2024 has seen many groundbreaking new announcements for Oracle Database services in the cloud. We released Oracle Database 23ai with native Vector search, which helps bring AI-powered similarity search to your business data. We introduced Exadata Exascale, an exciting new intelligent data architecture, and the new Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure providing a low entry cost to the cloud while making Exadata’s unique capabilities available for small workloads. In June we expanded our multicloud partnerships with the announcement of Oracle Database@Google Cloud and did so again in September with the announcement of Oracle Database@AWS.
We also introduced the ability to deploy Single VM clusters for Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure, eliminating the need to provision a minimum of two VMs per cluster. And finally, we added support for AMD E5 flexible shapes in Base Database Service.
As we wrap up the year, it’s a great time to look back and recap these key announcements as we prepare for even more innovative advances in 2025. In case you missed any of them, here’s a summary of the top announcements from 2024 for Exadata Database Service and Base Database Service:
- Oracle Database 23ai with Vector Search
- Exascale and Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure
- New Multicloud Partnerships – Google Cloud and AWS
- Single VM Clusters
- Support for AMD E5 Flexible Shapes in Base Database Service
Oracle Database 23ai with Vector Search
In May we announced General Availability of Oracle Database 23ai, the next long-term support release of the Oracle Database, which runs on both Exadata Database Service and Base Database Service. Among the many new features included, perhaps the most significant innovation is AI Vector Search, which allows you to encode a vector representation of objects such as documents, images, sounds, etc. and search for similarities between them using simple, standard SQL.
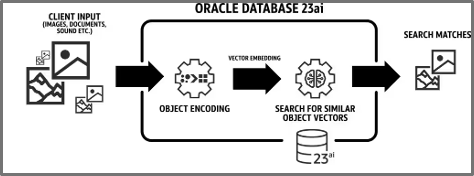
The related introduction of Exadata System Software 24ai enables Vector Search on Exadata to be offloaded to the intelligent storage tier using AI Smart Scan to provide 30X faster queries, making the full potential of Oracle Database 23ai on Exadata available to support AI-powered similarity search across all your business data.
Exascale and Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure
In July we introduced a unique new intelligent data architecture, Exascale, and a new infrastructure option for Exadata Database Service based upon it, Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure. The Exascale architecture makes it possible for multiple tenants to share both database compute and the intelligent storage tier provided by Exadata. This eliminates the need for dedicated infrastructure and makes it possible for the new service to offer Exadata performance, reliability, availability, and security at a much lower entry point, effectively combining the best aspects of Exadata and cloud.
New Multicloud Partnerships – Google Cloud and AWS
Following up on last year’s introduction of the revolutionary cloud partnership between Oracle and Microsoft, Oracle Database@Azure, in June we announced a similar partnership with Google, Oracle Database@Google Cloud, which also became generally available in September. Also in September we announced another new partnership, this time with Amazon Web Services, Oracle Database@AWS.
With the announcement of this partnership, we are very pleased to offer customers their choice of deployment options across all the major hyperscaler clouds for Exadata, the best technology to run Oracle Database, and the Cloud Services based on it, Exadata Database Service and Autonomous Database. All three of these Multicloud partner offerings will continue to expand rapidly to additional Regions in 2025.
Single VM Clusters
In September we introduced the ability to deploy single VM clusters on Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure, which was previously introduced on Exadata Database Service on Cloud@Customer. This new capability eliminates the previous requirement to provision a minimum of two VMs per cluster, and allows customers to make more efficient use of the resources available in their dedicated infrastructure when some workloads don’t require the resiliency provided by a multi-node cluster running Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC). In a Bring Your Own License (BYOL) model this also enables the customer to optimize their use of Oracle RAC licenses, deploying them only in those cases where it makes business sense to do so.
Support for AMD E5 Flexible Shapes in Base Database Service
Finally, in June 2024 we added support for AMD E5 flexible shapes in Base Database Service, making the next generation of AMD shapes available for your Oracle Database workloads in OCI. The new VM.Standard.E5.Flex shapes are based on 4th Generation AMD EPYC ™ Processors, and allow you to provision any number of OCPUs from as few as 1 up to a maximum of 64, providing the latest processor innovations and flexible and economical compute and storage options for your database workloads when your business requirements don’t require Exadata level performance.
Those were the highlights, but there’s much more…
In 2024 we also released many additional features and enhancements. Review the new features section in the documentation at the links provided below for more details. Looking ahead, 2025 should be another very exciting year with many more great announcements planned.
We’d like to close by thanking the Exadata and Oracle Database cloud engineering and support teams for their tireless efforts in making Exadata and OCI the best place to run Oracle Database in the cloud and all our customers and partners for their trust and support.
