Online Migration: Leveraging Oracle GoldenGate
In today’s fast-paced, always-on business landscape, reducing downtime during database migrations is crucial. Whether you’re migrating to a new platform, upgrading to Oracle Exadata, or performing cross-platform migrations, Oracle GoldenGate for Oracle Databases offers a robust solution for online migrations. With real-time data replication, GoldenGate ensures minimal disruption to business operations while maintaining data integrity across the source and target systems.
To further ensure data consistency throughout the migration process, Oracle Veridata plays a key role in data verification and validation. Veridata continuously compares data between the source and target databases, enabling the detection and resolution of discrepancies. This ensures that the migration process maintains data accuracy, contributing to a seamless and reliable cutover.
This post will explore the high-level phases of an online migration using Oracle GoldenGate, outline best practices for ensuring data integrity, and introduce key Oracle GoldenGate features that enhance the migration process: Microservices Architecture and Oracle Veridata.
Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Architecture
Oracle GoldenGate’s modern microservices architecture is key to its flexibility and scalability, making it ideal for large-scale and complex migration scenarios. This architecture modularizes key processes, with Extract capturing data from the source database, Distribution Path routing the data, and Replicat applying it to the target database. Together, these components enable GoldenGate to handle distributed environments more efficiently, with streamlined management and improved load balancing.
Additionally, GoldenGate’s automatic heartbeat functionality, managed via a heartbeat table, offers real-time monitoring of replication lag, helping ensure timely data replication across distributed systems. This functionality is especially beneficial for tracking and diagnosing any delays during migrations.
When the source and target databases are located close to each other, a single GoldenGate deployment can suffice, reducing setup complexity and optimizing performance for migrations within proximate environments.
Why Choose Online Migration with Oracle GoldenGate?
Key Benefits
- Minimal Downtime: With GoldenGate’s real-time replication, downtime is reduced to the brief period needed to switch applications to the new environment.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Oracle GoldenGate supports complex cross-platform migrations, ensuring data consistency even when migrating between systems with different architectures and endian formats.
- Real-Time Data Validation: Oracle Veridata is used to provide continuous validation of data between the source and target systems during the migration, ensuring data integrity throughout the process.
- Flexible Recovery Options: GoldenGate’s decoupled architecture and asynchronous replication design offer a seamless recovery option if needed during migration. With minimal downtime or interruption, businesses can easily switch back to the original environment, ensuring continuity and safeguarding data integrity. This flexibility provides peace of mind during critical migration processes.
High-Level Phases of Online Migration Using Oracle GoldenGate
To better understand the high-level phases of online migration, refer to the diagram below, which illustrates the major key phases of the migration workflow, including identification, backup, data capture, validation and switchover:
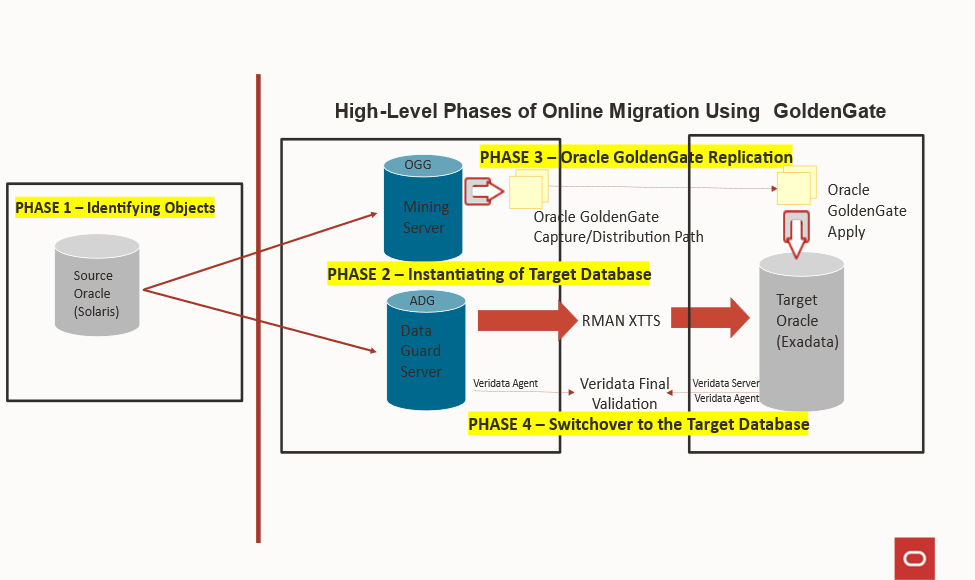
The diagram outlines the following major phases:
Phase 1: Identifying Objects for Reload (Source Application Online)
At the beginning of the migration, certain database objects might not be suitable for replication due to unsupported data types or lack of indexes. These objects should be identified in advance to prepare for their manual reloading on the target system. By limiting or avoiding major schema changes and application patching during the migration window, you can further streamline the process and reduce potential disruptions.
Phase 2: Instantiating the Target Database (Source Application Online)
This phase involves preparing the target database environment. The methods for instantiating the target database can be broadly categorized into Physical Methods, which involve transferring the datafiles or storage directly, and Logical Methods, which focus on exporting and importing database objects and metadata.
Physical Methods
Physical methods are well-suited for large databases or scenarios where the source and target share compatible storage technologies. These methods typically offer faster data transfer by working at the storage or file system level.
- Oracle RMAN Cross Platform Transportable Tablespaces (XTTS) enables the bulk transfer of large datasets from one platform to another, making it ideal for cross-platform migrations where physical data movement is required.
- Storage-Level Replication can instantiate the target database by replicating storage at the hardware level. Solutions such as Oracle ZFS and other enterprise storage replication technologies efficiently create a copy of very large databases on the target.
- Oracle Data Guard can be used for migrations within the same platform and architecture. By creating a standby database on the target, Data Guard allows quick synchronization that can be converted to the primary database as needed.
Logical Methods
Logical methods are more flexible and allow for migrations where the source and target systems differ in structure or architecture. These methods focus on exporting and importing database schemas, objects, and metadata.
- Oracle GoldenGate Initial Load leverages GoldenGate’s replication capabilities to perform a direct initial load from the source to the target. However, because GoldenGate Initial Load operates on a transactional level, it may be slower than bulk physical methods.
- Oracle Data Pump (expdp/impdp) is another option for moving metadata and data, especially when a logical copy of specific database objects or schemas is required.
This phase is also an opportunity to make necessary improvements in the target system, such as:
- Upgrading the Database Version to align with the latest performance and security standards.
- Converting to Bigfile Tablespaces to improve manageability.
- Converting Basic LOBs to Secure LOBs for enhanced data security and space management.
Phase 3: Online Migration Window Using Oracle GoldenGate (Source Application Online)
During this phase, Oracle GoldenGate starts replicating live data changes from the source database to the target system. The application remains operational on the source while changes are continuously synchronized with the target. Initially, replication lag may be high due to the volume of data changes, but it should gradually decrease as the systems reach a steady state. This can be monitored using the heartbeat table, providing a reliable indication of lag reduction.
Monitoring Replication Lag with a Heartbeat Table
A critical part of this phase is monitoring replication lag to ensure that data is being applied promptly on the target. Oracle GoldenGate’s automatic heartbeat functionality uses a heartbeat table that tracks replication lag in real-time by writing heartbeat data on both the source and target databases.
To further enhance migration stability, administrators can configure proactive alert thresholds within the GoldenGate environment or through Oracle Enterprise Manager. These alerts provide early warnings when replication lag approaches the predefined limits, helping to prevent performance issues before they impact the migration process.
Why the Automatic Heartbeat is Important
- Real-Time Monitoring: With its automatic updates, it provides immediate insights into the status of data replication, highlighting any delays.
- Proactive Alerts: Administrators can set thresholds based on acceptable lag limits, helping them to identify and resolve potential delays before they impact the migration.
- Troubleshooting: The automatic heartbeat functionality helps to locate the source of any delays, whether in the Extract, Distribution Path, or Replicat stages, facilitating quick resolution.
As the migration progresses and replication lag is minimized, it’s essential to evaluate and confirm switchover readiness based on established business rules or requirements. Ensure that the source and target systems are fully synchronized, replication lag is reduced to near-zero or zero, and all other business-defined criteria are met. This preparation minimizes the transition time required in Phase 4, ensuring a seamless cutover to the target system.
Phase 4: Switchover to the Target Database (Application Downtime)
This final phase involves transitioning operations from the source to the target database. Although the target system has been synchronized during the online migration window, a brief cutover period is required:
- Take the application offline on the source database.
- Wait for all changes to be applied on the target, verifying that replication lag is zero.
- Run final data validation checks using Oracle Veridata to ensure data consistency.
- Reload unsupported objects and non-replicated tables.
- Bring the application online on the new target system.
At this point, the migration is complete, and the application is now running on the new platform.
Cross-Platform Migration Example: Detailed Steps and Oracle MOS References
For those eager to explore an example of an online GoldenGate migration in a cross-platform migration scenario, the following resources provide comprehensive guidance based on real-world use cases. The primary document, MOS Doc ID 3074183.1, titled “Cross Platform Migration with GoldenGate and Veridata”, serves as the cornerstone guide. It outlines the detailed steps and configurations necessary for a successful migration.
In addition to this central resource, the following MOS documents offer valuable supplementary information to enhance your understanding and execution of the migration process:
- MOS Doc ID 2471245.1: “Reduce Transportable Tablespace Downtime using Cross Platform Incremental Backup” – Provides strategies to minimize downtime during data transfer.
- MOS Doc ID 2853054.1: “Using XTTS in a Data Guard Environment” – Offers insights into leveraging XTTS in conjunction with Data Guard for efficient data management.
- MOS Doc ID 805438.1: “How to Open Physical Standby for Read Write Testing and Flashback” – Details procedures for testing and utilizing standby databases without disrupting primary operations.
- MOS Doc ID 2713160.1: “Veridata Server Memory Tuning – How To?” – Guides you through optimizing Veridata server performance for effective data validation.
These documents provide a robust framework based on actual migration scenarios, supporting your migration efforts by offering detailed steps, configuration guides, and verification practices to ensure a successful transition.
Best Practices for Online Migrations
- Thorough Planning: Perform a detailed assessment of your current database environment and create a migration strategy tailored to your system’s needs. Consider network bandwidth and database load when planning synchronization windows.
- Use the Heartbeat Table for Monitoring: Set up a heartbeat table to leverage GoldenGate’s automatic heartbeat functionality, allowing continuous monitoring of replication lag and ensuring real-time alerts.
- Continuous Data Validation: Use Oracle Veridata throughout the migration to ensure that data remains consistent between the source and target databases.
- Have a Fallback Strategy with Flexible Recovery Options: Always prepare for contingencies by having a fallback strategy in place. GoldenGate’s decoupled architecture and asynchronous replication ensure that in case recovery is needed during migration, it can be executed with minimal downtime or interruption. This flexibility allows you to easily switch back to the original environment if necessary, safeguarding data integrity and ensuring business continuity.
Conclusion
Oracle GoldenGate provides a powerful and flexible solution for performing online migrations with minimal downtime. By following a high-level, phased approach, and leveraging features such as the automatic heartbeat functionality for monitoring replication lag and Oracle Veridata for real-time data validation, businesses can ensure that their migrations are seamless and risk-free.
Whether migrating across platforms, upgrading to Oracle Exadata, or ensuring business continuity during database transitions, Oracle GoldenGate offers the capabilities needed to keep operations running smoothly while transitioning to a new database environment.
