We’re excited to announce the release of the new Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Zero Trust Landing Zone – a new solution that enables one-click provisioning for both a secure, high-performing architecture for your cloud tenancy, with deployment and hardened configuration of key services needed in order to meet certain requirements of zero trust. The approach of zero trust is based on recommendations set forth by the US Government Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the UK Government’s National Cyber Security Centre’s Principles, and other government agencies world-wide.
Why zero trust?
Cyberattacks continue to plague business and government organizations. Older perimeter-based security postures can’t keep up with the quantity and sophistication of the attacks. When perimeters are breached, attackers get access and authorization to an even wider set of critical data, with aftermaths that can cripple an organization.
Zero trust is an advanced security paradigm for protecting enterprise data and assets, which adopts an “Assume breach” mentality. A zero trust architecture focuses on protecting the critical components of the enterprise and blocking lateral movement to limit exposure and minimize the blast radius of a possible breach. Zero trust is an approach that both protects data and assets, while implementing constant monitoring to identify anomalies and act quickly to lock down any systems that indicate possible breach.
To achieve this goal, zero trust introduces the concept of “never trust, always verify” and imposes continuous verification, where every request undergoes reauthentication and reauthorization by the Policy Engine (PE) before access to a resource is permitted or denied by a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP).
The US Government executive order and zero trust requirements
Many governments and enterprises in the broader industry have begun to require implementing zero trust principles. In the US, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has published Special Publication 800-207, detailing principles and objectives for zero trust deployments. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) published guidelines for implementing a zero trust approach. The National Security Agency (NSA) has published several technical guidance papers on embracing a zero trust security model and several papers on advancing zero trust maturity on each of the pillars. Finally, the office of President of the United States issued a directive for US Government agencies to implement zero trust baseline principles by the end of fiscal year 2024.
Many of the published guidelines decompose the implementation of zero trust around pillars of protection. CISA and the DOD define the key pillars of zero trust: User, devices, applications and workloads, data, network environment, automation and orchestration, and visibility and analytics.
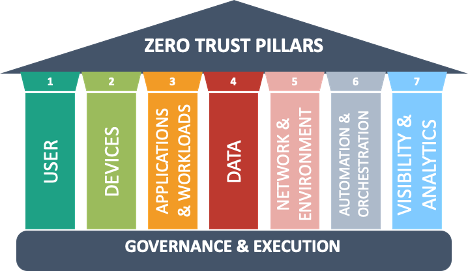
These pillars all require technical solutions. The visibility and analytics and automation and orchestration pillars crosscut with overarching enterprise-wide capabilities of the first five pillars. Our view is that governance and execution is key to ensuring the successful implementation and management of all these technology pillars are required to protect all aspects of mission-critical systems.
Enterprises’ journey to zero trust and how OCI Landing Zones help
Rolling out initiatives like adopting a zero trust architecture that require significant organization-wide changes can take considerable time and resources in the organization and must be done in a methodical and repeatable way to ensure that new technology implementations don’t jeopardize the enterprise’s security posture.
Landing zones are infrastructure-as-code solutions that provide curated, preconfigured templates with certified architecture and best-practices based configurations for provisioning cloud resources in a repeatable and consistent way. OCI already offers several landing zones for different use cases, such as the CIS-certified Core Landing Zone and SCCA for government workloads. Like all other templates, the newly added Zero Trust Landing Zone is comprised of open source, Terraform-based modules that are part of the OCI Landing Zones framework. We have recently revamped this framework to offer greater extendibility and scale, and updated existing landing zones to utilize its new capabilities. You can learn more about the new framework on GitHub.
OCI zero trust landing zone
The new OCI Zero Trust Landing Zone accelerates customers’ journeys to zero trust on OCI with an easy consumption vehicle and consistent deployments that simplify the learning curve, trial and error, and decision points for customers to help ensure optimal provisioning for zero trust. Further, the OCI zero trust landing zone was designed as an adaptable solution, enabling customization to meet customers’ needs and future extendibility as we launch more related services to address various requirements across the zero trust pillars.
Like all OCI landing zones, the zero trust landing zone is based on CIS guidance and compliant with CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark v2.0.0. The CIS framework already met most of the UK’s NCSC Zero Trust requirements—see the mapping in this tech brief—and has now been extended to meet the US’ NIST requirements.
The OCI zero trust landing zone provisions the following cloud services and components:
- Base tenancy: The solution provisions a best practices-based architecture for your base tenancy with all OCI services recommended for an optimal cloud foundation. These services include Identity and Access Management (IAM), Networking, Key Management (KMS), Oracle Cloud Guard, Vulnerability Scanning, Bastion, Logging, Events (Auditing), Notifications, and Security Zones. You can also implement other controls, such as zero trust network access (ZTNA) around application and workload, devices, and visibility by integrating with our partners in the Oracle Cloud Marketplace.
- The following OCI services to support requirements around the data pillar of zero trust architectures as defined by NIST, CISA, DOD and NCSC:
- Oracle Access Governance (OAG): Enables attribute-based and policy-based access controls. OCI Access Governance provides customers with the ability to implement attribute-based access controls (ABAC) and policy-based access controls (PBAC), which directly support zero trust requirements to support dynamic policies, based on identities, devices, and applications that require more attribute or contextual information, such as location, user attributes, and previous behaviour. Access Governance provides the answer to the security and identity universe: Who has access to what?
- OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing (ZPR): A new OCI service that applies network microsegmentation at the virtual cloud network (VCN) level, enabling the detection of any data-in-motion violations and providing data loss prevention capabilities. ZPR simplifies data security by allowing customers to use human-readable policy to describe the security intent, and ZPR enforces the data protection. Working at the VCN level, ZPR policies provide data loss prevention (DLP). If your workloads or virtual machines (VMs) are separated at the VCN level, ZPR can help ensure that data leakage doesn’t happen, either inadvertently because of misconfiguration or deliberately from a cyberattack.
- Oracle Access Governance (OAG): Enables attribute-based and policy-based access controls. OCI Access Governance provides customers with the ability to implement attribute-based access controls (ABAC) and policy-based access controls (PBAC), which directly support zero trust requirements to support dynamic policies, based on identities, devices, and applications that require more attribute or contextual information, such as location, user attributes, and previous behaviour. Access Governance provides the answer to the security and identity universe: Who has access to what?
- Pluggable ZTNA capability: ZTNA satisfies the requirements around the network environment pillar of zero trust architectures. In discussion with customers, some had already decided on a standard ZTNA solution for their multicloud and on-premises environments. We collaborated with our partners to develop ZTNA integrations into our zero trust landing zone solution, such as the Fortinet ZTNA plugin that’s included in this version of the landing zone, developed by our partner Derrick Gooch from Fortinet. This integration enables customers to plug in their preferred firewall-based ZTNA solution, such as Fortinet, Palo Alto, and Cisco, and have it enabled across all their OCI, multicloud, or on-premises environments.
- Networking enhancements: The zero trust landing zone uses a hub-and-spoke architecture with a demilitarized zone (DMZ) VCN with a next-generation firewall like Fortinet’s FortiGate. The OCI network design allows applications to be isolated in VCNs and all the traffic in and out of those VCNs to go through the firewall for advanced inspection. In addition to advanced inspection, the next-generation firewalls provide ZTNA features, which assess the user’s device and act as an enforcement point directing the user’s authentication and authorization to the centralized identity store.
Also at the network layer, we enable ZPR to provide positive security for host communication based on security attributes. Similar tags are also used by the next-generation firewall to expand the control across all the VCNs.
- Observability enhancements: All this context from the next-generation firewall, server logs, OCI Logging, and OCI Audit data is aggregated into security information and event management (SIEM), such as Stellar Cyber, to provide visibility and analytics to monitor the activities. SIEM also enables you enrich the logs with threat intelligence to allow for effective detection and response.
Reference architecture
The following diagram highlights the key services that are provisioned with the OCI zero trust landing zone.
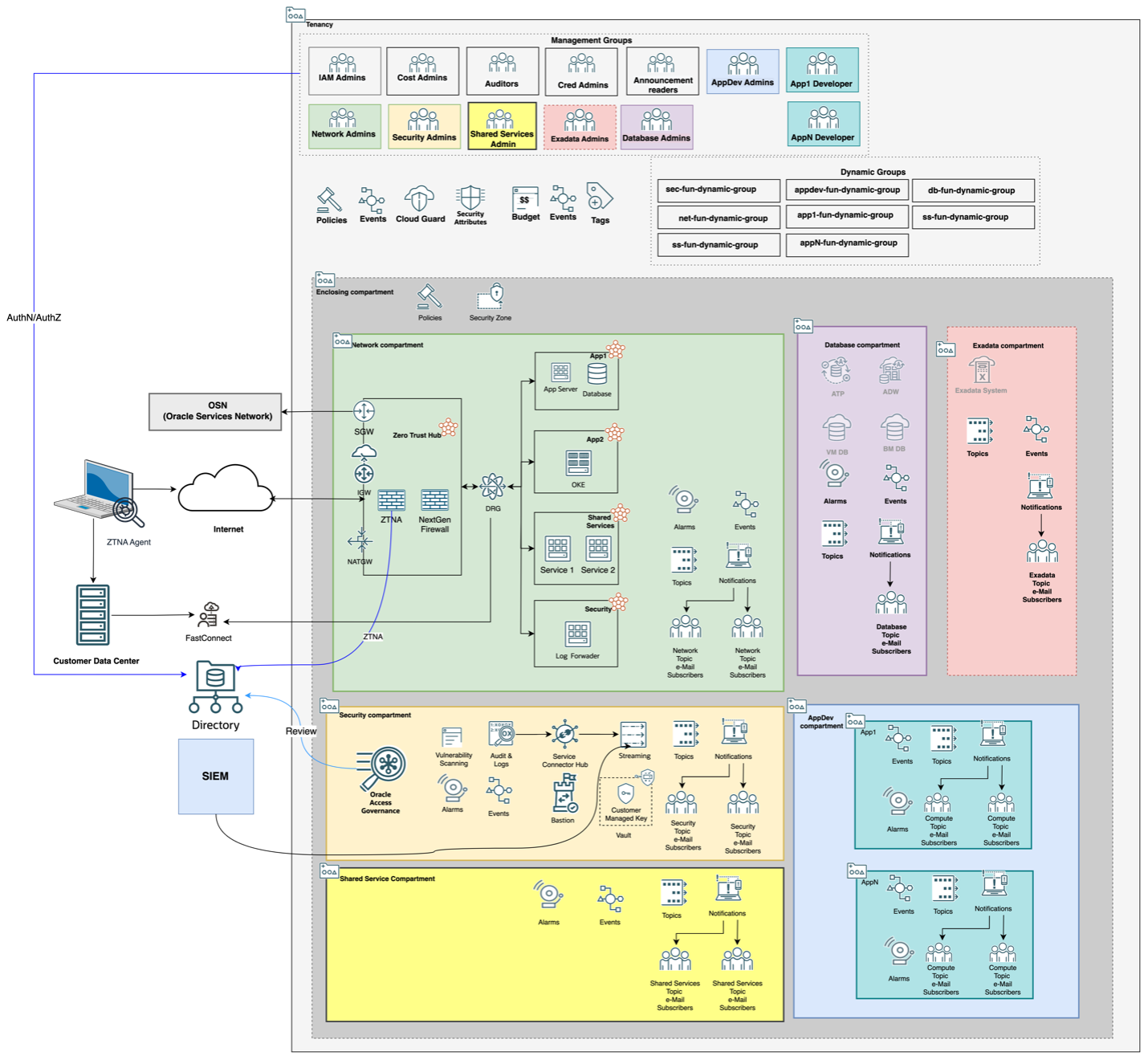
With the combination of the services provisioned by the OCI zero trust landing zone, customers can accelerate their journey to zero trust and bolster their security posture. As more services that enable various zero trust capabilities are supported, the landing zone is updated, and customers can update their cloud tenancies to continue to evolve their zero trust architectures.
Get an early preview of the new OCI zero trust landing zone today!
Check out the new OCI zero trust landing zone on GitHub today – currently available in early preview and will be generally available soon. You can also read this blog post to learn more about the new standardized OCI Landing Zones Framework that this solution is built on – also available in early preview. If you have any questions or comments, don’t hesitate to contact the authors or add a comment on GitHub!
Attending Oracle CloudWorld this week? Come by the Security and Identity OCI demo pod at the expo hall to see the new solution demo and chat with security experts about your use case. Also check out the following talks for more details on the OCI Landing Zones Framework, Zero Trust, and related services:


