OpenVPN Cloud is next-generation private networking solution that eliminates the need for installation of a VPN server. You can simply connect to OpenVPN-hosted service in any region around the world. OpenVPN Cloud is a managed cloud solution that provides secure networking over the internet between private networks and remote users in the form of a private network in the cloud.
OpenVPN Cloud provides a built-in domain name system (DNS)-based content filtering feature, Cyber Shield, which protects against threats without tunneling internet traffic. OpenVPN Cloud with Cyber Shield also helps you establish zero-trust network access by defining and enforcing identity-based policies and, for added security, it authenticates users and authorizes user access.
Features and benefits
-
Security by encrypting your DNS traffic to eliminate various DNS attacks
-
Prevent being blocked from legitimate access to websites because of using a shared and possibly blocked IP address provided by your online security VPN provider
-
Protection by allowing you to block cyber threats and unwanted content
-
Fortifies protection by letting users decide which content to block from a network
-
Includes easily accessible reporting with insights that simplify fine-tuning security measures to mitigate threats
Securing your infrastructure using OpenVPN Cloud
Without the need to set up VPN infrastructure and server or hire a team or service provider to manage the VPN network setup, you can integrate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) with the OpenVPN Cloud solution and explore the benefits.
Physical design and architecture
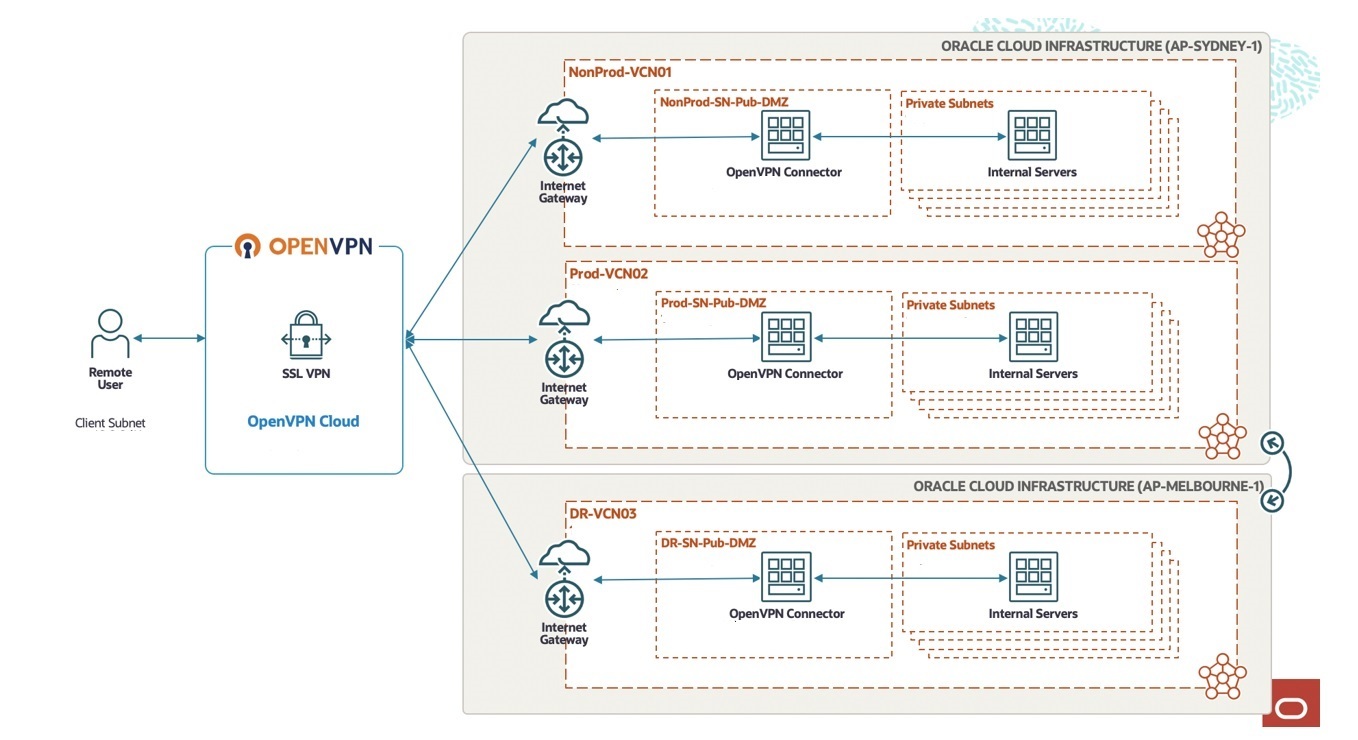
The Connector is installed on an OCI virtual machine (VM) instance in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) subnet and the same virtual cloud network (VCN) with the internal servers. The public subnet DMZ is connected to the internet by the OCI internet gateway that provides the Connector with access to the internet and OpenVPN Cloud. IP forwarding is enabled on the Connector. The network address translation (NAT) is chosen as a packet response approach because all traffic sessions are initiated by the remote client. NAT is also enabled on the Connector instance.
Logical design and architecture
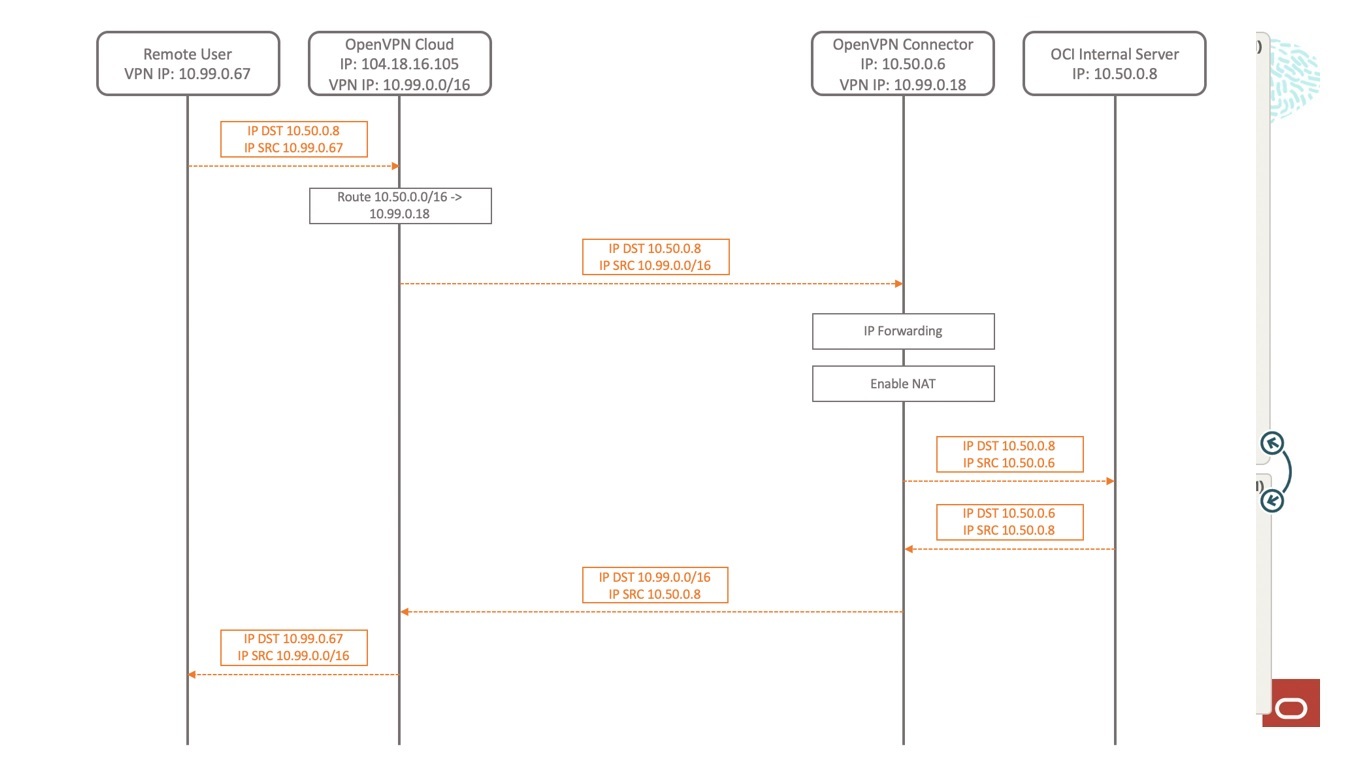
A remote user accesses the OCI internal server. Because the internal server is in the OCI VCN network, the packet is routed through the VPN interface. When OpenVPN Cloud receives the packet, it checks its routing table and directs the packet to the Connector in the OCI VCN because the destination IP address is in the subnet configured for the OCI VCN.
The Connector instance forwards the received packet on the LAN interface to reach the OCI internal server. The Connector instance substitutes its IP address for the source IP address. After receiving the response, it switches the destination to the source IP.
The packet now gets forwarded by the Connector instance and undergoes NAT so that when the packet is received by the internal server, it doesn’t need to forward the response to the router and instead sends the response back to the Connector instance. After receiving the response, the Connector instance translates the destination and can forward the response on the VPN interface.
The response reaches the Connector instance and is sent to OpenVPN Cloud. OpenVPN Cloud forwards the packet to the remote user.
How to set up site-to-site private network
-
Create an OpenVPN Cloud account and select an identity for your cloud.
-
Go to the Shield section and turn on blocking dangerous and unwanted categories.
-
Configure site-to-site private connectivity.
-
Add networks and their IP address ranges using the OpenVPN Cloud Administration portal.
-
Install the Connector software on Linux, Windows, or macOS hosts in OCI and connect them to any one of our worldwide VPN regions.
-
Enable routing and add static routes for reachability.
-
Access the admin portal to allow hosts and networks to connect to VPN.
-
Add users to your network to connect to the VPN and access the required resources.
-
Using the user portal, download and launch the OpenVPN Connect app.
- Add a profile in the Connector app using your OpenVPN Cloud URL, authenticate, and select a region to connect.
Conclusion
OpenVPN Cloud provides secure access worldwide with constant protection against cyber threats and quick full-mesh connectivity to on-premises or infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) cloud private networks without requiring capital and operational hours to manage, scale, and host VPN servers.
For more information on OpenVPN and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, see the following resources: