We’re excited to announce a new release of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Data Integration. This release adds new transformations, connectors, and two of the most highly requested features by our customers: Pipelines for orchestration and schedules for scheduling data integration tasks.
Cloud native, serverless integration
OCI Data Integration is a cloud native, fully managed serverless extract, transform, and load (ETL) solution. Organizations building data lakes for Data Science on OCI and departments building data lakes, data marts, and data warehouses using Autonomous Databases can gain great business value by using a solution that can simplify, automate, and accelerate the consolidation of data for use.
OCI Data Integration is graphical, providing a no-code designer, interactive data preparation, profiling options, and schema evolution protection, all powered by Spark ETL or ELT push-down running. If you’re not familiar with this new service, check out this blog to find out more: What is Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Integration?
OCI Data Integration is available in all OCI commercial regions.
Pipeline and orchestration
A pipeline is a design-time resource for connecting tasks in a sequence or in parallel to facilitate a process. It manages and orchestrates the execution of a set of related tasks and processes. To construct the overall orchestration, you can add data loader and integration tasks, set up sequential or parallel execution paths, and define how errors are handled in your pipeline. Pipelines support runtime parameters, which can pass through the UI, APIs, or schedules.
A parameter is a type of variable that you can assign to an operator’s details, so that you can reuse the data flow or pipeline design in Data Integration with different resources and values. When you use parameters and set default values during design time, you can change the values later, either in tasks that wrap the data flow or pipeline or when you run the tasks. This option can save significant amounts of time designing data integration processes and maintaining them as the business evolves.
You can create a pipeline from the home page or through projects.
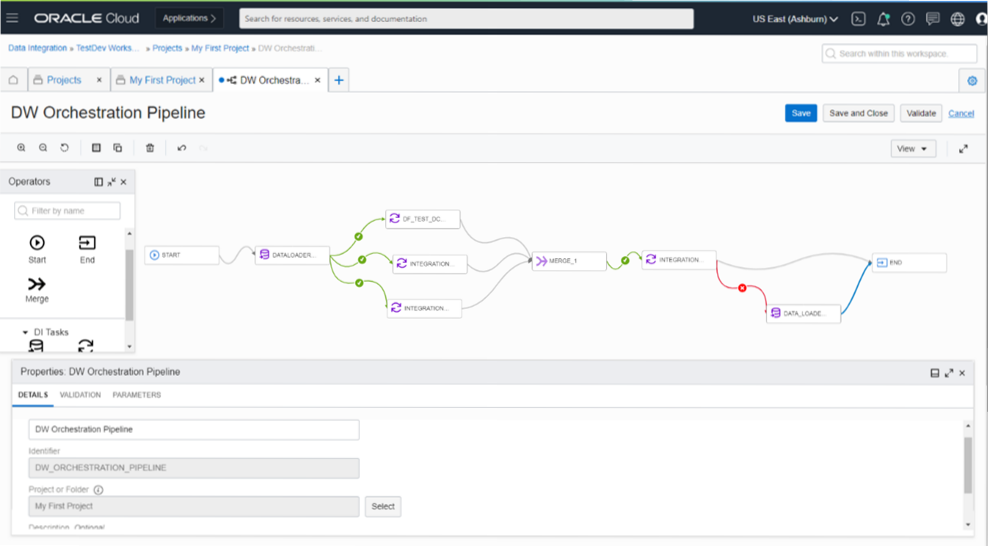
Figure 1. Pipeline editor
A task is a design-time resource that specifies a set of actions to perform on data. You then publish tasks into an application to test them or roll them out to production.
Specifically, this release adds the pipeline task, which allows you to take your pipeline design and choose the parameter values you want to use at runtime. You can select your pipeline, optionally configure parameters with new values or skip to use values set, and then validate the task to ensure that settings are correct.
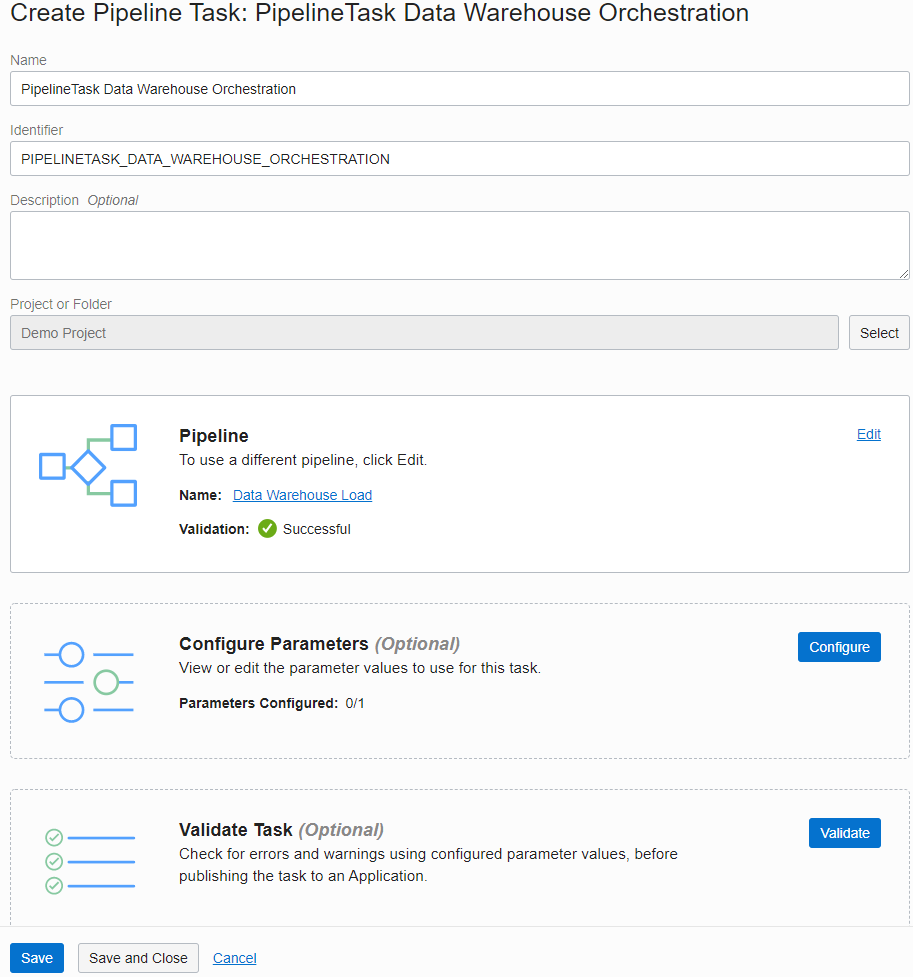
Figure 2. Pipeline task editor
Scheduling
We’re happy to add scheduling capabilities to this release. A schedule is a runtime resource that defines when and how often any published tasks run automatically. You have options for frequency: Hourly, daily (repeats every N days at a specific time), or monthly (repeats every month on a specific day at a specific time). After publishing tasks to an application, you can run a task manually on-demand or use schedules to automate when your tasks run. You can create a schedule by selecting a time zone and configuring the frequency at which the associated task schedules run.
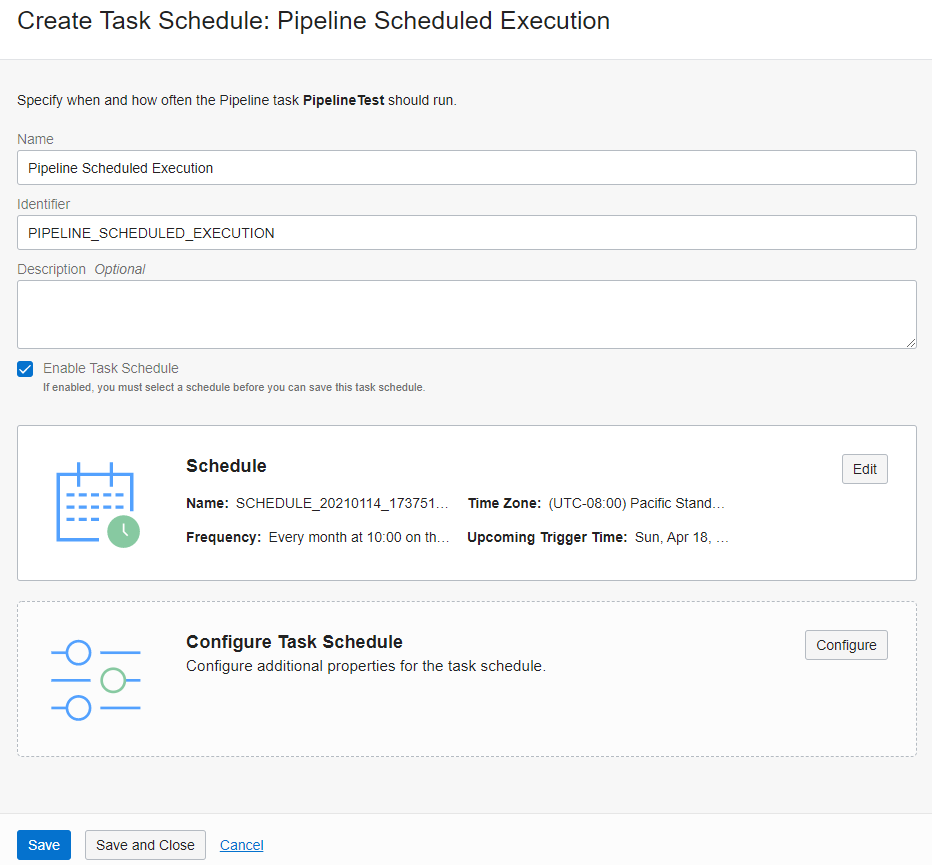
Figure 3. Scheduling a pipeline task
A task schedule also associates a published task with a schedule. The task schedule is associated with a specific published task, such as data loader, integration, and pipeline tasks, and an existing schedule to define when and how often the task runs automatically.
To bring more sophistication to your data integration processes, you can reuse schedules across multiple task schedules. You can manage and monitor these task schedules in Data Integration.
Connectivity and transformations
Data Integration also now supports Amazon S3.
We continue to work on providing more transformation and operator options. This release adds the following features:
-
Split: Divides one source of input data into two or more output ports based on split conditions that are evaluated in a sequence.
-
Lookup: Performs a query and then a transformation using an input source, a lookup source, and a lookup condition.
-
Full SQL pushdown: All transformations defined in a data flow are pushed down to databases, and the data moves directly from the source database to the target database. OCI Data Integration now supports full SQL push-down processing when the source and target databases are the same data asset such as an Autonomous Data Warehouse instance.
These operators allow you to quickly and easily express complex transformations. Check out the full review of OCI Data Integration operators.
These major enhancements for OCI Data Integration round out functionality, well before the service is even one year old. Stay tuned for more!
Want to know more?
Organizations are embarking on their next-generation analytics journey with data lakes, autonomous databases, and advanced analytics with artificial intelligence and machine learning in the cloud. For this journey to succeed, they need to quickly and easily ingest, prepare, transform, and load their data into Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Data Integration’s journey is just beginning! Try it out today!
For more information, review the OCI Data Integration documentation, associated tutorials, and the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Integration blogs.
