Oracle Database@Google Cloud is the most recent addition to Oracle’s multicloud portfolio, enabling applications running in Google Cloud regions to use Oracle Exadata Database Service and Oracle Autonomous Database as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) resources collocated in the same regions. Google Cloud applications and services such as Looker and Vertex AI can now have low-latency, native access to Oracle databases running on Exadata Cloud Infrastructure and take advantage of Oracle Database 23ai features like AI Vector Search.
Exadata has become the cloud and on-premises platform of choice for organizations around the world that need the fastest possible performance, highest possible availability, and strong security for their mission-critical Oracle Database workloads. Exadata Cloud Infrastructure in Oracle Database@Google Cloud is equivalent to what’s used in OCI data centers and can scale up to meet demanding database and workload requirements. It includes dozens of unique features that deliver differentiated capabilities for OLTP, analytics, AI, mixed workloads, and database consolidation.
Benefits of Oracle Database@Google Cloud
Oracle Database@Google Cloud helps you migrate mission-critical Oracle Database workloads to Google Cloud, innovate with the best capabilities of Google Cloud and Oracle Database, and simplify multicloud management and operations.
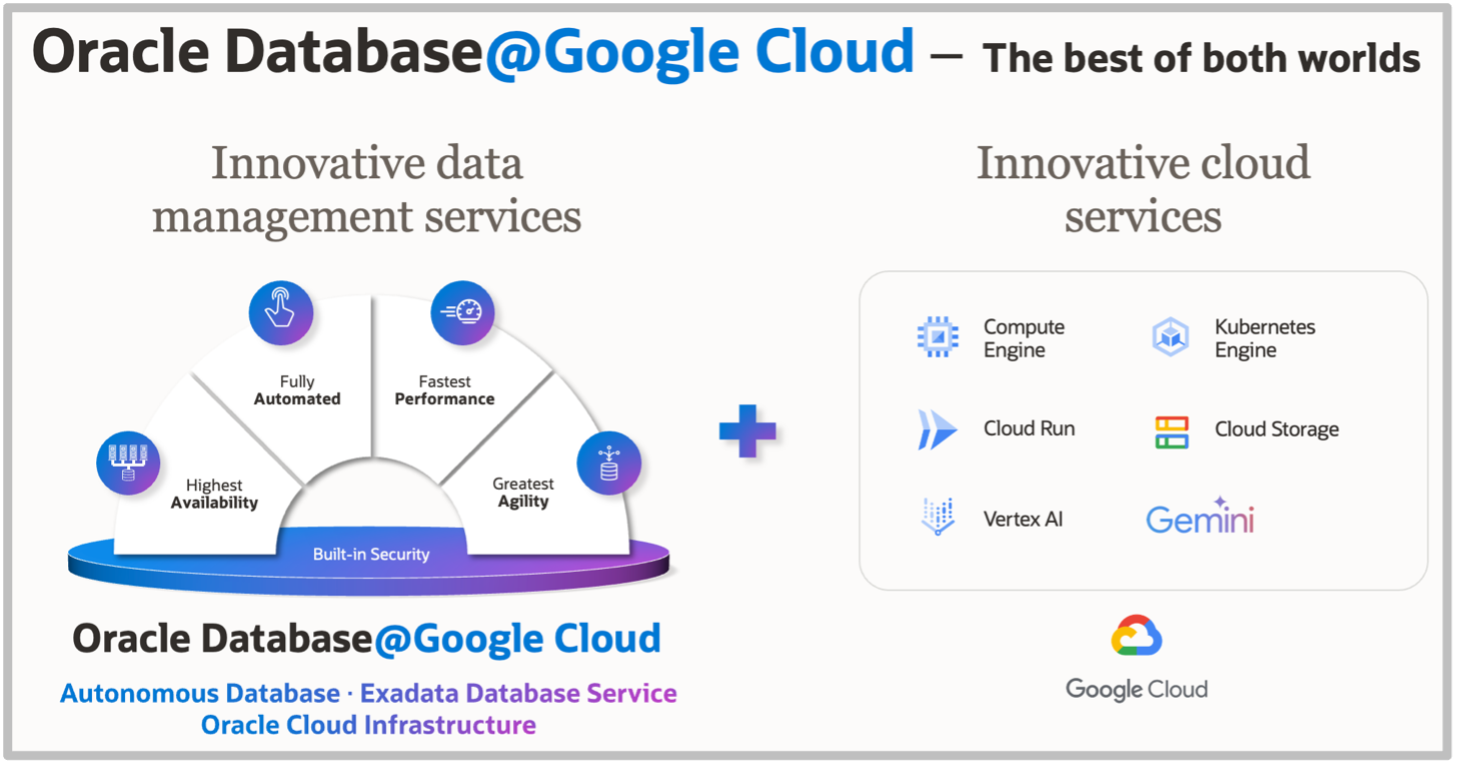
You can use Oracle Zero Downtime Migration (Oracle ZDM) to migrate on-premises Oracle databases to Oracle Database@Google Cloud and leverage full compatibility with Oracle Database and Exadata—including Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC). In addition to you running production workloads, developers can also build new cloud native applications using industry-leading generative AI capabilities from platforms like Google Cloud’s Vertex AI, Gemini foundation models, and Oracle Database 23ai which supports diverse workloads and data types and is optimized when running on Exadata.
