Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is pleased to announce IP CIDR address support for Virtual Network Interface Cards (VNIC) in all commercial regions. This feature enables you to assign a block of contiguous host IPs to a VNIC quickly, using only a single configuration. This addresses requirements for greater scalability of private IP addresses per VNIC, enabling containerization and other workloads to achieve IP density for scaling requirements. Using this feature can lower costs through:
- Increased private IP assignments per VNIC
- Improved scaling behaviors
- Simplified IP address management at scale
This blog provides an overview of this feature, what new benefits are unlocked, and how to get started.
IP CIDR Address
Within the networking industry, Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is used to optimize IP network sizes for network routing, allowing flexibility to choose network mask sizes instead of using fixed, classful IP routing boundaries. Within OCI VCN, an IP CIDR address enables you to assign a subset of the VCN subnet prefix as a block of contiguous secondary host IPs to a VNIC. The IP CIDR address is a single private IP object with an additional CIDR length represented as <network IP/netmask # of bits>. This simple, yet powerful feature allows multiple IPs to be readily available for use on a single VNIC through a single configuration element.
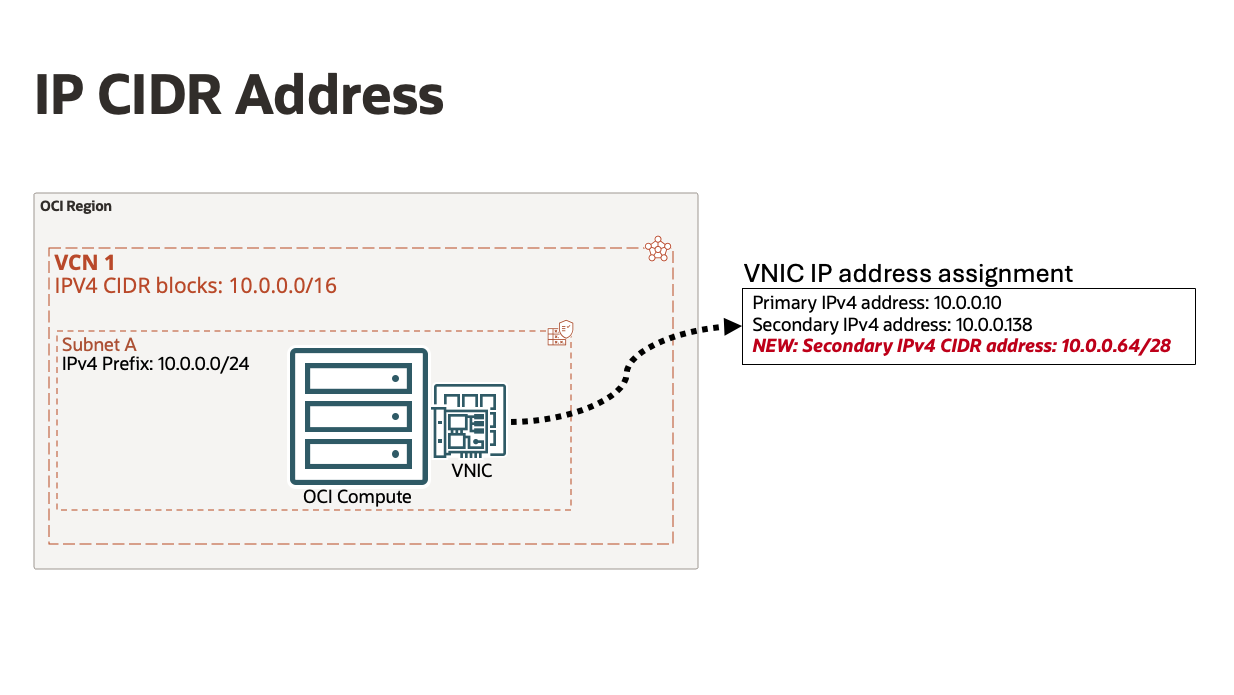
Figure 1. IP CIDR Address assigned to a VNIC
Within a Virtual Cloud Network (VCN), private IP addresses are assigned and managed individually as IP objects. Secondary IPs can be assigned to VNICs directly providing additional IP addresses for a compute resource. With the new IP CIDR address feature, you can assign, move, or delete up to 16,384 IPv4 (/18) or ~281.5 trillion IPv6 (::/80) secondary IP addresses as a single IP object for a simple and efficient experience.
IP CIDR addresses are also flexible in size. You can allocate differing netmask lengths per IP CIDR address as seen in figure 2. This lets you pick different numbers of IP addresses to assign based on your needs, whether for an initial service deployment or during periods of increased demand.

Figure 2. IP addresses used with IP CIDR address assignments
IP CIDR addresses also provides a significant increase to the number of individual IP addresses a VNIC and VCN overall can support. This feature primarily enables large virtualization deployments beyond the 64 IPv4 or 32 IPv6 secondary IP addresses per VNIC limit. You can also use it to host all your workloads requiring dense IP addressing within a single VCN without going over the 64000 private IP objects within a VCN service limit.
New Possibilities
Improved scaling behaviors – more IPs without cost
IP CIDR addresses provide a way to assign more than 64 private IPv4 addresses to a VNIC, as a single IP CIDR address object can represent thousands of private IP addresses. Scaling through IP CIDR addresses allows for independent compute OCPU scaling, as Flexible Compute Shape OCPUs require proportional OCPUs for equivalent VNICs. This provides benefits of scaling flexibility, reduced configuration complexity, and additional cost optimization. See figure 2 of running self-hosted Kubernetes clusters on OCI with VCN native assigned private IPs as example.

Figure 3. IP CIDR address for Kubernetes worker node
Improved scaling behaviors – reduced provisioning times
In scaling of enterprise systems using hundreds or thousands of IPs, each IP address assignment is a single configuration that must be made. This time might increase delays in overall service readiness. Using IP CIDR addresses, thousands to trillions of IPs can be assigned or moved to a compute resource within seconds. This can reduce scaling times and disaster recovery rebuilds when maintaining availability for the most critical workloads. As shown in figure 4, when a Kubernetes worker node pool needs to increase for pending pod deployments, a single configuration element of an IPv6 ::/116 CIDR address is used to in step 3 assigning 65,536 IPv6 addresses. This IP CIDR address assignment reduces private IP allocation timeframes and enables dense IP utilization.
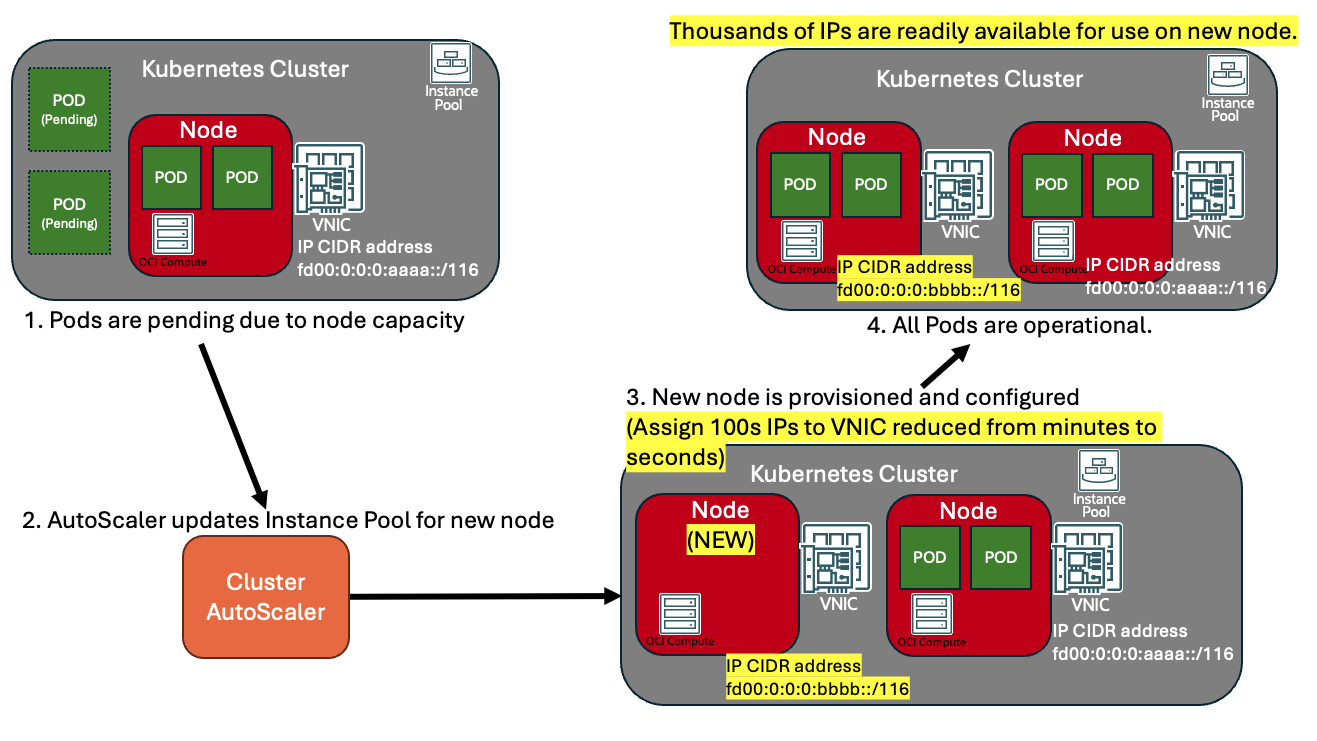
Figure 4. Adding IP CIDR address during auto scaling activity
Getting Started
To take advantage of IPv4 CIDR addresses, you need a compute instance with a VNIC attached. You can use an existing compute instance or you can create a new compute instance . Then simply, view the VNIC details. From here you can view the current IP addresses assigned under the “IP administration” tab.
To create an IP CIDR address, select “Assign secondary private IP address”, and in the optional CIDR prefix length field, enter the desired netmask value. You can also manually assign the exact IP network by selecting the “Manually assign IPv4 addresses” radio button (not shown below).

Figure 5 – IP CIDR address request
Once assigned, you’ll see the network and netmask value within your IPv4 addresses assigned as a Private IP address object. It’s that simple.

Figure 6 – IP CIDR address assigned
Conclusion
With the launch of this new capability, OCI offers more efficient use of compute resources with improved scaling of IP allocations for VNICs and VCNs. This also makes it easier to manage thousands of IPs through a single API call. Concurrently, we are also releasing increased IP support within a VCN, allowing for more CIDRs block assignments to a VCN and IP networks per subnet. Check out the launch announcement for improved IP flexibility within VCN.
We’re pleased to deliver this capability to address your networking needs. Thank you for your interest in OCI and learning how OCI can handle enterprise scale networking requirements. We encourage you to share feedback via email here.
To learn more, please review the following resources:
