Introduction
Oracle Data Transforms offers an intuitive, graphical interface that simplifies data integration for Oracle Autonomous Database users. With this tool, users can visually design and manage data transformations, eliminating the need for complex coding. This functionality accelerates data integration, ensuring a seamless user experience.
You can launch Data Transforms in any of the following ways:
- Oracle Cloud Marketplace: Create a Data Transforms instance from the Oracle Cloud Marketplace under the listing Data Integrator: Web Edition.
- Autonomous Database Data Tools Page: Navigate to the Autonomous Database Data Tools Page, select Data Transforms from the Database Actions page, or access it via the Data Tools menu.
If you have already registered a Data Transforms instance with an Autonomous Database, the Data Transforms card on the Database Actions page will direct you to the Marketplace instance.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to implement incremental data loads using Oracle Data Transforms for efficient and optimized data integration.
Pre-Requisites
Before using Oracle Data Transforms, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- An active Oracle Cloud Account
- Access to an assigned Oracle Cloud Tenant
- Available compute node resources within your Oracle Cloud Tenant
Additional Setup
- Create a Dynamic Group and define the necessary policies for the compartment where the Autonomous Database will be provisioned.
- Assign the DATA_TRANSFORM_USER role to the database user.
- Ensure the database user password complies with the CLOUD_VERIFY_FUNCTION validation rules for Autonomous Database.
- Provision the Autonomous Database by following the guidelines outlined in the Oracle documentation for provisioning Autonomous Data Warehouse Cloud.
Launch Data Transforms
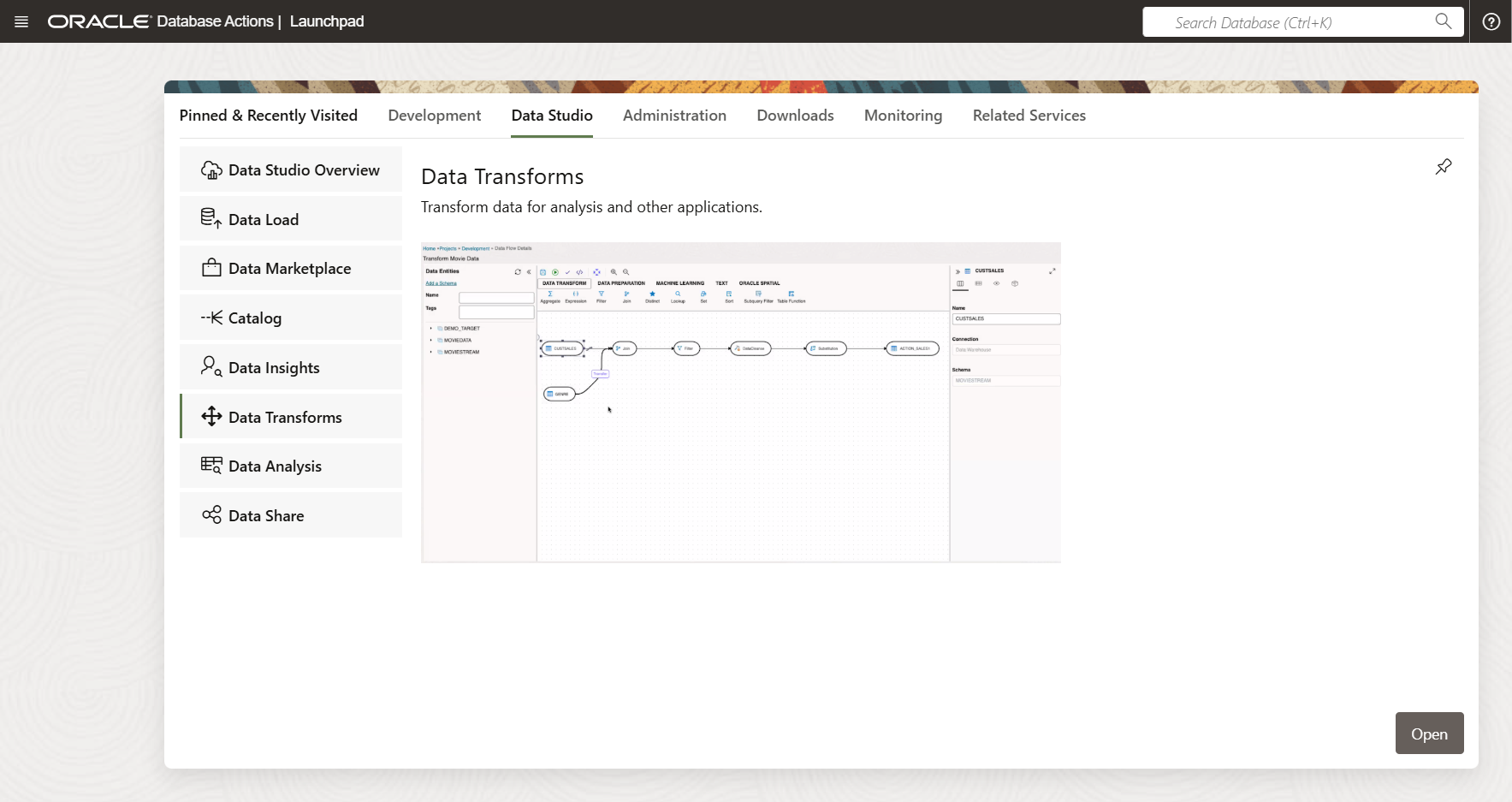
Connect as the database user and navigate to the Database Actions page then select Data Transforms from the Data Studio section.
Enter the credentials for DB_USER and click Connect. The service will take approximately two minutes to start.
Once started, you’ll be taken to the Data Transforms home screen.
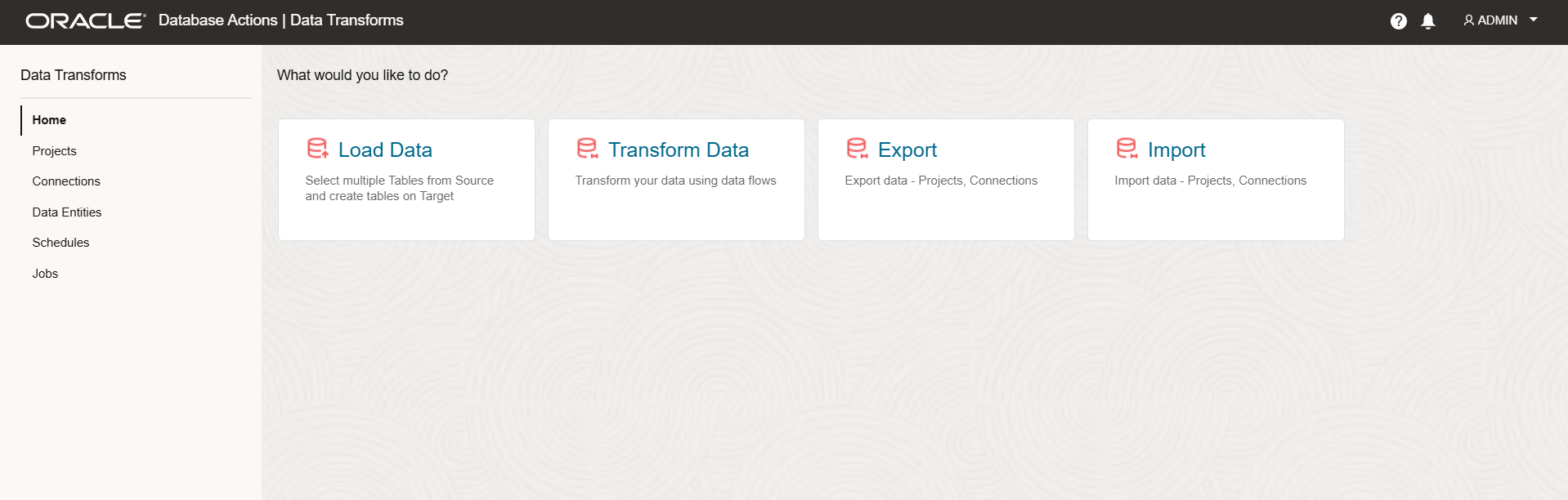
Create Connections
From the home screen, click on Connections in the left-side menu then select the Oracle Database connection type.
