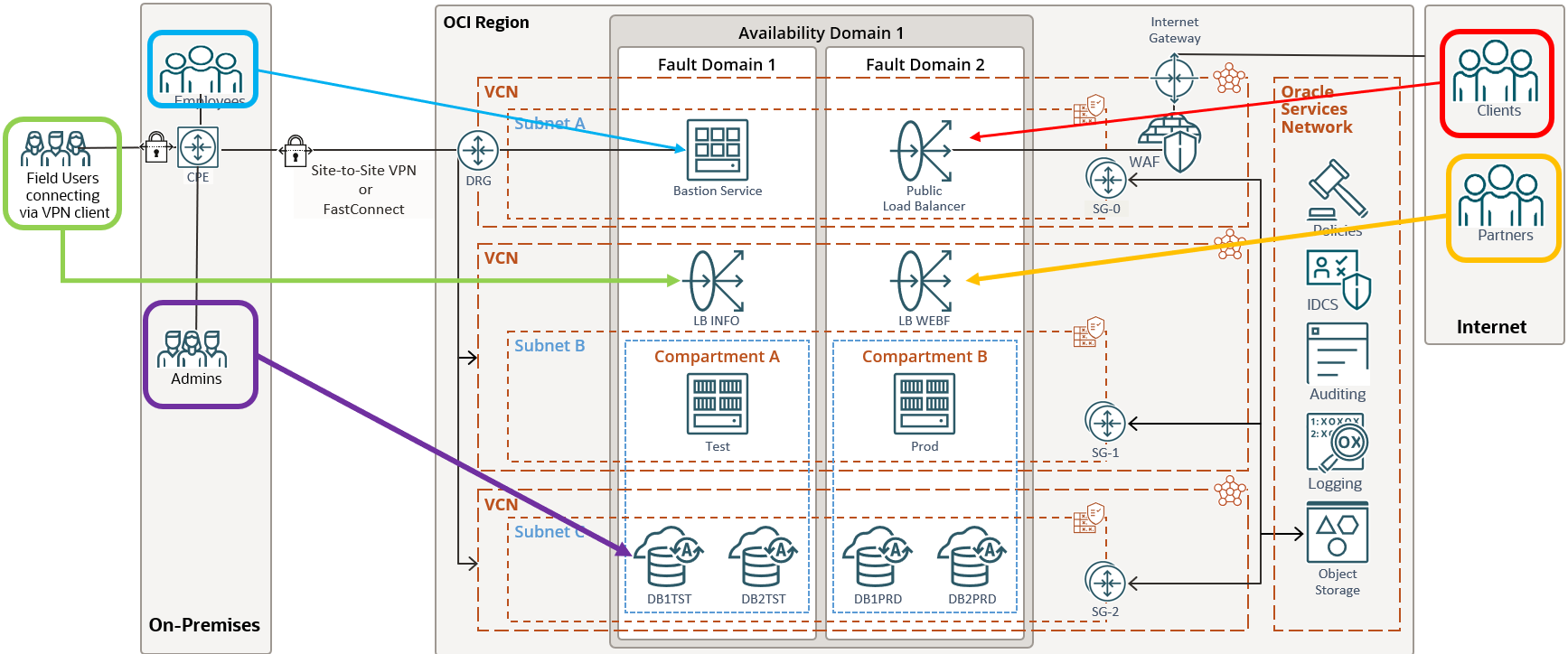
A recent study indicated that the global average cost of a single data breach is nearly US$4.45 million, and it’s getting more expensive each year. In Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), security is a foundational feature, and customers have no compromise between security and cost. OCI offers several security options to help ensure protection at all layers, such as the data center, physical hardware, network, OS, storage, database, and application access.
One of the fundamental ways of securing any infrastructure is by securing the network traffic. OCI controls network traffic at packet level with security lists at the subnet level and with network security groups (NSGs) at the virtual network interface card (VNIC) level. OCI also provides a smart, no-cost feature called “network sources” to manage access to OCI resources based on the IP address. A network source is an originating IP address or IP range that you can reference in a policy or tenancy authentication settings to control access to OCI based on the originating IP. These can be private IPs from within OCI (east-west traffic) or public IPs (north-south traffic).
Network source example use case
You have a set of users who need access to OCI resources. However, these users work in the field and connect through devices from the field using public networks, making their devices vulnerable to security breaches while accessing OCI network. One way to contain this issue is providing access to OCI through the corporate VPN to which the users can log in using the corporate sign in process. How does network source get involved? You can use the corporate VPN IP range to create a network source in OCI, which can be then used to define a policy in OCI to allow access for the field users to OCI, if and only if they’re accessing OCI resources through the corporate VPN (IP range in the network source).
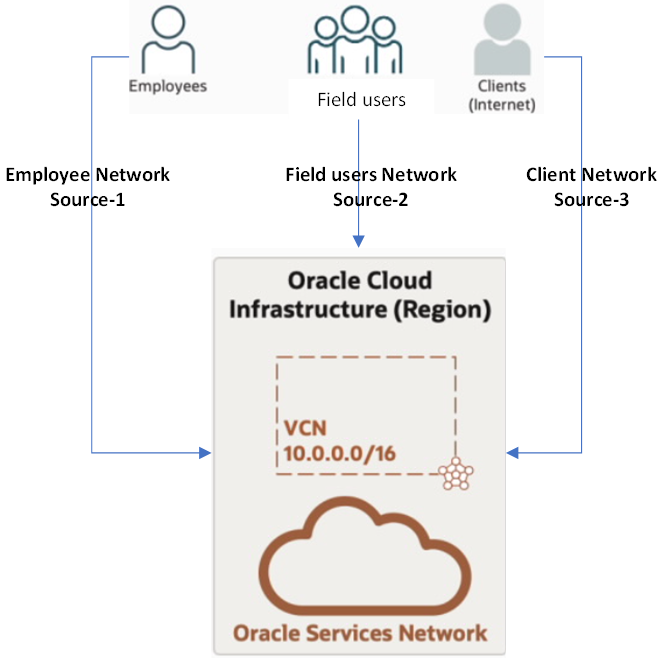
You might argue the corporate VPN is still being used for protection. However, the network source provides an extra layer of security by not allowing any user to bypass the corporate VPN to access OCI resources.
The following figure visualizes the advantage of the extra protection that network sources provides when various users require access to different types of OCI resources.
Let’s set up some network sources.
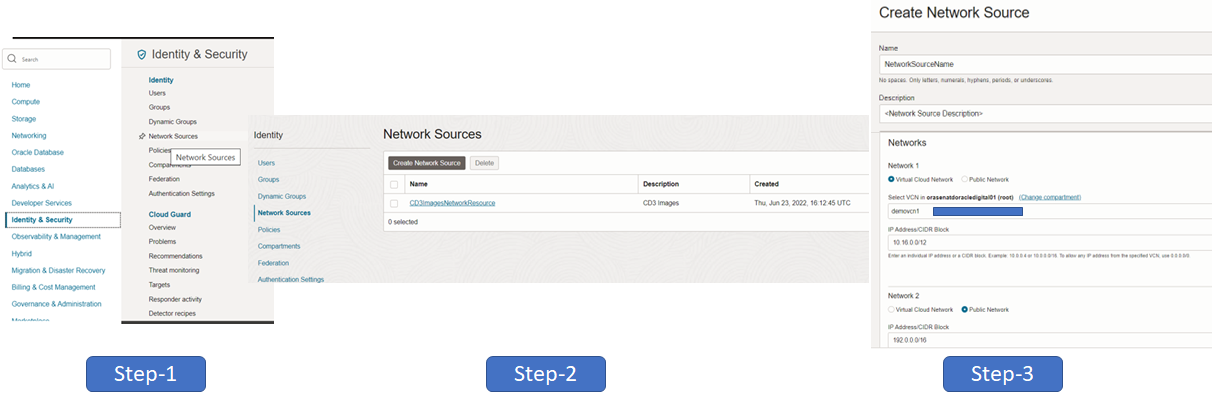
Create a network source
In the Oracle Cloud Console, under Identity & Security, select Network Sources. Here, you can either create network sources or manage existing ones. To create a network source you need to provide a name for the network source and a meaningful description. Then under Networks you need to select an OCI VCN (for entering private IP’s) and/or public IP’s to create the network source. You may add a mix of public and private IPs in the same network source, if required.
While all users in the Administrators group have the required access for managing network sources, you can also control access to network sources through policies using the network-sources resource type, such as “Allow group <group-name> to manage network-sources in tenancy.” This policy allows all users in a group to create and administer network sources in OCI.
You can only create network sources in the tenancy or root compartment, and they reside in the home region but can be used across the tenancy.
Write policies to manage access to OCI resources through the network source
Consider the following policy:
Allow group <group-name> to <inspect/read/use/manage> instance-family in tenancy where request.networkSource.name='<NetworkSourceName>'
This policy allows users in a particular group to access and manage Compute instance resources, such as instance-family, only when their requests originate from an IP address allowed in the network source specified by “request. networkSource.name.” You can use network source-based policies to restrict access to resources of all OCI services .
Other use cases
In large companies dealing with highly confidential and proprietary data and information, network sources provide an easy way to provide another layer of security to restrict access to sensitive data and make it accessible only to specific group consisting of specific personnel or resources within the company.
You can also use network sources to restrict access to the Oracle Cloud Console. Create the network source with IP addresses from where access to Console is allowed and then add the created network source to the Authentication settings.
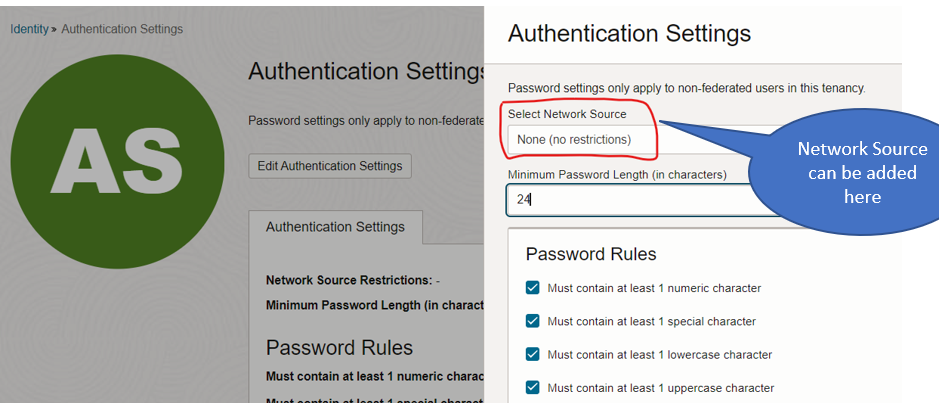
If you add an incorrect IP address while creating network source or the admin loses access to allowed network, the only way to regain access to OCI is by logging in using authentication software developer kit (SDK) using an API signing key and programmatically changing the network restriction setting. If you’re unable to log in using this method, contact Oracle Support to change the settings.
Network sources provide a simple yet powerful way to restrict access to OCI resources. It doesn’t provide network traffic control at packet level like security lists and NSGs, but it’s a useful access control mechanism to restrict access to OCI resources based on the originating IP range.
Explore more
Every use case is different. OCI also provides a network firewall service for packet-level network filtering, which not only allows and denies traffic based on source and destination IP, port, and protocol, but also provides URL and fully qualified domain name (FQDN) filtering, an intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS), and a logging system, including traffic and threat log.
For more information on network sources and security offerings in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, refer the following resources: