A few months back, we announced the availability of real-time data replication into Snowflake with OCI GoldenGate. We published blogs and video recordings along with OCI GoldenGate Snowflake documentation. You can review them from the following links:
- Using OCI GoldenGate for Snowflake Initial Load and Real-time Data Sync
- Using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) with Snowflake
- Measuring end-to-end lag using Snowflake Handler
- Quicstart: Replicate data from PostgreSQL to Snowflake
Since the release, we’ve had many new customers adapting real-time data replication to Snowflake tables with OCI GoldenGate. As the use case matures in a very short time, we’ve seen customers who wants to have more control on the Snowflake replication process. I can say that DDL replication is one of the hottest topics when we start talking about any supported data warehouse replication. As you may already know, OCI GoldenGate Snowflake replication currently does not support DDL replication and it’s on our roadmap as one the highest importance items.
However, you can control the replication process for applying DDL operations manually on your data warehouse target tables. The content of this blog can be applied to Snowflake, Azure Synapse, GCP Big Query and AWS Redshift replicats.
Let’s start with the default behaviour:
Default Extract and Replicat behaviour in case of source DDL:
When the Snowflake replicat is started, it resolves a static snapshot of metadata from target table. And replicat mapping functionality uses the target schema information for mapping, no matter what comes from the source. So, even if your extract process captures the source DDL operation, your replicat will ignore the DDL operation and replicat will not fail. Replicat will map existing fields and changes will be ignored.
The reason why replicat does not fail by default is, replicat mapping is driven by target Snowflake schema and it maps what exists in the target table. Advantage is, replicat does not fail and continues the replication of existing mappings.
On the other side, user does not receive any notifications about DDL and user does not know that target table needs to be updated.
Controlling extract or replicat behaivour during DDL
You can abend the extract or replicat to handle DDL operation. If your extract supports multiple replicats or if you’re running the extract on mission critical systems, it is better to control DDL on replicat level.
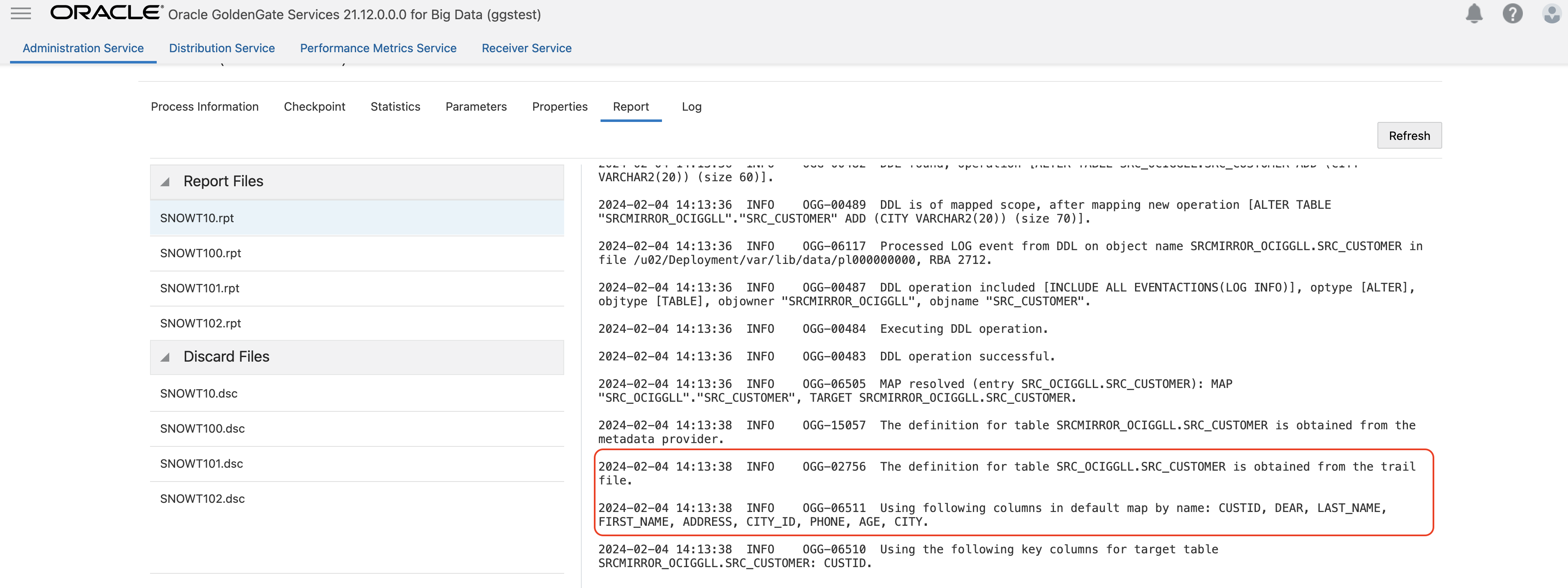
To control DDL opetations, we can use 2 parameters together: DDL and EVENTACTIONS. DDL parameter is used for enabling, filtering and configuring a processing action based on a DDL record. EVENTACTIONS triggers a defined action based on the DDL record. Both parameters can be applied to extract and replicat. If you want to control replicat behaviour in case of DDL, please make sure that DDL is enabled in extract. You can simply do it by adding DDL INCLUDE to extract parameters. For example: DDL INCLUDE ALL EVENTACTIONS (LOG INFO) will capture the DDL operation from source table and log a notification in the report file.
