We’re pleased to announce that Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) API Gateway adds the following capabilities that help API developers create more secure APIs:
-
TLS certificate management for API Gateway is fully managed inOCI Certificatesmaking the process of creating and managing TLS certificates much easier for API developers. You can create an API gateway with an automatically defined host name, using a built-in, common certificate, which is ideal for simple cases, development, and testing. When publishing APIs into production, companies often want to use their own DNS and use their own TLS server certificates. API Gateway offered this capability already, but now that OCI Certificates aregenerally available, you can create, and manage your certificates in OCI Certificates and select the certificates from API Gateway when creating or updating a gateway.
-
API Gateway can use customer provided certificate authorities to validate the authenticity of backend services, also known as defining a trust store. Securing connections using TLS is a best practice, but sometimes customers don’t want to purchase signed TLS certificates for all their private backend services. Using OCI Certificates, you can maintain and use certificate authorities with API Gateway to trust self-signed TLS certificates.
-
API Gatewaynow supports client mutual-TLS (mTLS). Developers cancreate APIs that enforce mTLS client verification, also known as two-way transport layer security (TLS). Client mTLS helps developers create more secure APIs by providing an extra layer of security over open authorization (OAuth2) alone.
Integration with OCI Certificates
OCI Certificatesmakes it easier to create and maintain TLS certificates and certificate authorities offering automation to manage expiration and renewal. Instead of manuallymanaging TLS certificates and loading them into OCI API Gateway, developers can simply choose from TLS certificate and certificate authority resources maintained inOCI Certificatesservice.
Support for verifying privately signed TLS certificates
Customers can now use privately signed TLS certificates with OCI API Gateway. Customers can secure access from both clients and backends using privately signed certificates allowing greater freedom and increasing security.
Client mTLS
OAuth2 is a great way to handle delegated authorization through a bearer token, but if that token is intercepted, another client can use it. Using mTLS, OCI API Gateway requires the client to provide a signed TLS certificate that verifies its identity, allowing OCI API Gateway to provide internet-accessible APIs and block any requests from clients that don’t possess the TLS certificate.
Use case: Open banking
Banks are facing new realities where they need to make their customer account information available. Initiatives, such as the EU Payments Services Directive 2 (PSD2), define the required approaches for banks to provide secure APIs to enable the free integration of banks and financial technology for the benefit of customers. However, APIs are rapidly becoming the top attack surface making security more critical than ever before. Mutual-TLS helps banks support requirements for open banking and PSD2 with more secure APIs. Using Oracle Open Banking APIs with OCI API Gateway, banks can innovate to meet their customers’ needs and comply with government regulators.
Adding a certificate authority to an API gateway
Client mTLS requires a certificate authority to be created in OCI Certificates. Clients use this certificate authority to sign the TLS certificates who invoke APIs on the gateway that enforces mTLS. If routing to HTTPS backends that use a private TLS certificate, the gateway can also use a private certificate authority fromOCI Certificates.
When creating an API gateway, choose the certificate authority that you want the API gateway to use to validate TLS certificates.
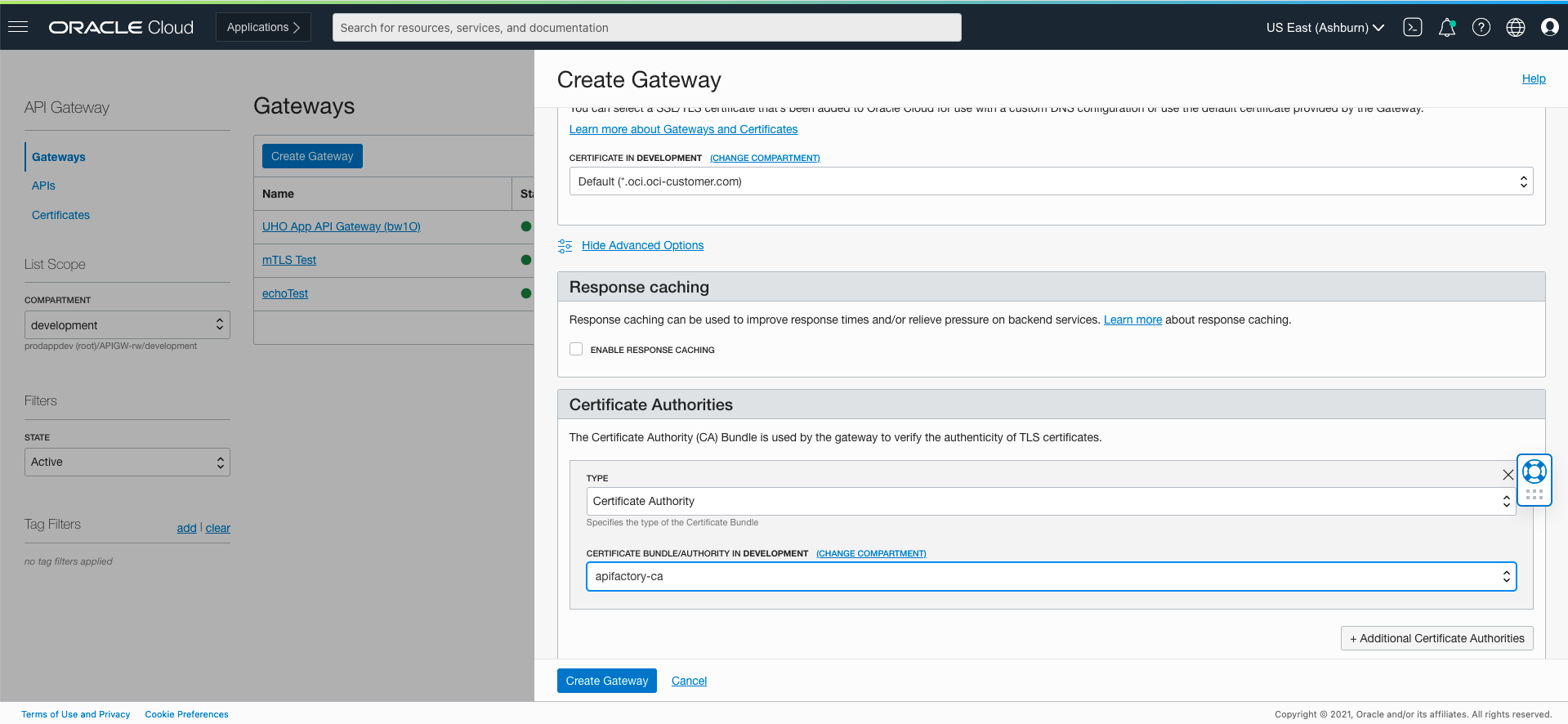
An existing gateway can be updated to add or remove certificate authorities.

When creating an API for which you want to enforce mTLS, selectENABLE MTLSand add the subject alternate name or common name that you want to validate. Clients that present TLS certificates that are signed by the certificate authority are allowed, while all other clients are denied. The API further restricts access to TLS certificates created with the specified common name or subject alternate name.
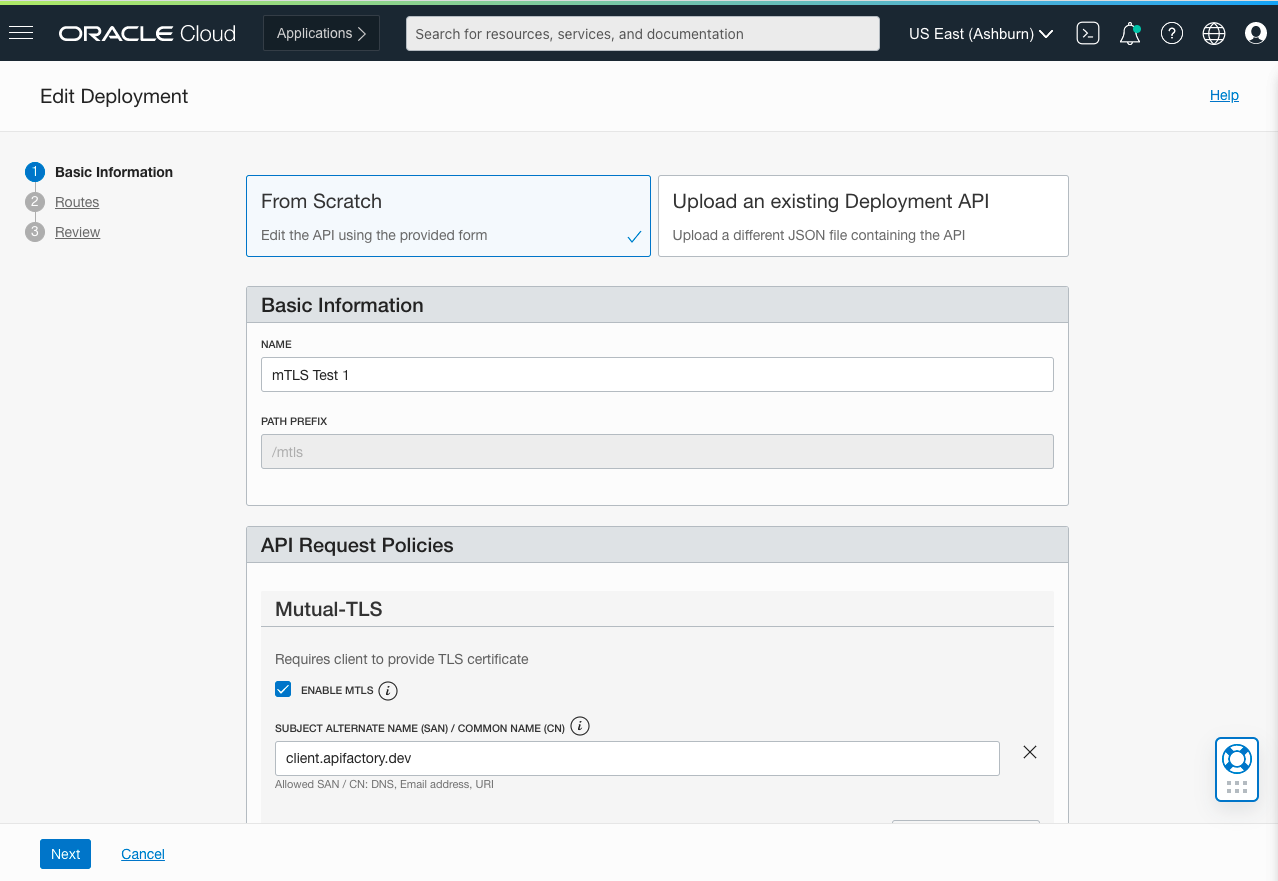
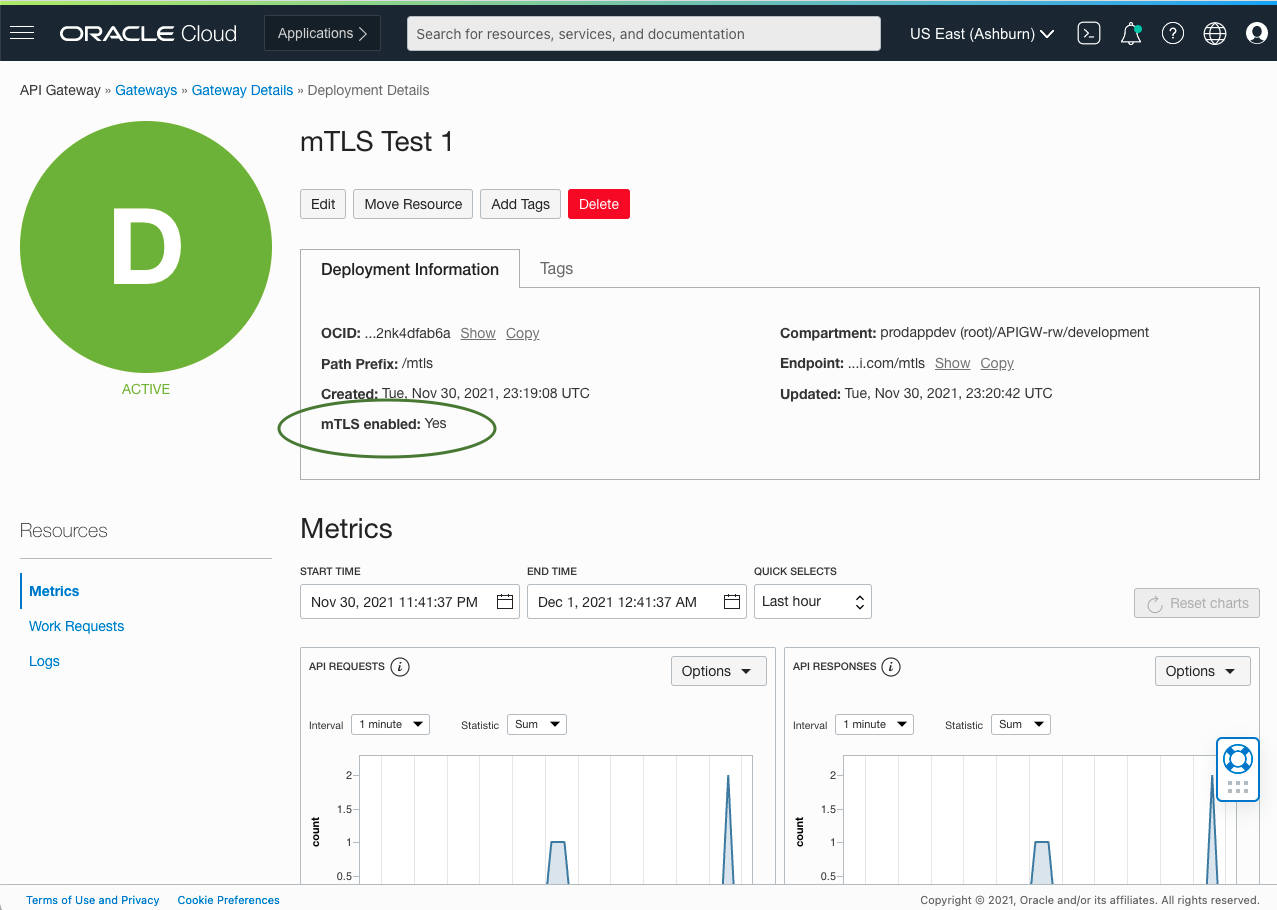
When the API deployment is created, you seemTLS enabledin the deployment information.
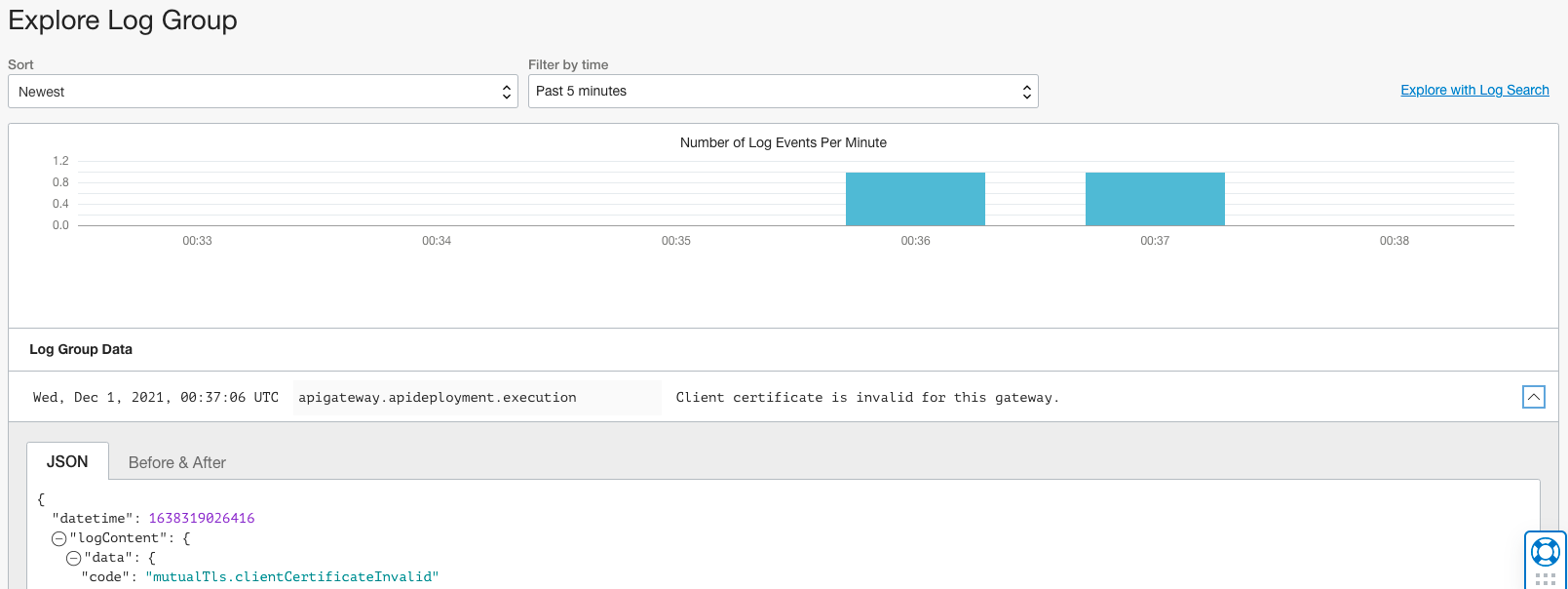
Clients that attempt to invoke the API without providing a valid TLS certificate are denied with an HTTP401 error.
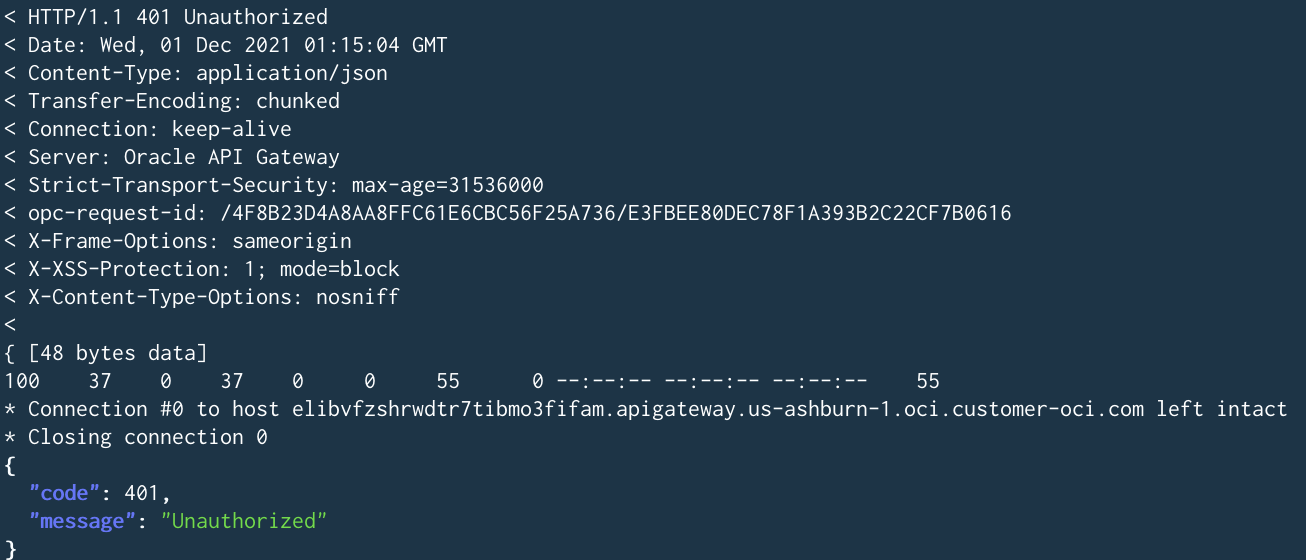
Rejections for invalid TLS (or no TLS) certificates are included in the logs.
Conclusion
Security is the most critical element of API Management. API Gateway further enhances the ability to create secure APIs by supporting client mTLS. Integration withOCI Certificatesmakes it easier for API development teams to create, manage, and use TLS certificates and certificate authorities with API gateway. With the support of self-signed TLS certificates validated by certificate authorities, you can secure and verify connections without the cost of publicly signed certificates.
For more information, see the following resources:
