Have you ever wondered how easy it is to configure your Autonomous Database for disaster recovery scenarios? Do you need to migrate your Autonomous Database to cross-region but are worried about downtime and data loss? With this latest Autonomous Database feature, you now have an option to have a backup-based disaster recovery database in addition to Autonomous Data Guard. When you create a database, it now defaults to the backup-based disaster recovery method. You can always update the disaster recovery option from “backup-based” to “Autonomous Data Guard,” depending on your needs.
This blog post takes Autonomous Database Shared deployments into consideration.
Backup-based disaster recovery uses backups to start a peer database at the time of switchover or failover. This backup enables you to have a lower cost and higher recovery time objective (RTO) disaster recovery option for your Autonomous Database compared to Autonomous Data Guard. For local backup-based disaster recovery, existing local backups are used. Local backup-based disaster recovery incurs no extra costs.
When you add an Autonomous Data Guard standby database, the system creates a standby database that is continuously updated with the changes from the primary database. You can use Autonomous Data Guard with a standby in the current region, a local standby, or a cross-region standby.
How to change disaster recovery options
To change your disaster recovery method from the default method of backup based disaster recovery, navigate to the details page of your Autonomous Database. Under Disaster Recovery, click Upgrade to Autonomous Data Guard or Switchover. Then, select the disaster recovery option you want and save the changes.
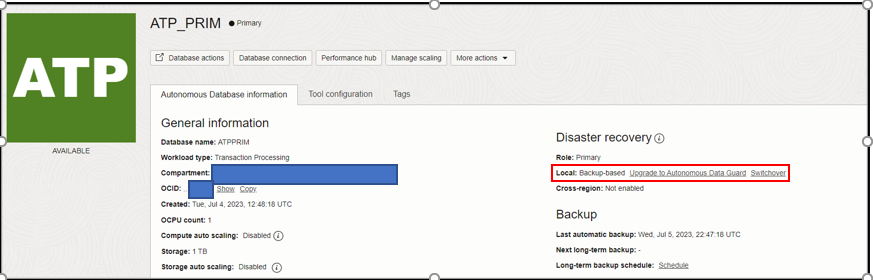
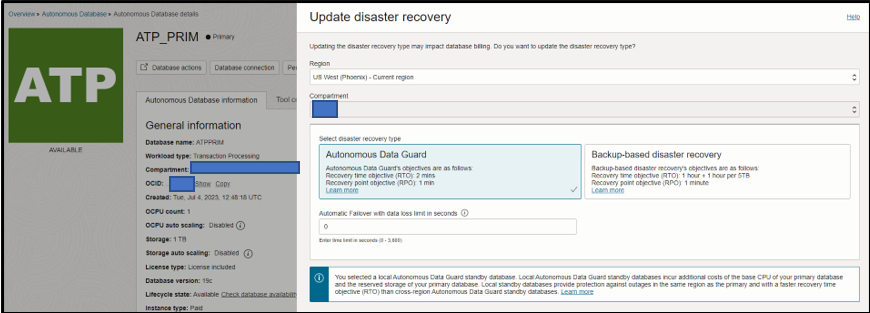
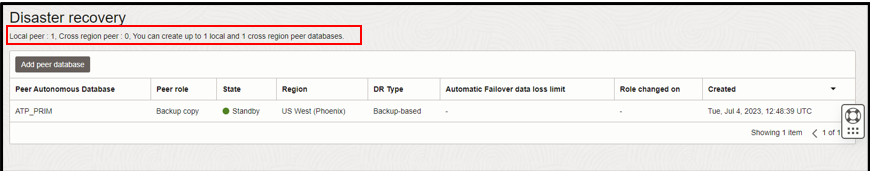
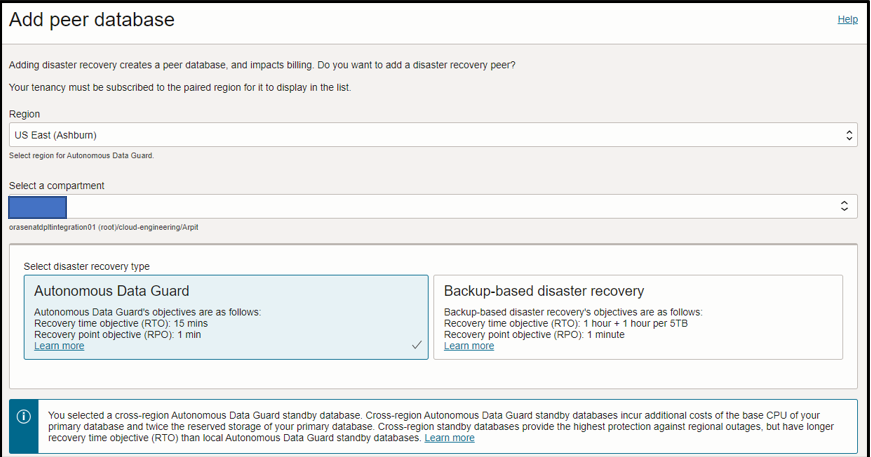
Currently, Autonomous Database allows only one local and one cross region peer database. By default, it automatically uses the local peer to be a backup-based disaster recovery option. We can add one cross region peer database to act as disaster recovery option, which can be either Autonomous Data Guard or backup-based.