Applying DDL on the target by abending the replicat:
Once you enable DDL in extract you, can control the replicat behaivour for DDL operations. You can use the same DDL and EVENTACTIONS parameter settings. For this blog, I used DDL INCLUDE ALL EVENTACTIONS (LOG INFO, STOP) parameter in my replicat. It will include all the DDL operations coming from the source and it will stop the replicat in case of any source DDL. You can create more complex rules. For example, you may want your replicat fail in case of source DDL, but, not for truncate. In such case, you can use EXCLUDE OPTYE in the same parameter. For example, DDL INCLUDE ALL EVENTACTIONS (REPORT, STOP) EXCLUDE OPTYPE TRUNCATE
You can also add DDLOPTIONS REPORT into your parameter which would log the details of the DDL operation in the replicat report file.
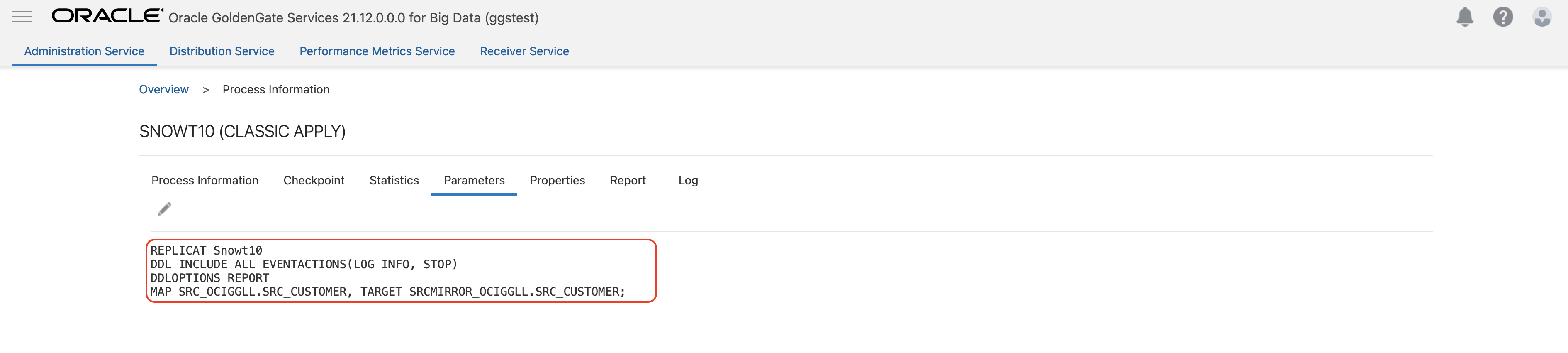
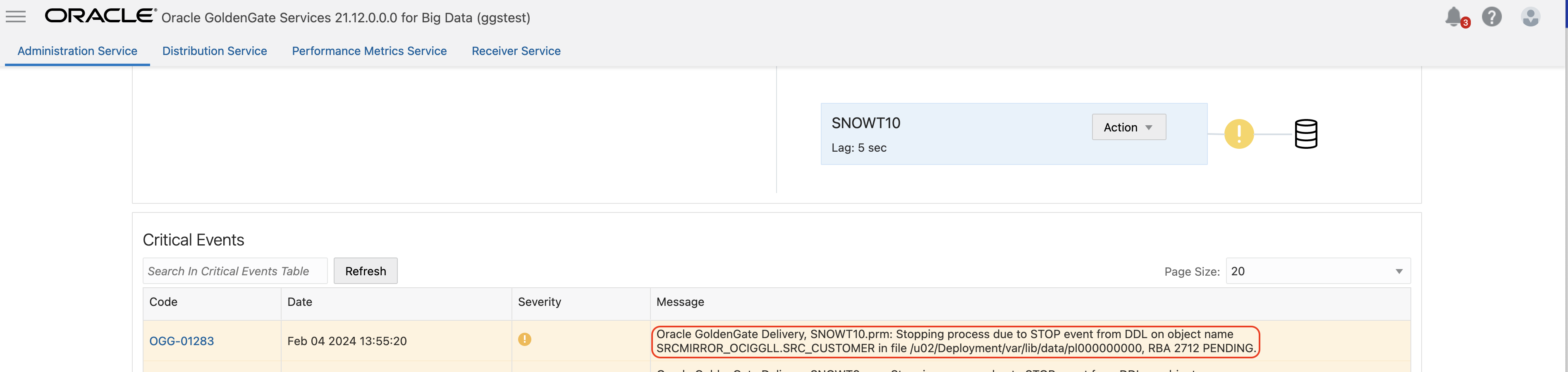
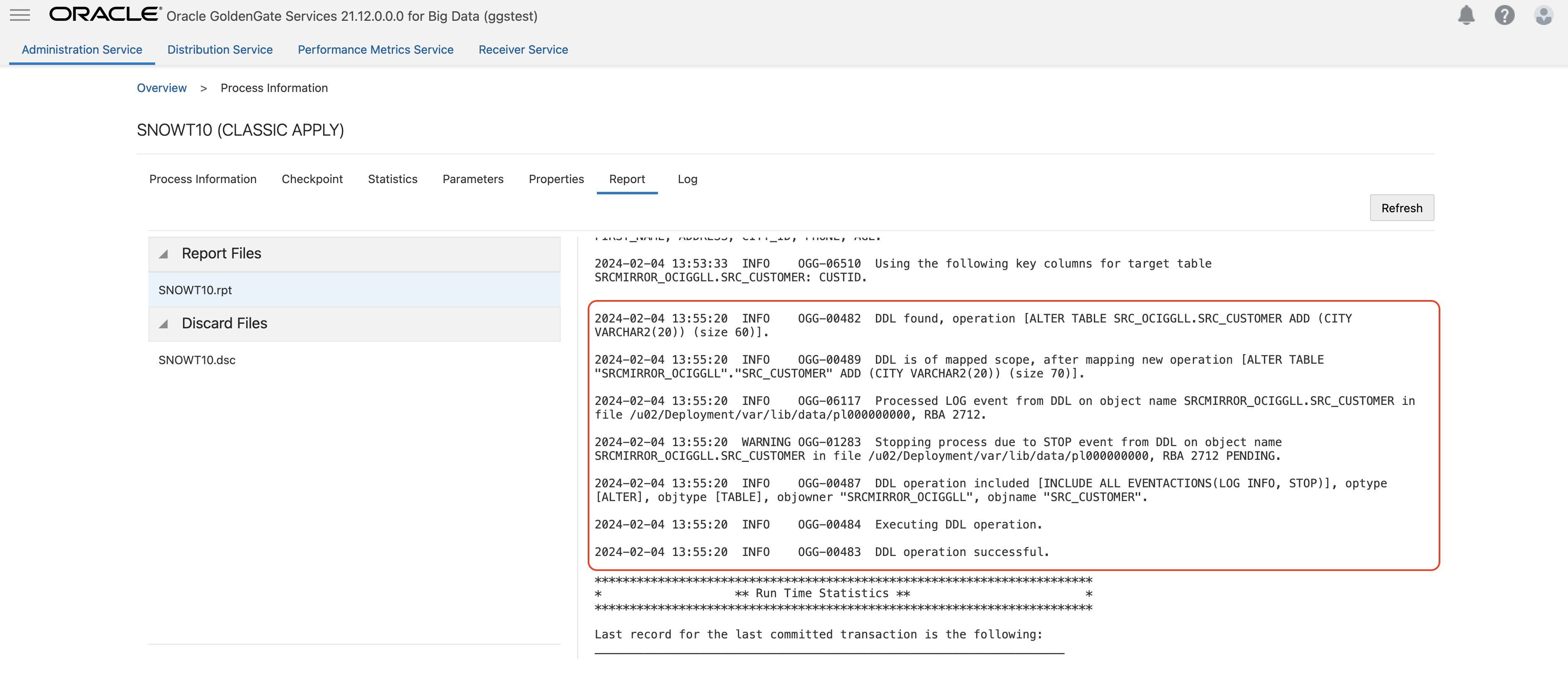
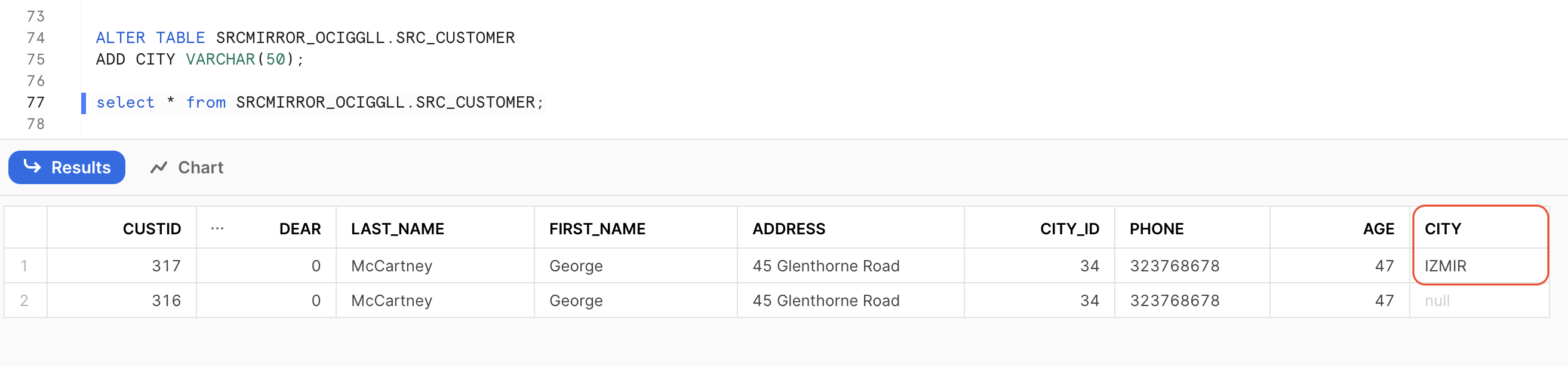
When replicat stops, update target table and then re-start the replicat. While restarting the replicat, remove STOP from EVENTACTIONS; so that replicat can start and map the new column.
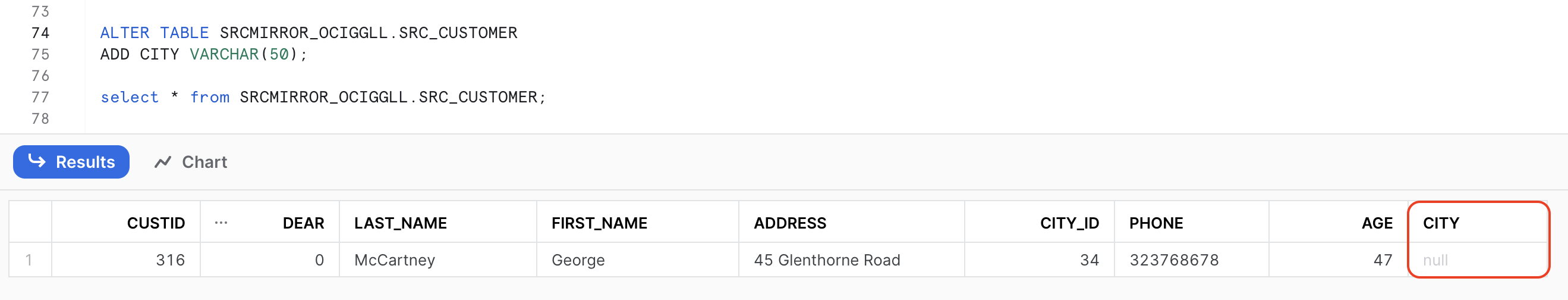
Conclusion:
You can configure OCI GoldenGate Extract and Replicat processes to manually apply the DDL changes on the target. Parameters used in the extract and replicat for controlling the DDL behaviour provides a great configuration flexibility. Failing the extract or replicat in case of source DDL will be users’ notification for applying the target DDL. Also, this DDL handling design guarantees no data loss while applying the changes in the target.