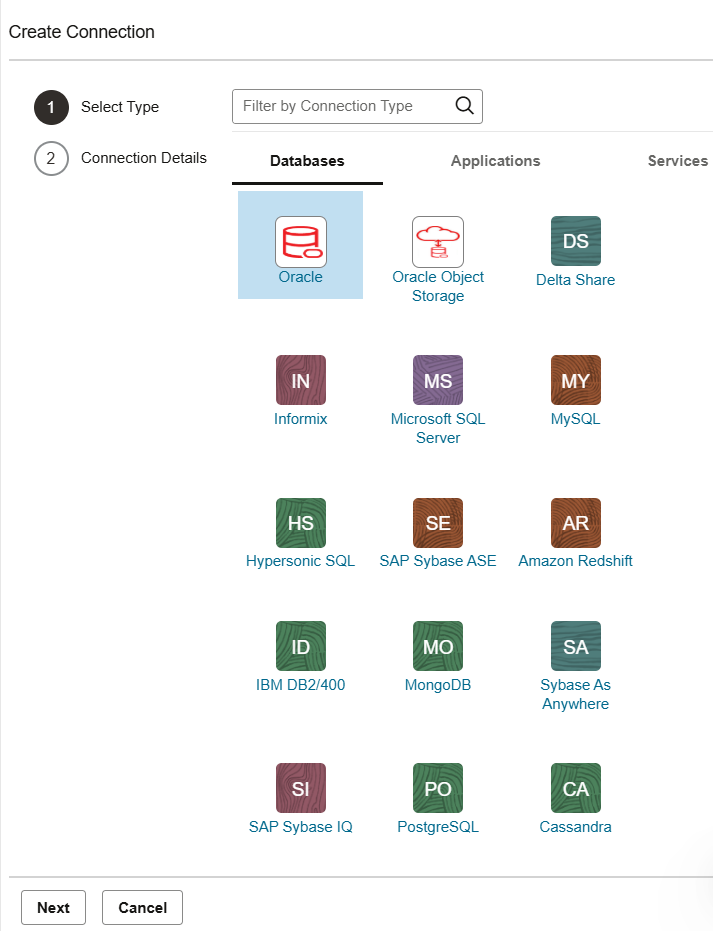
Upload the wallet for your Autonomous Database and provide connection authentication details.
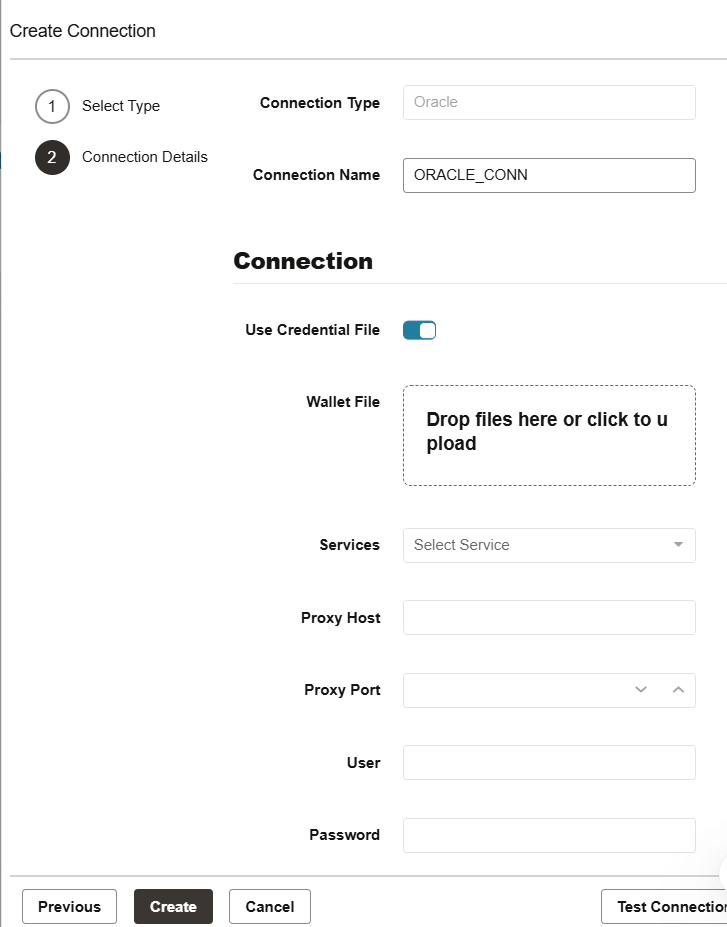
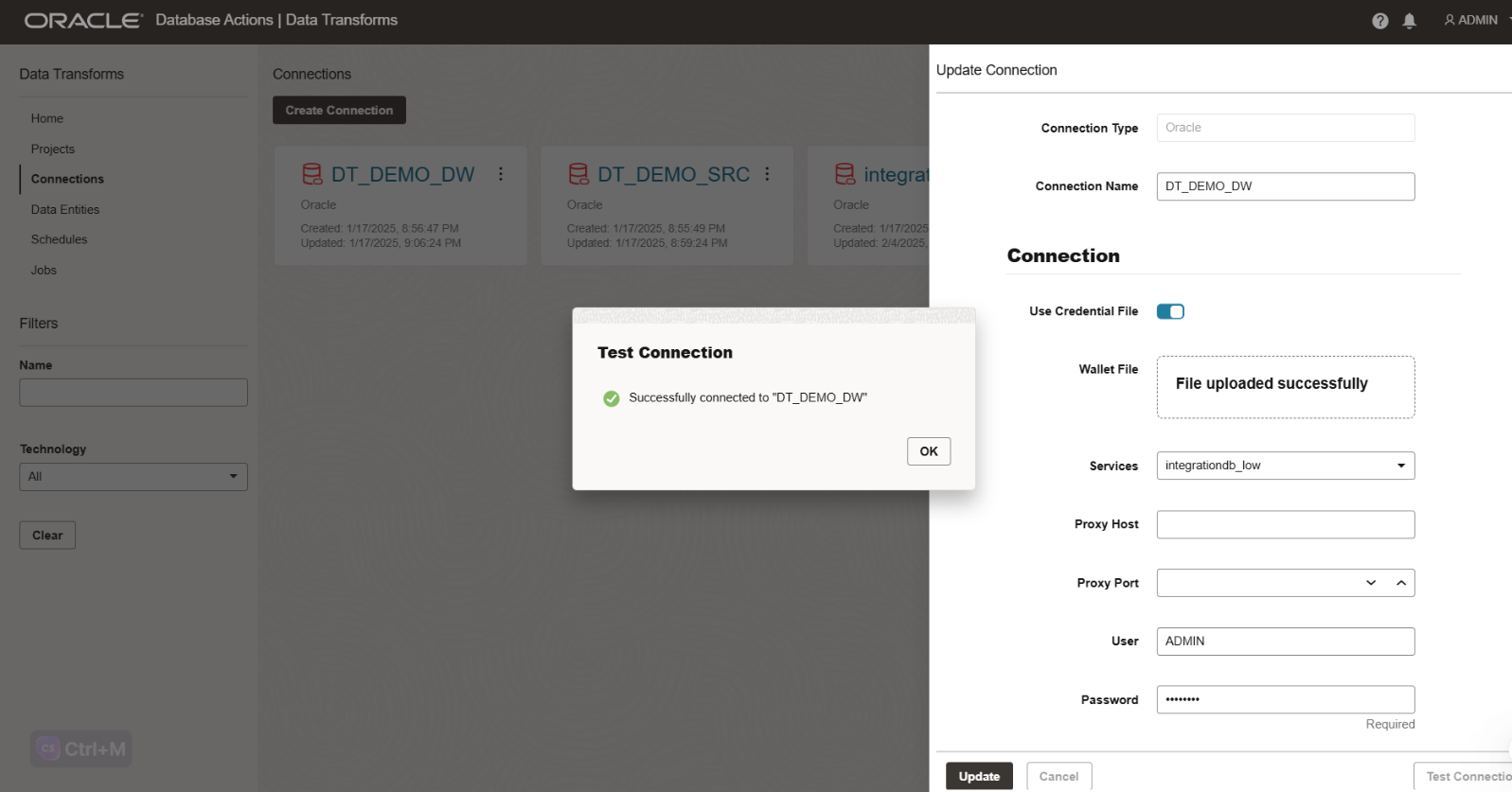
Test the connection and click Create.
Repeat these steps to create a connection to the target database if applicable.
Importing Data Entities
Now we have the connectivity to respective source and target databases, we need to import the data entities. A Data Entity is a tabular representation of a data structure.
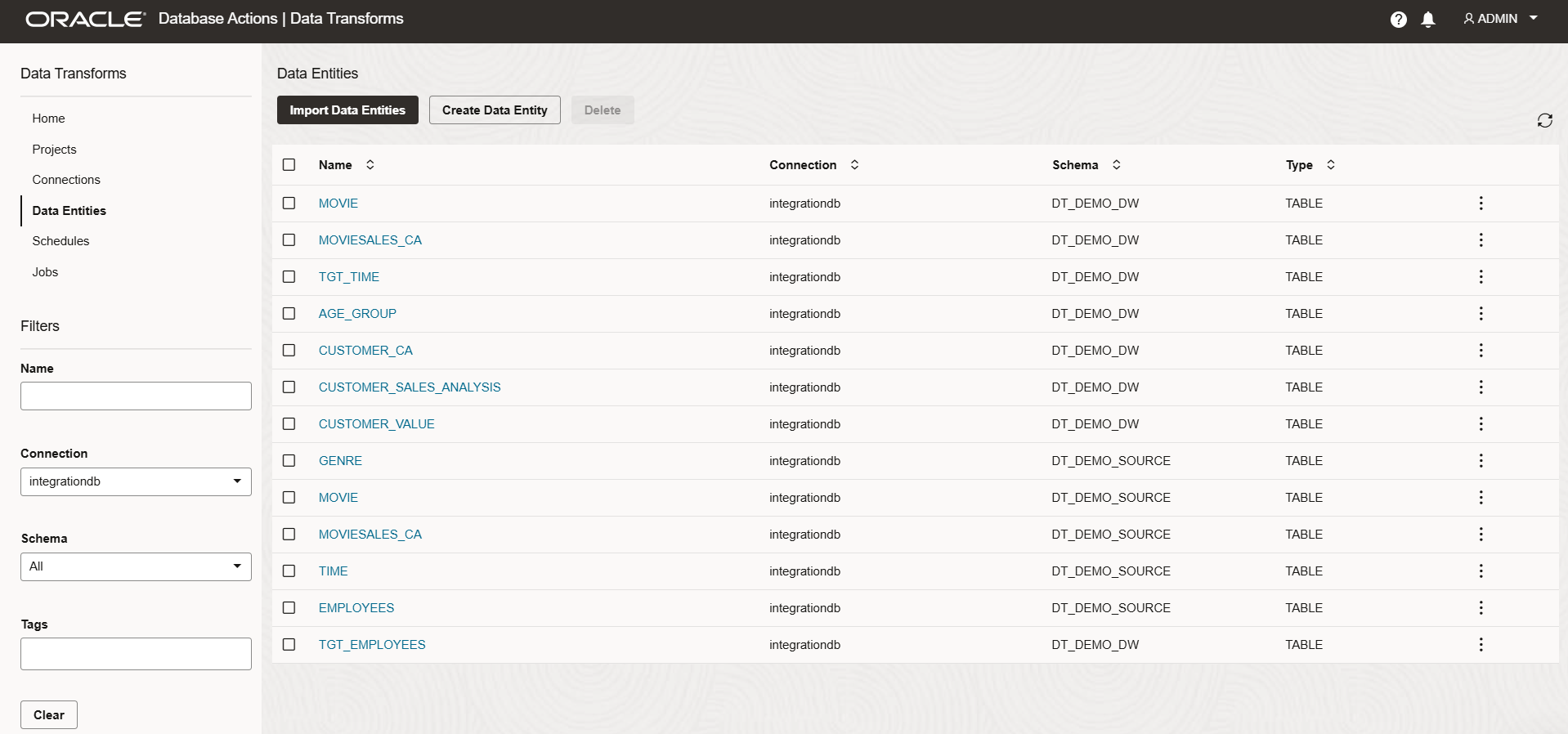
- Navigate to the Data Entities menu.
- Click Import Data Entities and provide connection and schema details.
- Click Start. After the job completes, the tables from the specified schema will be available in the Data Entities menu.
- Follow the same steps to import data entities from the target database, if required.
Creating a Project
Click Create Project, type DEMO, and click Create.
Incremental load using DATA LOADS
Navigate to your project and click Create Data Load then enter the data load name.
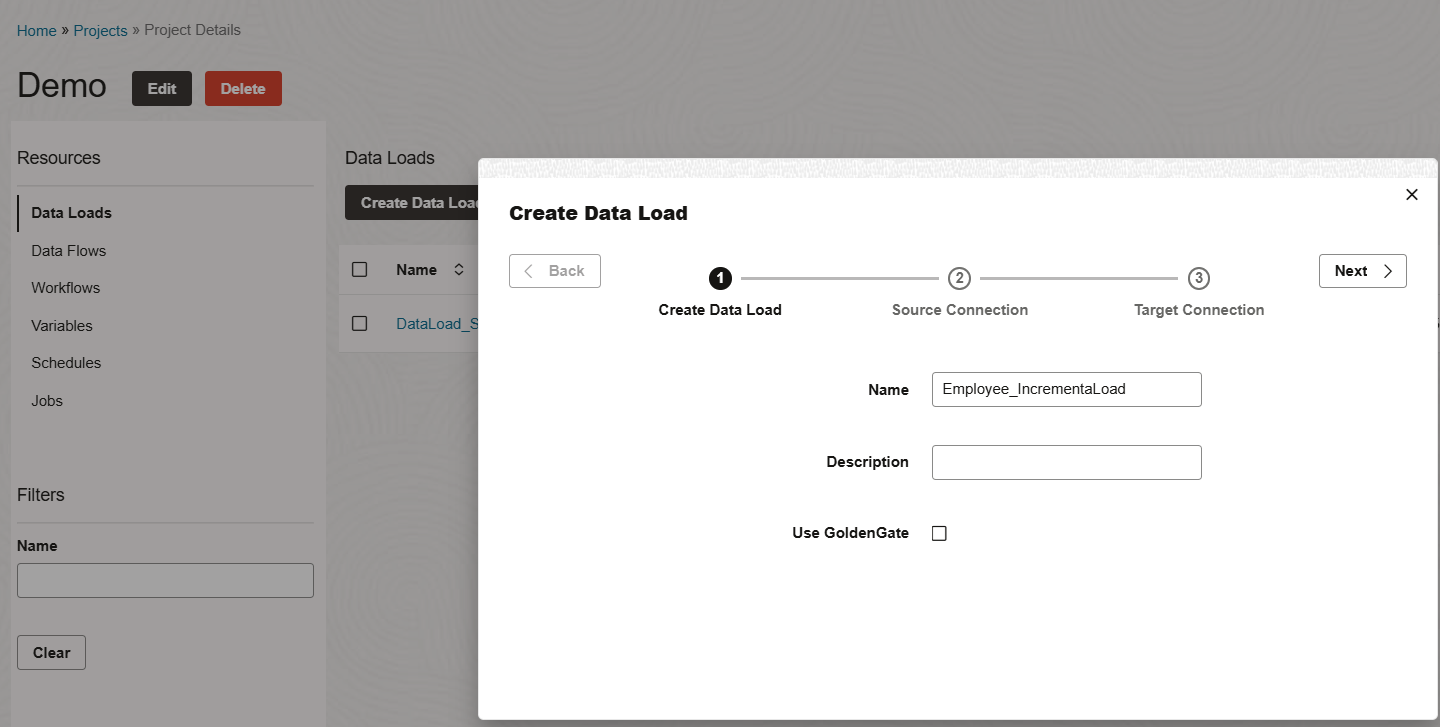
For the time being, Leave the Golden Gate option unchecked and click Next.
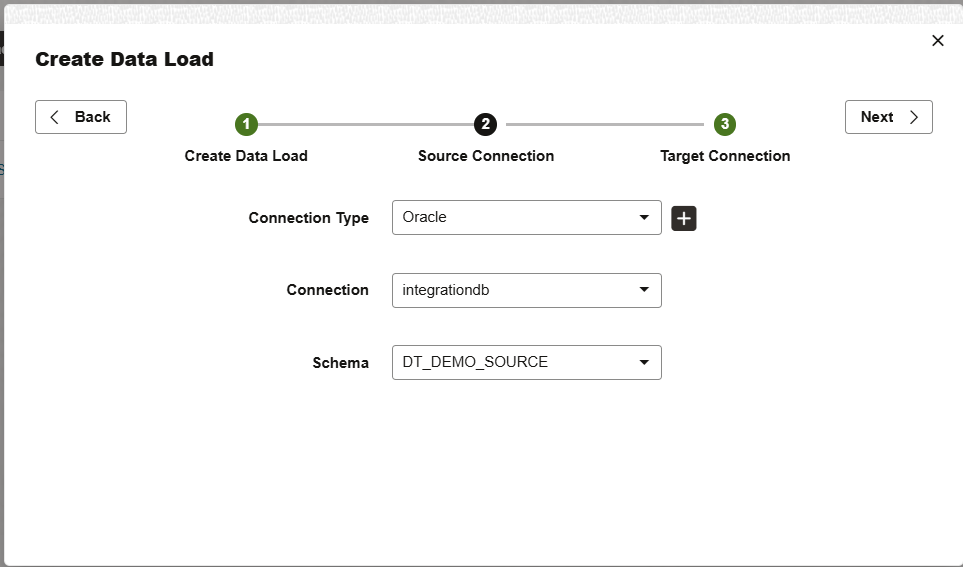
Provide the source connection and schema information and click Next.
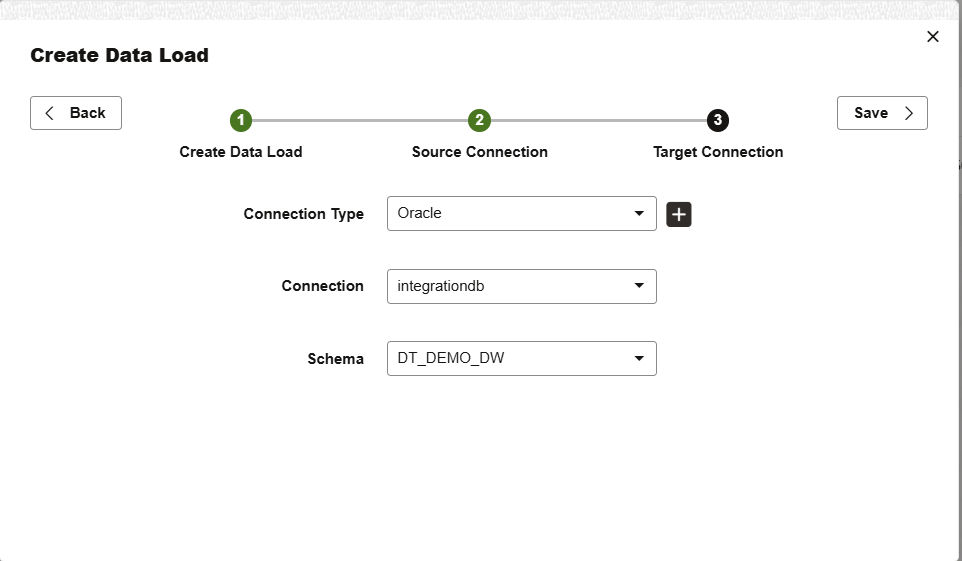
Enter the target connection and schema details and click Save.
Select the EMPLOYEES table and configure the incremental merge options:
- Target Action: Incremental Merge
- Incremental Column: EMPLOYEE_ID
- Merge Key: EMPLOYEE_ID, DEPARTMENT_ID, JOB_ID, MANAGER_ID
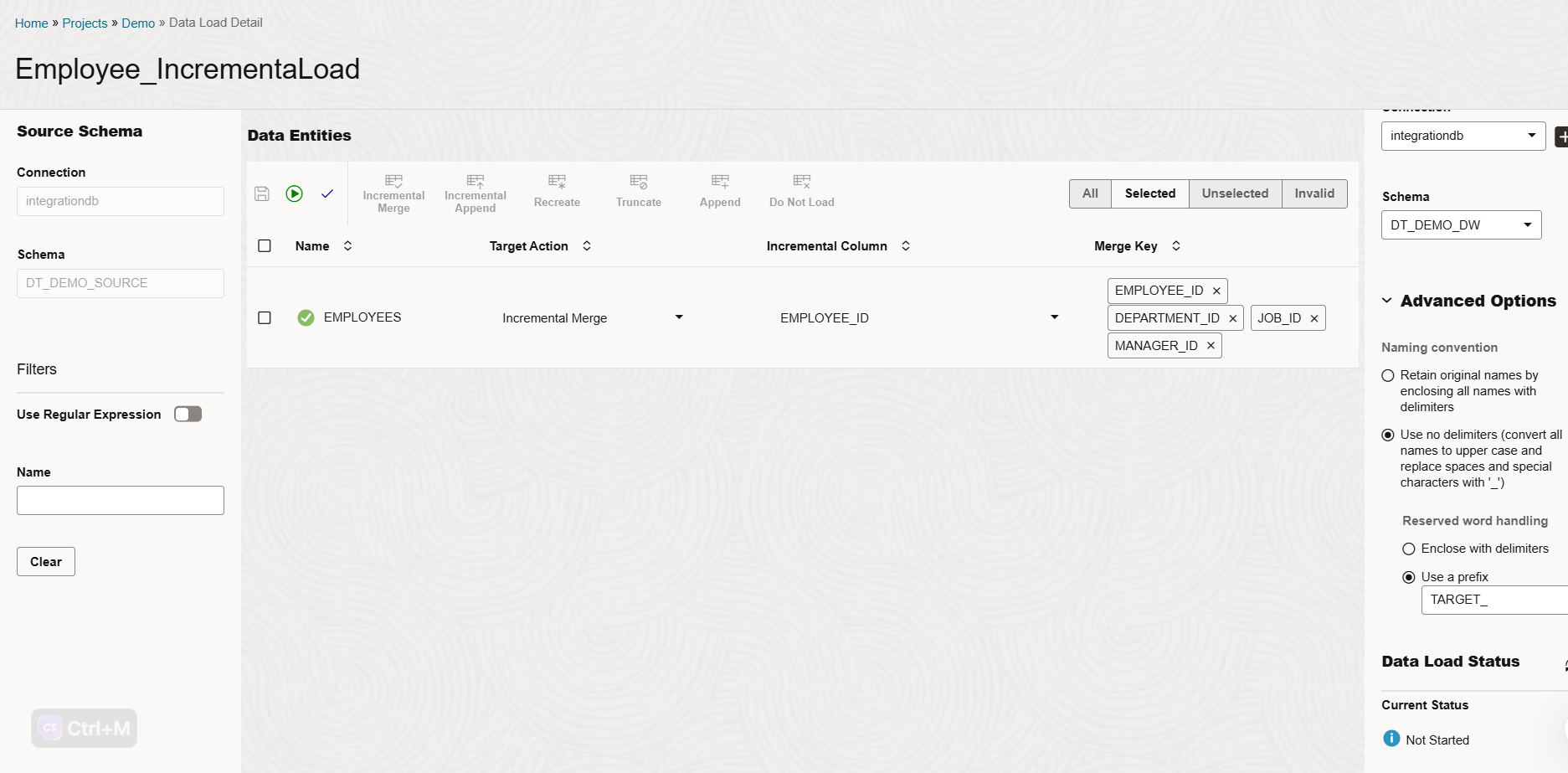
Click Save to store the data load job definition.
Click Execute to start the data load process.
The process creates target tables, performs a full load on the first run, and tracks extracted rows for future incremental loads, ensuring only new or modified rows are loaded in subsequent runs.
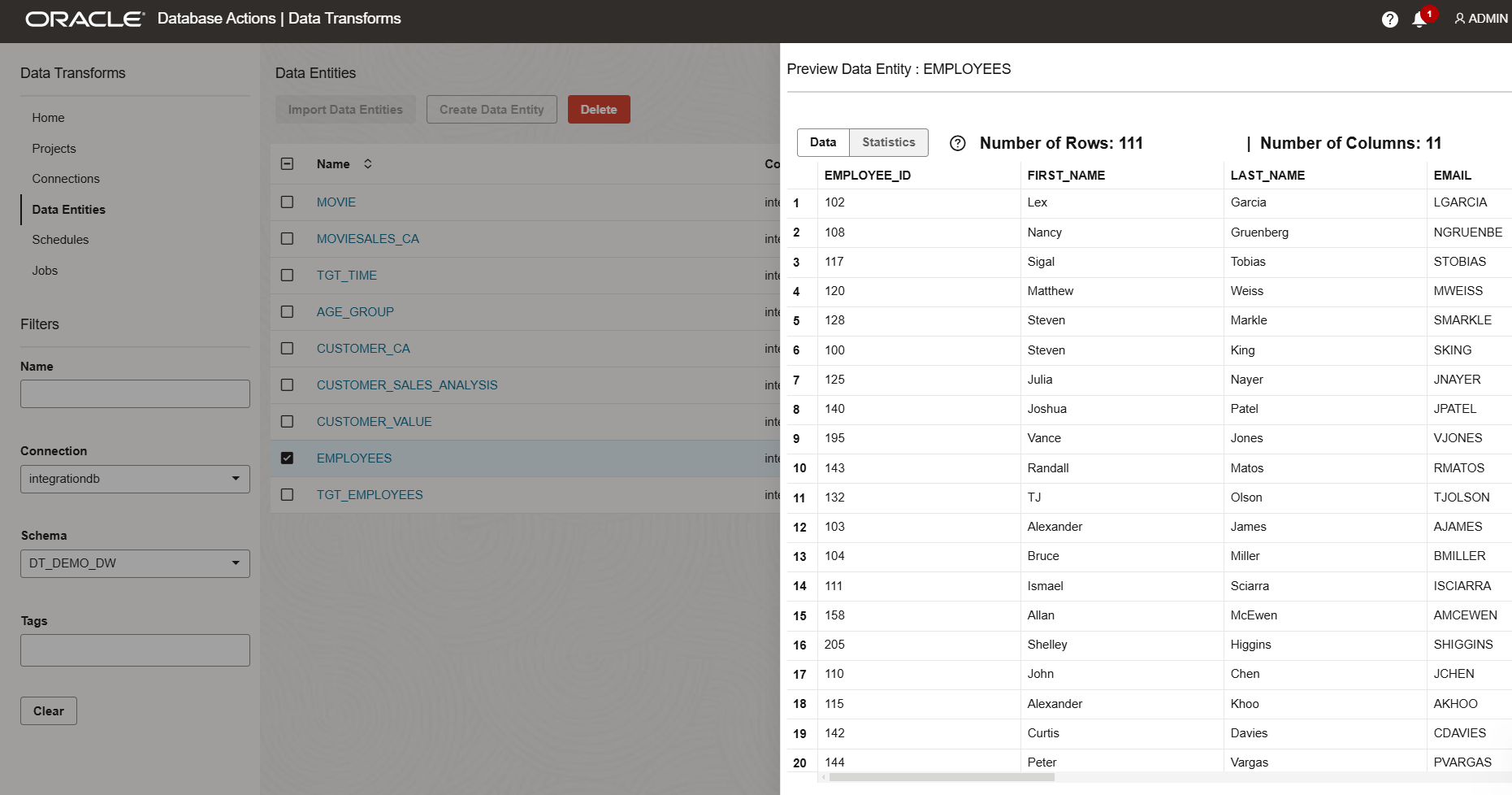
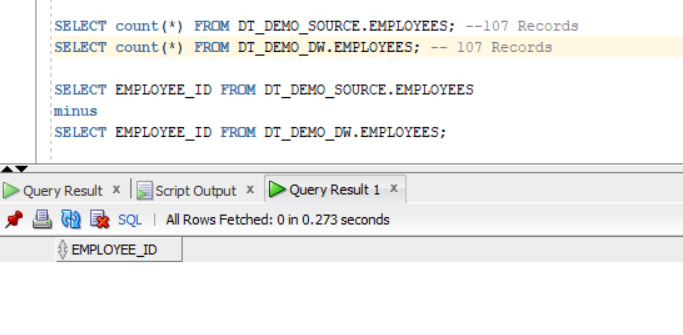
After Data load, note that the number of rows in the target table is the same as the number of rows observed in the source table.
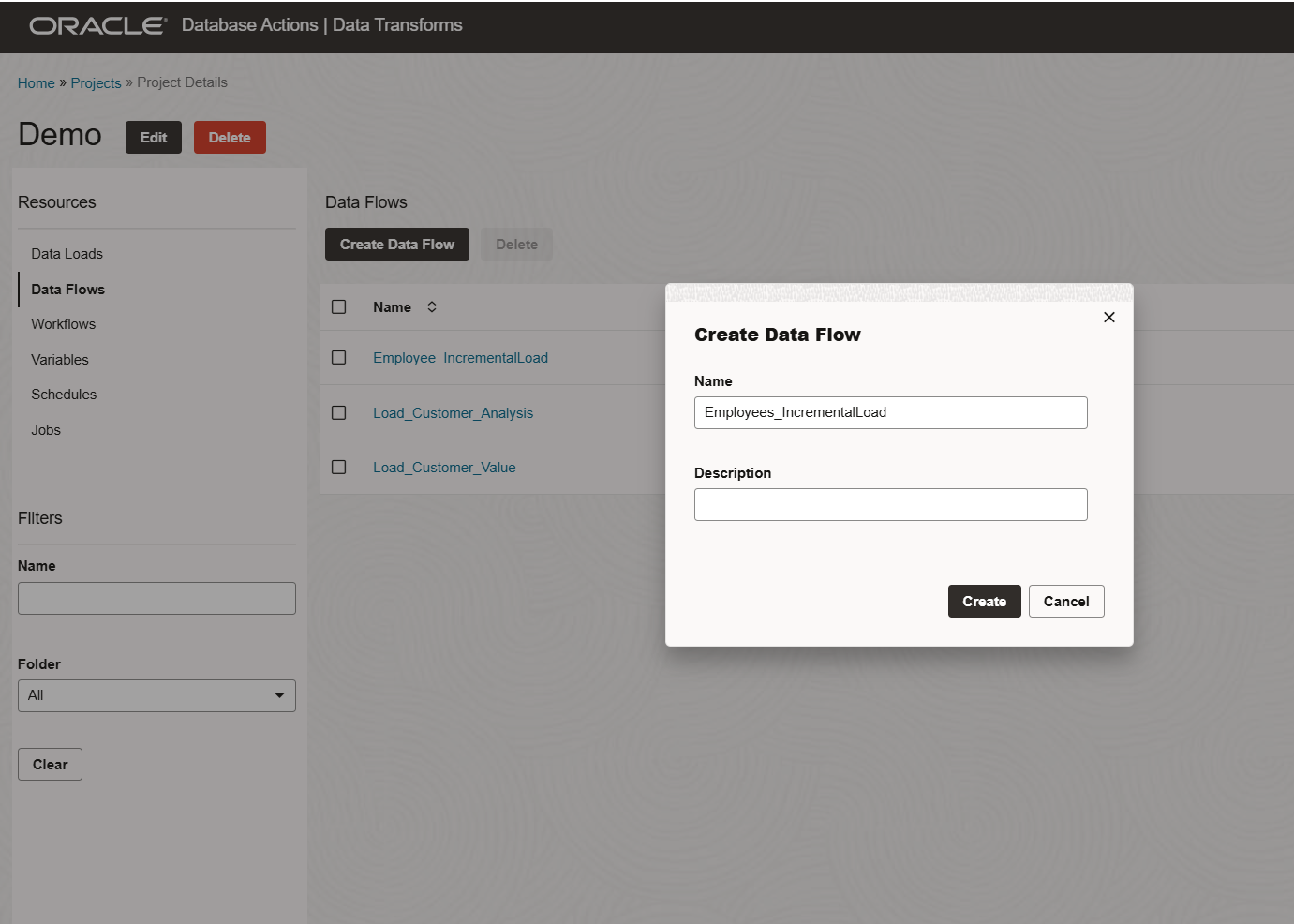
Incremental load using DATA FLOW
Navigate to your project DEMO and select Data Flow from the left-side menu then Click Create Data Flow.
For the first time, it will ask you to add a schema from your connections that will be used to get source or target tables. At any time more schemas can be added to the data flow as needed.
In our use case, this is our first data flow, and we will add the source schema from our SOURCE connection. Click OK.
We will be implementing a similar flow as below based on our use case.
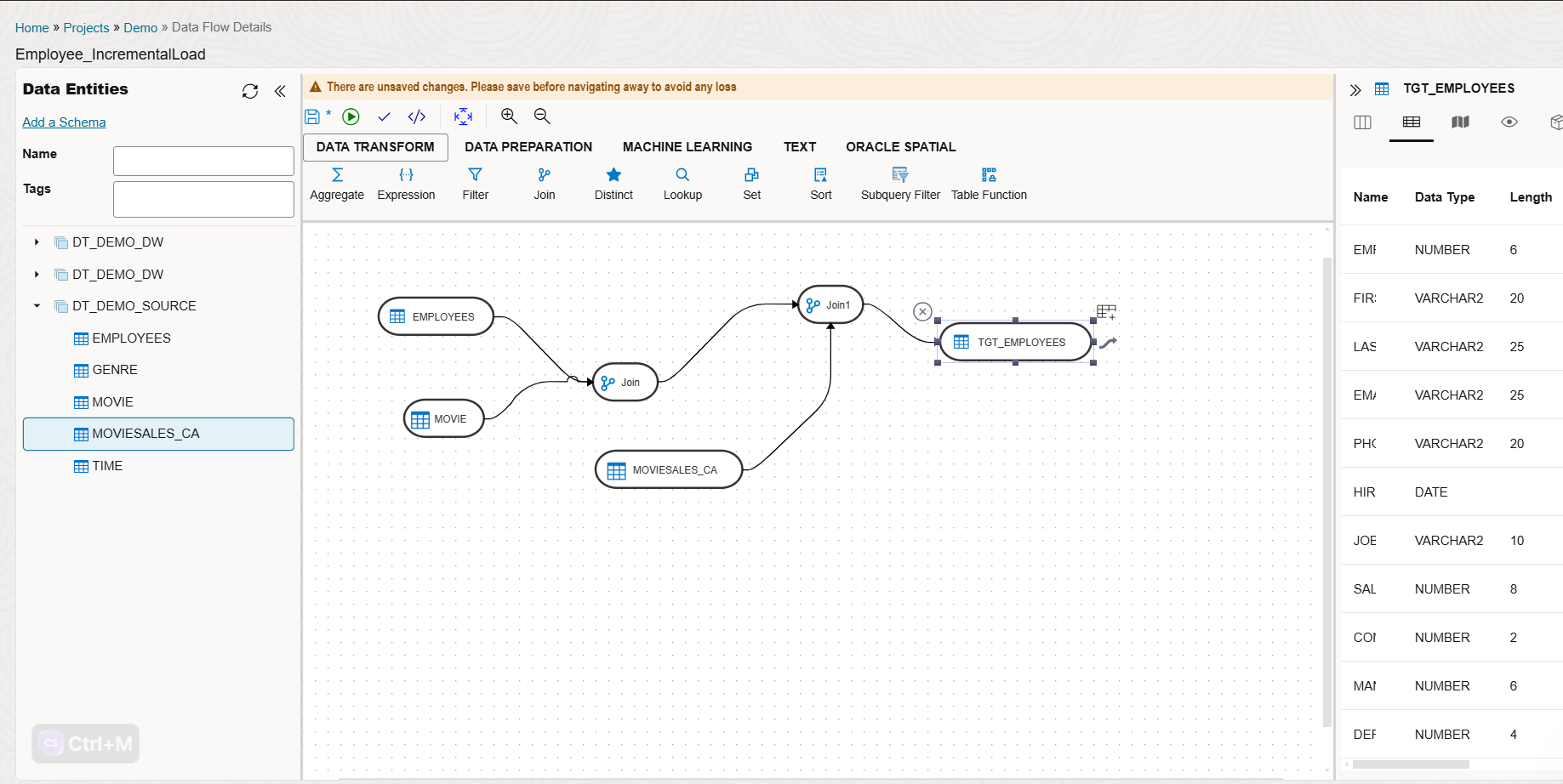
We need to specify how we are going to populate the target:
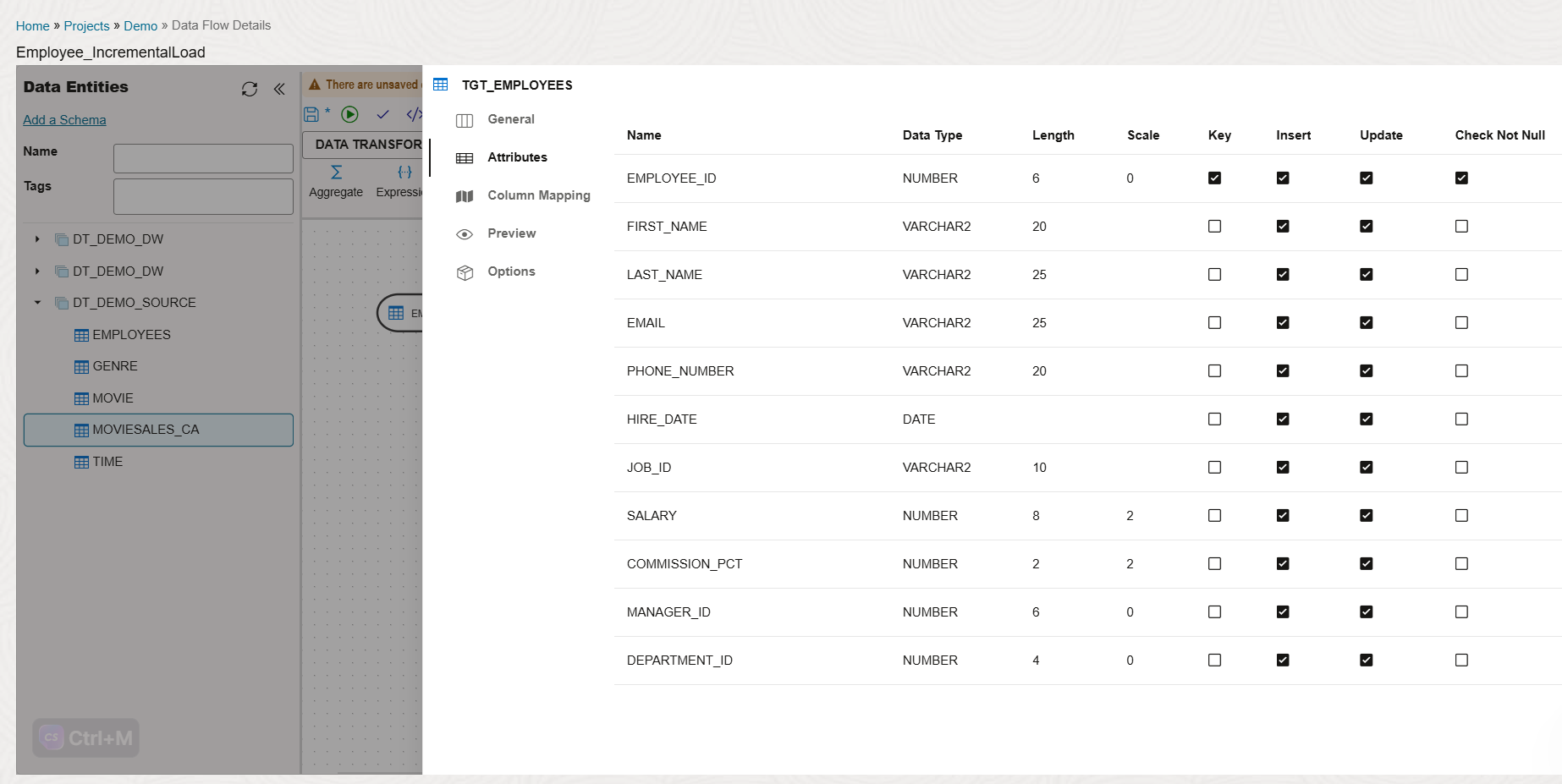
In the Attributes section, identify the key column and enable the Key and Check Not Null options.
Disable the Update option.
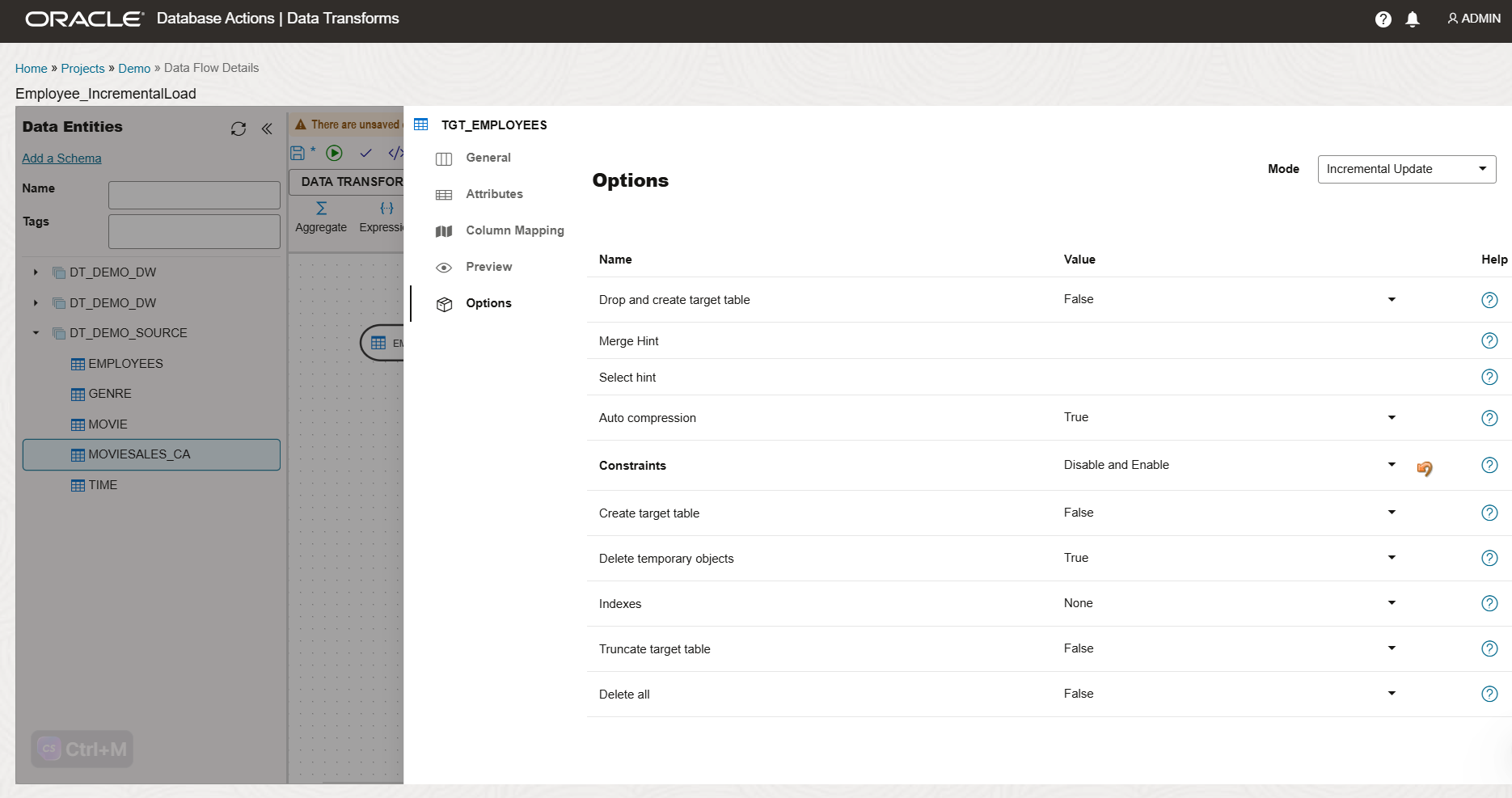
In the Options section, set the mode to Incremental Update and adjust values as required.
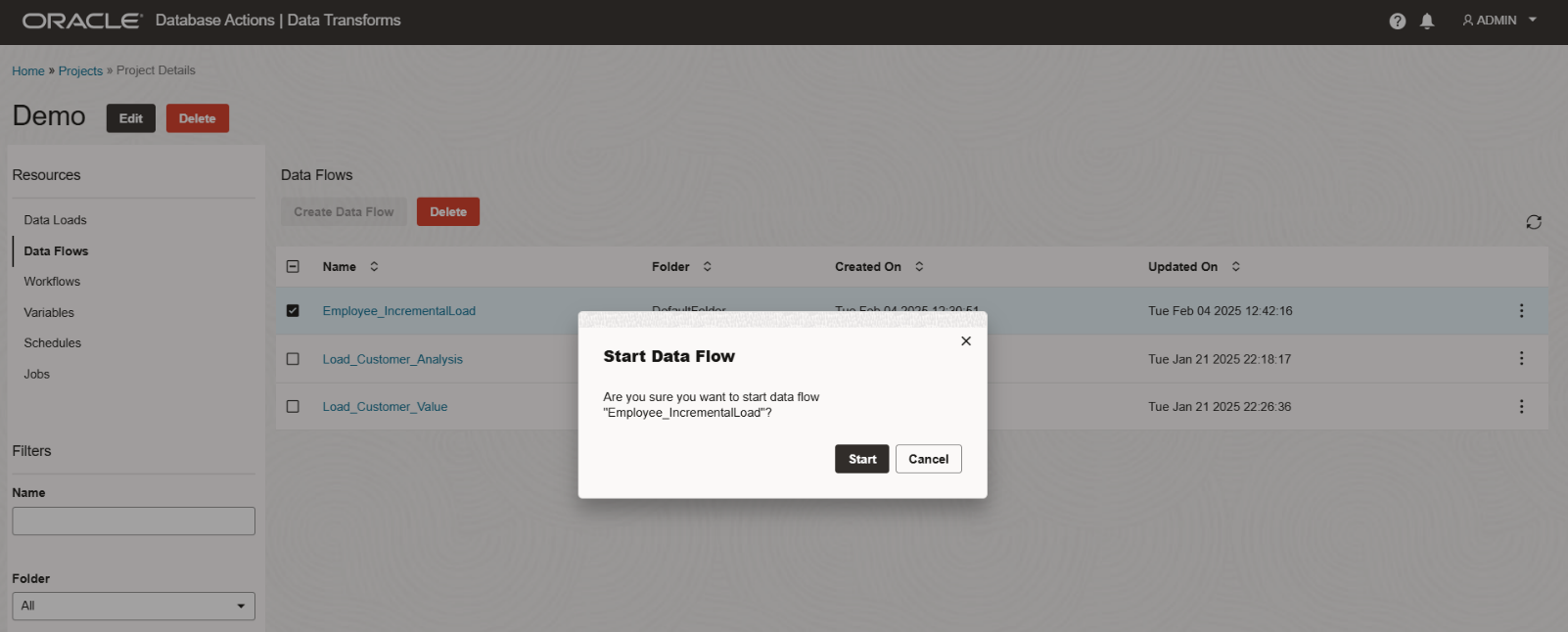
Save the data flow and execute it by clicking the green arrow.
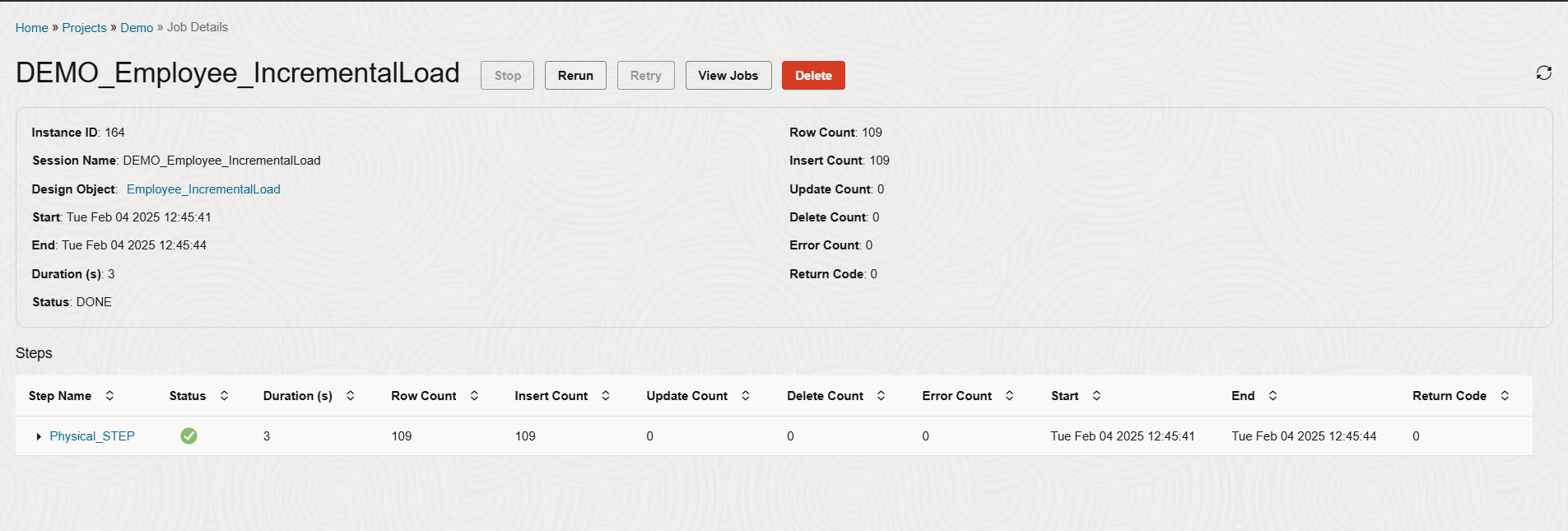
Monitor the job’s progress and metrics.
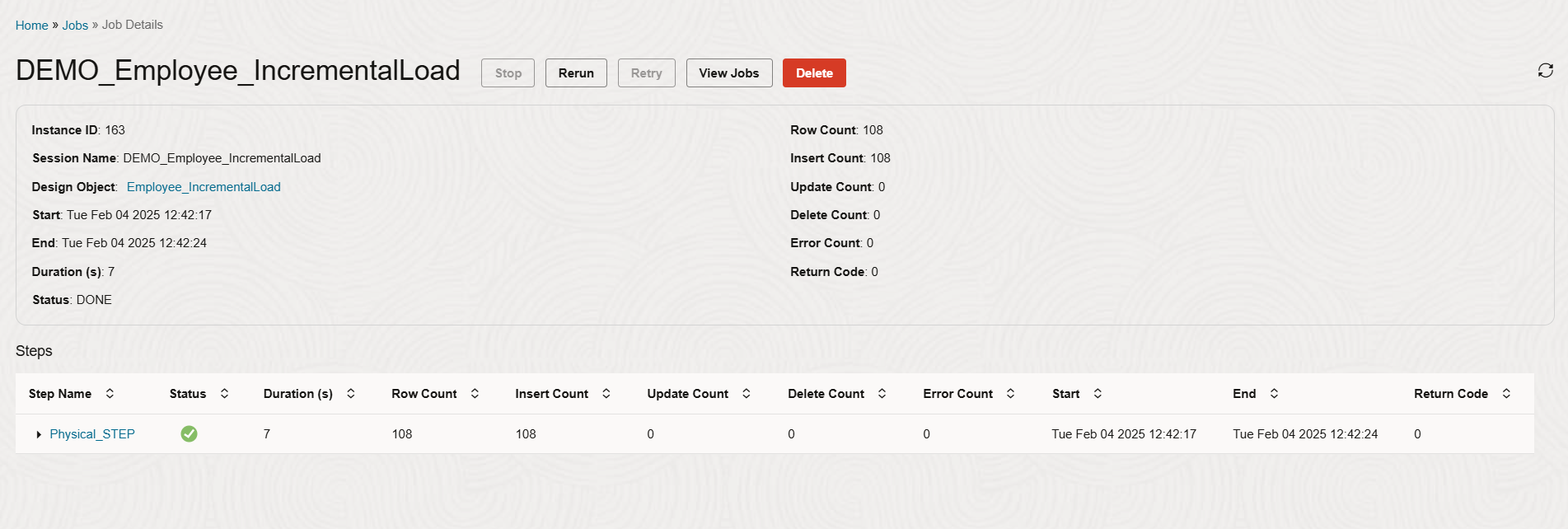
Insert a new record into the source table and re-trigger the job to validate the incremental logic.