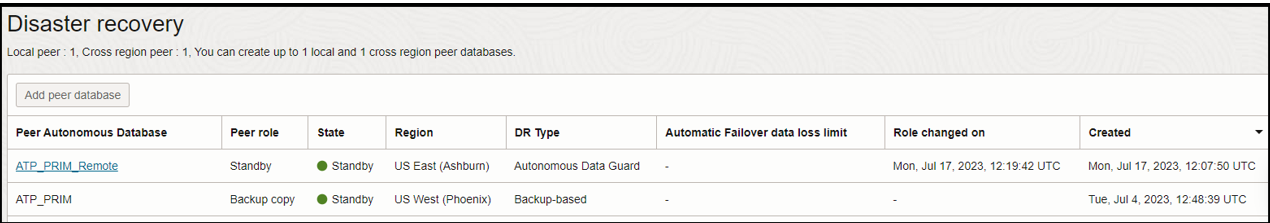
And the below image shows two peer Autonomous Database for disaster recovery, one backup-based and the other is Autonomous Data Guard located in cross region.
Migration scenario
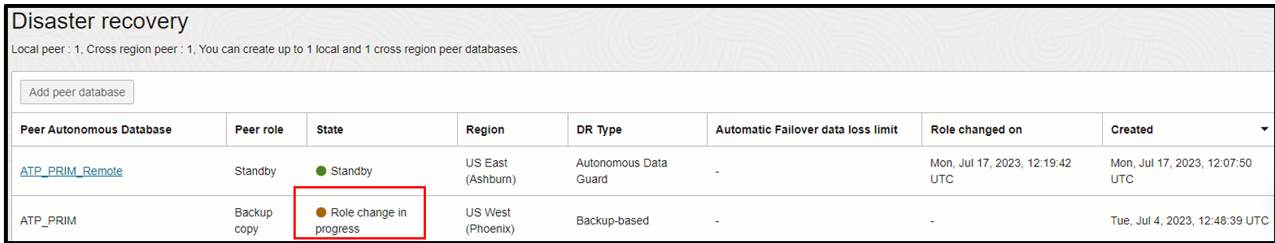
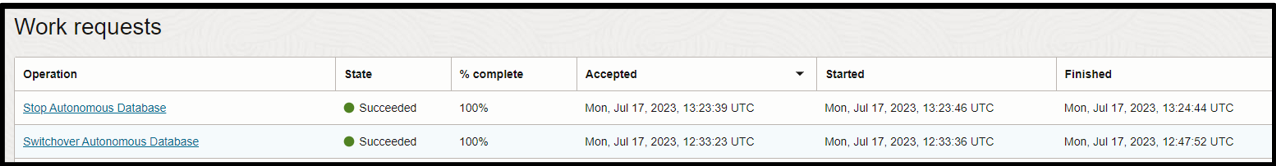
Now, let’s simulate a data migration where a switchover was initiated to local standby copy, and then the local standby took over the role of primary database without any data loss. You can achieve the same goal with the cross region standby database pair.
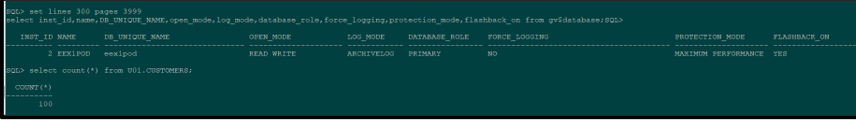
We create a user, U01, in the primary database, and create a table, CUSTOMERS, of 100 rows. Then, we initiated a switchover, and the standby database becomes the primary database. The table has same number of rows it had in primary.
New Primary Database state after switchover: As a result of the switchover getting completed , we can see below that the earlier standby database has now taken the role of primary database and the data is in complete sync between the two databases.
Conclusion
Backup-based disaster recovery adds a significant milestone to Autonomous Database’s disaster recovery. Setting up a disaster recovery is crucial for your business use case because it minimizes the RTO and recovery point objective (RPO) when an outage happens.
For more information on this Autonomous Database disaster recovery feature, visit our documentation, Autonomous Database Disaster Recovery. For more information on Autonomous Database, see the Autonomous Database documentation. To get hands-on experience, you can get started with a free trial.
