GoldenGate is an essential resource for migration scenarios when business disruption cannot be tolerated, that is when applications cannot be interrupted or experience downtime. GoldenGate is now certified for supporting highly automated online MongoDB migrations into any GoldenGate supported technology.
There are several reasons that MongoDB customers need to migrate data.
- Upgrade to a new version of MongoDB or Atlas
- Migrate to an entirely different NoSQL technology
- Stream data into an event streaming platform
- Load data into object storage, data lakehouse, or data warehouse
With this announcement, Oracle GoldenGate for Big Data versions 21.5 and later are certified to accomplish all these scenarios and more.
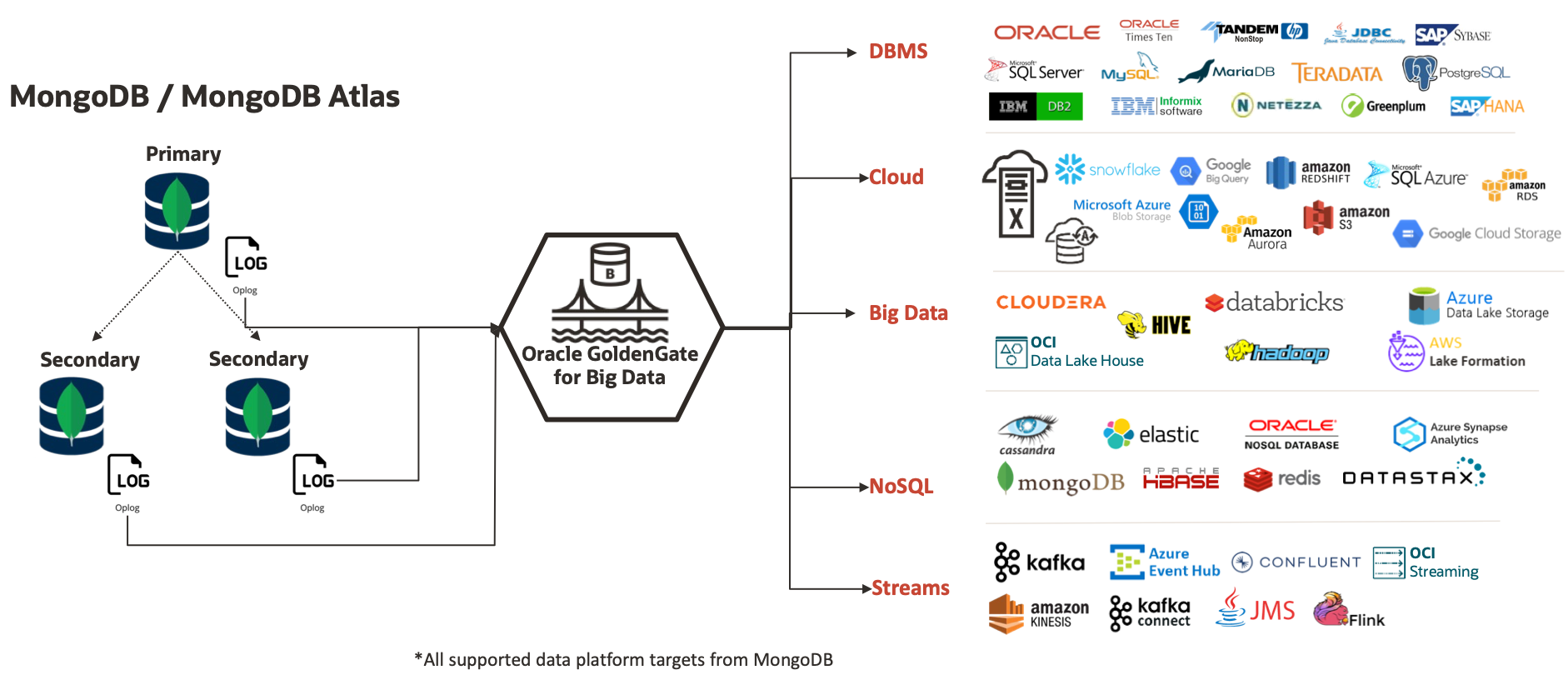
Unique capabilities that GoldenGate for Big Data offers supporting MongoDB migrations:
- Captures changed data from all current MongoDB versions (3.x, 4.x, 5.0 and 6.0) and all platforms (MongoDB Enterprise, MongoDB Community or MongoDB Atlas)
- Replicates data into +30 target data platforms
- Enables zero-downtime, online migrations
- Migrates data across on premises and cloud platforms (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and 3rd party clouds)
- Hub deployments architectures, GoldenGate for Big Data and MongoDB can run on different servers
Oracle GoldenGate Migration Architecture
There is a difference between an offline and online migration. For an offline migration, an application is shut down and records are copied to a target technology. If there is a problem, the entire process can be stopped, reset, and restarted. But, for an online migration, applications are not shutdown, and there is no restart. Instead, the requirements are more demanding. While applications are running, there can be no data loss, even if there are hardware, software, and network failures.
GoldenGate is a zero-disruption technology which makes it perfect for database migrations, patching, upgrades, data integration, and high availability. The migration process is straightforward. An initial load of source data is copied to a target. Then, from that point in time, all the discrete data and schema changes are captured is a special log file. Next, all the changes are applied to the target on an ongoing basis. If there is a disruption in the process at the source or the target, then the process picks up after the time of the last disruption. In this way, all failures are tolerated. And it turns out that this technique is also an excellent way to do data integration, such as loading a data warehouse or publishing a message into an event stream.
GoldenGate for Big Data and MongoDB
GoldenGate for Big Data supports MongoDB as both a source and target. So, for all the MongoDB data migration use cases mentioned above, you can move data from source to target without shutting down your applications.
For some insight on the MongoDB migration setup and operations, you identify the path and security credentials for both the source and target, then GoldenGate for Big Data captures the change data from MongoDB oplog files. The initial load and the ongoing changes are written into a GoldenGate trail file which in turn, writes the data into one or more data targets.
For a step by step MongoDB migration process with all the details, you can check out the No Downtime Migrations blog post.
At Oracle Cloud World you can learn more
Learn more here:
- GoldenGate for Big Data Documentation
- Oracle Blogs
- GoldenGate Youtube Channel
- GoldenGate for Big Data Hands On Lab
- GoldenGate for MongoDB Migrations: GA blog, documentation, overview video, technical walkthrough video
