With the huge demand of generative AI opportunities worldwide, planning for the required compute capacity is crucial. While NVIDIA A100 and H100 Tensor Core GPUs offer great performance for large scale LLM deployments, they can be complemented with mainstream GPUs like T4 , P100, and A10 for smaller scale deployments.
With the well-engineered Oracle Generative AI services, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) also allows customers to bring their own models (open source or custom) for inferencing on the highly efficient OCI Servers. When running bring-your-own models purely on OCI, one might need to benchmark and optimize by running the LLMs on mainstream NVIDIA-accelerated OCI servers. This blog details how mainstream GP U s accelerated OCI servers (both bare metal and virtual machine) can be used for running a wide range of inferencing scenarios using Opensource LLMs.
Benchmarking parameters
Following are the different set of parameters which influence the inferencing test scenarios and results:
- Generative AI model specifications: Model type and size
- GPU specifications: Model and number of GPUs
- CPU specifications: CPU type and number of CPUs
- Maximum context window
- Performance optimizations
- Quantized and unquantized models
- Different LLM models like transformer , transformer with KV cache optimization and paged attention, transformer with flash attention etc
- Performance measured in terms of tokens per second
Testing environment
The following server configurations are used for the benchmarking purposes:
- OCI server types and specifications
- GPU accelerated bare metal
- Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 CPU @ 2.60GHz (128 cores)
- Four NVIDIA A10 Tensor Core GPU s , each with 24GB GDDR6 memory
- 1TB RAM
- GPU accelerated VM
- Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 CPU @ 2.60GHz (60 cores)
- Two NVIDIA A10 GPUs, each with 24GB GDDR6 memory
- 480GB RAM
- GPU Accelerated Roving Edge Device ( RED)
- Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6230T CPU @ 2.10GHz ( 32 cores)
- One NVIDIA T4 GPU with 16 GB GDDR6 memory
- 512 GB RAM
- GPU accelerated bare metal
The following LLM models ( quantized and unquantized versions ) are used for this benchmarking exercise:
- Llama 2 models (7B, 13B, and 70B)
- Llama 2 HF models (7B, 13B, and 70B)
- Llama 3 models ( 8B , 70B )
- Fin-llama-33B
Single-server, single-user inferencing tests
The following table shows the test results done on fin-llama models using llama.cpp on a single OCI bare metal server.
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs(tokens/second) |
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q2_K.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
29. 2 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q3_K_L.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
28. 2 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q3_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
2 9 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q3_K_S.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
28. 4 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
30.9 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33B-GGUF.Q5_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
29. 2 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q4_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
28.5 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q4_K_S.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
28. 6 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33B-GGUF.Q5_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
29. 2 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q5_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
27. 7 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q5_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
27. 6 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q5_K_S.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
28 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q6_K.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
25.1 |
|
| fin-llama-33B-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, fin-llama-33b.Q8_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
23. 5 |
The following table shows the test results done on Llama 2 models using llama.cpp on a single Oracle Roving Edge (RED) server.
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-7b |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
llama-2-7b.Q4_0.gguf · TheBloke/Llama-2-7B-GGUF at main (huggingface.co) |
RED |
T4 |
1 |
51.9
|
| Llama-2-13b |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Llama-2-13B-GGUF/blob/main/llama-2-13b.Q4_0.gguf |
RED |
T4 |
1 |
28. 6
|
| Llama-2-70b |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Llama-2-70B-GGUF/blob/main/llama-2-70b.Q4_0.gguf |
RED |
T4 |
1 |
1. 6
|
The following table shows the test results done on quantized LLaMa2 70B models using llama.cpp on a single OCI bare metal server.
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GPTQ |
llama.cpp, gptq |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
11.2 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GPTQ |
llama.cpp, gptq |
TheBloke/Llama-2-70B-Chat-GPTQ at gptq-3bit–1g-actorder_True (huggingface.co) |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
10.5 |
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-AWQ |
llama.cpp,AWQ |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
13. 6 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q3_K_L.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
17.5 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
19. 2 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q4_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
17. 9 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q5_K_M.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
16. 8 |
Single-server, multiuser concurrency inferencing tests
The following table shows the test results done on Llama 2 models using llama.cpp for concurrent users on a single OCI bare metal server.
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator Type |
Number of GPUs |
Concurrent users |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
5 |
10.3 |
|
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-GGUF |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-70b-chat.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
10 |
8.7 |
|
| fin-llama-33b.Q4_0.gguf |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-33b-chat.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
5 |
22 |
|
| fin-llama-33b.Q4_0.gguf |
llama.cpp, GGUF, llama-2-33b-chat.Q4_0.gguf |
BM with 4 A10s |
A10 |
4 |
10 |
10.2 |
Distributed inferencing results on multiple servers
The following table shows the test results done on quantized Llama 2 models using llama.cpp with four OCI RED servers and using Message Passing Interface (MPI).
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-7b MPI Run |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
llama-2-7b.Q4_0.gguf · TheBloke/Llama-2-7B-GGUF at main (huggingface.co) |
4 REDs |
T4 |
4 |
52. 2
|
| Llama-2-13b MPI Run |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Llama-2-13B-GGUF/blob/main/llama-2-13b.Q4_0.gguf |
4 REDs |
T4 |
4 |
28.7
|
| Llama-2-70b MPI Run |
Llama-cpp , ggml-model-q4_0.gguf |
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Llama-2-70B-GGUF/blob/main/llama-2-70b.Q4_0.gguf |
4 REDs |
T4 |
4 |
1. 6
|
Memory calculation for unquantized LLaMA 70B Models
For running a unquantized Llama transformer model on A10s, the following memory calculation is used:
- Model type: Llama
- Model size: 70B
- Total memory requirement: 70B X 2 byte (16 bit) = 140 GB
- Memory of 1 A10 GPU = 24 GB
- Memory of 8 GPU = 160 GB (excluding GPU memory overheads on each A10 GPU).
Based on this calculation, the Llama 70B unquantized model can run on two OCI bare metal servers with eight A10 GPUs using any distributed inferencing framework, such as torchrun, Ray or MPI.
| Model Type |
Transformer Model, Quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-70b |
Llama2 , 70B model, torchrun |
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
8.8 |
The following table shows the test results of the Llama 70B unquantized model using four VM servers with two A10s each:
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantization |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-70b |
Llama2 , 70B model, torchrun |
4 VM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
4 |
The following table shows the test results of Llama2 models using vLLM transformer model ( with Paged Attention) using two bare metal servers with four A10s each:
| Model type |
Transformer model, quantiation |
Deployment config |
OCI instance type |
Accelerator type |
Number of GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Llama-2-7b |
vLLM /PagedAttention/Ray
|
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
30. 1 |
|
| Llama-2-13b |
vLLM /PagedAttention/Ray
|
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
27.3 |
|
| Llama-2-70b |
vLLM /PagedAttention/Ray
|
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
12.9 |
Following are the results of LLama3 Runs on 2 BM with 8 A10 GPUs using any distributed inferencing framework like torchrun, Ray , MPI etc.
| Model Type |
Transformer Model, Quantisation |
Deployment Config |
OCI Instance Type |
Accelerator Type |
Num GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Meta-Llama-3-70B |
llama 3, 70B model, torchrun |
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
12.44 |
|
| Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct |
llama 3, 70B model, torchrun |
2 BM Servers |
A10s |
8 |
12.24 |
|
| Meta-Llama-3-8B |
llama 3, 8B model, torchrun |
1 BM Server |
A10 |
1 |
27.10
|
|
| Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct |
llama 3, 8B model, torchrun |
1 BM Server |
A10 |
1 |
27.04
|
The following table shows the test results of Llama3 models using vLLM transformer model ( with Paged Attention) using two bare metal servers with four A10s each:
| Model Type |
Transformer Model, Quantisation |
Deployment Config |
OCI Instance Type |
Accelerator Type |
Num GPUs |
Throughput across all GPUs (tokens/second) |
| Meta-Llama-3-8B |
vLLM /PagedAttention/Ray
|
BM 2 Servers |
A10s |
8 |
24.61 |
|
| Meta-Llama-3-70B |
vLLM /PagedAttention/Ray
|
BM 2 Servers |
A10s |
8 |
11.23 |
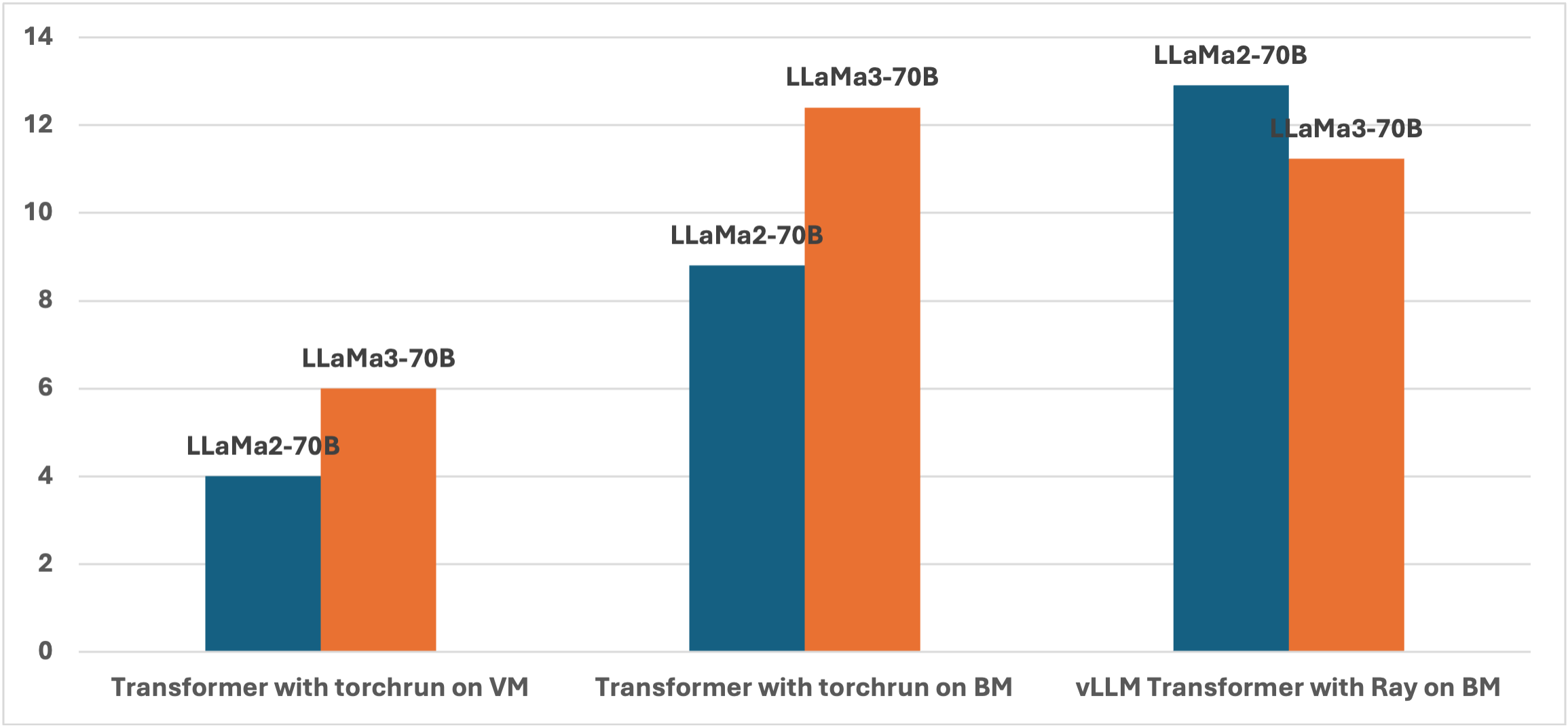
The following chart summarizes the inferencing performance of LLaMa2 and LLaMA3 unquantized models of Transformer and vLLM on A10 accelerated OCI VM and BM servers.
Conclusion
The above benchmarking exercises show t hat mainstream GPU accelerated OCI servers (like A10s) can be used for inferencing activities of different sizes of Opensource large language models (LLMs) . When the best performance is needed for larger scale deployments, OCI offers advanced NVIDIA GPUs deployed with NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, which delivers great results as shown in the recent MLPerf Inference v4.0 benchmarks. Depending on the requirements and the scale of the solution,one can start working with smaller LLMs, such as 7B and 13B models on mainstream GPU-accelerated servers, and then migrate to larger clusters with advanced GPUs ( A100s, H100s etc) as demand and model size increases. This scaling helps in quicker adoption of generative AI solutions for the customer.
Acknowledgments
The author wants to thank Mohan Srinivasan, Sreedhara Narayanaswamy, Ram Sivaram, and Hiten Goradia for their guidance, leadership, and support in this endeavour. The author also wants to thank James George for his expertise in setting up the MPI cluster on Oracle Roving Edge Devices(RED) .
Disclaimer
The benchmarking exercise published in this paper are for general guidance only. Individual test results can vary based on model size, testing parameters,performance techniques and the hardware/software stack used.
References
For further information, please visit the following links
Oracle Generative AI Solutions: https://www.oracle.com/artificial-intelligence/generative-ai/
Oracle GPU accelerated BareMetal Servers:https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/References/computeshapes.htm#bm-gpu
Oracle GPU accelerated VM Servers:https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/References/computeshapes.htm#vm-gpu
Oracle Roving Edge Servers: https://www.oracle.com/a/ocom/docs/data-sheet-roving-edge-device.pdf
NVIDIA A10 GPUs: https://www.nvidia.com/en-au/data-center/products/a10-gpu/
LLaMA CPP Source Code: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
Meta LLaMA2 : meta-llama/llama: Inference code for Llama models (github.com)
Meta LLaMA3: meta-llama/llama3: The official Meta Llama 3 GitHub site
