Blog was co-authored by each of the follow:
Michael Hernandez – Master Principal Cloud Architect, Oracle on Oracle
Premkumar Kancheepuram Sivaprakasam – Principal Cloud Architect, BigBets
Picture archiving communication system
The picture archiving communication system (PACS) is a system that electronically collects, stores, and reports from multiple imaging modalities. Having a PACS solution allows imaging specialists to make a faster diagnosis, leading to rapid care of their patients and an accelerated patient recovery time. These images are protected under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), so they need to be encrypted both at rest and in motion. You can achieve encryption by placing the images on a secured, encrypted network for transferring and uploading images. PACS allows specialists to view their patients’ images from a secured workstation to study how to better serve their patients. Supplementing with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can further enhance visibility and enhance speed to analysis while decreasing human error and manual curation.
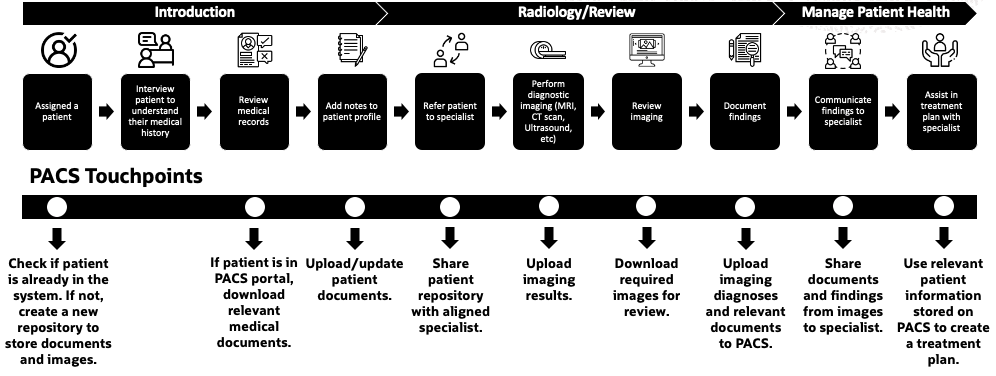
Steps of the specialist journey
-
Specialist is assigned a patient and checks to see if the patient profile exists. If a patient profile doesn’t exist, create a repository to store medical records and images.
-
The specialist hosts an interview with the patient to discuss previous medical history and what brings them in to see a specialist. All notes are documented.
-
If the patient has medical records or images already uploaded, then the specialist downloads these documents for review of what treatment has been done in the past.
-
Specialist uploads or updates all new and old medical records to the patient’s profile.
-
After the review of the patient’s current and previous health records, the specialist aligns the patient to a treatment specialist. Share the patient profile with the aligned treatment specialist.
-
If needed, the specialist places an order for diagnostic testing to be done on the patient. Upload all images to the patient profile.
-
The diagnostic testing images are then downloaded by the specialist for thorough review.
-
The specialist documents the diagnosis and uploads recommended treatment to patient profile.
-
The specialist shares the diagnosis and reviews it with the treatment specialist.
-
Using the patient’s medical records, images, and diagnosis, the specialist and treatment specialist create a treatment plan for the patient.
Current industry challenges
Today’s microscopy is marred with challenges, such as difficulties in integrating multiple units and applications both within and between hospitals as a single source of truth. Most health care systems or applications aren’t equipped to share large amounts of medical images (unstructured data) with growing digital demand needs from the end consumer. Issues arise when integrating imaging sources with other hospital systems, limited storage capacity, access issues such as synchronous, multiple, and remote access, solutions for backup and recovery, and problems in data migration.
Most enterprises store images in raw format, in cloud-based or on-premises storage, from back-up or archive. These issues prevent the business from looking for new opportunities and revenue streams. To innovate and modernize the business, we need to identify meaningful patterns to accelerate patient treatment by using automation and AI and ML techniques that helps a specialty clinician decide faster.
The industry also faces the following challenges:

-
Infrastructure demands: Storage requirements outpacing budgets, data security and adherence to compliance requirements, and slow and inconsistent retrieval from different locations.
-
Regulation and data protection: Restoring data from traditional backups often failing, unequal protection of business and mission-critical data, access to traditional offsite services too slow, and uneven data security and security management.
-
Cloud service provider: Limited service level agreements for data and vendor lock-in with proprietary APIs.
How Oracle cloud solutions provide business value for PACS systems
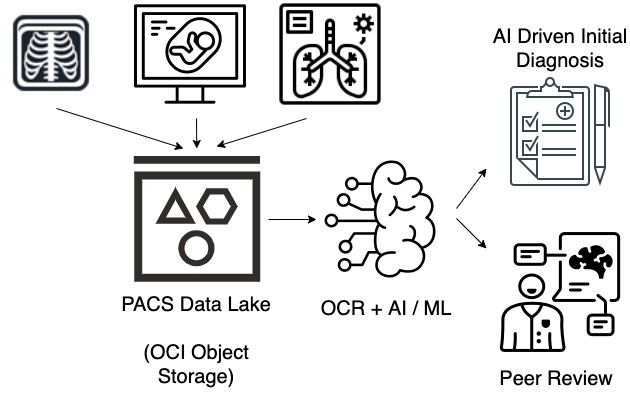
The power of AI and ML can address various complex medical imaging problems, such as image segmentation, detecting the borders of the scanned images, and anomaly detection, automatically scanning images and returning analysis. AI and ML can extract the relevant information from the medical images and relay the AI-assisted diagnosis to medical personnel. This assisted diagnosis only needs the peer review of medical personnel, saving time in diagnosis and communication of information to the patient.
The use of AI in the medical field has the following benefits:
-
AI analysis to quickly provide initial results to doctors for prioritization
-
DICOM imaging, including x-rays, CT, ultrasound, and MRI studies. Data analysis holds the key to identifying diagnostic and therapy insights.
-
Advanced analytics using AI and ML algorithms for anomaly detection can help identify deviation.
-
Quickly index and search through billions of images and studies. Use natural language processing (NLP) tools to extract medical information from unstructured reports.
-
Create and curate cohorts of relevant research data based on patterns without using personal identifiable information (PII).
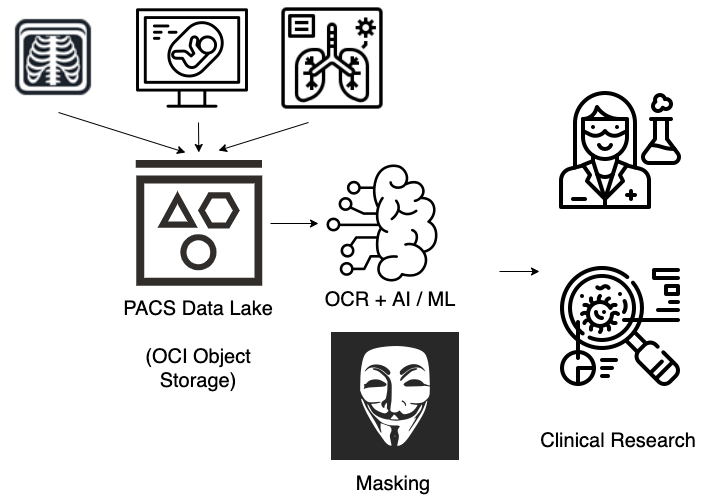
-
Deidentify large amounts of pixel data (DICOM images) to provide information to clinical research workflows.
-
Identify text strings from images containing PHI data and mask PHI data.
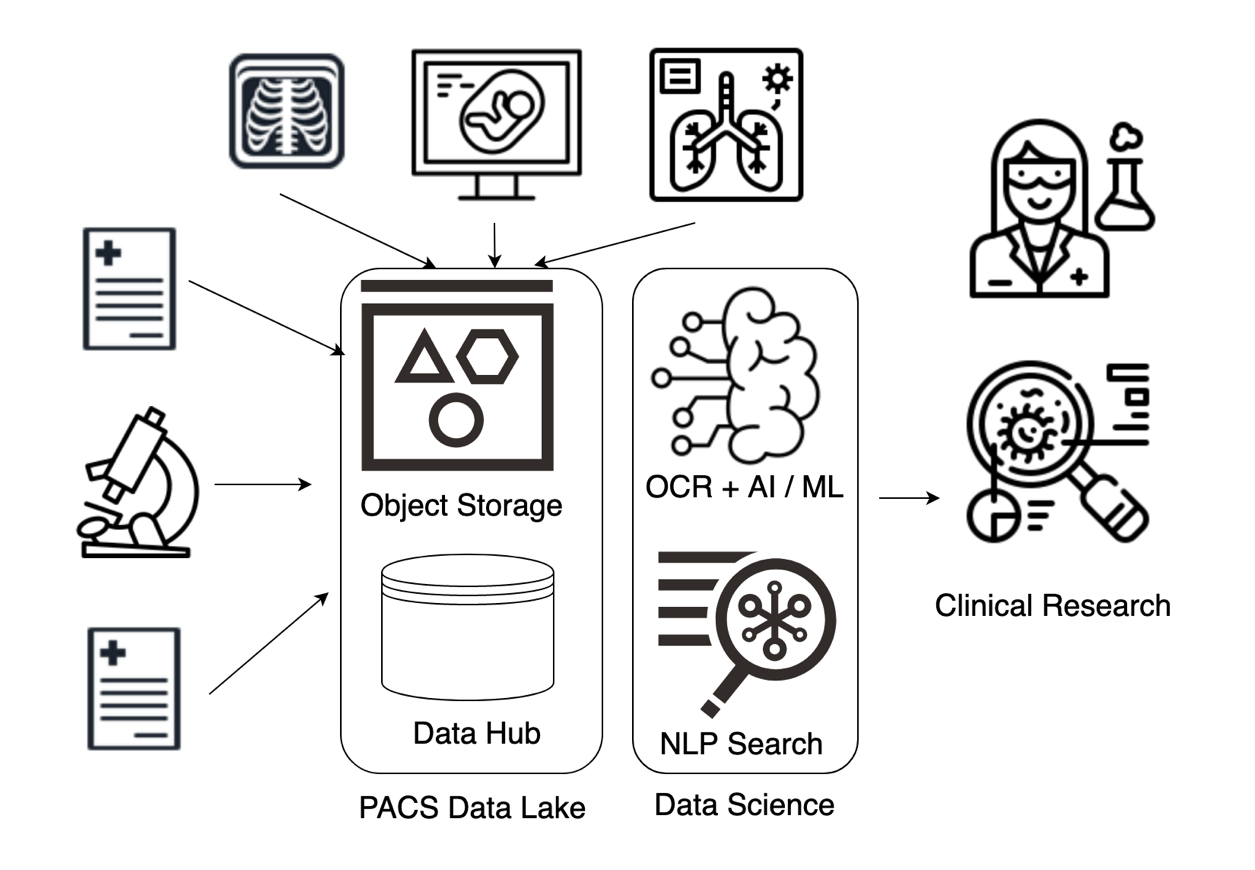
To support the demands from the business in a timely fashion, data from different siloed applications needs to be aggregated and transformed. Enterprises need to invest in building a modern data platform such as a data lake house using cloud services. This transformation provides valuable insights to help the business explore new models and markets.
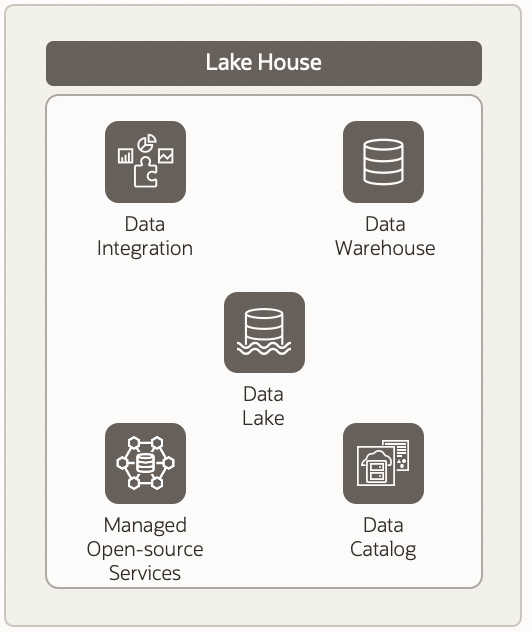
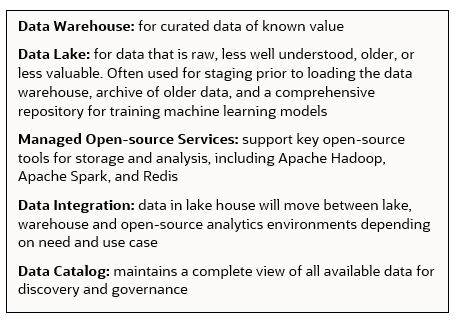
The following graphic provides key high-level capabilities and a process flow for building a modern data platform in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI):
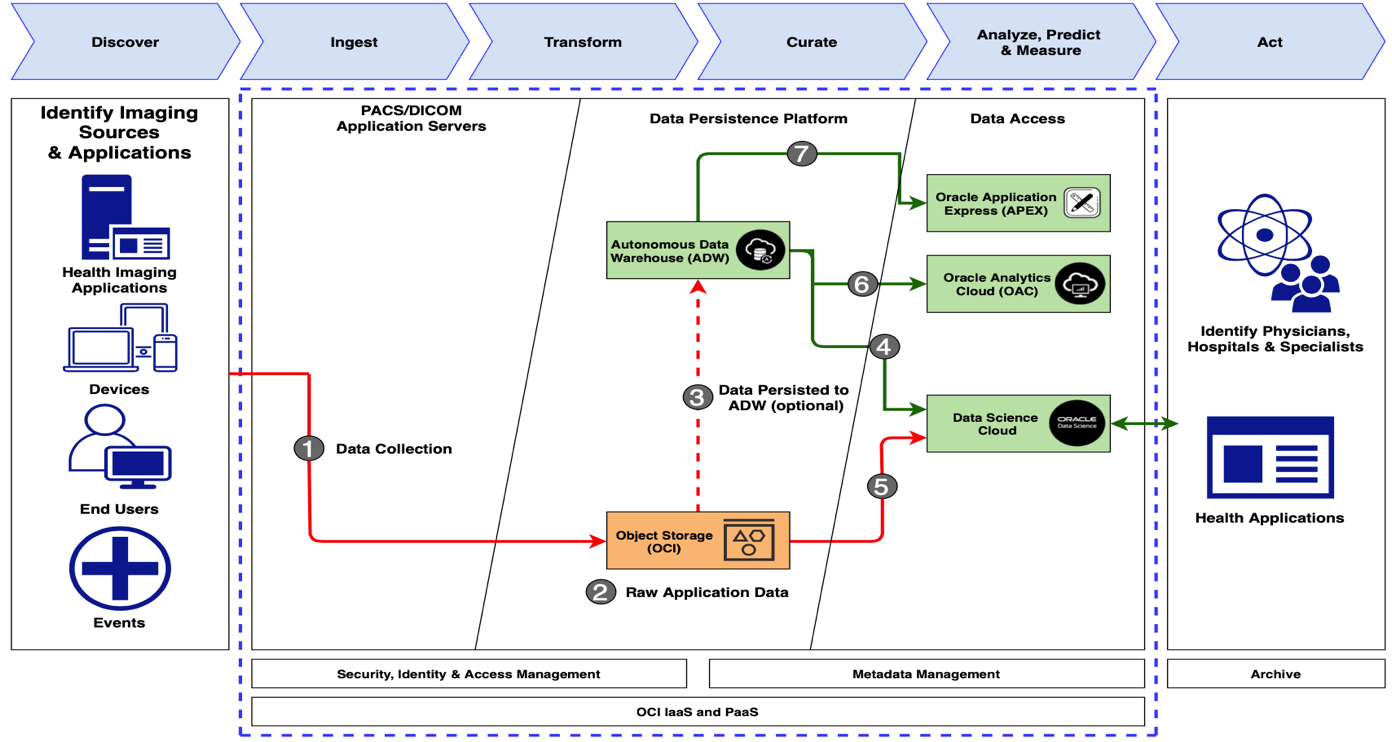
-
Data is collected from imaging modalities (MRI, CT, ultrasound, and so on).
-
Data is sent to OCI Object Storage service where it’s cleaned and reindexed.
-
Indexed data is sent to Autonomous Data Warehouse or directly to Data Science Cloud for AI and ML capabilities.
-
Autonomous Data Warehouse sends data to Oracle Analytics Cloud where it can be manipulated to display a multitude of informative visualizations.
-
Autonomous Data Warehouse sends data to Oracle APEX, where it can be transformed into various healthcare applications.
How to get started with an OCI PACS data lake
Oracle offers a highly available and fault-tolerant solution, which is provided by storing images on OCI Object Storage. Oracle guarantees that Object Storage is available more than 99.9% of the time. Object Storage can store as many patients’ records as the doctor wants. Oracle’s inexpensive and available storage allows doctors to only pay for what they use while utilizing all the benefits the cloud offers: Flexibility, scalability, data sovereignty, and compliance.
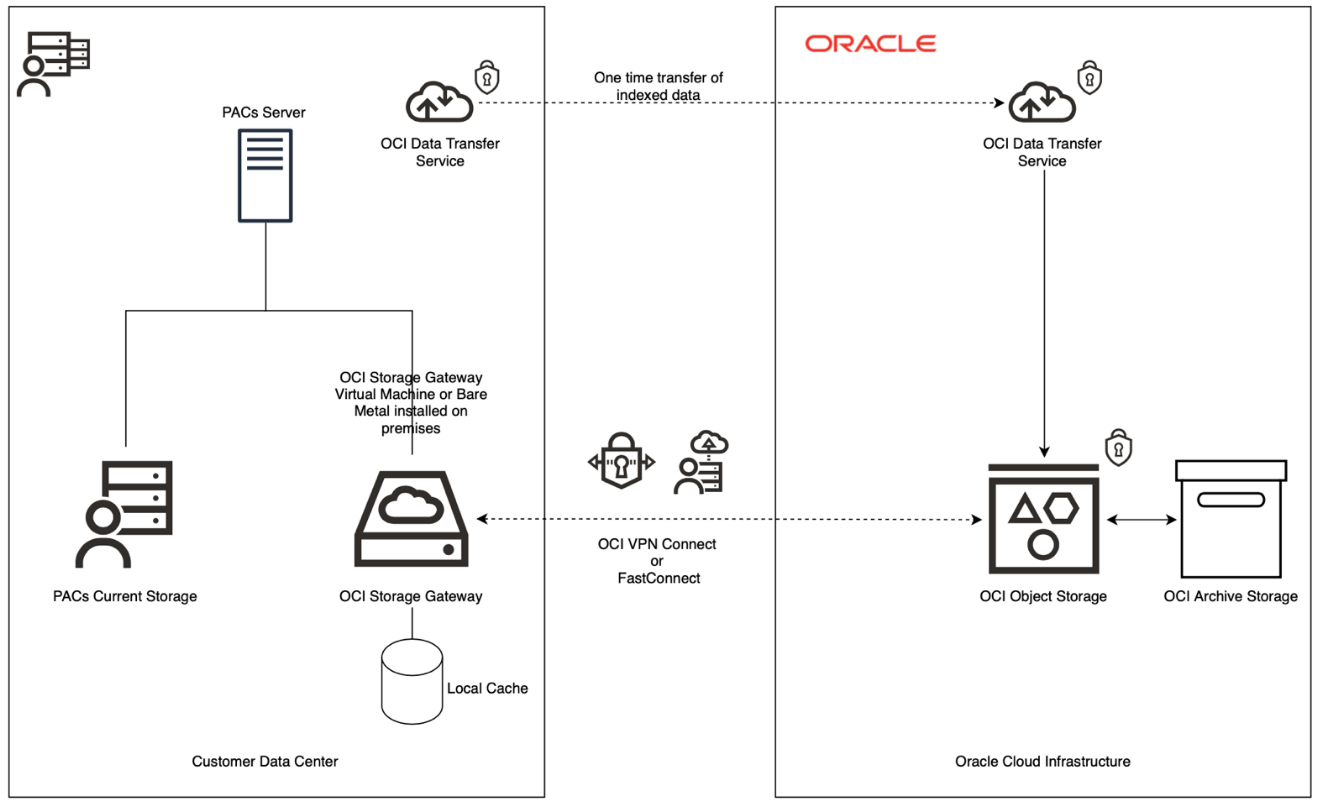
Oracle’s PACS solution begins by mounting an encrypted Oracle Data Transfer service appliance in the customer’s data center. The appliance copies and reindexes data from the PACS current storage unit to the Data Transfer service.
The indexed data in Data Transfer is then exported to OCI to move into OCI Object Storage. With storing large amounts of data on Object Storage, Oracle also attaches OCI Archive Storage to store longer-term data. Archive Storage has a lower price point than Object Storage and grants the doctor the ability to determine when to move customer records to long-term, such as 30 days. If a doctor’s patient needs to be viewed years later, the doctor can store this information at a low cost and retrieve the patient’s data before the patient’s appointment.
When the Data Transfer finishes reindexing the data, Oracle Storage Gateway mounts a storage gateway in the customer’s data center. This gateway allows the customer to connect their on-premises applications with OCI. This connection is encrypted by using Oracle VPN Connect or FastConnect. The storage gateway reads and writes data securely to OCI Object Storage, without requiring application modification for REST APIs.
The customer can pull or push data securely between their storage gateway and Object Storage in real time. Oracle’s PACS solution offers the secure storage of patient medical records and a modern and affordable system entirely in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Patient data is always HIPAA-compliant and can be analyzed from anywhere.
Final remarks
Oracle’s PACS solutions allow customers to electronically collect, store, and report from multiple imaging modalities in Oracle’s secured cloud environment. This ability results in faster diagnosis, leading to rapid care of patients and an accelerated patient recovery time. PACS is HIPAA-compliant, so data needs to be encrypted both at rest and in motion. Images are placed on a secured, encrypted network for transferring and uploading images. Specialists unlock the ability to view their patients’ images from a secured workstation to study how to better serve their patients. Supplementing with AI and ML can further enhance visibility and enhance speed to analysis, while decreasing human error and manual curation. Oracle’s affordable, highly available, and fault tolerant PACS solution guarantees seamless care between specialists and their patients.
For more information on the Oracle services involved in this solution, see the following resources:

