OCI GoldenGate is a fully managed service providing a real-time data mesh platform, which uses replication to keep data highly available and enable real-time analysis.
Recently, I wrote an article about using OCI GoldenGate with MySQL databases, including OCI MySQL Database HeatWave Service. Today, I am back with an article on integrating OCI GoldenGate with PostgreSQL databases. We will learn more about the PostgreSQL deployment and connection types, and how simple it is to move data in and out of PostgreSQL databases using GoldenGate.
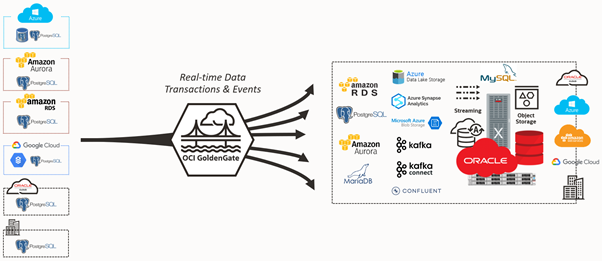
The OCI GoldenGate PostgreSQL deployment type includes support for PostgreSQL databases running on-premises, or in 3rd party clouds:
- PostgreSQL Server 10, 11, 12, 13, 14
- Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, 13
- Amazon RDS PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, 13, 14
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, 13
- Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, 13, 14
Creating a PostgreSQL Deployment
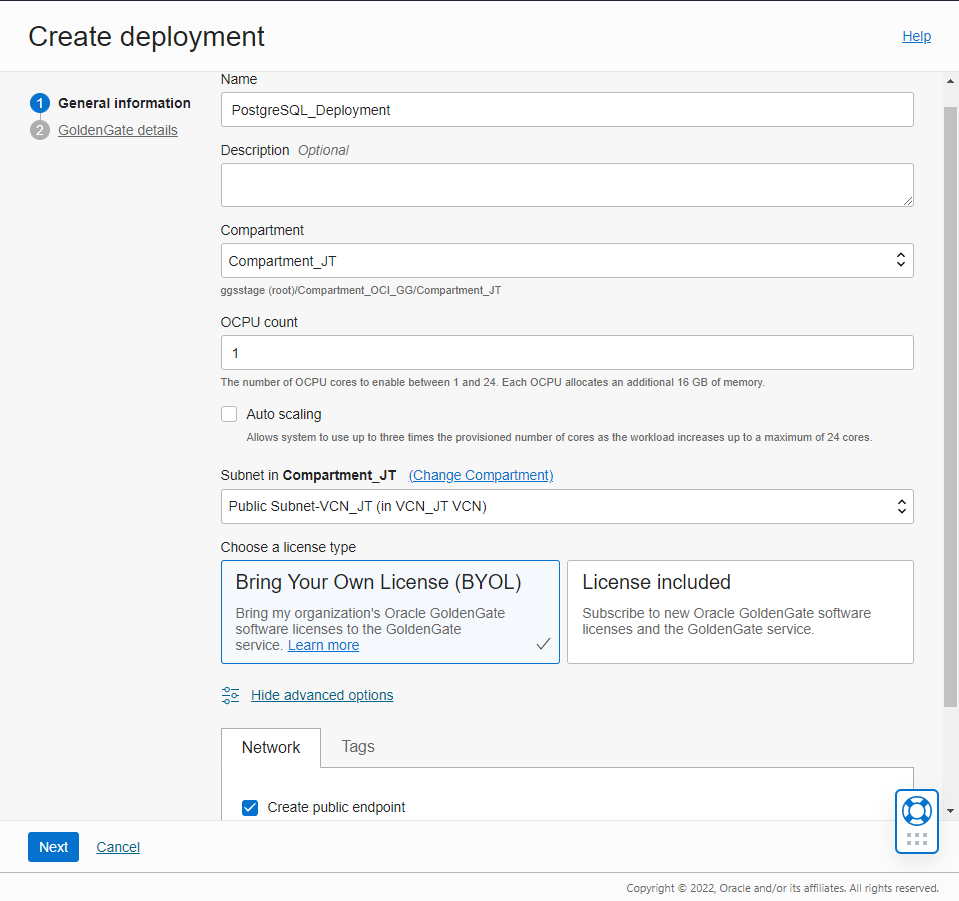
You can create a PostgreSQL deployment using the OCI Console, CLI, or APIs. From the OCI Console menu, go to Oracle Database, click GoldenGate and click Create deployment.
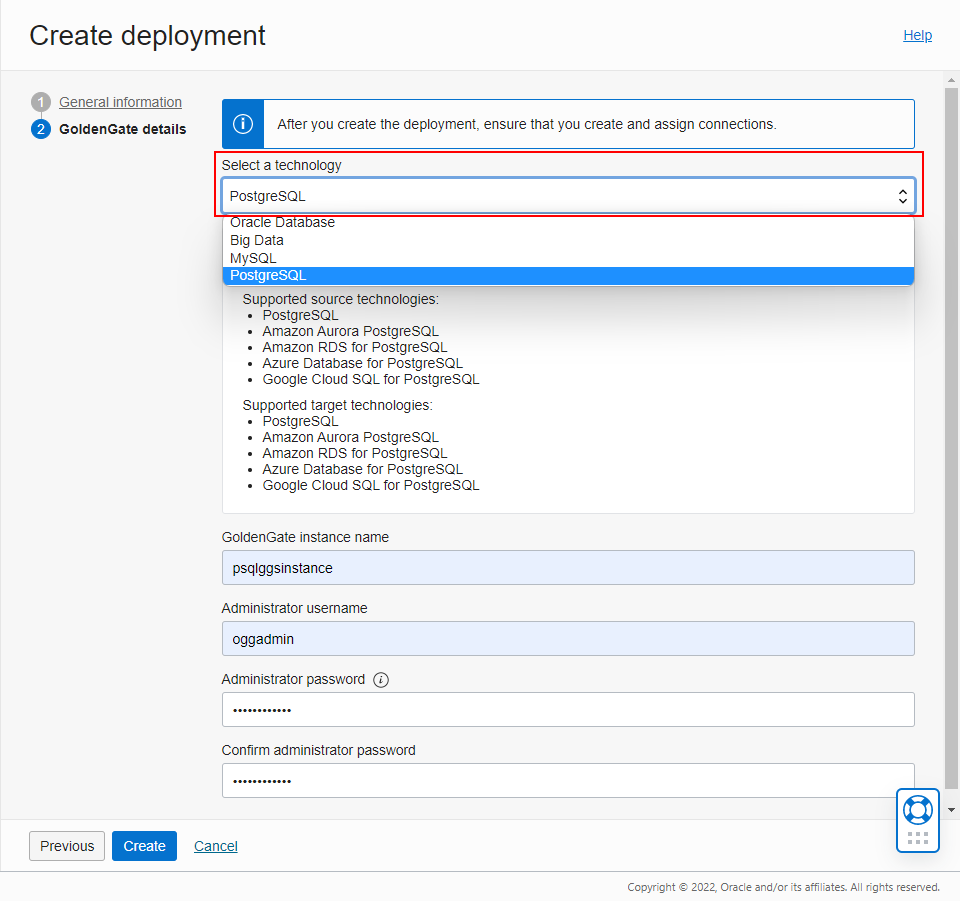
Go through the deployment creation screens, and select PostgreSQL when prompted for a technology. Finally, click Create to start the creation of the deployment.
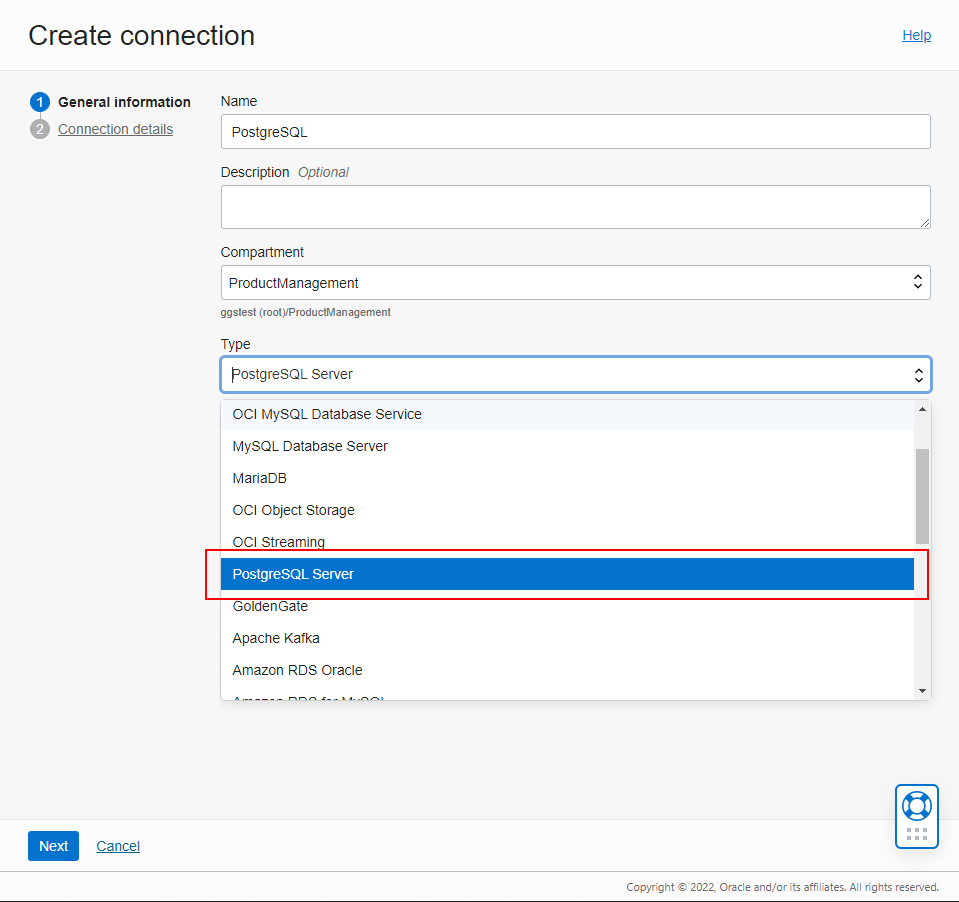
Create a Connection to PostgreSQL
To create a Connection, go to the Overview or Connections page and click Create connection. Pick PostgreSQL Server as the Type and click Next.
Enter your database information manually to connect to a database running on-premises or on a Compute instance. In this article, we use a PostgreSQL database installed on a Compute instance in OCI. Provide the database name, its host and port (5432 by default), then enter a username and password. Finally specify the SSL details if any.
Enable Network connectivity via private endpoint if your PostgreSQL database can only be accessed using a private IP address.
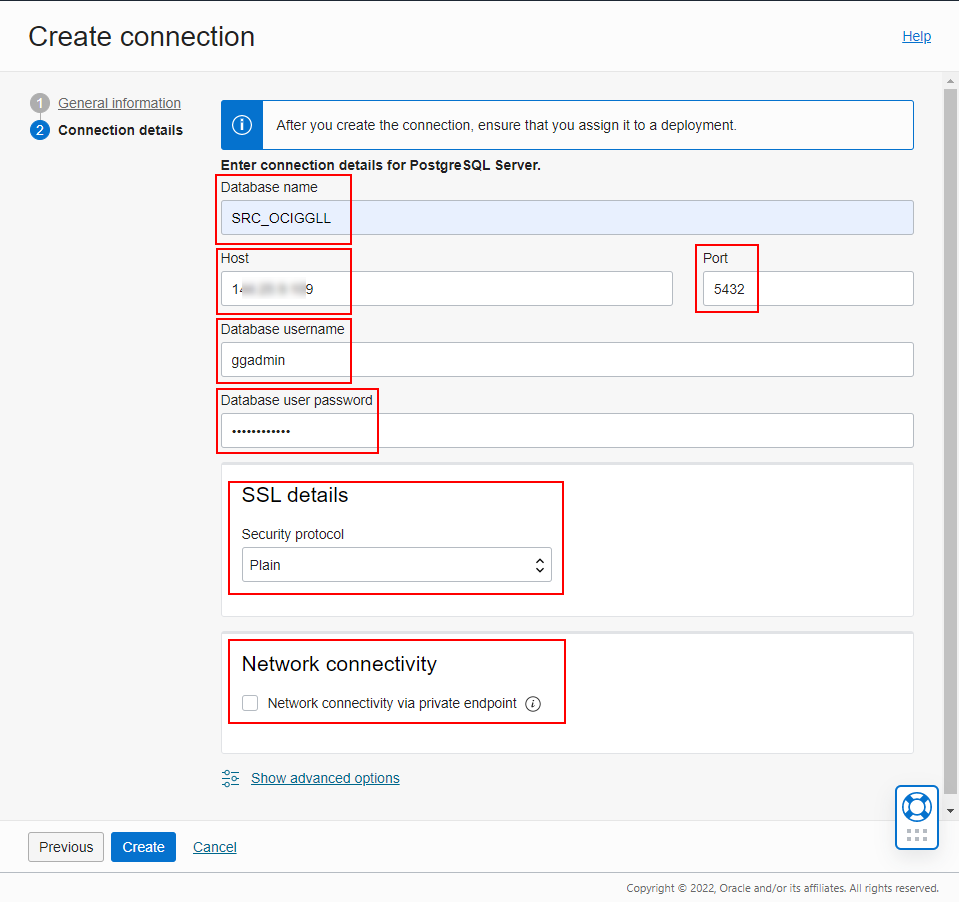
Click Create to proceed with the Connection creation.
Assign a Connection to a Deployment
A Connection must be assigned to a Deployment before it can be used. The assignment can be done from the Deployment or the Connection. You don’t need to wait for the Connection to be Active to assign it to a Deployment.
Open your Deployment, click Assigned connections, then click Assign connection.
Select your Connection in the list and click Assign connection to create the assignment.
