We’re happy to announce OCI Object Storage support for CRC32C, SHA256, and SHA384 checksum algorithms, in addition to MD5. Now, customers can use their preferred checksum algorithms for integrity checking and to meet their operational and compliance requirements. For example, SHA256 and SHA384 are secure and robust, and are best used with sensitive data. CRC32C is faster and is good for detecting upload errors as well as for simplifying data integrity checks for applications that use multi-part uploads for large objects.
New checksums enable flexibility
OCI Object Storage is the backbone for several mission-critical applications. Object Storage helps ensure the data integrity of all PUT and GET operations with MD5 checksums by default. An MD5 checksum is computed for each uploaded object or for each part of a multi-part object during a PUT operation, which helps ensure that the object stored is the object that was uploaded. During a GET operation, this checksum helps ensure that the object retrieved is the object that was stored.
Applications that that have large objects use multi-part uploads. With MD5, this process can get complex as each part of a multi-part upload generates its own checksum. This checksum can vary based on its size, location from where it’s uploaded, and the upload settings. Applications that require a checksum validation maintain their own systems to track the object ID and its associated checksum value to commit a PUT operation as well as during a GET operation.
In particular, multi-part uploads benefit from CRC32C checksum. Customers can now easily verify object data integrity with the CRC32C checksum. The CRC32C checksum is designed to return the same checksum for the same object regardless of how it’s uploaded. This functionality enables customers to compare the CRC32C checksum calculated by Object Storage with the CRC32C checksum calculated by local storage or other clouds, regardless of the multi-part upload settings.
Additionally, some industries have regulatory requirements (such as HIPAA, PCI, DSS, GDPR) to use a checksum method considered stronger than MD5. Those requirements often explicitly require SHA256 or SHA384 checksums. You can select the algorithm required by the compliance standard when using Object Storage.
These checksum options are provided in addition to MD5. Object Storage will continue to use MD5 checksums for data integrity checks. Adding another checksum method provides an extra integrity check.
Getting started
You can pick the checksum algorithm that suits your needs from the Oracle Cloud Console, in the OCI CLI, and through our various SDKs.
To get started in the Oracle Cloud Console, select a checksum option when you upload an object in Object Storage.
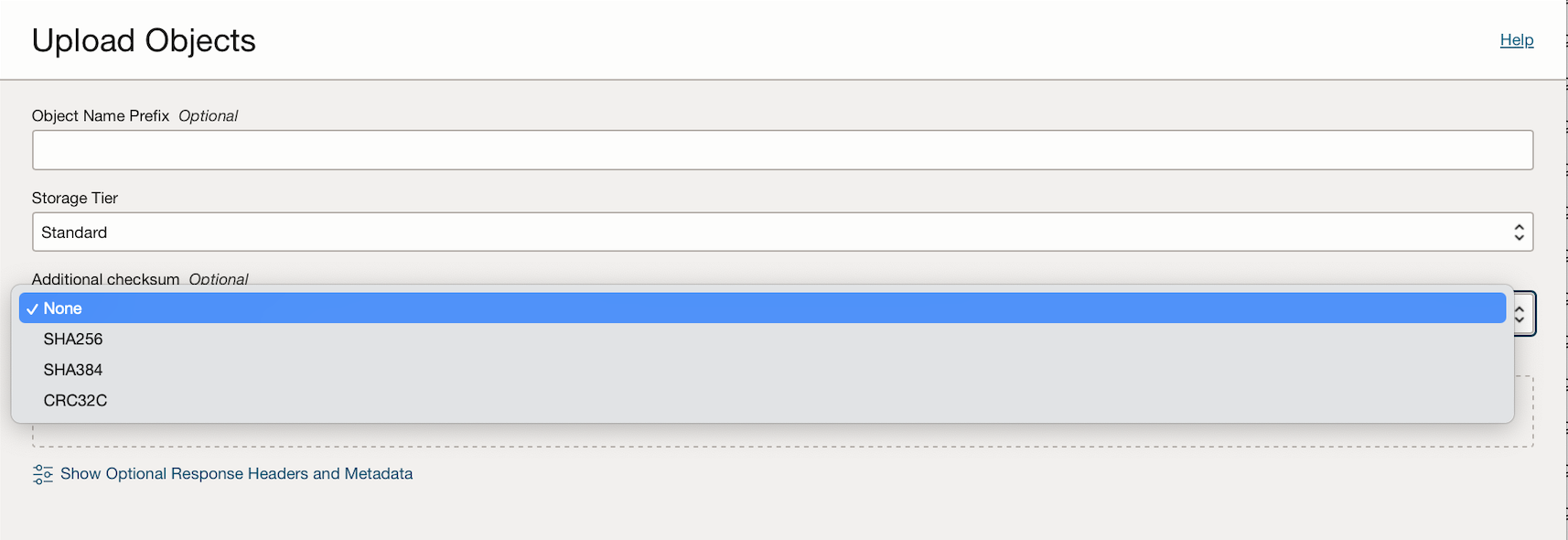
The rest of the PUT and GET operations are the same.
Learn more about using checksums with OCI Object Storage by reviewing the Checksums in Data Security documentation, using the OCI CLI, or exploring the OCI SDKs.
We want you to experience these new features in OCI Object Storage. Interested in trying OCI Object Storage? Sign up for a free trial.
