Last fall, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) introduced OCI Cache, enabling customers to launch new Redis clusters and scale them, both in terms of memory and nodes, without downtime. The service offers easy cluster creation, scaling, and automated high availability. With its in-memory key value store, it speeds up data retrieval by accessing data stored in memory rather than performing disk operations on a database, thereby reducing the load on disk resources. OCI Cache can help boost your application response time with submillisecond latency.
Since its launch, OCI has implemented several enhancements, making the service even more robust and user-friendly. Let’s look at some of the key new features that have been added.
Network security group support
A network security group (NSG) provides a virtual firewall for a set of cloud resources that all have the same security posture. For example, a group of compute instances all perform the same tasks, so they all need to use the same set of ports.
OCI Cache now supports NSGs that provide a mechanism for controlling network-level access to your data caches. By managing traffic flow, NSGs aim to contribute significantly to the overall security posture of your applications, complementing other access control measures within the system. This support helps ensure that sensitive data is shielded from unauthorized network access, while maintaining the high availability and performance of OCI Cache. OCI Cache allows customers to specify NSGs during cluster creation or updates to existing clusters by adding or removing NSGs, as shown in Figure 1.

You can specify up to five NSGs per cluster, offering flexibility in managing network traffic and providing tighter security.
Lua scripting support
Redis is known for its capability to run Lua scripts on the server, allowing complex operations across multiple keys in a single transaction, and enables efficient reading and writing of cluster data. Often, developers use libraries that rely on Lua without even realizing it. With the recent update, OCI Cache now supports Lua scripting for all managed Redis clusters. This feature is available by default, providing customers with enhanced functionality without any additional configuration.
Sharding support
Sharding, or cluster mode, is a well-known feature of open source Redis, which allows data to be distributed across multiple nodes for improved performance and scalability. Previously, OCI Cache only supported Redis in non-sharded mode. Now, customers can choose between sharded and non-sharded configurations at the time of cluster creation, as illustrated on Figure 2.
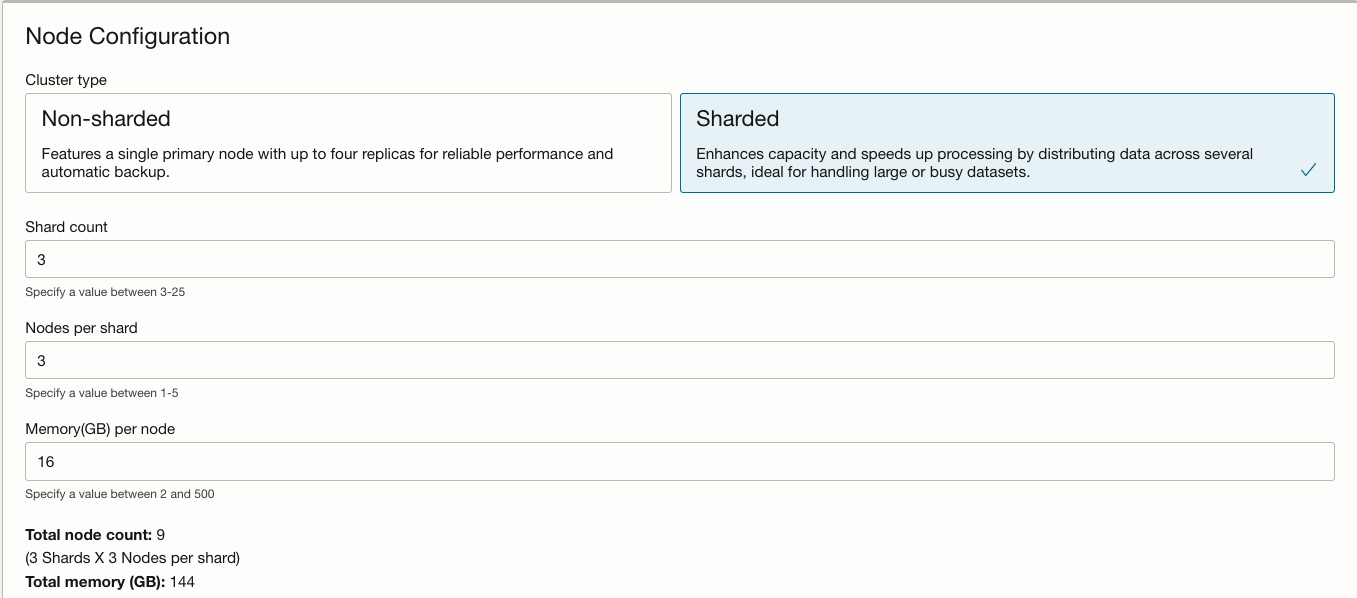
Sharded clusters have three or more shards, with the data split across the shards in the cluster, so that each shard holds part of the data. Each shard is like a cluster, with one primary node and up to four replica nodes. Sharded clusters support scenarios where you need to store more data than the 500GB limit, because while these clusters are still limited to the 500GB of memory per node, it’s really 500GB per shard.
After a cluster is set up, customers can resize shards as needed. OCI Cache automatically launches new servers, add them to the sharded cluster, and move data accordingly, all without any downtime and benefit from boosted performance. Additionally, customers can independently resize nodes (per shard) and memory (per node) within sharded clusters, providing granular control over resource allocation.
Key Takeaways
The continuous enhancements to OCI Cache reflect Oracle’s commitment to providing a highly scalable, secure, and user-friendly caching solution. By introducing support for NSGs, Lua scripting, and Sharding, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Cache is now more versatile and powerful than ever, offering customers the tools they need to optimize their Redis deployments with ease.
To learn more, see the following resources:


