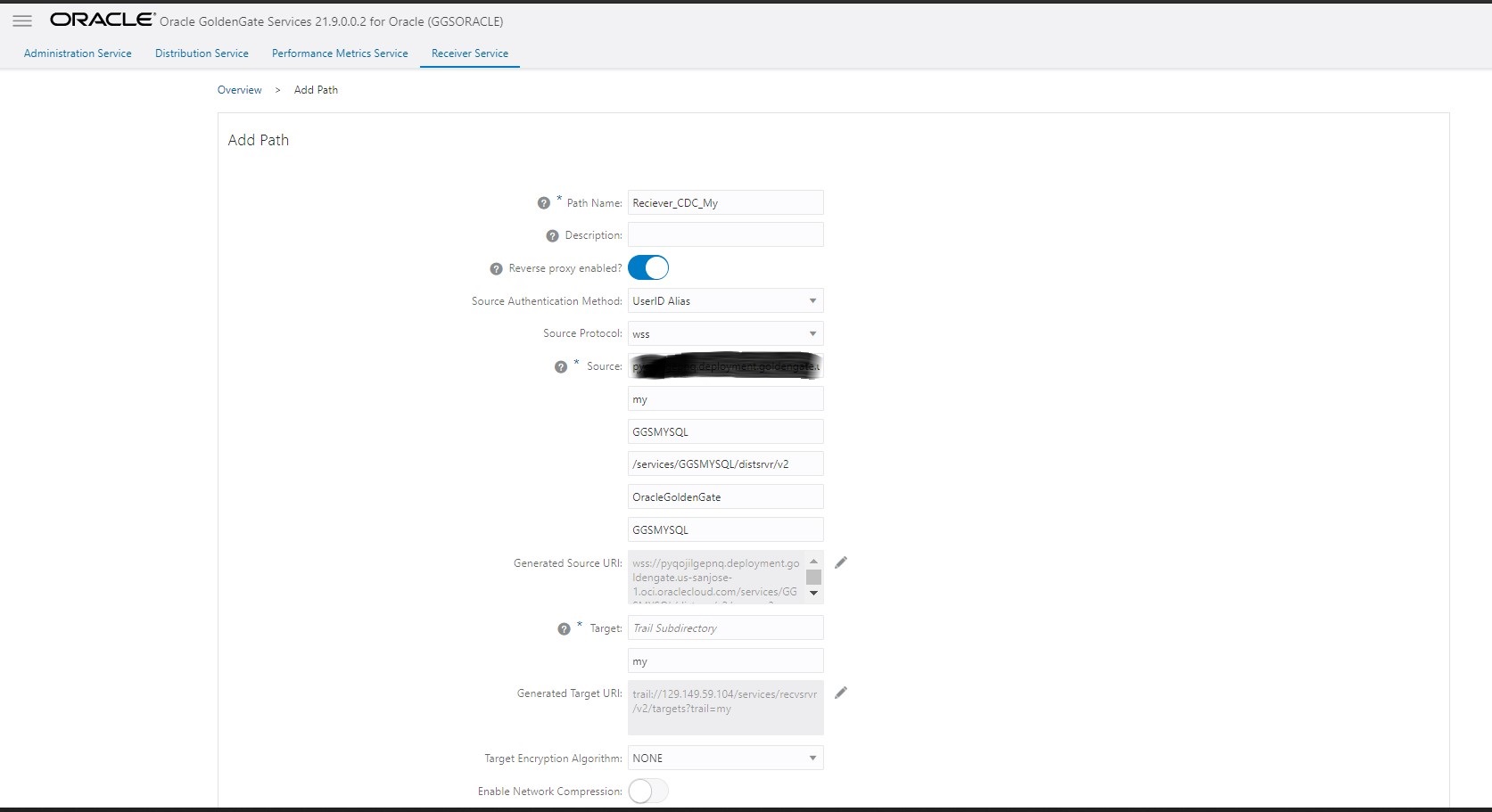
Then, create the Receiver service to pull both CDC and Initial Load trail files into Oracle deployment.
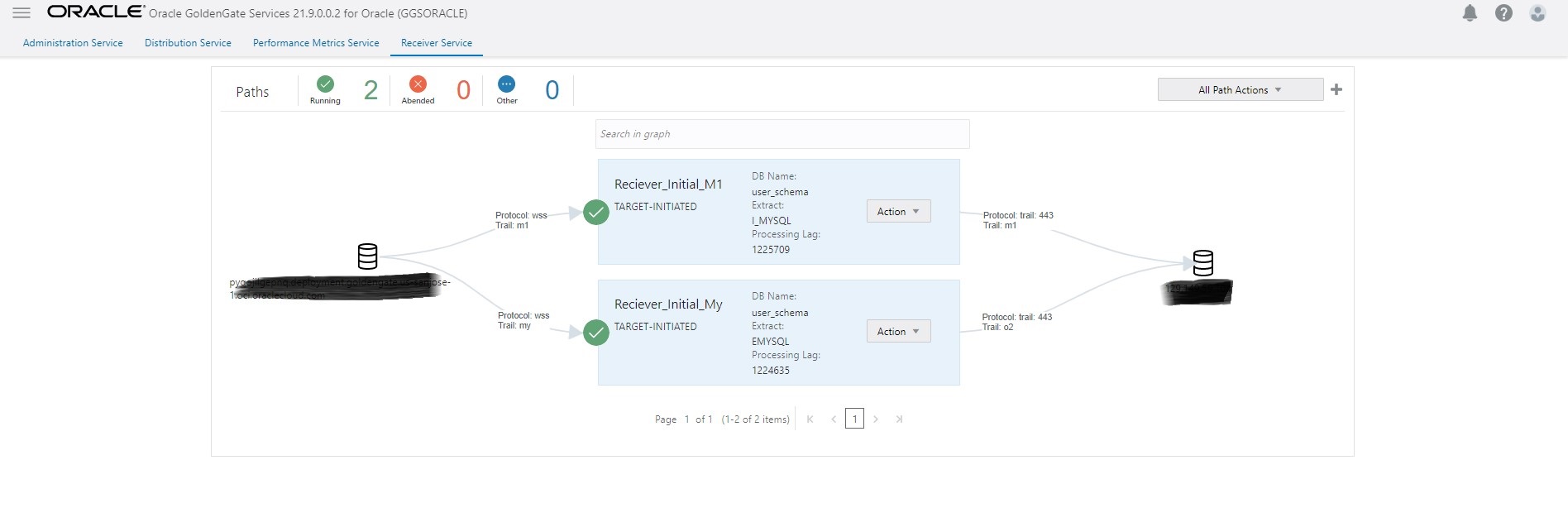
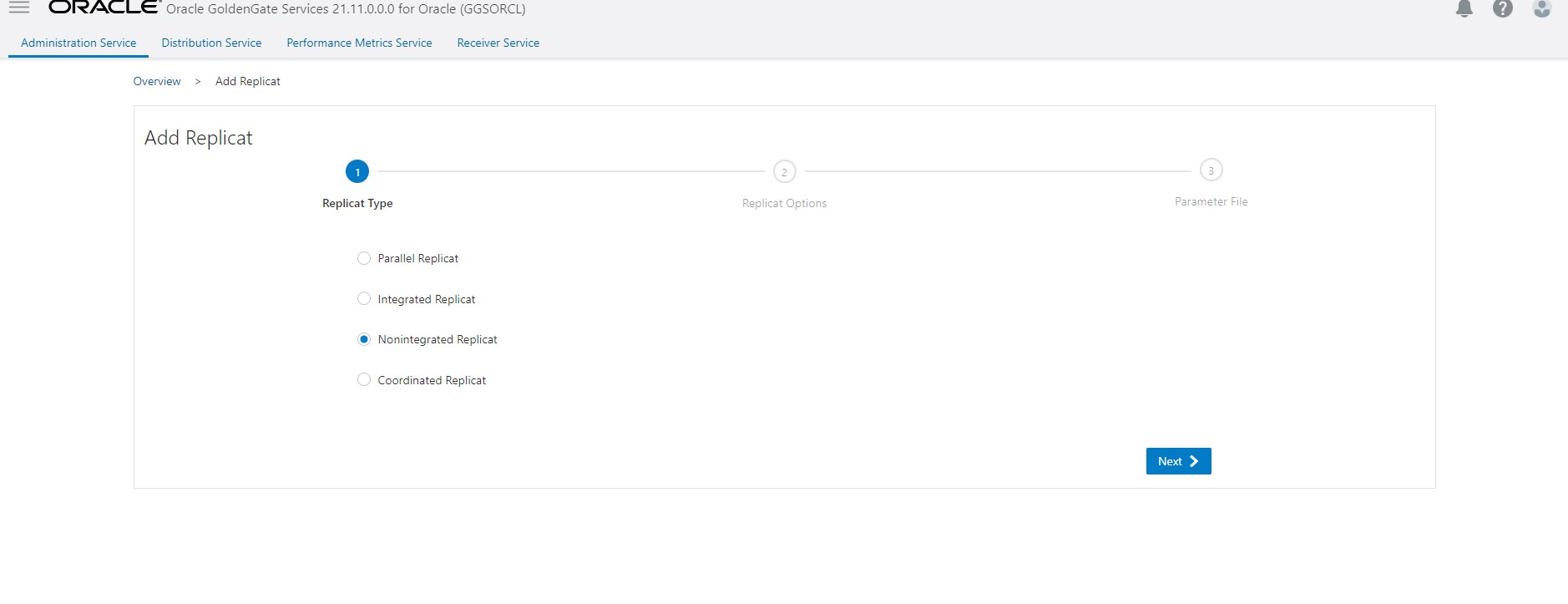
- Create a new replicat to consume the initial load trails generated in Step 2. Wait for completion and then stop replicat.
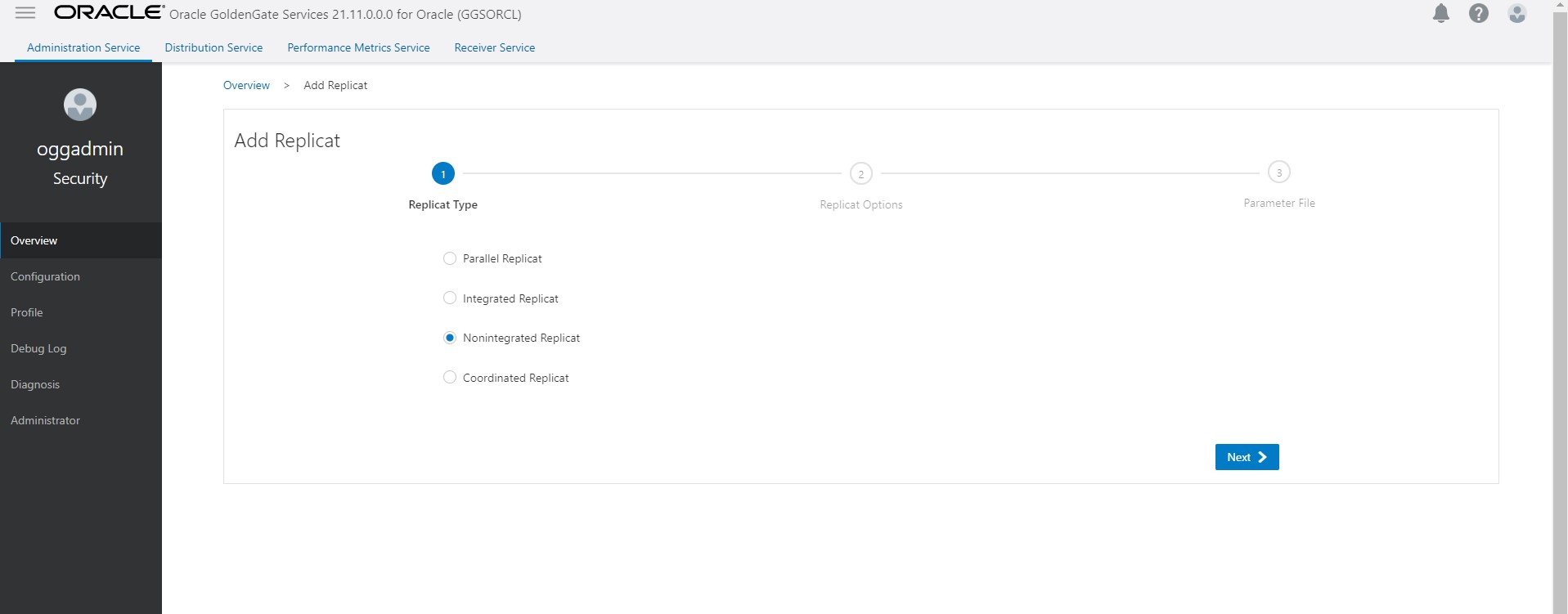
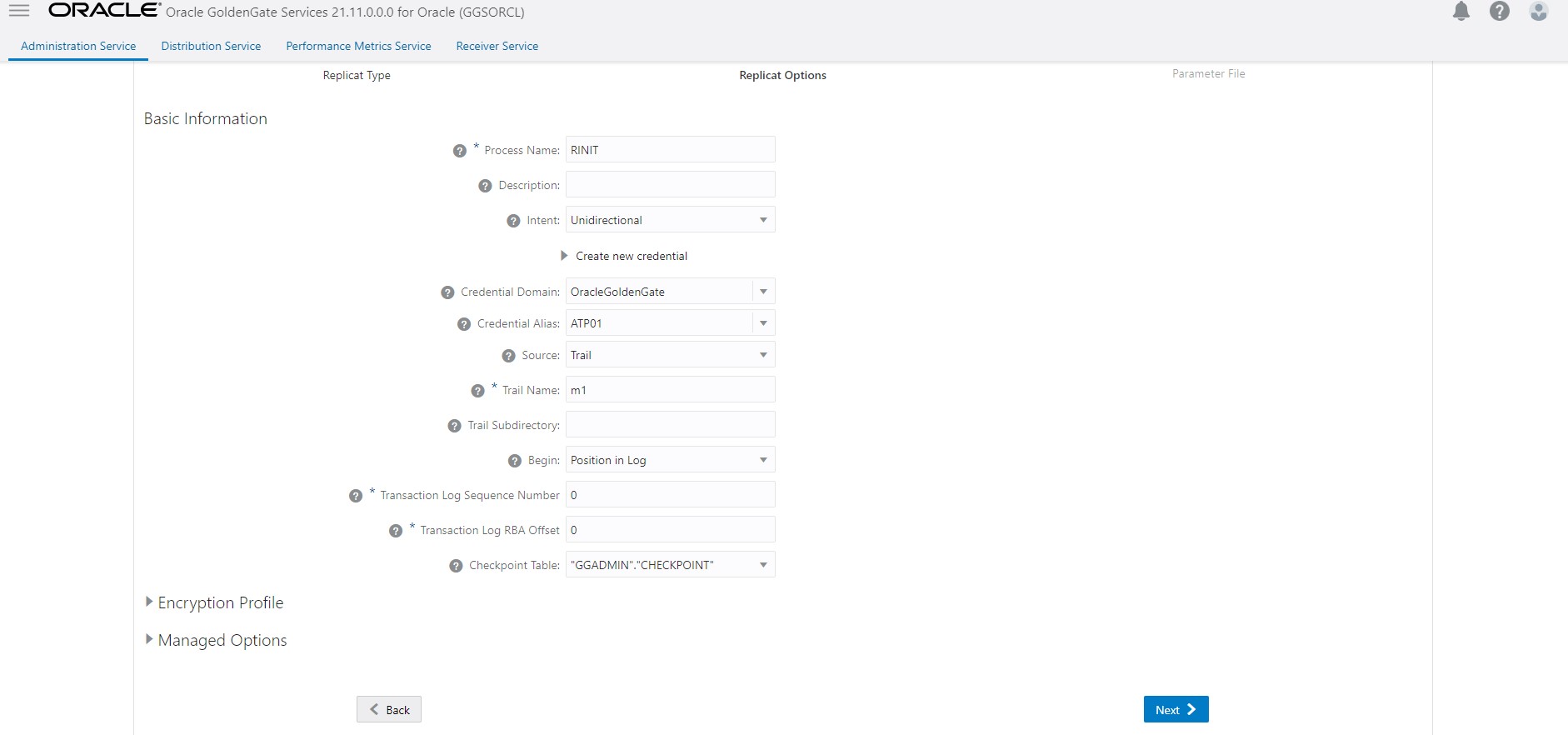
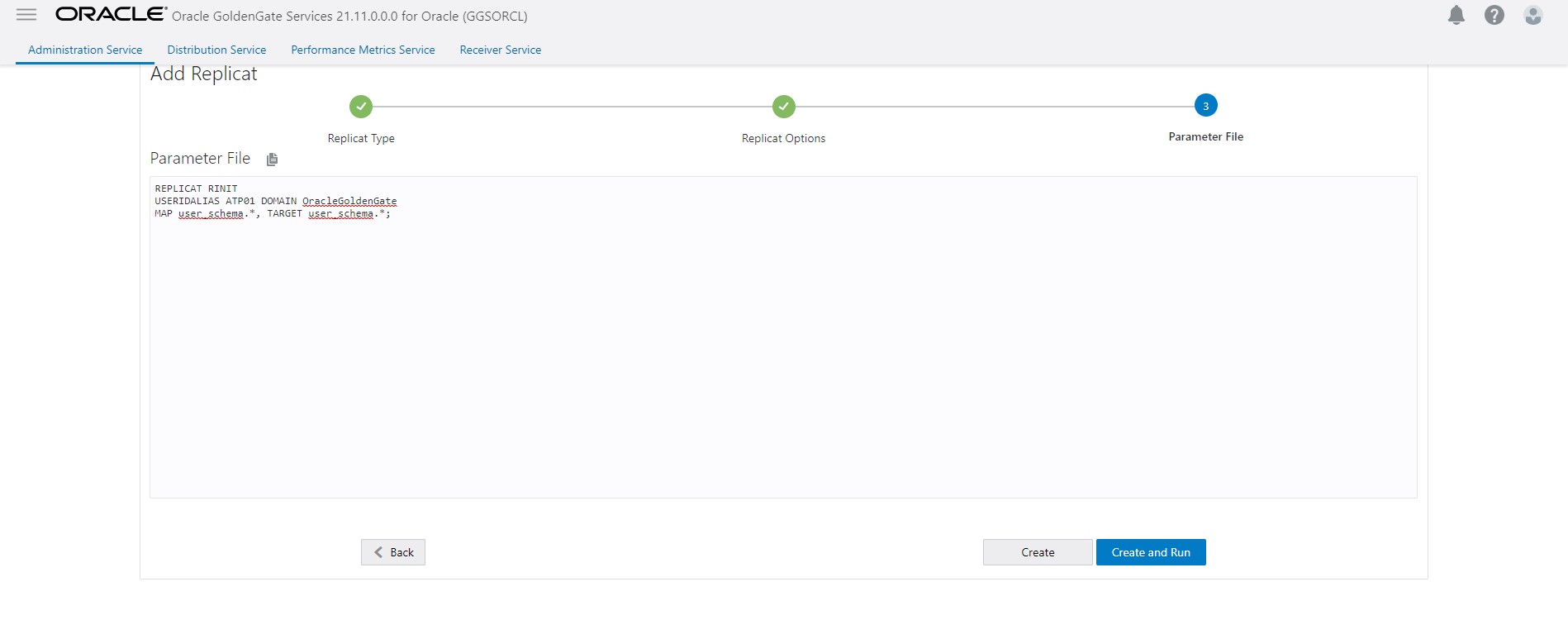
Once it completes all initial load data stop it and drop the initial load replicat
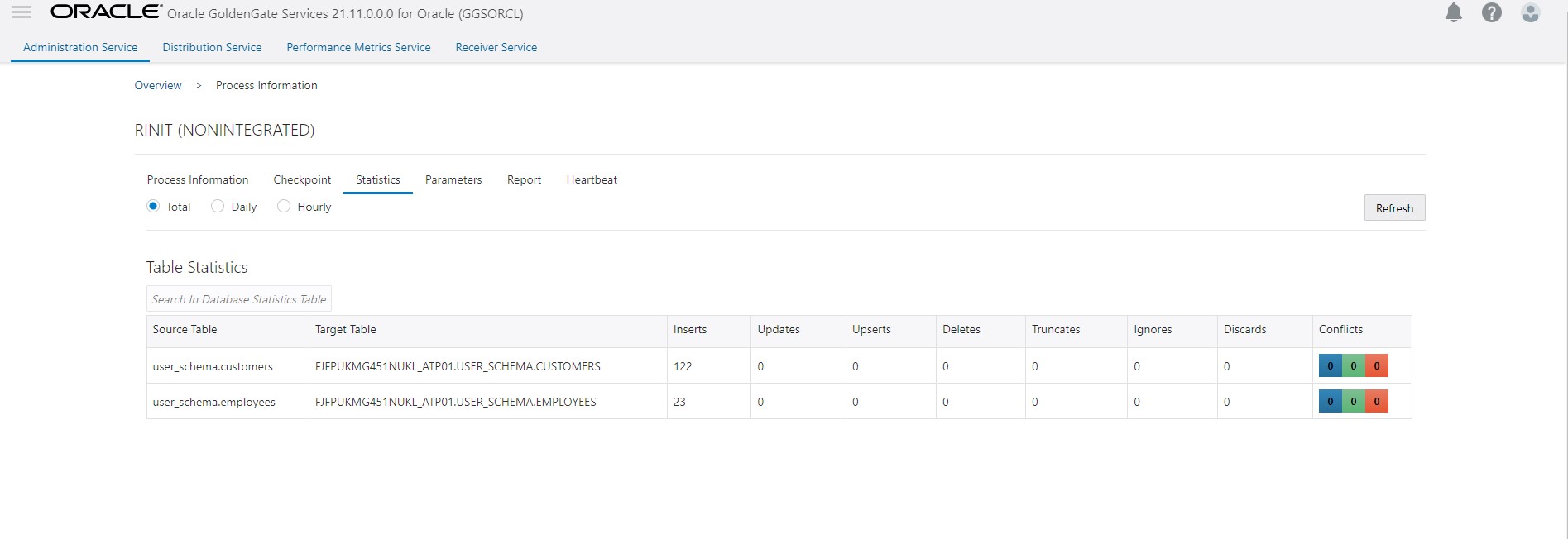
- Create a new replicate to consume the CDC trails. Configure this replicat to use HANDLECOLLISIONS and then start replicat.
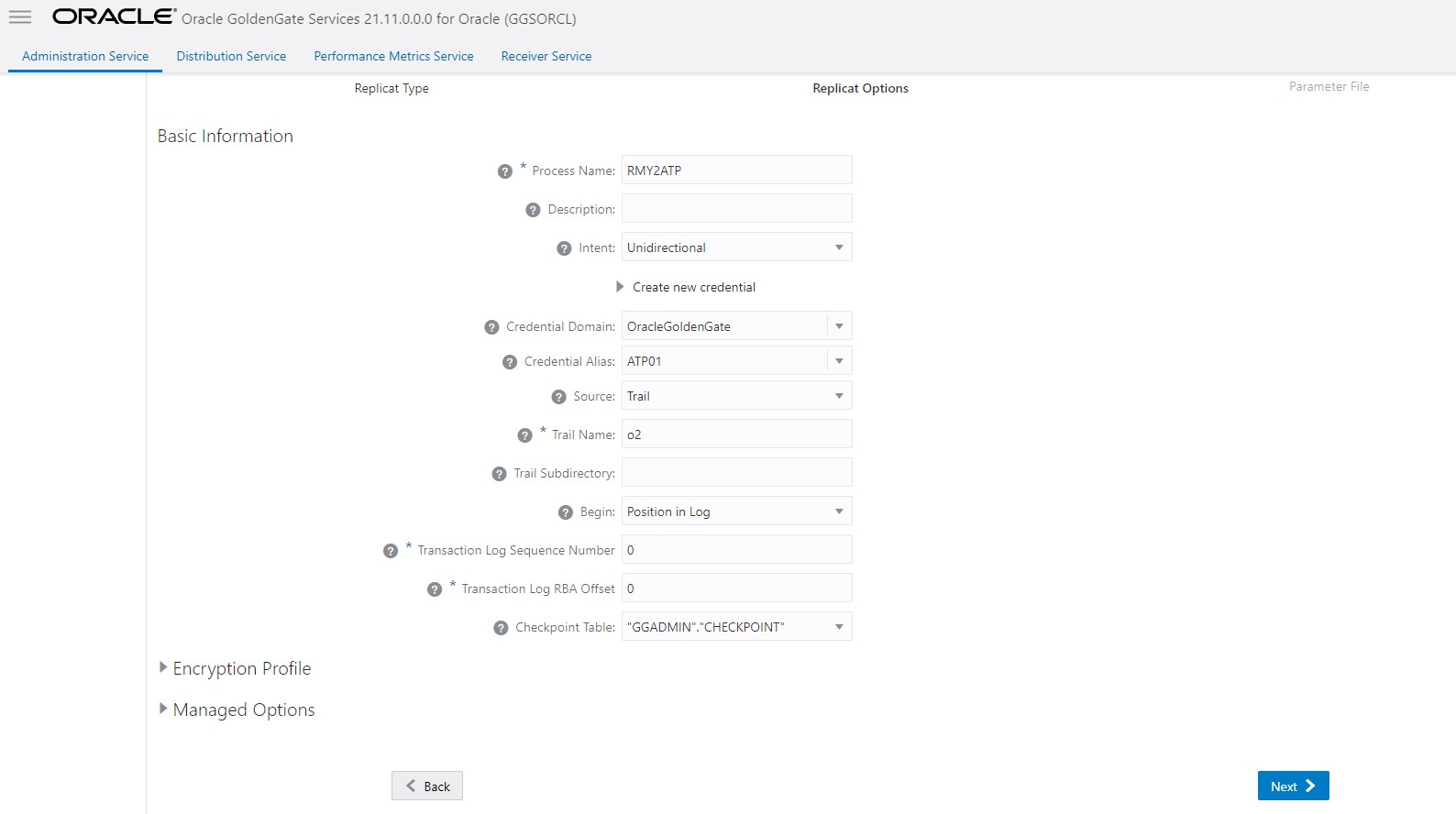
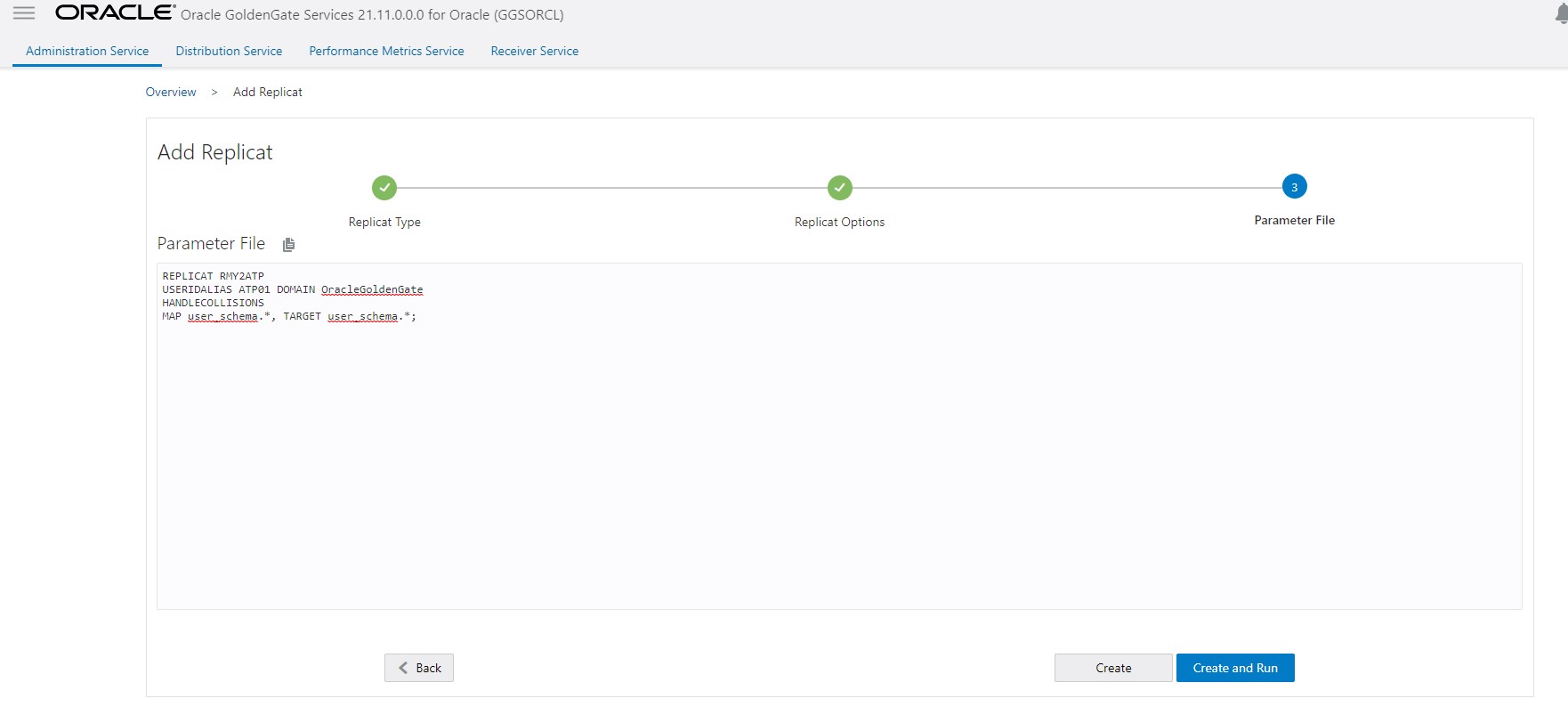
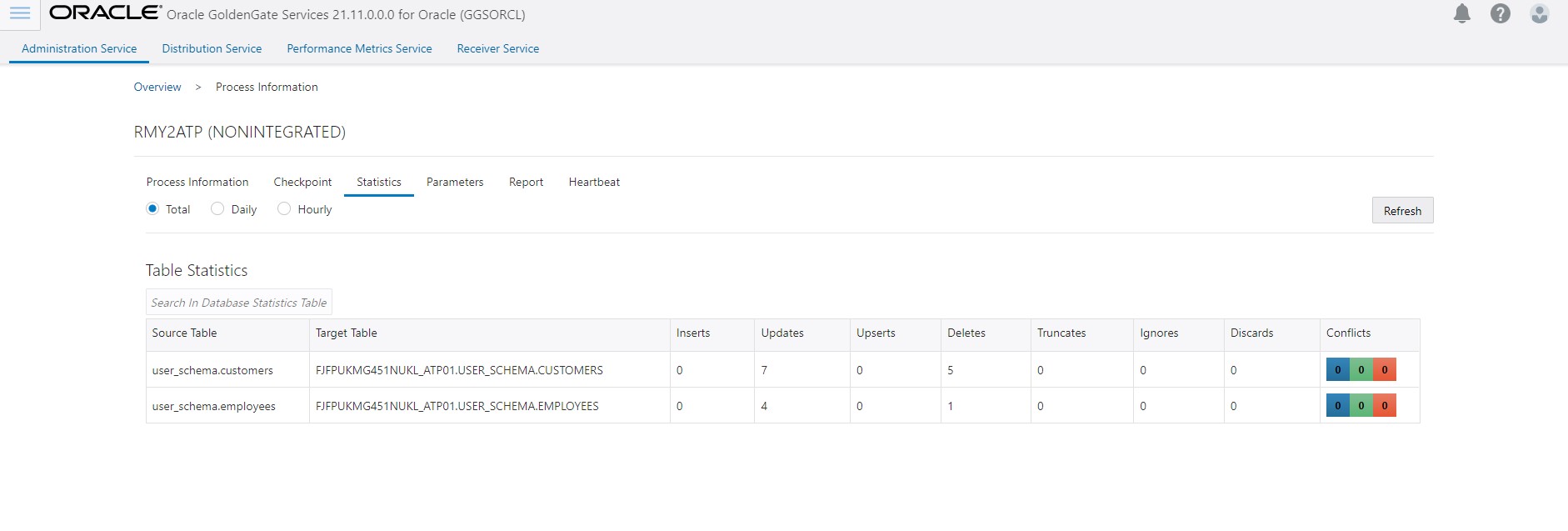
Wait for the CDC replicat (Step 5) to consume all the trails, check replicat lag, and replicat RBA to ensure that the CDC replicat has caught up. At this point, the source and target databases should be in sync.
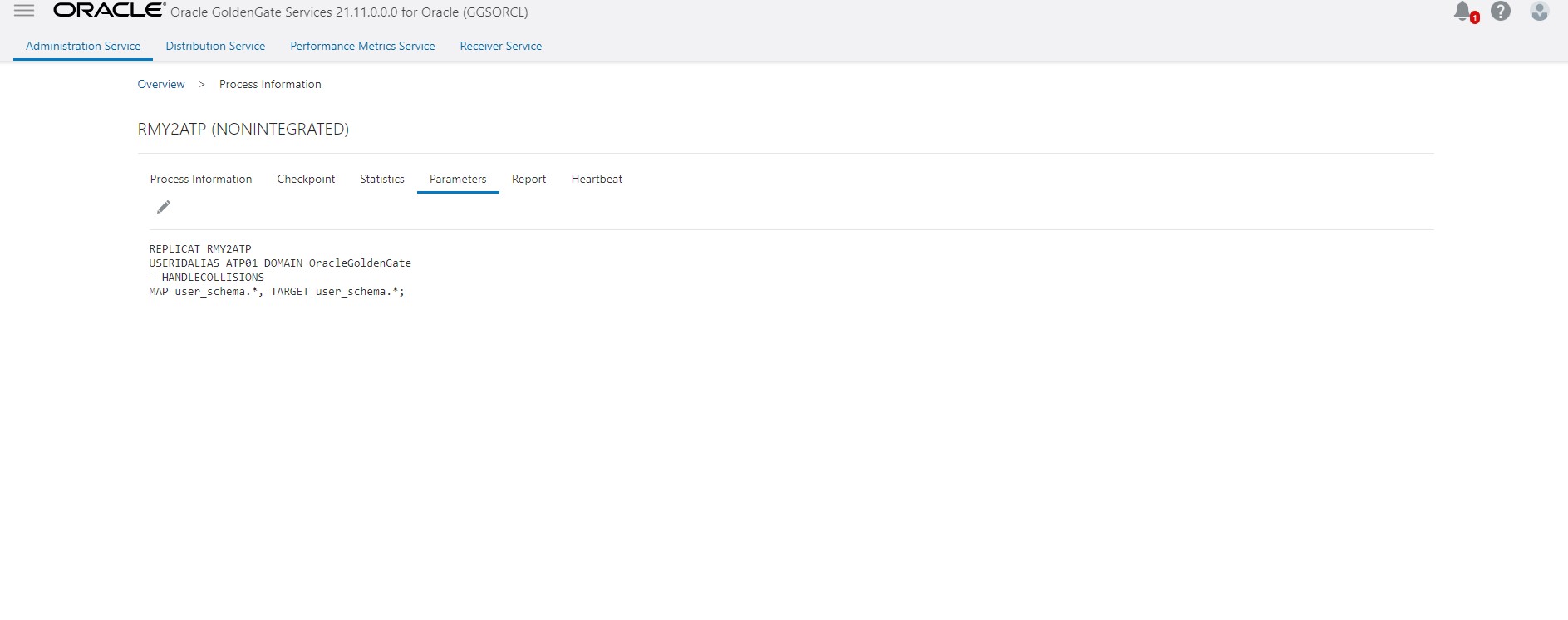
Stop the CDC replicat, remove HANDLECOLLISIONS parameter, and then restart the CDC replicat.
Conclusion
In this blog , we learned end to end OCI Goldengate configuration for migrating AWS MySQL RDS/ Maria DB to Oracle Autonomous Database.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Goldengate provides a very powerful data integration platform which can be used for a variety of use cases with multiple source and target databases.
