As you might already be aware, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is the best choice for high-performance computing (HPC) workloads among all cloud service providers because of its unique offerings, starting from no hypervisor bare metal shape to RoCEv2 RDMA interconnect.
In most HPC systems, ranging from a few-node cluster to multimillion dollar super computer, network file share (NFS) file service is vital to fulfill its file sharing needs. This file sharing needs come from the fact that various types of files, such as source program, executable, and input and output data to and from simulation, must be shared among all login nodes and Compute nodes in the cluster. Because this file sharing service plays so crucial role that its service halt easily leads to a nightmare for system administrator, NFS server durability and performance are among the most important factors when you design file sharing architecture for your cluster.
Then one question arises when running HPC cluster on OCI: What’s the best choice for an NFS server among the various shapes that OCI offers? This blog answers the exact question for you.
Since its release in Spring 2021, the BM.Optimized3.36 bare metal shape has been the best choice for compute-intensive HPC workloads by utilizing its Xeon Ice Lake NFS file service running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure processors. However, looking at the fact that it accommodates not only Ice Lake processors, but two 50-Gbps NICs at competitive price, it should also be the best choice for NFS server by utilizing the two high-bandwidth network interface cards (NICs) in two connections separately, NFS file service, and iSCSI storage access.
In this article, I explain how durable BM.Optimized3.36 is as an NFS server by carrying out stress tests and showing its performance.
Test environment
Archtectural diagram
The following architectural diagram shows the test environment for the stress test.
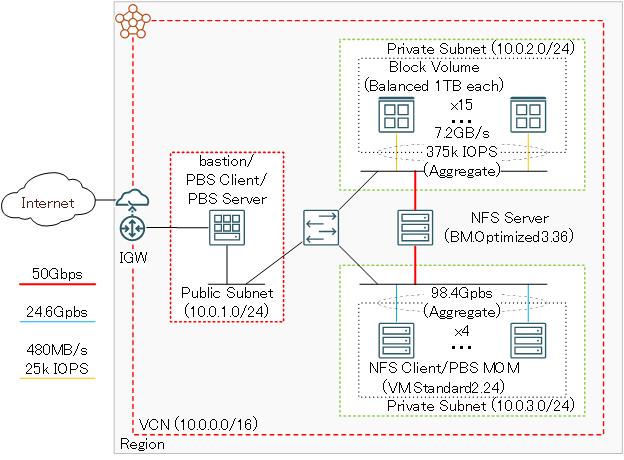
Because this test aims to confirm the durability and performance of BM.Optimized3.36, NFS clients and the block volume attached to NFS server must be carefully configured to overwhelm 50 Gbps NIC bandwidth to avoid the situation where components other than NFS server becomes a bottleneck.
In this configuration, storage and NFS clients have the following configurations:
| Specification | Aggregate bandwidth | Aggregate IOPS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | 15 1-TB block volumes balanced | 7.2 GB/s (More than 50 Gbps) | 375k |
| NFS clients | 4 VM.Standard2.24 | 98.4 Gbps (Network bandwidth) | – |
As you can see in the table, the aggregate bandwidth of both storage and NFS clients exceeds theoretical 50-Gbps NIC bandwidth of BM.Optimized3.36.
Software configuration
In this stress test, IOR and mdtest put pressure on the NFS server for bandwidth and metadata.
As you might already know, these tools are evaluated as highly as the ones for measuring storage performance of bandwidth and metadata by read/write large files and create, stat, and delete a huge number of small files, identical to carrying out stress test.
We used OpenPBS to run these benchmark jobs to maintain IO pressure on NFS server and Oracle Linux 7.9 for NFS server and client operating systems.
Test method
Stress test policy
To evaluate the durability of the NFS server, IOR and mdtest are run alternatively for five days, with each job elapse time set to 30 minutes. It’s unusual for a production NFS server to keep delivering its peak performance without any rest for such a long time.
From an NFS client process placement perspective, two processes are placed on each node, with eight processes run on four NFS client nodes. This placement is determined through trial and error to get the best performance with a minimum number of total processes.
Evaluation metrics
The following metrics are set when we evaluate the test results:
-
No NFS file service halt
-
No significant IOR or mdtest performance deviation from average
-
No abnormality observed in NFS server statistics for CPU utilization, unused memory space, storage bandwidth, or network traffic bandwidth for both NICs
Test result
Evaluation
I concluded that BM.Optimized3.36 NFS server passes the stress test with the following details:
-
No NFS file service halt for five days
-
No significant IOR or mdtest performance deviation from average
IOR Write min 3.3 GiB/s (Average: 3.9 GiB/s) IOR Read min 4.4 GiB/s (Average: 4.8 GiB/s) mdtest Create min 5.7 kIOPS (Average: 6.0 kIOPS) mdtest Stat min 62.2 kIOPS (Average: 65.7 kIOPS) mdtest Delete min 5.8 kIOPS (Average: 6.0 kIOPS) -
No irregular system statistics observed on NFS server (See the NFS server statistics section.)
-
Total test duration: 5 days 6 hours 51 minutes 10 seconds (Total number of jobs: 336)
Performance
The following chart shows IOR and mdtest performance distribution during the five-day test period. As you can see in the chart, 5 GiB/s for read and 4 GiB/s for write are consistently achieved with no abnormality observed.
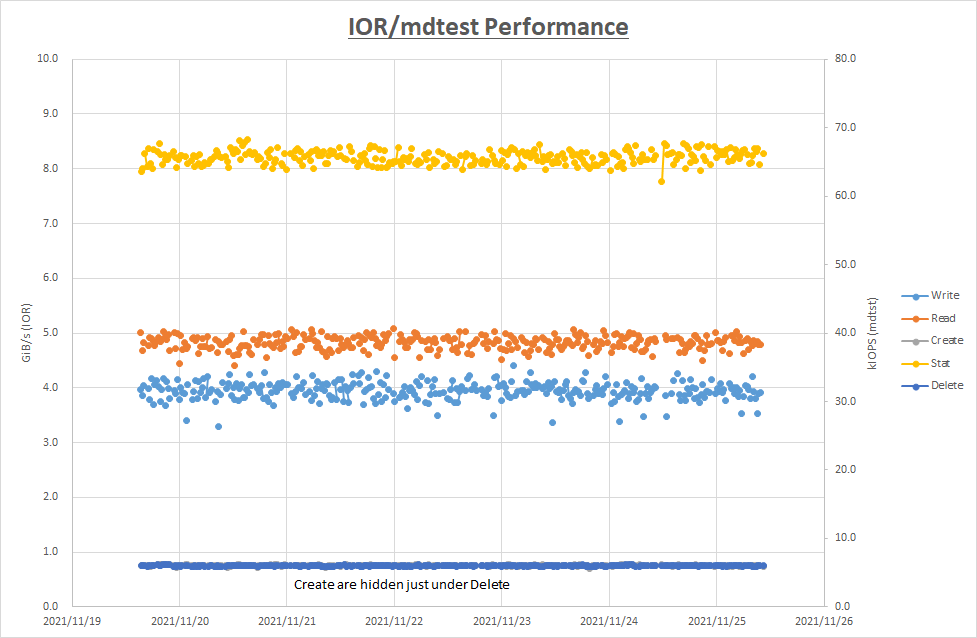
| Max | Min | |
|---|---|---|
| IOR write | 4.4 GiB/s | 3.3 GiB/s |
| IOR read | 5.1 GiB/s | 4.4 GiB/s |
| mdtest create | 6.2k IOPS | 5.7k IOPS |
| mdtest stat | 68.3k IOPS | 62.2k IOPS |
| mdtest delete | 6.2k IOPS | 5.8k IOP |
NFS server statistics
The following table shows no irregular statistics observed on NFS server during the five-day test period:
| Max CPU utilization (Sys) | 20.9 |
|---|---|
| Max CPU utilization (IOwait) | 14.9 |
| Min free memory | 1.6 GiB |
| Max disk bandwidth | 5.0 GiB/s |
| Max disk bandwidth (Read) | 5.0 GiB/s |
| Max NIC bandwidth (Storage subnet receive) | 5.2 GiB/s |
| Max NIC bandwidth (Storage subnet transmit) | 5.2 GiB/s |
| Max NIC bandwidth (NFS subnet receive) | 5.2 GiB/s |
| Max NIC bandwidth (NFS subnet transmit) | 5.2 GiB/s |
Cost
Before the release of BM.Optimized3.36, BM.Standard2.52 was a competitive candidate for NFS server. The following table shows that BM.Optimized3.36 is 20% cheaper than BM.Standard2.52 with 50-Gbps NICs, which has twice the bandwidth as the ones for BM.Standard2.52.
| Number of core | Memory | NIC | Cost per 30 days | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM.Standard2.52 | 52 | 768 GB | 2 25-Gbps | $2,388.67 |
| BM.Optimized3.36 | 36 | 512 GB | 2 50-Gbps | $1,952.64 |
When I look for cost disadvantages of BM.Optimized3.36, it doesn’t stop billing when you stop it because of the NVMe storage attached locally. However, considering that the NFS server runs its service constantly, most use cases don’t consider this fact a negative factor.
Conclusion
The best choice of shape when running NFS server on OCI is BM.Optimized3.36 from the perspectives of durability, performance, and running cost. You can easily deploy the same NFS cluster in this blog through Oracle Cloud Marketplace stack in minutes by specifying a few options on Oracle Cloud Console.
The dedicated bare metal server provides a consistent high-performance NFS server for a fixed cost appropriate for HPC workloads that have a continuous demand.
