In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, organizations are increasingly seeking ways to use the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to automate processes and enhance productivity. As we stand on the cusp of a new era in technology, integrating AI models into our daily activities is becoming less a question of if and more a matter of when. This blog post explores the concept of agentic workflows using different models and highlights the benefits of using AI models in today’s world, with a specific focus on NVIDIA NIM microservices, part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform available in the Oracle Cloud Marketplace, deployed on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Introduction to agentic workflows
Agentic workflows represent a sophisticated approach to task automation, utilizing multiple AI models, each specialized for different aspects of a complex process. In our upcoming Oracle CloudWorld 2024 session, we showcase a compelling use case that demonstrates the power and versatility of this approach.
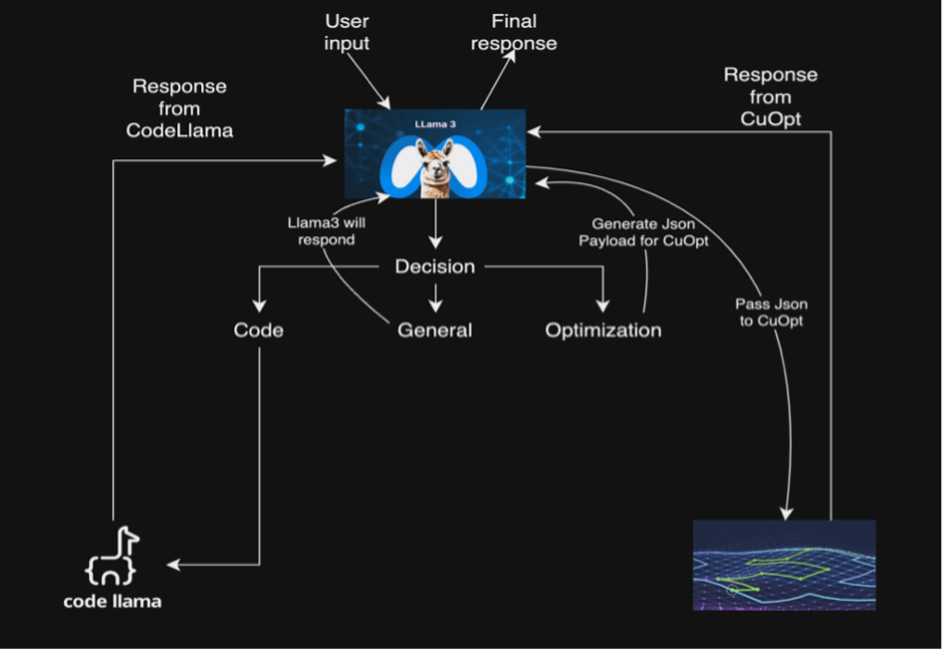
Imagine that you need to find an optimized route for a complex logistics problem. The agentic workflow we’ve designed seamlessly integrates multiple NVIDIA models to process this request efficiently. Your text query is first sent to the NVIDIA Llama 3.1 NIM microservice, which acts as the primary agent. This model processes the query and intelligently routes it to the NVIDIA Code-Llama NIM microservice, which specializes in code generation. The Code-Llama NIM then generates an SQL query to extract relevant data from a database and constructs a JSON query for NVIDIA cuOpt, an optimization model. Finally, NVIDIA cuOpt processes this information and presents an optimized response, providing you with the most efficient route based on your initial query.
Model deployment on OCI
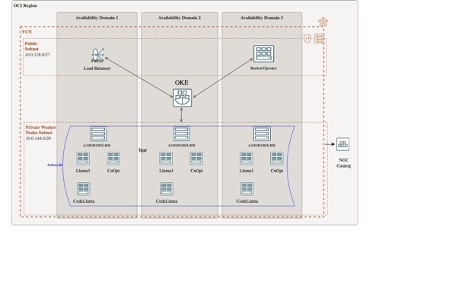
To bring this agentic workflow to life, we use NVIDIA NIM, a collection of containerized microservices optimized for deploying AI inference workloads. NIM offers scalability, flexibility, and efficiency, making it an ideal choice for our complex AI pipeline. You can deploy these models on OCI virtual machines (VMs) or Oracle Kubernetes Engine (OKE) clusters, providing flexibility to suit various infrastructure preferences.
For users looking to quickly get started, we offer the following deployment options:
- Automated deployment on NVIDIA A100 and NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU instances using Terraform and Ansible-enabled stacks
- Oracle Cloud Marketplace image for direct deployment on an NVIDIA A10 Tensor Core and NVIDIA L40S GPU instance
- Deployment on OKE using a provided GitHub repository or a one-click deployment button to an existing OKE cluster
Each of these options is designed to streamline the setup process, allowing you to focus on using the power of the agentic workflow, rather than getting bogged down in complex deployment procedures. These assets are also integrated with adjacent OCI services like Object Storage, Block Storage, and File Storage. For scalability and security, we have integrated with OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM), Load Balancing, and Certificates services.
Details of the agentic workflow
Our agentic workflow consists of the following primary models, each playing a crucial role in the process:
- The NVIDIA Llama 3.1 NIM: This microservice serves as the main agent, responsible for query classification, routing queries to other specialized agents, and generating general responses.
- The NVIDIA Code Llama NIM: Specializing in handling code-related queries, this microservice excels at providing syntax examples and generating code when needed.
- NVIDIA cuOpt: Focused on optimization tasks, cuOpt can solve complex routing and logistical problems.
The workflow applies the unique strengths of each microservice to provide targeted, efficient responses to user queries. When you submit a query, Llama 3.1 classifies it, determining whether it relates to code generation, route optimization, or general topics. Based on this classification, the workflow branches into different chains.
For code-related queries, Code Llama takes the lead, generating the necessary code before passing the result back to Llama 3.1 for final response formulation. cuOpt handles optimization queries, with Llama 3.1 generating the required JSON input. cuOpt then calculates the optimal route and returns a JSON output, which Llama 3.1 interprets to provide a user-friendly explanation. Llama 3.1 addresses general queries directly, showcasing its versatility as the primary agent.
This intricate dance between microservices allows for a comprehensive, efficient approach to complex problem-solving, far surpassing what any single one can achieve alone.
Conclusion
The agentic workflow we’ve explored represents a significant leap forward in using AI for real-world applications. By integrating Llama 3.1, Code Llama, and NVIDIA cuOpt, we’ve created a system capable of handling a wide array of complex tasks with remarkable efficiency and accuracy. This approach not only showcases the power of LLMs in automating intricate processes but also points the way toward a future where AI assistants can seamlessly collaborate to solve multifaceted problems.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with AI, the North America Cloud Engineering AI solutions launchpad stands ready to support organizations in their journey to implement these cutting-edge solutions. By combining the power of NVIDIA NIM microservices with the robustness and scalability of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, we’re creating possibilities for innovation and efficiency across industries.
The future of AI is about more than individual models. We must create intelligent ecosystems where multiple AI agents can work in concert to tackle the complex challenges of our modern world. As we look ahead, the potential applications of agentic workflows are boundless, promising to revolutionize how we approach problem-solving in business, science, and beyond.
To start prototyping for free with NVIDIA-hosted NIM microservices or to download and deploy NIM microservices, visit the NVIDIA API catalog. To try out various hands-on labs, including agentic workflows, visit Oracle LiveLabs.

