When running database workloads in the cloud, optimizing the cost of infrastructure and providing adequate compute resources to fulfil the business needs is important. You need compute resources to easily scale up or down to match the demands on the workload.
Oracle Exadata Cloud Database service is a managed database service optimized for performance, availability, security, and cost effectiveness. With Exadata Cloud service, billing is based upon the number of CPU cores allocated to virtual machines (VMs). You can configure dynamic scaling to meet CPU requirements when workloads are high and optimize costs by lowering the number of CPU cores when the workload demand is reduced.
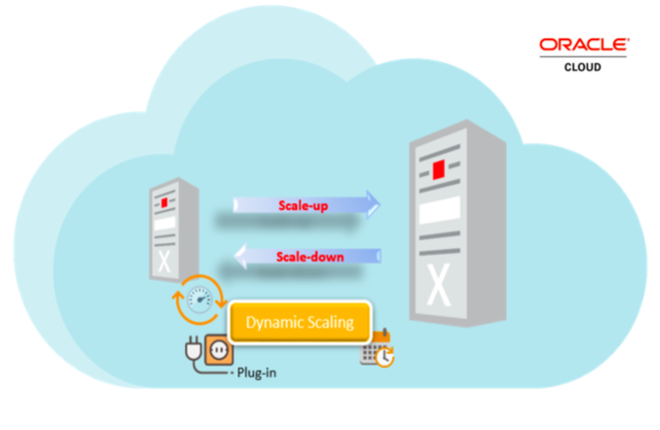
Dynamic scaling is configured based on CPU load and scheduling parameters. You can enable it by installing the dynamic scaling tool on an Exadata VM and configuring the scaling parameters as needed. After scaling-related parameters are defined, you can schedule dynamic scaling as a daemon process or high-availability cluster resource.
Implementation
-
Install the dynamic scaling tool. Dynamic scaling is installed using RPM with the following command:
# rpm -i Dynamicscaling-2.0.1-X.el7.x86_64.rpmAfter installation, we start the service.
-
Configure dynamic scaling parameters. Dynamic scaling has some default parameters that you can override using specific parameters.
Parameter name Default value Usage –ocicli
–
Run dynamic scaling runnable using the OCI CLI –maxocpu
DBSystem max OCPU
If no value is provided, the maximum OCPU value of the database system is considered. –minocpu
4
Minimum OCPU number –ocpu
DBSystem number of OCPUs
Number of OCPU factor –interval
180
Number of seconds to monitor load and perform scale operation based on configuration –maxthreshold
80
Maximum load threshold 20–90 –minthreshold
60
Minimum load threshold 10–80 –loadtype
max
Nodes load type, either max or average –nodaemon
–
If this option is provided, dynamic scaling runs as standby. –dryrun
–
Scaling operation is not performed. -
Run dynamic scaling. You can perform dynamic scaling using the OCI command line interface (CLI) as shown in the following screenshot. Run it from all the nodes of the Exadata VM cluster. It considers the parameter values and starts the dynamic scaling process with the OS process ID (PID). This process continuously monitors the load on the VM cluster nodes.
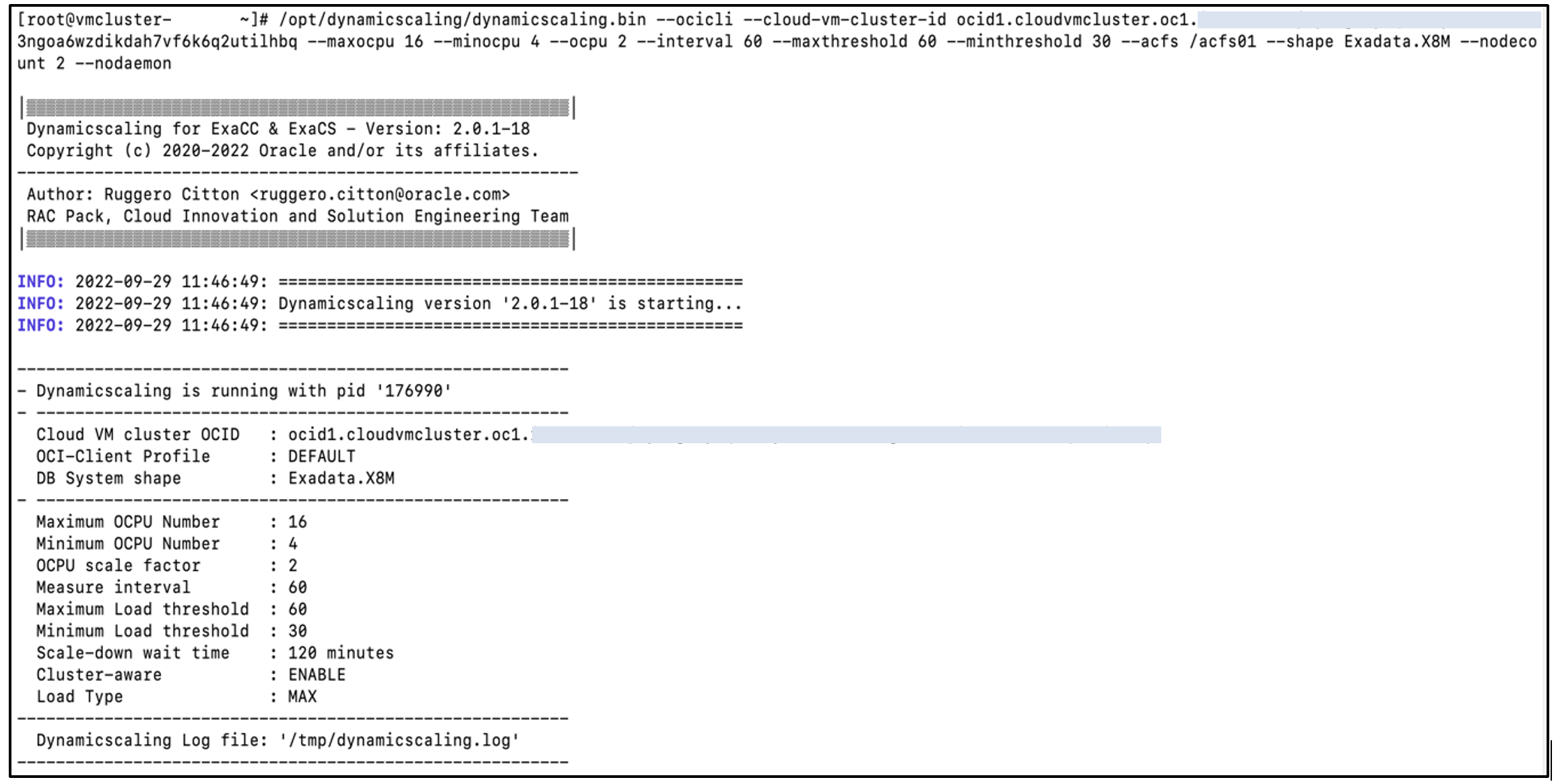
Scaling information is written to a scalingtime.json file. A node-specific file is automatically created when the dynamic scaling parameter cluster-aware is enabled. The dynamic scaling process considers the max CPU load value from node-specific JSON files and performs the scaling operation. Each time a scaling operation is performed, it updates the status in the scaling-time.json file.
After a scale-up operation is performed, the next scale-down operation must wait for the time defined by the parameter ‘scale-downwait time’.

-
Monitor dynamic scaling operation. The dynamicscaling.bin process running on the Compute node monitors the load from the JSON file and performs a scale-down operation if the current CPU load is below the minimum threshold. If the current CPU load is above the maximum threshold, a scale-up operation runs.
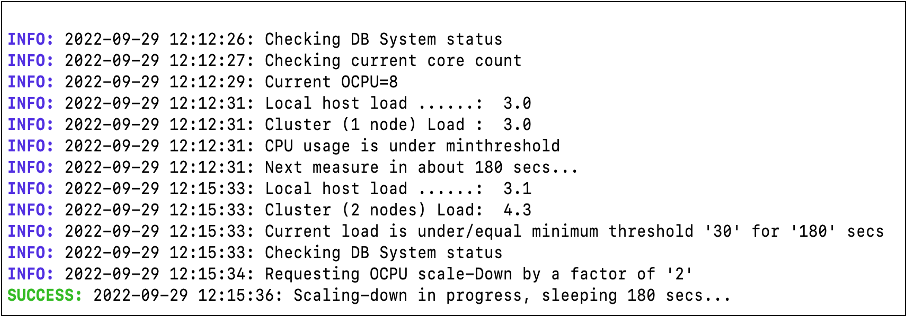
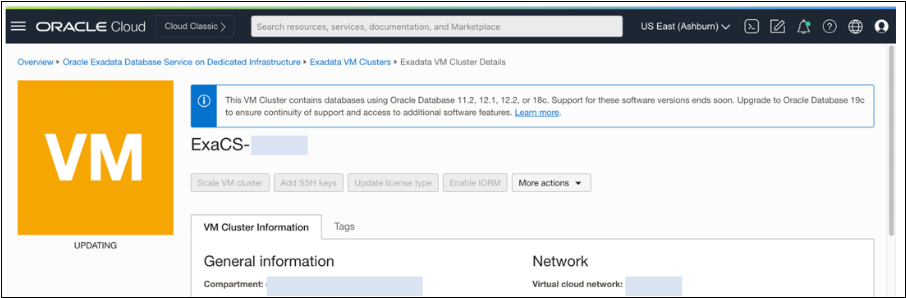
The status is reflected in the Oracle Cloud Console, and the VM cluster is updated. The status is indicated as updating during a scale operation. Scale-down runs according to the scale factor parameter. In the previous screenshot, the process is scaling down by 2 OCPUs because the scale factor is defined as 2.
After the scale-down operation is complete, the updated CPU count is displayed in the Console. This operation is logged in the scaling-time.json file.
Conclusion
Every use case is different. The only way to know if Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is right for you is to try it. You can select either the Oracle Cloud Free Tier or a 30-day free trial, which includes US$300 in credit to get you started with a range of services, including compute, storage, and networking.
For more information on Oracle Exadata Cloud Infrastructure, see the documentation.