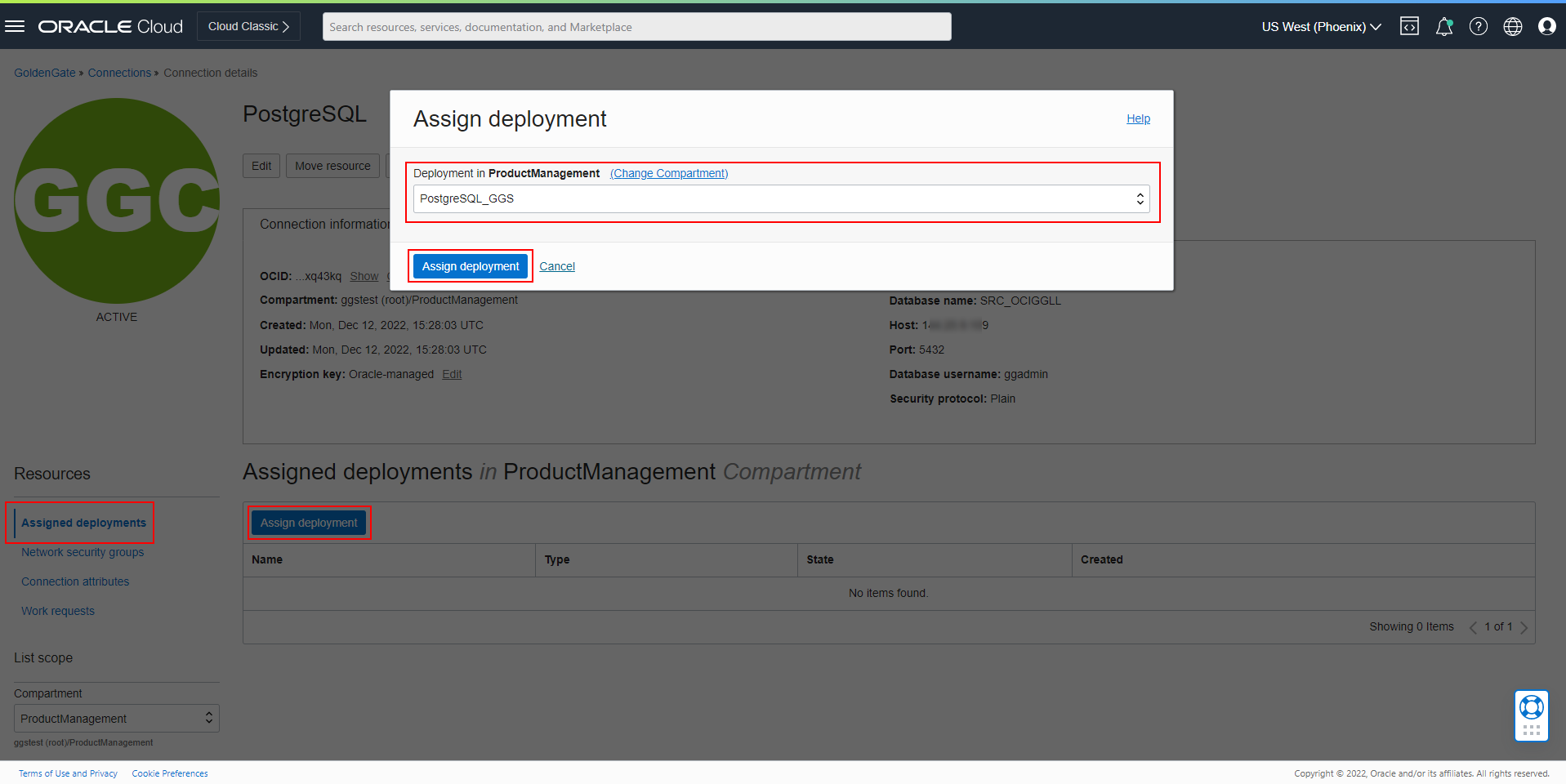
Note: Connection types are compatible with specific deployment types. PostgreSQL Connections can only be assigned to PostgreSQL Deployments, for example. In heterogeneous use cases, you must use different Deployments and connect them using Distribution Paths.
So, if you plan to send data from a PostgreSQL database into an Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) database, you will need two OCI GoldenGate Deployments:
- One for PostgreSQL (deployment type: PostgreSQL)
- One for ATP (deployment type: Oracle)
Create data replication processes using PostgreSQL databases
You can start designing your Extracts and Replicats once you have assigned the required Connections to your Deployment(s).
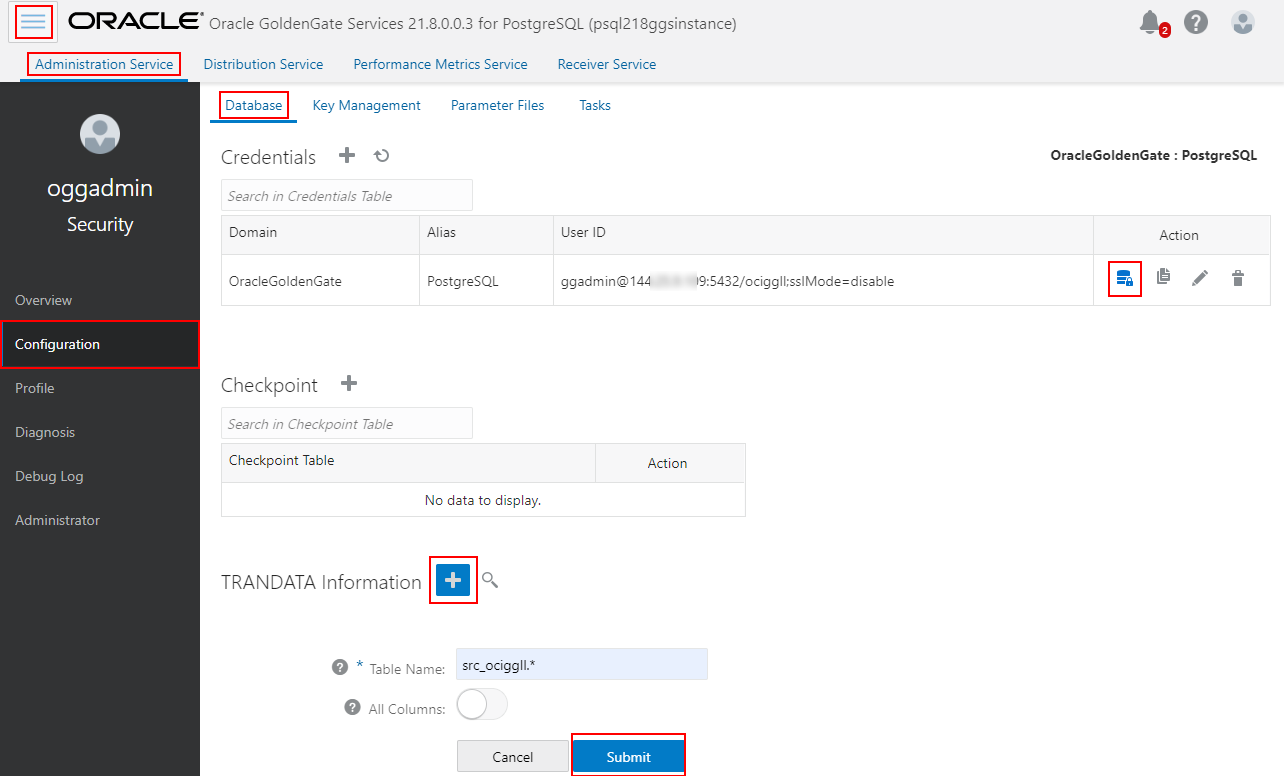
Go to your Deployment details page and click Launch console to start the OCI GoldenGate Console. Open the menu, click Configuration, review your Credentials, and click Connect to test the connectivity to your sources and/or targets.
Once connected, you must click on the plus sign next to TRANDATA information to enable GoldenGate to acquire the transaction information that it needs from the transaction records. Provide a table name, or schema name along with wildcards, then click Submit.
Now click Overview and click Add Extract (plus icon) in the Extracts panel to create either an Initial Load Extract or a Change Data Capture Extract.
We will start with an Initial Load Extract to initialize the target schema. Enter a Process Name, specify the Credential Domain and Alias, and type the Trail Name. Click Next.
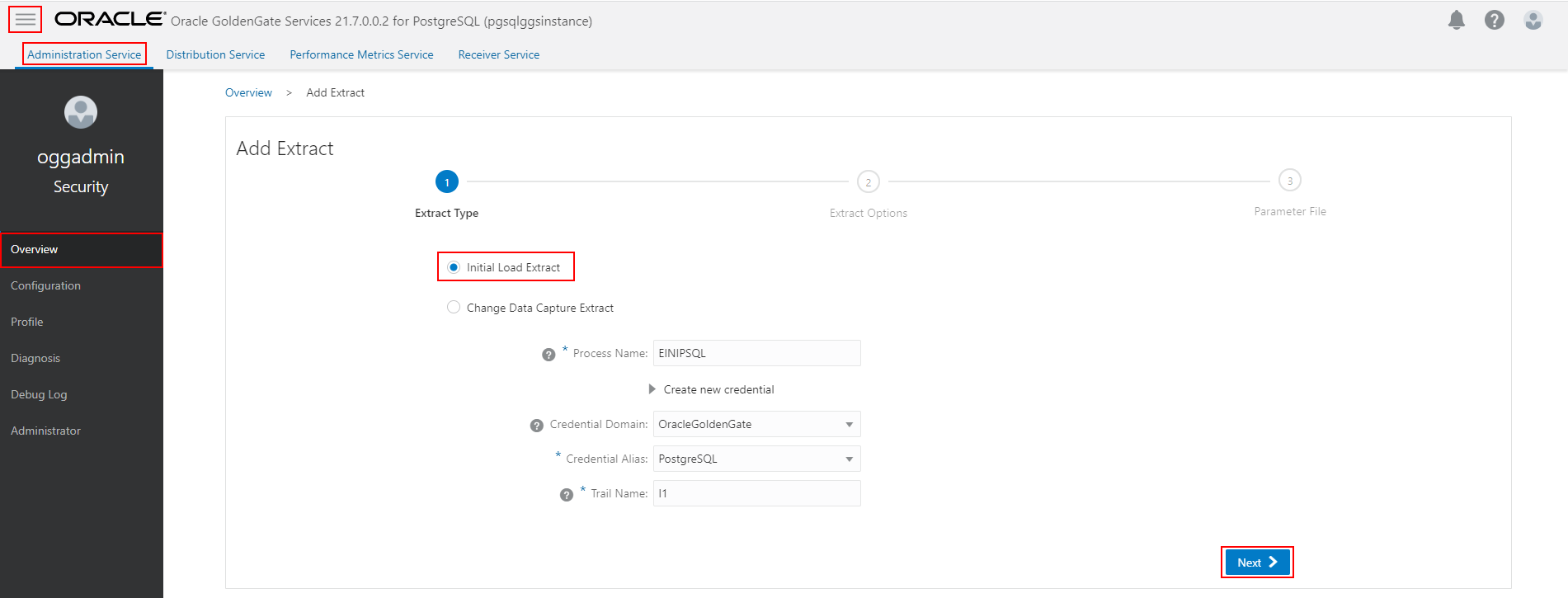
Specify which tables and schemas GoldenGate will capture data from in the Parameter Files page, then click Create and Run.
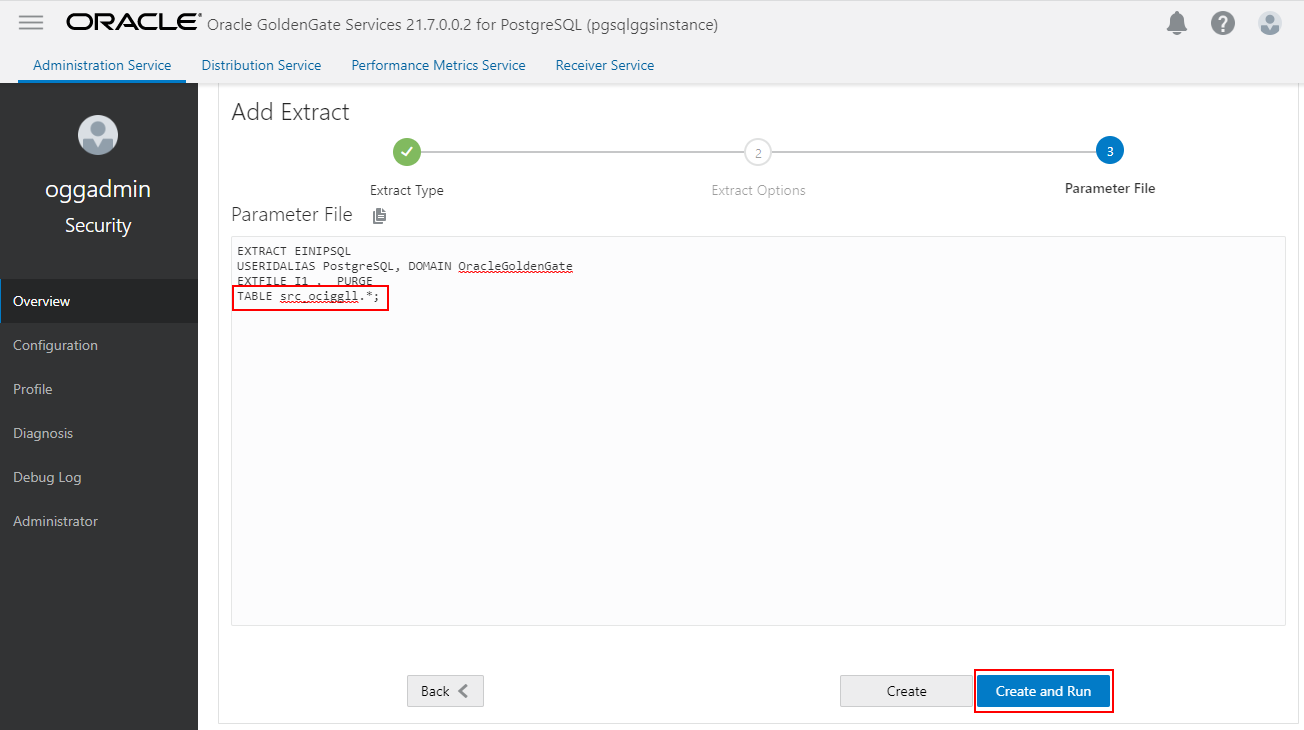
Next, we will create a CDC Extract, select Change Data Capture Extract. Enter a Process Name and select the Credential Domain and Alias. Click Next.
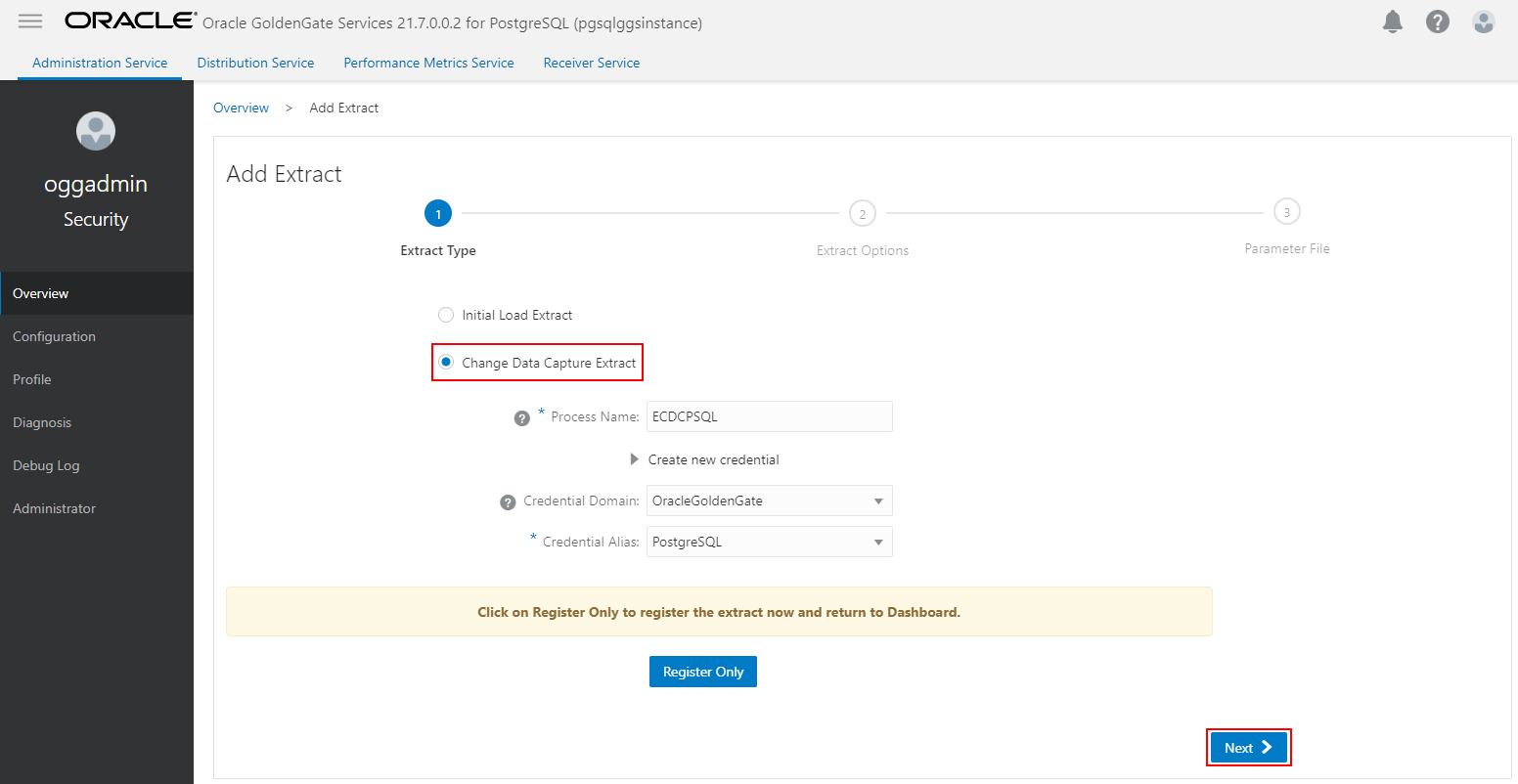
Provide the Trail Name, and optionally alter the other Extract options. Click Next.
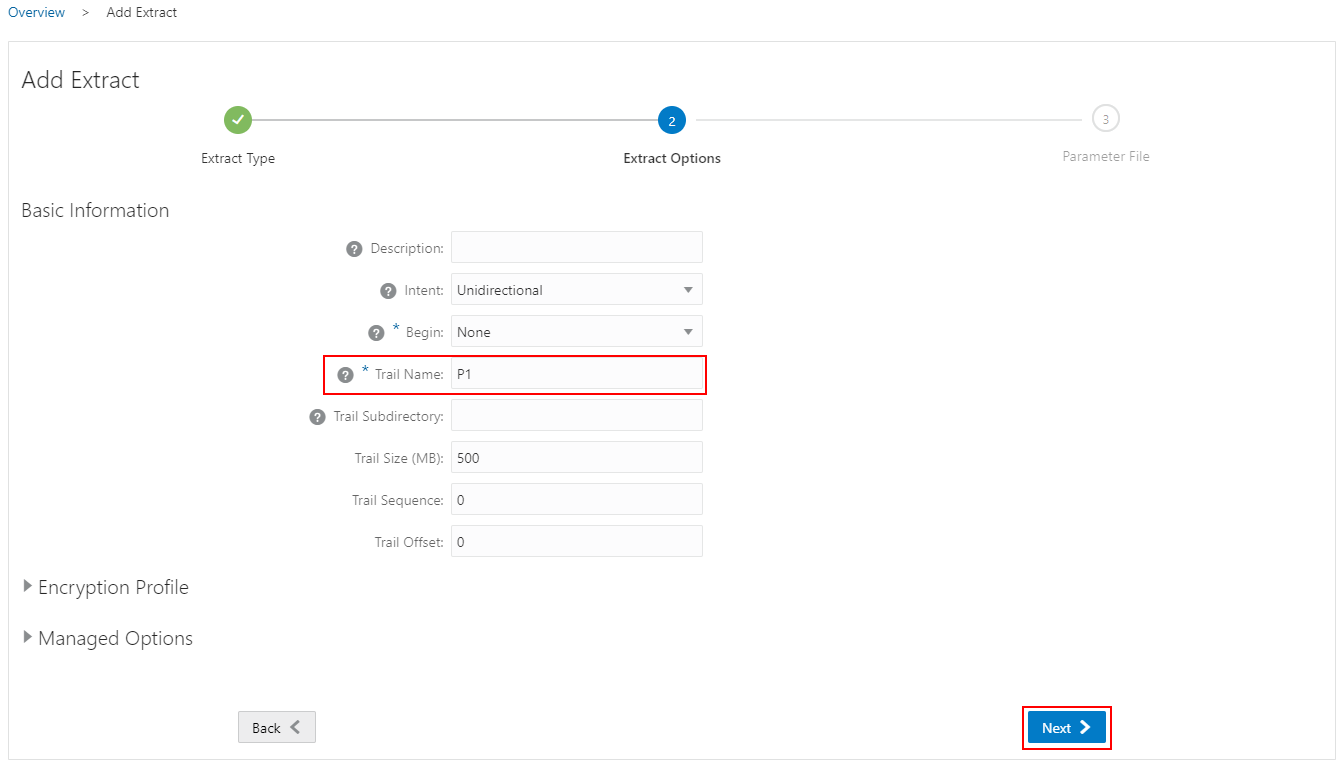
Specify which tables and schemas GoldenGate will capture data from in the Parameter Files page, then click Create and Run.
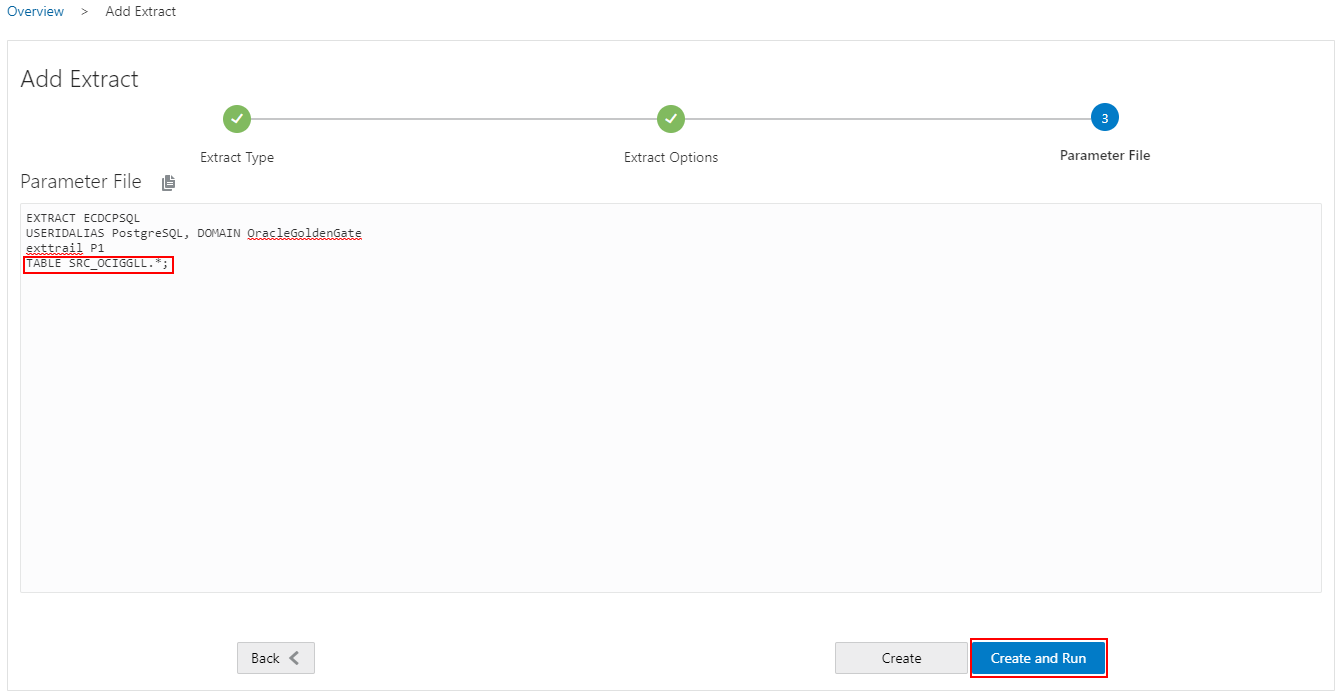
You should now have two Extracts listed in the Administration Service page. The Initial Load Extract will stop once it has processed all the records, and will display a yellow status icon.
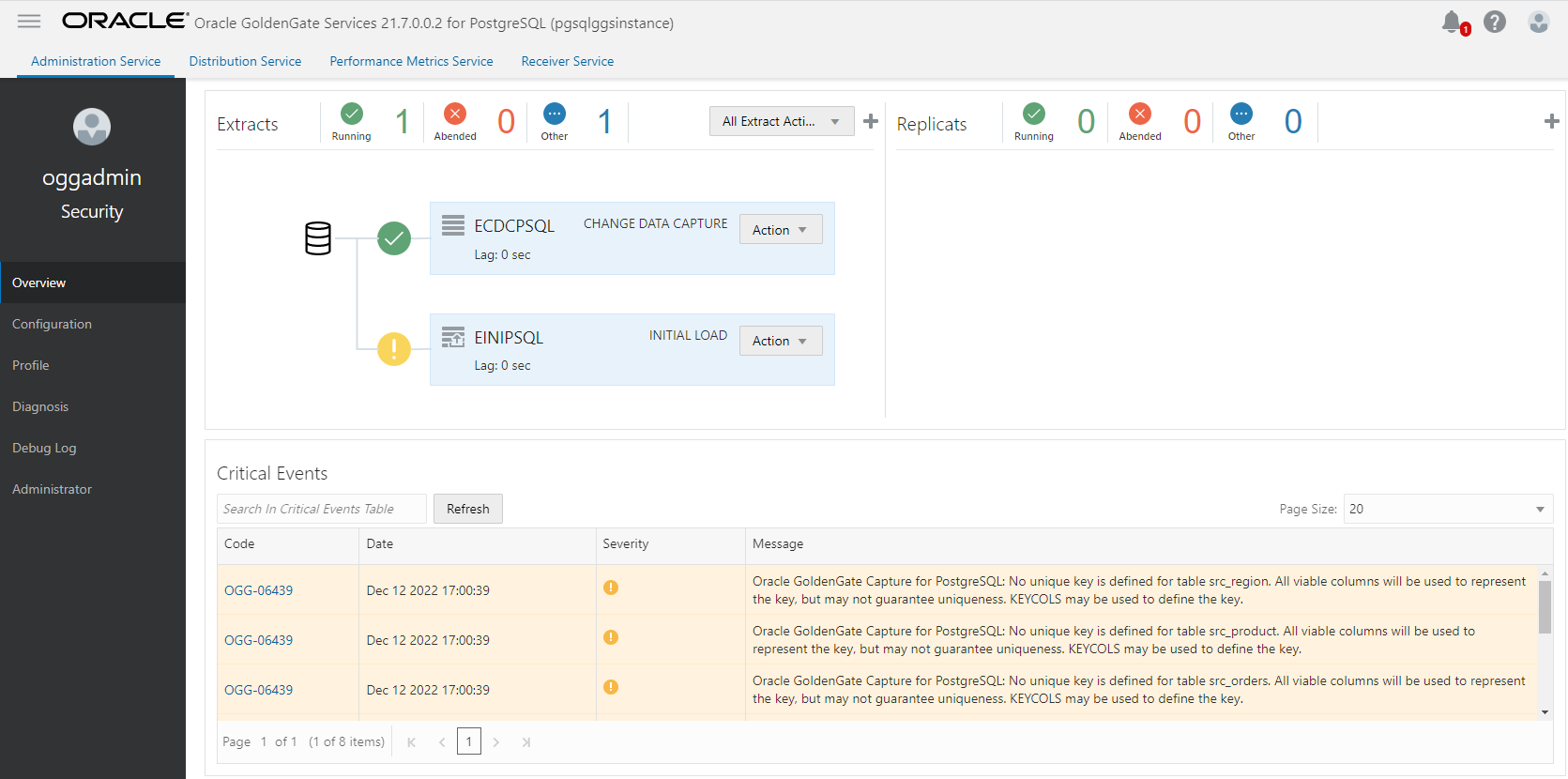
Creating a Replicat follows a similar process: click Overview and click Add Replicat (plus icon) in the Replicats panel. Select a Replicat type from Classic, Coordinated, or Parallel. You can find more information about the different Replicat types here. We will select Parallel in this example and click Next.
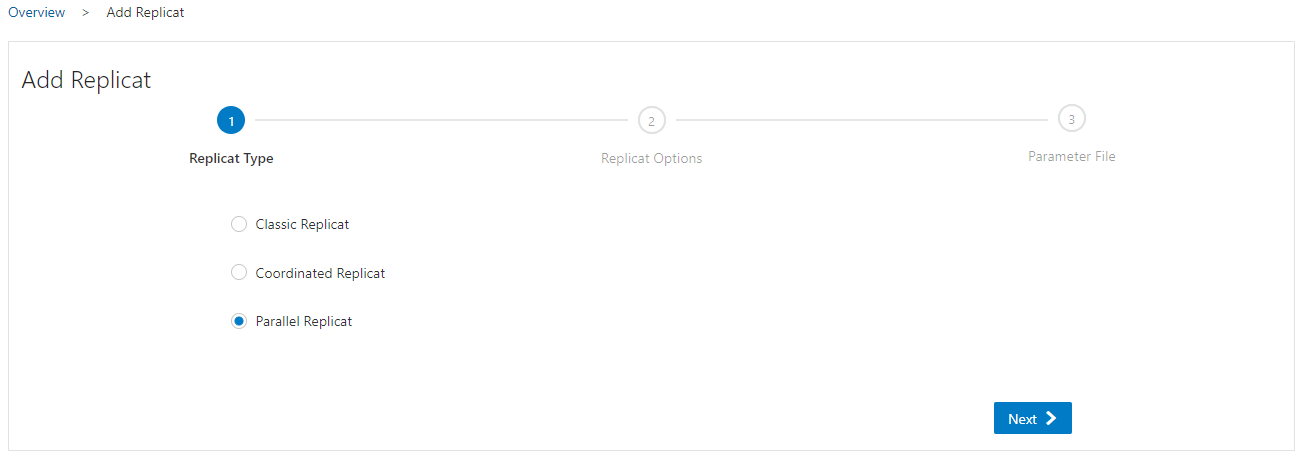
Enter a Process Name, select a Domain and Alias, specify the initial load Trail Name and enter a Checkpoint Table name (previously created at the Configuration > Credentials level). Click Next.
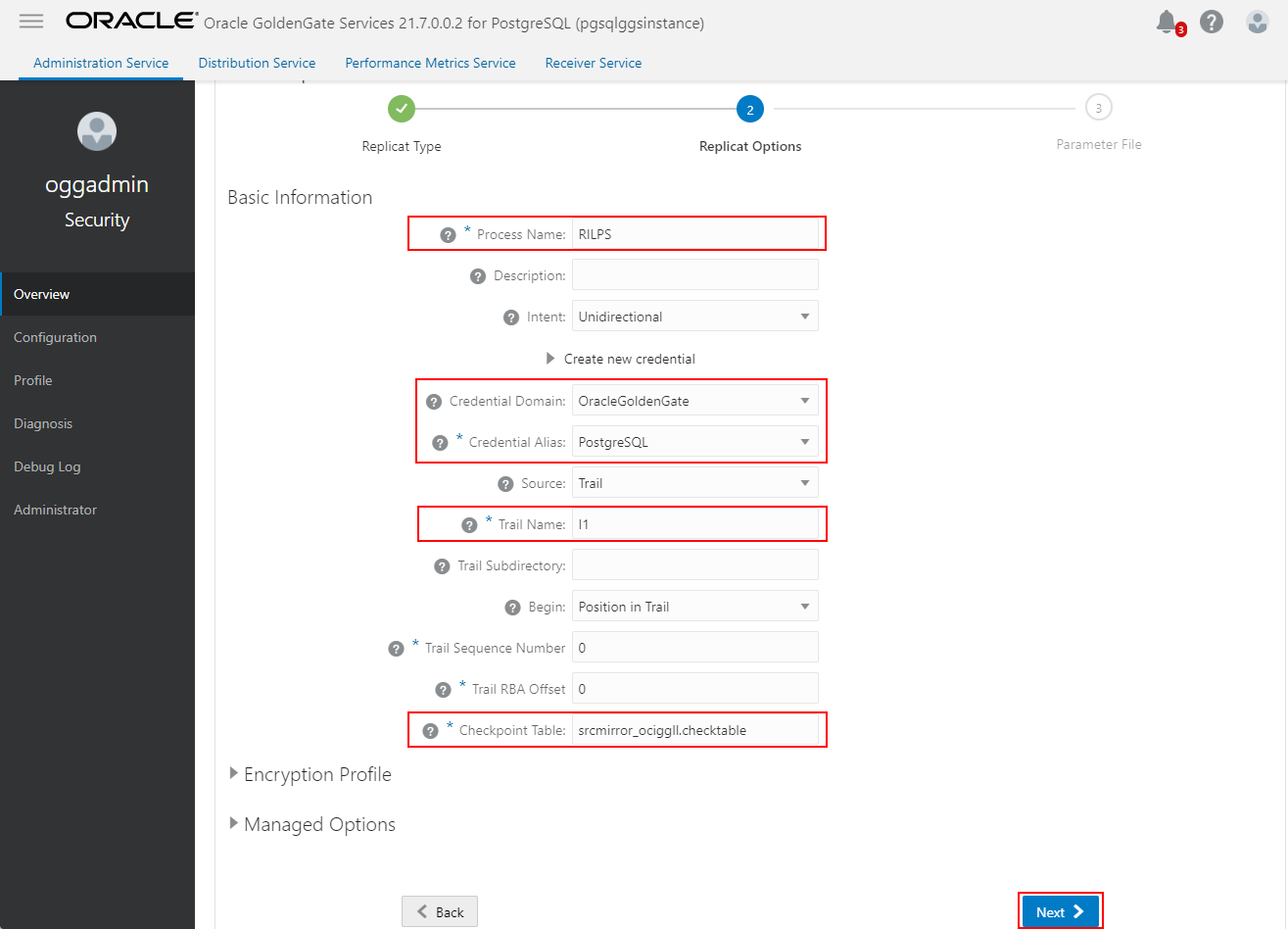
Specify how the source and target tables will be mapped by the Replicat and click Create and Run.
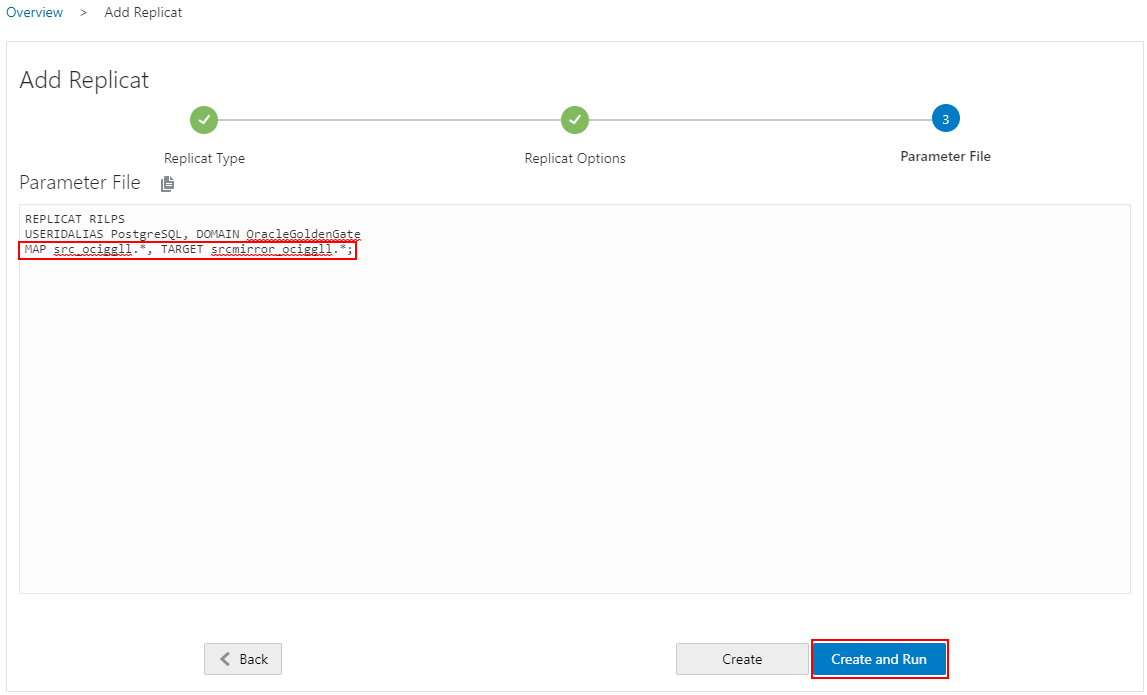
Our Extracts (initial load and CDC) and Replicat (initial load) processes are now up and running and show as Active in the OCI GoldenGate Console.
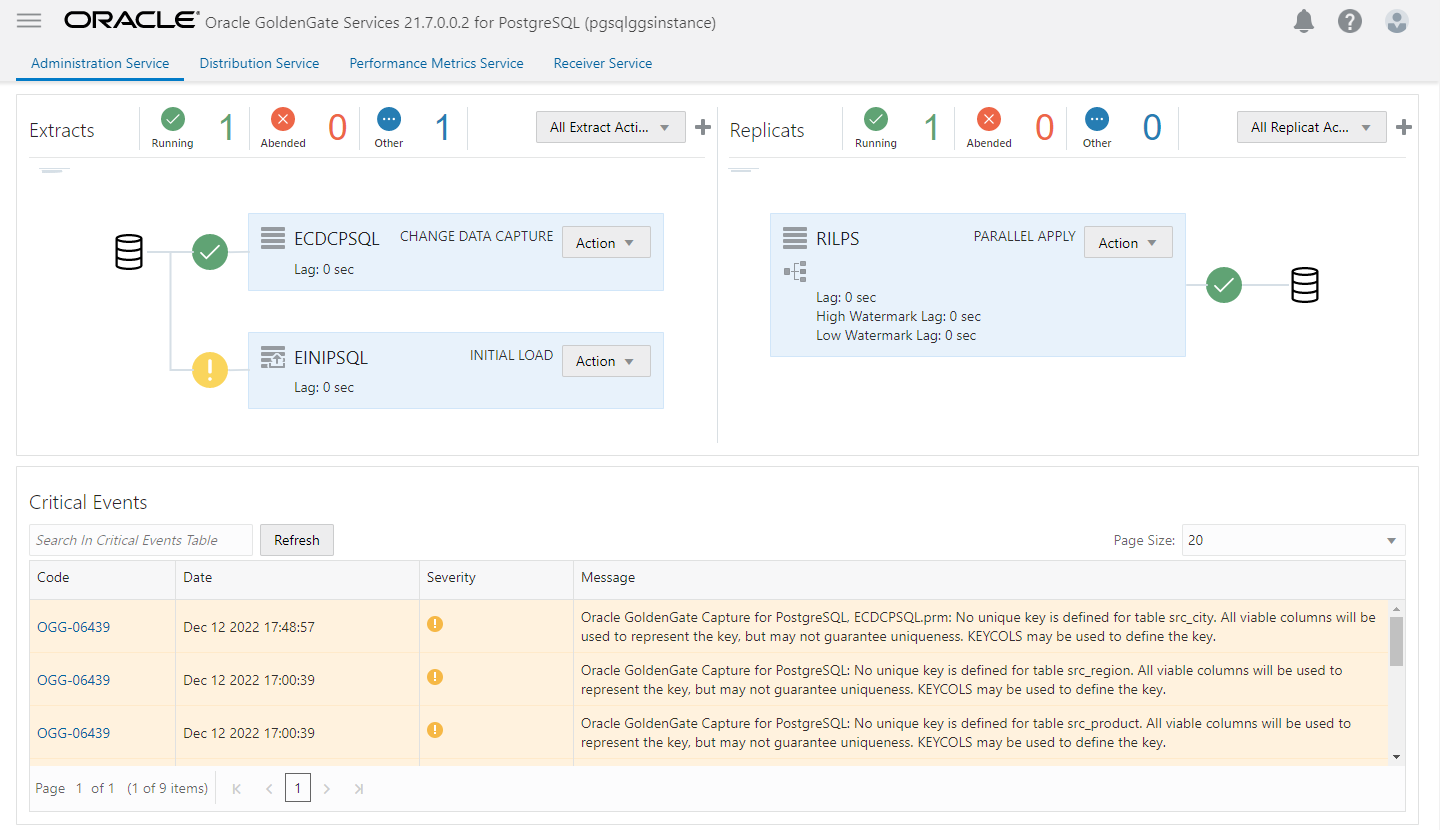
Once the Replicat consuming the trail from the Initial Load Extract has finished processing the records, stop it and add a Replicat to consume the trail file created by the CDC extract. Follow the same steps outlined above to create the new Replicat.
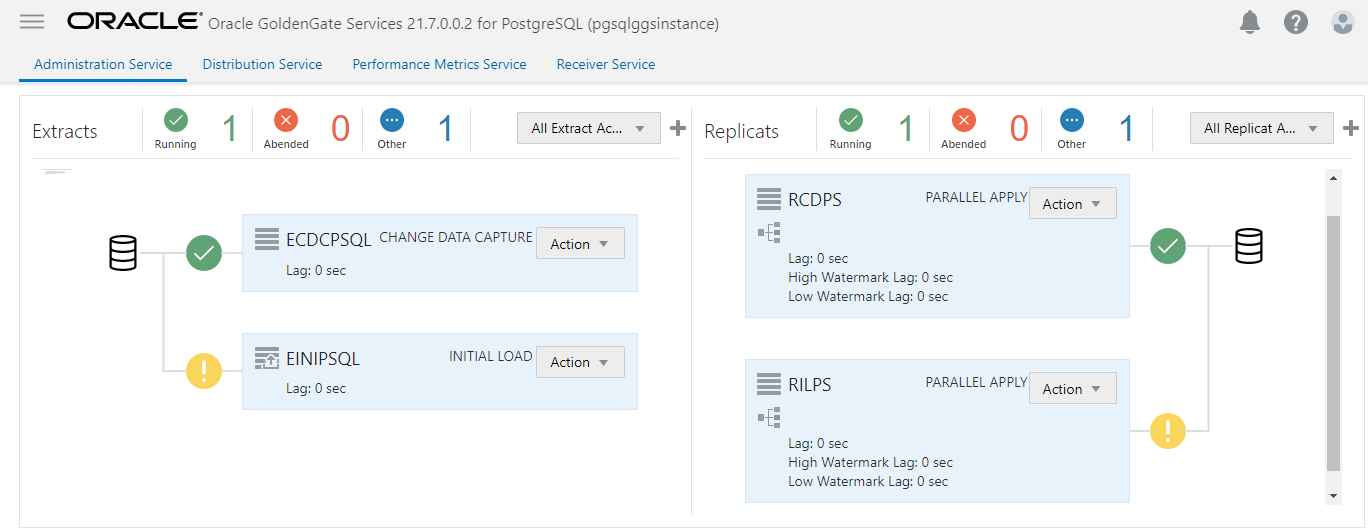
We have seen how easy it is to replicate data from and into PostgreSQL databases with OCI GoldenGate. You can follow similar steps to integrate PostgreSQL with any source and target supported by GoldenGate on-premises and OCI GoldenGate. As a next step, I recommend going through the following quickstart to get familiar with OCI GoldenGate and how it integrates with PostgreSQL: Replicate data from PostgreSQL to Autonomous Transaction Processing. Stay tuned for new blogs coming up soon!