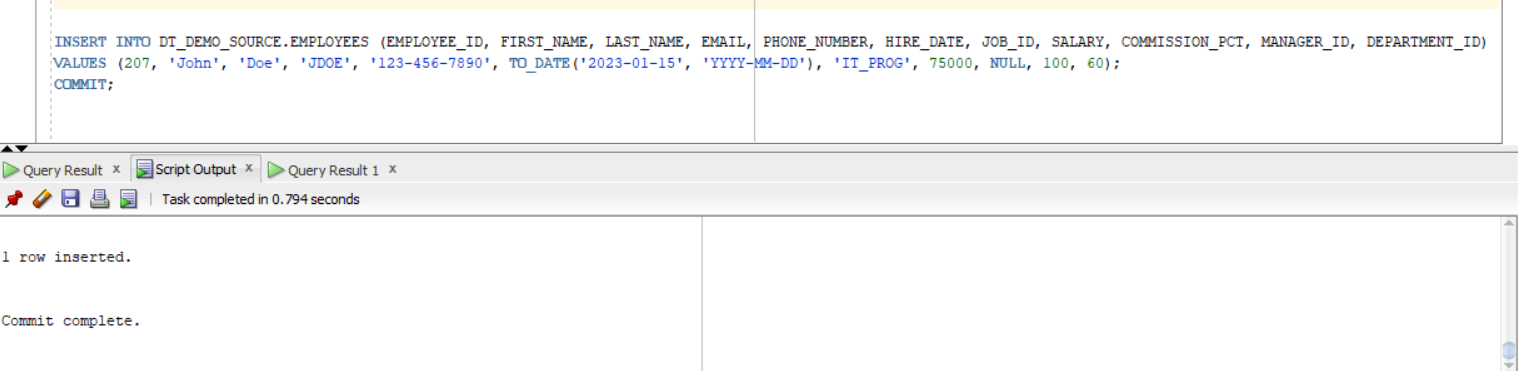
The job should be completed successfully, inserting the new record into the target.
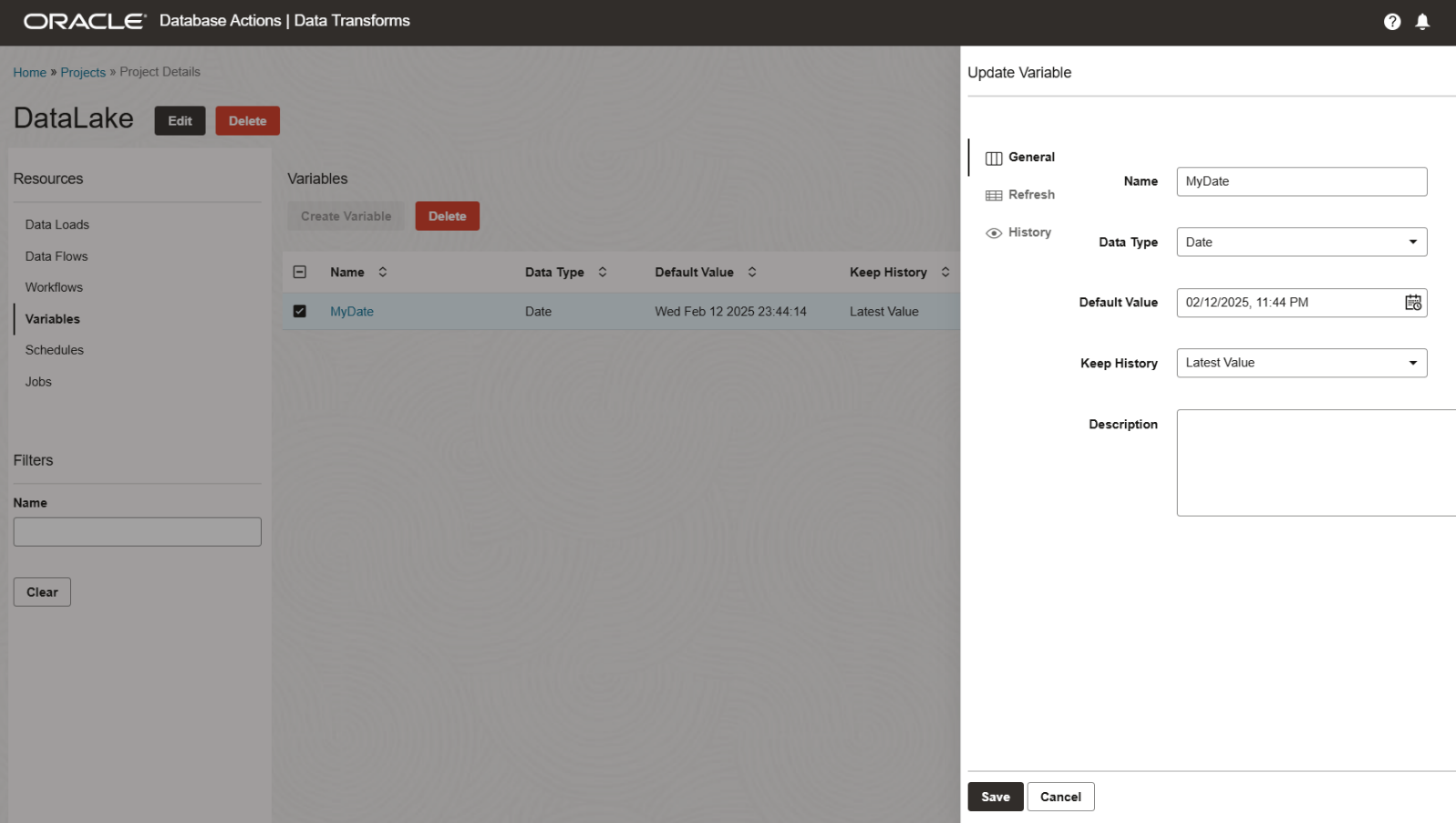
Variables
Variables can be used to implement incremental logic, but only if the source table contains a data column.
Create a variable with a refresh query to retrieve today’s date, e.g., SELECT SYSDATE FROM DUAL.
This variable can be used in a Data Flow as a filter condition.
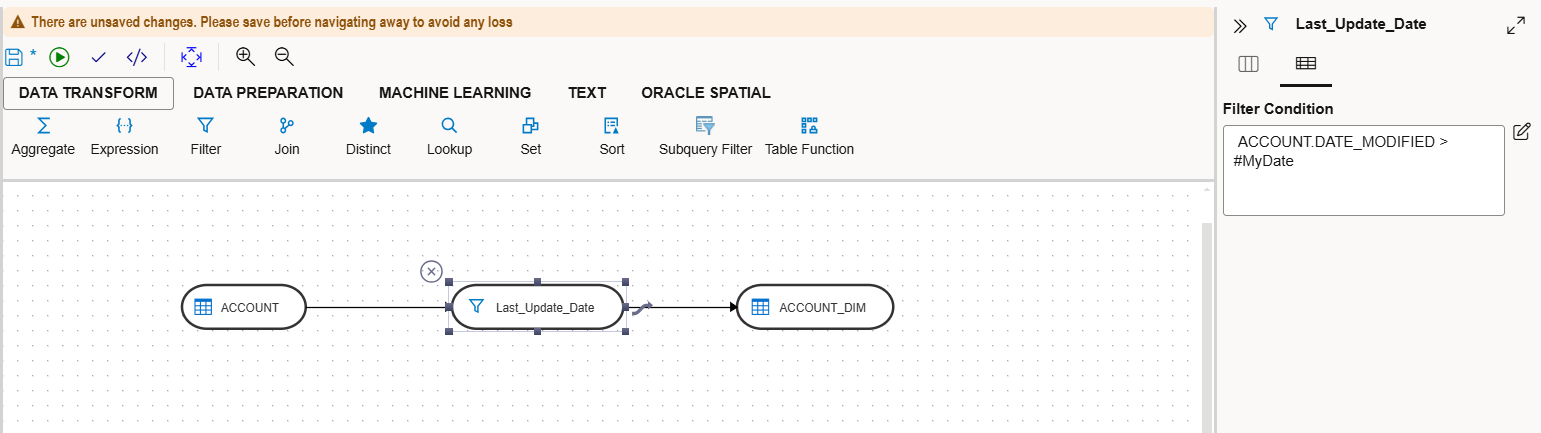
Each time the job runs, it checks the date column in the source, validates the filter condition, and loads only the data that meets the condition into the target table.
This wraps up our overview of implementing incremental loads using Oracle Data Transforms.
Conclusion
Oracle Data Transforms is a powerful built-in tool for Oracle Autonomous Database that simplifies data integration and transformation. It allows users to create data pipelines for analytics, data science, and AI without writing SQL or using external tools. By implementing incremental logic using Data Loads and Data Flows, organizations can streamline their data integration processes, reduce manual effort, and improve data accuracy.
For further details, check out the following resources.
Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless
Introducing Data Transforms: Built in Data Integration for Autonomous Database

