Summary
On June 11, 2024, Oracle and Google announced a cloud interoperability partnership that enables customers to migrate and run mission-critical enterprise workloads across Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Google Cloud. Enterprises can seamlessly connect Google Cloud services, such as analytics and AI, to Oracle Cloud services, such as Exadata and Autonomous Database. For organizations seeking to optimize and elevate their cloud infrastructure capabilities and commercial calculus, such a native multicloud model offers the best-of-both-clouds customer experience that encompasses a unified and interoperable technical and commercial stack. The Interconnect offers organizations access across their cloud solution providers, so workloads and data can be in an environment best suited to their capabilities and seamlessly interact as needed. To empower customers to create an integrated multicloud experience, the solution offers customers a direct, low-latency, and high-throughput cross-cloud connectivity between OCI and Google Cloud through OCI FastConnect and Google Cloud VLAN attachments.
This blog provides a step-by-step demonstration of how to set up the interconnection between OCI and Google Cloud. In places, it refers to other documentation for detailed background information and detailed steps.
Prerequisites
- An Oracle Cloud account. If you don’t have an account, you can sign up for an Oracle Cloud Free Tier account.
- A Google Cloud account. If don’t have an account, you can sign up for a Free Google Cloud Account.
- Required permission and resources quota to deploy resources per topology shown in the Figure below.
- Collect OCI Region, Google Cloud Region, interconnect peering location and throughput requirements.

Step by step guide
This section includes the initial steps which will be used to set up and validate interconnect between Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Google Cloud.
Step 1: Locate Your Desired Regions.
You need to reference Google Cloud and OCI connectivity documentations embedded here and identify the desired regions that you would like to utilize to connect your Google Cloud and OCI workloads. The OCI-Google Cloud interconnect feature is currently supported in the regions listed below:
| OCI Region |
Google Cloud Region |
|
| 1 |
ca-montreal-1 |
northamerica-northeast1 |
| 2 |
eu-frankfurt-1 |
europe-west3 |
| 3 |
ap-singapore-1 |
asia-southeast1 |
| 4 |
eu-madrid-1 |
europe-southwest1 |
| 5 |
sa-saopaulo-1 |
southamerica-east1 |
| 6 |
ap-sydney-1 |
australia-southeast1 |
| 7 |
ap-mumbai-1 |
asia-south1 |
| 8 |
ap-melbourne-1 |
australia-southeast2 |
| 9 |
ap-tokyo-1 |
asia-northeast1 |
| 10 |
us-ashburn-1 |
us-east4 |
| 11 |
uk-london-1 |
europe-west2 |
Step 2 (in Google Cloud): Create Interconnect VLAN and Establish Pairing Keys.
Once the regions of choice have been identified, you can create Partner Interconnect VLAN attachments from the Google Cloud console (or using a gcloud command):
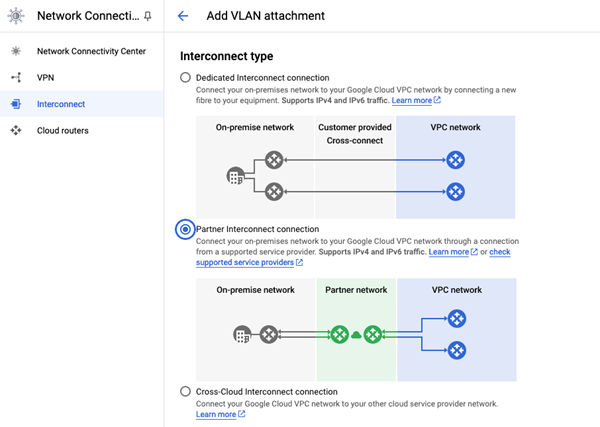
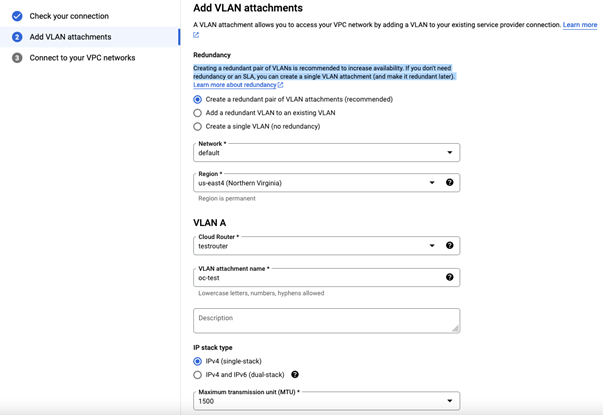
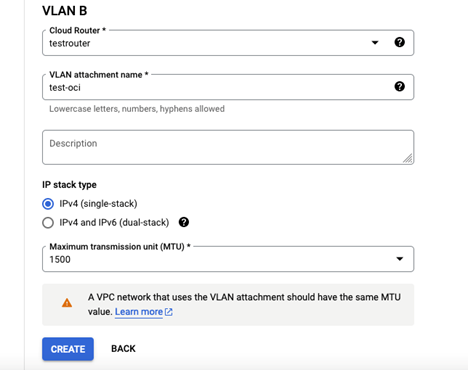
We recommend creating a redundant pair of VLANs to increase availability. The creation of a redundant pair of VLANs will result in 2 pairing keys. If you don’t need redundancy or an SLA, you can create a single VLAN attachment (and make it redundant later), which would result in only single pairing key.
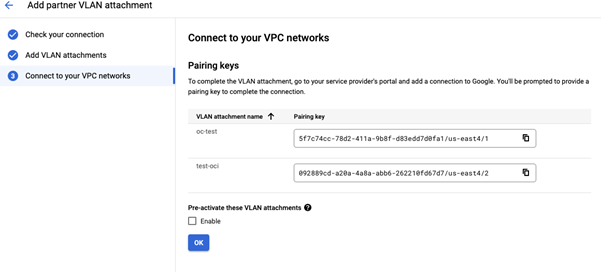
You can store the pairing key in a secure place so that you can utilize it in the OCI console. The pairing key is a unique key that lets OCI identify and connect to your Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network and the associated Cloud Router. OCI requires this key to complete the configuration of your VLAN attachment.
To avoid activating VLAN attachments post provisioning of Virtual Circuits, please pre-activate these VLAN attachments.
You may find more details on how to create a partner VLAN attachments can be found at the Partner Interconnect provisioning overview in Google Cloud. Additional Cloud Router documentation can be found here.
Step 3 (in OCI): Creating and Configuring a Virtual Circuit.
- In the Console, confirm that you are viewing the compartment that you want to work in. If you are not sure, use the compartment that contains the DRG that you will connect to. The choice of compartment, along with a corresponding IAM policy, would control who can access the virtual circuit that you are about to create.
- Open the navigation menu and click Networking. Under Customer connectivity, click FastConnect. The resulting FastConnect page is where you create a new virtual circuit and later return to when you need to manage the virtual circuit.
- Click Create Connection.
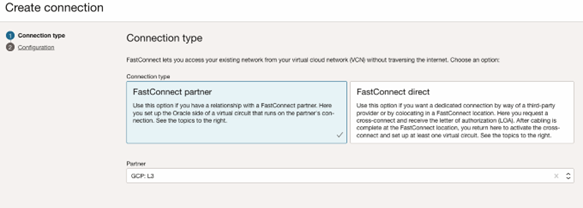
- Select FastConnect partner and choose Google Cloud: OCI Interconnect from the list.
- Enter the following for your virtual circuit:
- Name: Choose a familiar name. The value does not need to be unique across your virtual circuits, and you can change it later. Avoid entering any confidential information.
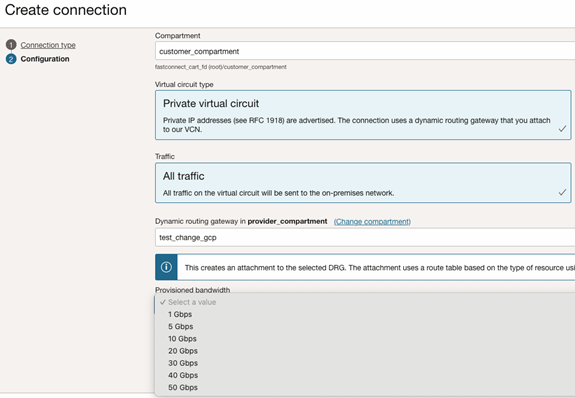
- Compartment: Leave as is (the compartment you’re currently working in).
- Virtual Circuit Type: Select Private Virtual Circuit.
- Dynamic Routing Gateway Compartment: Select the compartment where the DRG resides (it should already be selected).
- Dynamic Routing Gateway: Select the DRG.
- Provisioned Bandwidth: Choose the same bandwidth level. The Supported Bandwidth Shapes are 1 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 20 Gbps, 30 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and 50 Gbps.
- Partner Service Key: Enter the Pairing key that you received from Google Cloud when you set up the VLAN attachment.
- MTU: Choose MTU value as 1500.
- Click Continue. The virtual circuit is now created.
- Click Close.

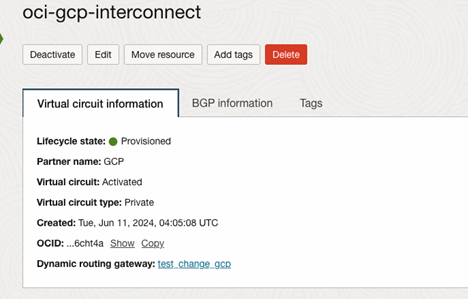
After you create the Oracle virtual circuit, wait until OCI configures your connections.
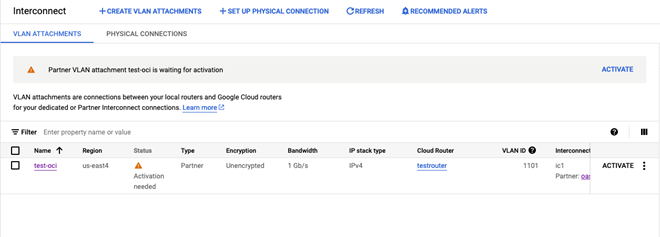
Step 4 (in Google Cloud): Activating the Connection.
This step is not required if pre-activate these VLAN attachments is Enabled in Figure.5 (Step 2)
Once configuration and provisioning have completed on the OCI side, you will receive an email notification from Google Cloud. After receiving the email, you must activate it from Google Cloud console. Activating the connection and checking its activation status enables you to verify that you have established connectivity with the Google Cloud.
Step 5 [OCI]:
Confirm that the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session that you have with Google Cloud is in an established state. BGP session can be verified from the OCI console as highlighted in Step 3. Don’t proceed until you confirm that it is in established state. Contact OCI or Google Cloud support team if BGP state is not established.
You should be able to launch an instance in your VCN and access it (for example, with SSH) from a host in your existing private network. See Creating an Instance. If you can, your FastConnect private virtual circuit is ready to use.


