We’re excited to announce a new feature in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Cloud Shell that offers more control over public network access, improving security for your cloud resources.
Previously, our customers faced limitations from a lack of control over outgoing traffic (egress) to the public network through Cloud Shell. Any user with access to Cloud Shell could potentially access unauthorized resources or services on the public internet, leaving potential vulnerabilities in their security infrastructure. With this new feature, you now have the power to implement more granular access controls, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and bolstering the overall security posture of your cloud resources.
This feature offers the following benefits:
- Improves data security: By restricting unnecessary public network access, you can help keep your sensitive data within your cloud environment, minimizing the risk of exposure.
- Manage risk of unauthorized access: Granular access controls restrict public network egress, making it harder for unauthorized users to access your cloud resources through Cloud Shell. This control reduces potential security breaches.
- Helps improve security posture: By implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Security Zone policies, you can define exactly who can access the public network from Cloud Shell .
In addition to these policy enhancements, we’re introducing the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Service Network, a dedicated network for customers to access OCI-wide services without relying on the public internet. This network serves as the default access for Cloud Shell unless your administrator has specified an identity policy.
Controlling access with Cloud Shell network policies
You can now govern Cloud Shell Public Network access through the following distinct policies:
- Cloud Shell Public Network IAM policy: This policy allows administrators to grant access to Cloud Shell-managed public networks to specific user groups. By defining an IAM policy, admins can control which user groups can use the public network.
- Security zone policy: While IAM policies establish user groups allowed to access the public network, security zone policies provide a more granular layer of control. They can restrict public network access for all users within a tenancy, overriding even tenancy administrator permissions. This feature enables you to create a locked-down environment where public network access is completely disabled by default and then grant exceptions only to specific user groups or use cases through IAM policies.
Implementing access control policies
To utilize these new capabilities effectively, use the following guides:
Granting access with an IAM policy
Use the IAM policies to enable users access to the Cloud Shell-managed public network. The resource name for this network is cloud-shell-public-network.
Run the following command:
allow group <GROUP-NAME> to use cloud-shell-public-network in tenancy
Enforcing a security zone policy
To enforce the security zone policy, use the following steps:
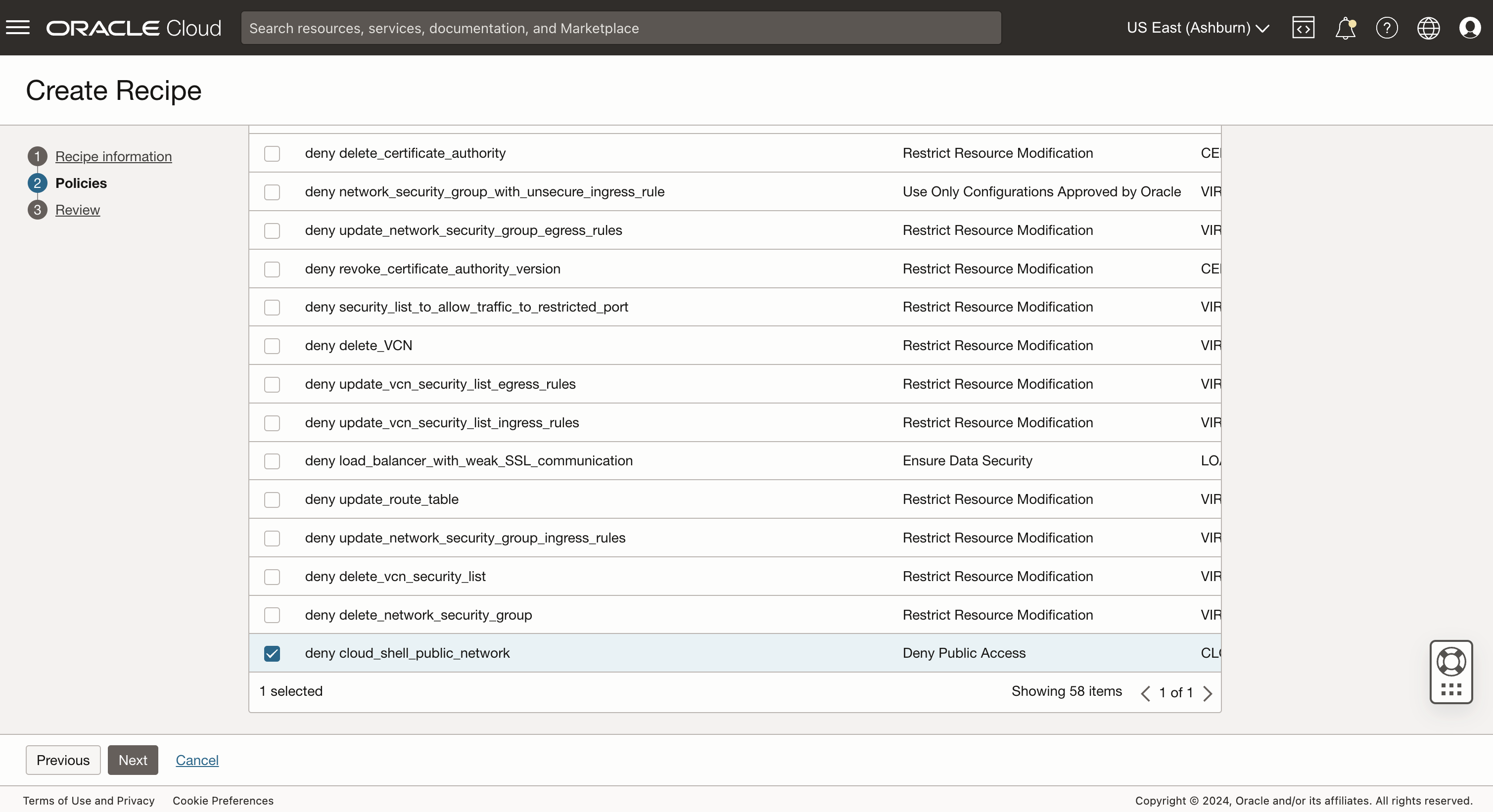
1. Create a recipe.
- In the Oracle Cloud Console, navigate to the Security Zones service and create a recipe.
- Within the recipe, ensure that the “deny cloud_shell_public_network” policy is selected.
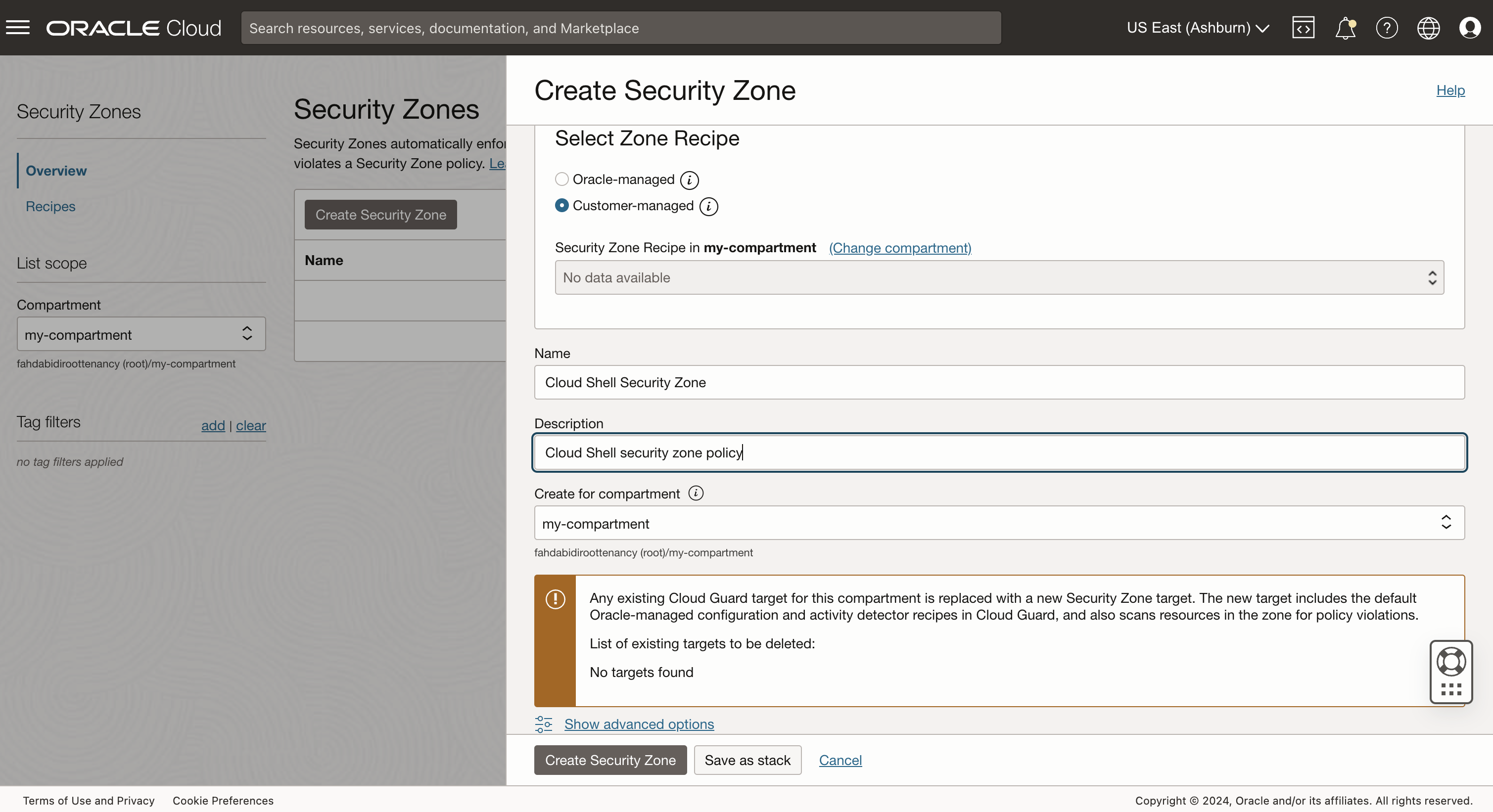
2. Create a security zone.
- When the recipe is established, create a security zone for your root compartment.
- Select the customer-managed security zone recipe during creation and choose your previously created recipe.
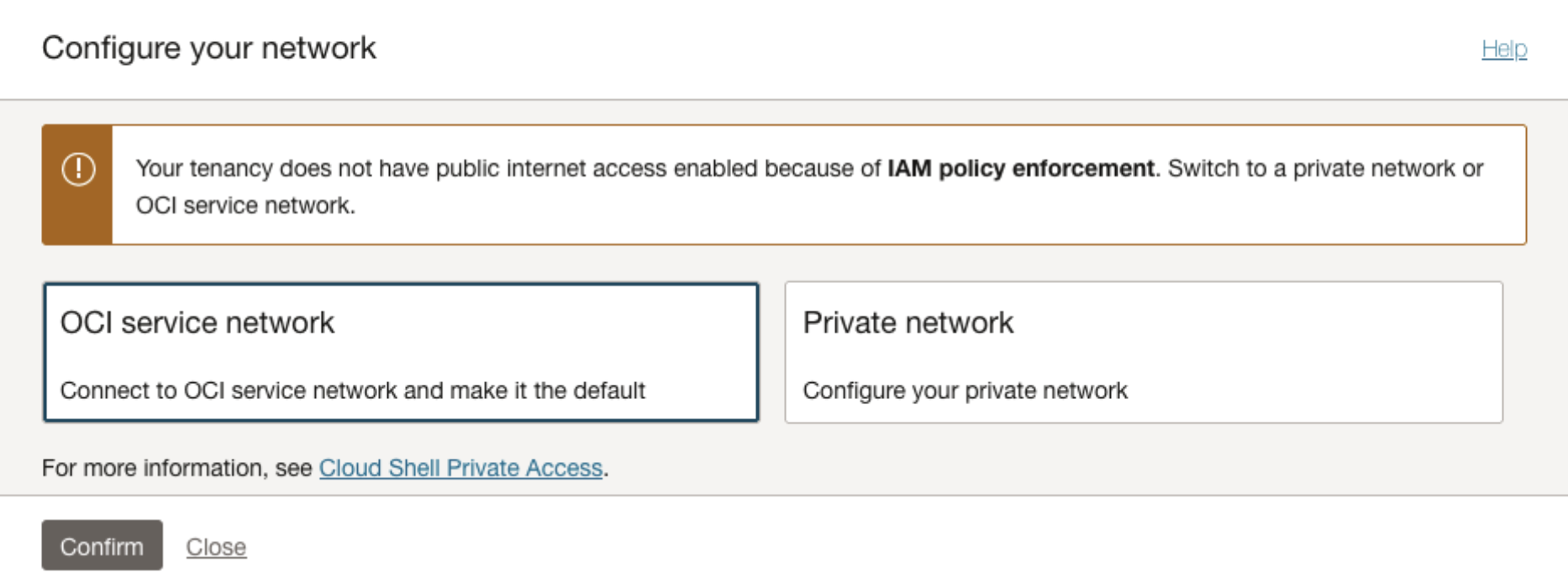
Accessing OCI service network
If your administrator hasn’t set up an IAM policy, Cloud Shell produces the following dialog when it starts. Select and confirm the OCI service network option to access OCI-wide services.
Get started today
These enhancements to Cloud Shell help increase the control over your network access, tailoring your method to secure your cloud resources. If you’re new to policies, see Getting Started with Policies and Common Policies.
If you’re new to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you can create your Oracle Cloud Free Tier to get acquainted.
For more information on this feature, see the following resources:
Cloud Shell Networking documentation