With Oracle Database@Google Cloud, you can simplify multicloud management and operations with streamlined purchasing through the Google Cloud Marketplace using existing Google Cloud commitments. Tight integration between the Google Cloud Console and OCI lets you get started faster while most administrative tasks for Exadata Database Service can be implemented in just a few steps. Exadata Database Service requires no service interruptions for routine maintenance, and you can scale database consumption online to match workload demand – reducing both costs and downtime.
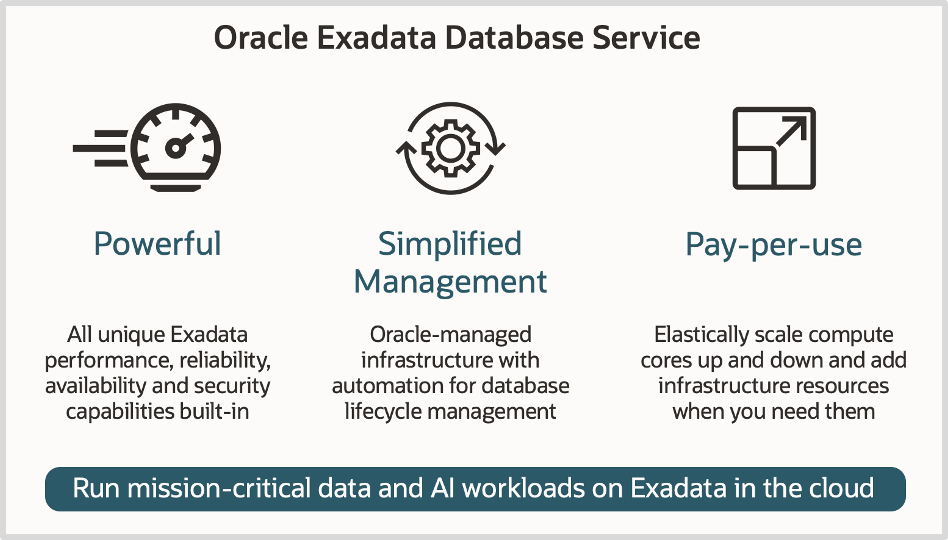
With Exadata Database Service, Oracle manages the infrastructure so you only need to manage your databases using robust cloud automation for common lifecycle management tasks. Automation implements proven Oracle Database best practices and reduces the administrative burden on you. These robust capabilities help you more easily create, scale, update, backup, and recover your databases.
Setting up Oracle Database@Google Cloud
Using Google Cloud’s private offer, your journey to Oracle Database@Google Cloud is activated with an Oracle subscription configured from your Google Cloud account or between existing Google Cloud and OCI accounts. Federating identity between these tenancies is accomplished by simply configuring permissions and roles. OCI automatically creates predefined groups with corresponding policies that will grant access to all projects within your Google Cloud entitlement.
The Oracle Database@Google Cloud architecture requires a Google Cloud project and a VPC to provide networking for application resources within a Google Cloud region. Using the OCI managed network, the VPC application subnet connects to Oracle Database@Google Cloud operating in an OCI child site collocated in the same Google Cloud region. The subnets for both Autonomous Database and Exadata Database Service extend into the OCI tenancy VCN so they are also accessible to other resources in OCI.
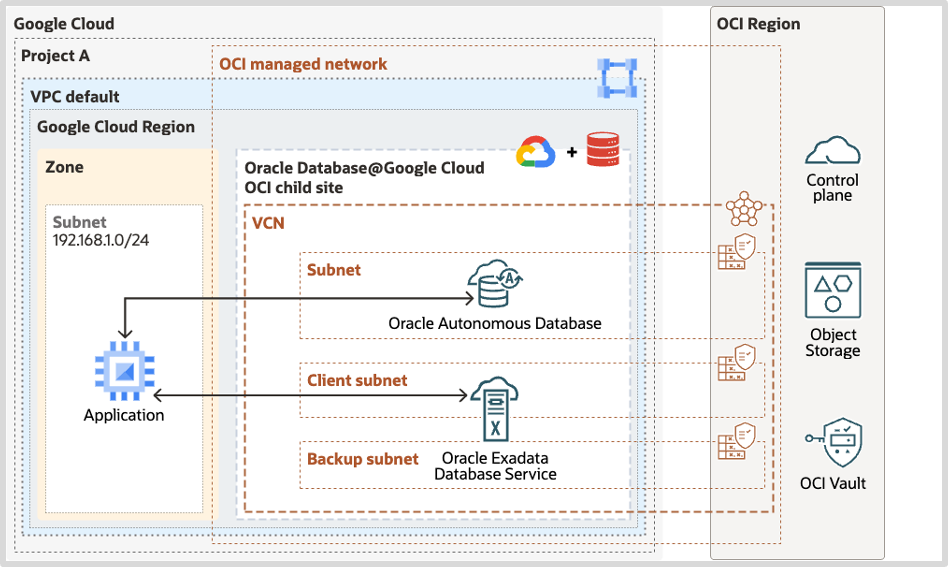
Leveraging native Google Cloud automation, it’s easy to start running Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@Google Cloud. Provisioning Exadata Database Service requires the following 3 simple steps:
- Create the Exadata Infrastructure
- Create an Exadata VM Cluster in the Exadata Infrastructure
- Create an Oracle Database in an Exadata VM Cluster
Create Exadata Infrastructure
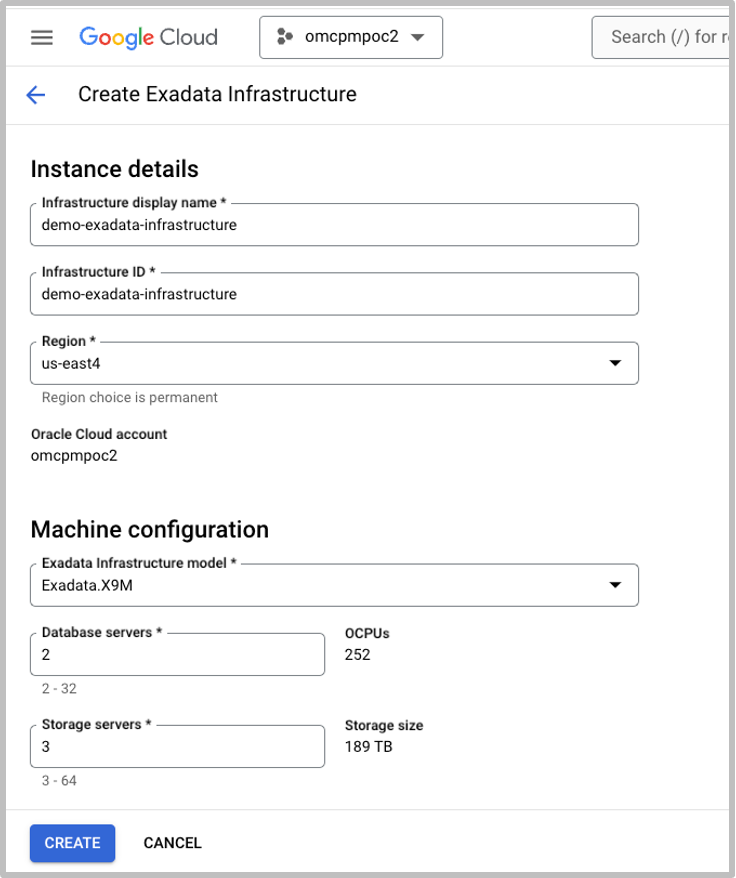
A Google Cloud project forms the basis for creating and managing all services, including configuring permissions, using APIs, and enabling billing and is required to use Exadata Infrastructure. Exadata Database Service collocated in Google Cloud supports Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure with a minimum configuration of 2 database and 3 storage servers that are internally connected by a high-speed, low-latency internal RDMA network fabric that requires no configuration. Additional database and/or storage servers can be added as needed. Exadata Database Service in Google Cloud integrates the Exadata Infrastructure with the networking resources needed to securely connect to other services in the cloud. With Exadata Database Service, Oracle performs monthly security and quarterly infrastructure updates. You can specify the quarterly infrastructure maintenance schedule that meets your business requirements.
From the Oracle Database@Google Cloud menu option, select Exadata Database to create your Exadata Infrastructure.
Create an Exadata VM Cluster
After you create your Exadata Infrastructure, you are ready to create an Exadata VM Cluster. You can create multiple VM Clusters to provide isolation for the Oracle Database workloads you consolidate on the Exadata Infrastructure. When you create a VM Cluster, you specify the compute, memory, and local storage resources and configure client and backup networks necessary to provide access to your VM Cluster and databases. To create your first VM Cluster, select the Exadata Infrastructure and click create an Exadata VM Cluster.
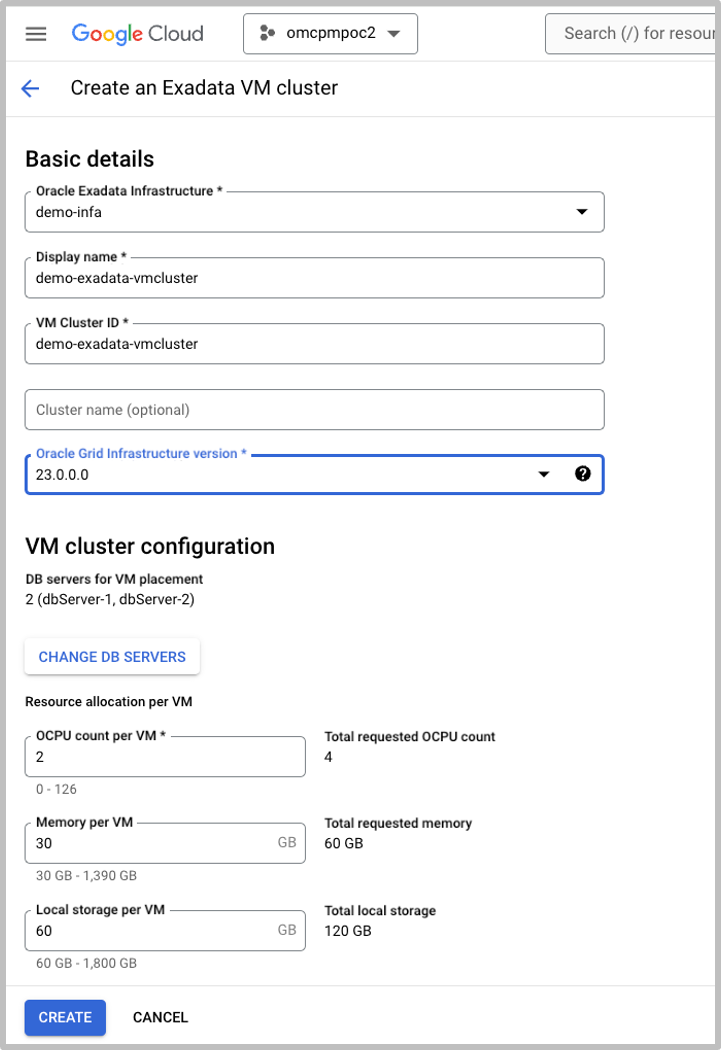
Create and Manage an Oracle Database
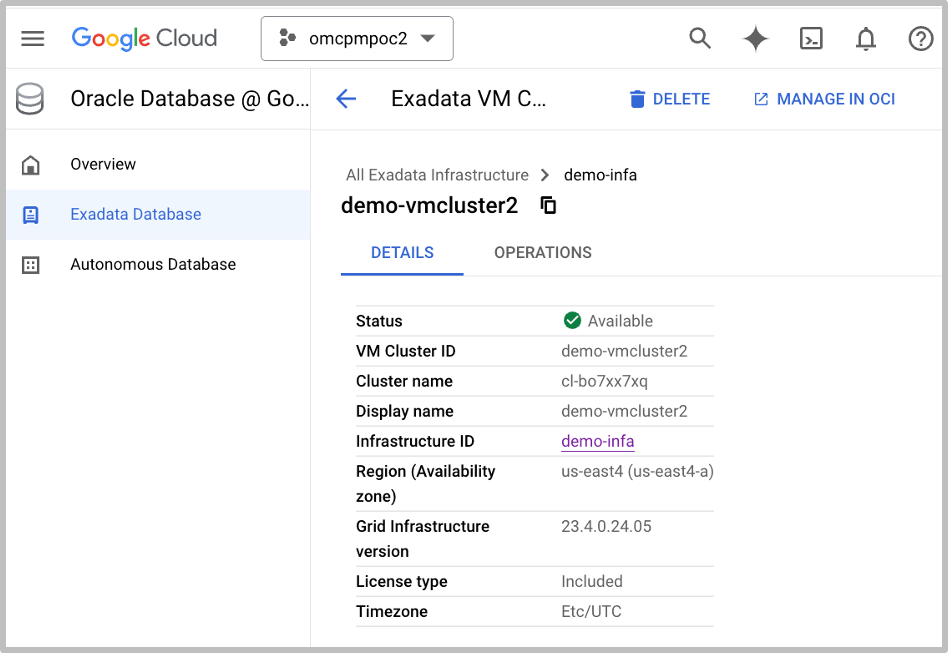
To create your first Oracle Database, select your Exadata VM Cluster and click Manage In OCI. With the Google Cloud and OCI integration, you are taken directly to the OCI Console where you will create an Oracle Database.
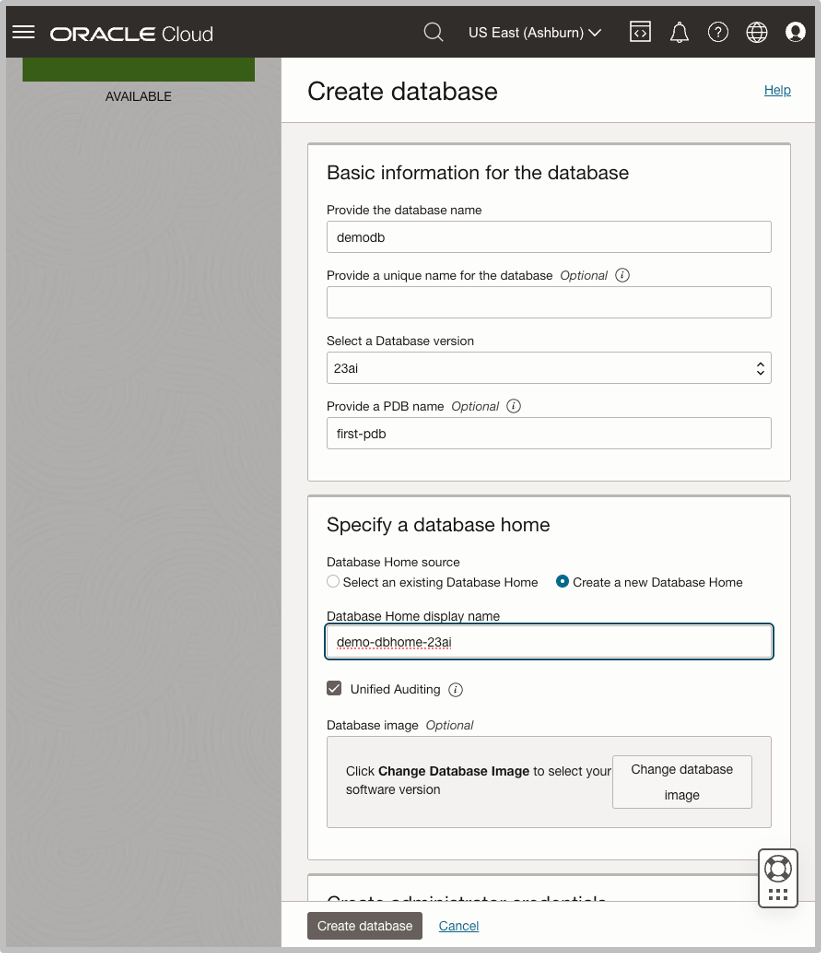
When creating an Oracle Database, you have the option to select Oracle Database 19c or 23ai. You can configure database-optimized automatic backups using the Oracle Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service, which protects Oracle Database changes in real-time and leverages an incremental backup forever strategy. Autonomous Recovery Service dramatically shortens backup windows and reduces recovery time by using virtual full backups to immediately restore instead of having to apply multiple days of incremental backups like a traditional recovery. Exadata Database Service automation simplifies backup and recovery with Autonomous Recovery Service.
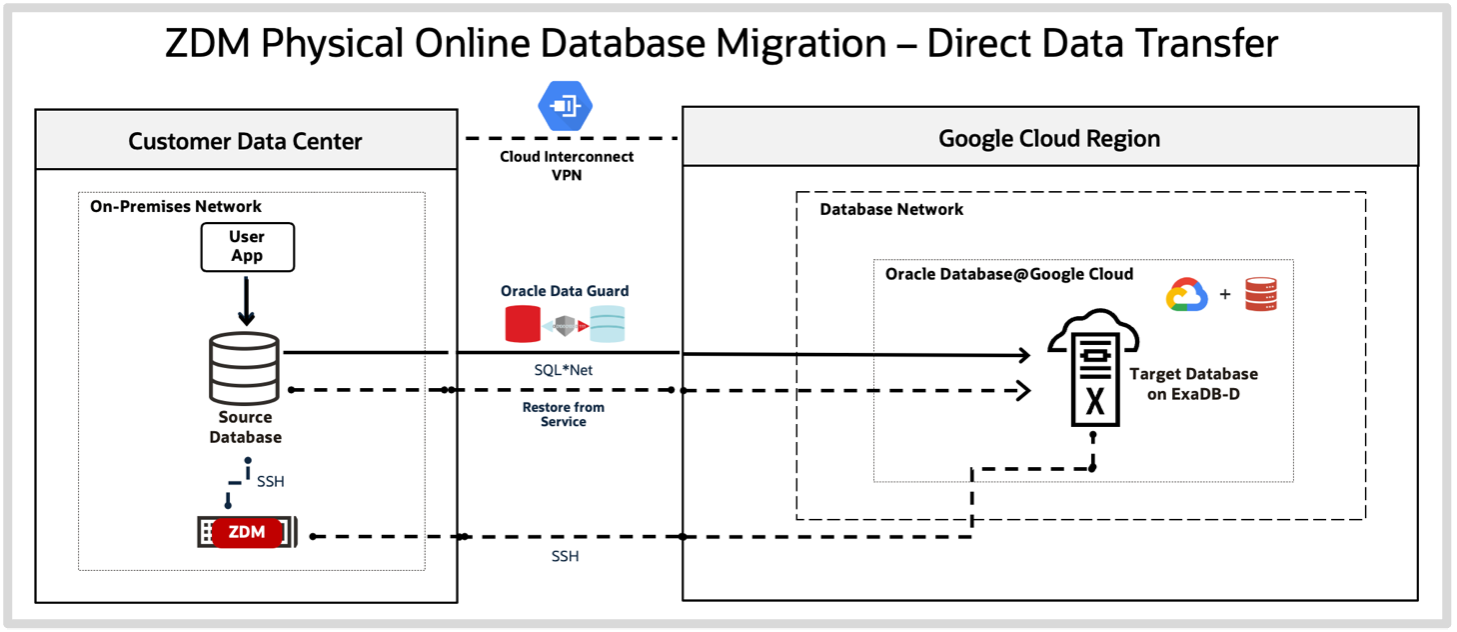
Migrate an Oracle Database
Once your Oracle Database is created, Oracle ZDM can be used to migrate your data. It deploys a replica database for your Exadata Database Service running on Oracle Database@Google Cloud that’s synchronized with your production database on-premises. Once you are ready, you switch your applications to the cloud database to complete your cloud migration.
Summary
With Oracle Database@Google Cloud, your organization can now run mission-critical Oracle Database applications in Google Cloud. You can easily migrate on-premises Oracle databases to Google Cloud and can take advantage of the high availability, performance, and scalability offered by Exadata Cloud Infrastructure. With this new deployment option for Oracle Database, you can now combine applications and services running in Google Cloud with the advantages of Oracle Exadata Database Service.
For more information:
- Documentation to deploy Oracle Database@Google Cloud in a zone
- How to Guide for Provisioning Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@Google Cloud
- Demo for provisioning Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@Google Cloud
- Demo for migrating databases to Oracle Database@Google Cloud using Oracle Zero Downtime Migration
- Oracle Database@Google Cloud web page

