-
Do you want to stop duplicating your machine learning datasets on all nodes of your GPU cluster?
-
Do you want to reduce the money spent on storage for your training datasets?
-
Do you have training datasets that can’t fit on the locally attached NVMe SSD of your cluster instances?
-
Are you running training on GPU instances with no local NVMe SSD storage and need high-performance storage for training datasets?
-
Does your workload need up to 2,680 MB/s IO throughput or 700K IOPS storage performance?
-
Do you want to avoid running a network file share (NFS) server or use any shared file system?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, keep reading this blog for a solution on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) using OCI Block Volumes with the multiattach and shared disk feature.
In this blog post, I present a step-by-step walkthrough of configuring OCI Block Volume for running any distributed training on multiple GPU instances. I show you how you can use a single volume to store your entire training datasets and attach it to multiple OCI instances. No more copying and duplicating datasets!
This process has the following steps:
-
Load training datasets onto a block volume or block volumes.
-
Attach the block volume with training dataset to GPU accelerated cluster nodes.
Load training datasets onto a block volume or block volumes
In your machine learning (ML) pipeline, add a step to load your OCI block volume or disk with your training datasets. You can do this step anytime before creating your GPU cluster, using any standard Compute instance.
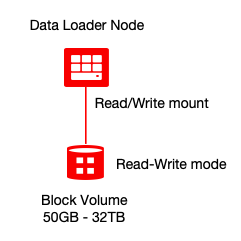
Create the block volume with the following command:
oci bv volume create --availability-domain VXpT:PHX-AD-3 --compartment-id ocid1.tenancy.oc1..xxxxxxx --display-name training-dataset-volume --size-in-gbs 100 --vpus-per-gb 10Provision a VM instance
Create a VM instance so that you can attach the volume you created to the instance to load training dataset. You can use any standard VM shapes (VM.Standard2.x, VM.Standard.E3.x, or VM.Standard.E4.x) and don’t need GPU or a high-performance computing (HPC) instance while loading data. You can also decouple the preparation of your training datasets from provisioning of your Compute cluster in your pipeline. You can use the Oracle Cloud Console, OCI CLI, software developer kit (SDK), or Terraform to provision a node.
After creating the instance, note the instance OCID value. We need it in next step. The following code string shows an example:
ocid1.instance.oc1.phx.anyhqljtpwneysacnejldd2nqbed2whiwljqtqj7kfevli7ojad6nwkcu2zaAttach the block volume to VM instance
Using an Oracle consistent device path (/dev/oracleoci/oraclevdX) is mandatory, especially when you plan to use the multiattach feature of OCI Block Volumes. It ensures that all Compute instances mount to the same device. The mapping of the block device to the /dev/sdX device name can change after reboot, so use the consistent device path.
oci compute volume-attachment attach-paravirtualized-volume --instance-id ocid1.instance.oc1.phx.anyhqljtpwneysacnejldd2nqbed2whiwljqtqj7kfevli7ojad6nwkcu2za --volume-id ocid1.volume.oc1.phx.abyhqljtm5jchrbfcrweeni7dinlih3ackrfsqdtqw26o3covvedzjf2em2a --device /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd --display-name attach-training-dataset-volumeTo validate, run the following commands:
ls -l /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 6 Nov 13 10:30 /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd -> ../sdd
lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sdd 8:16 0 100G 0 disk
sda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk
└─sda2 8:2 0 8G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 38.4G 0 part /
└─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot/efi
sudo file -s /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd
/dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd: symbolic link to `../sdd
sudo file -s /dev/sdd
/dev/sdd: data
Mount the block volume
sudo mkfs.xfs -b size=4096 /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd
mkdir -p ~/datasets
sudo mount /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd ~/datasets
sudo chown opc:opc ~/datasets
Next, load the dataset onto the block volume.
Detach the volume and delete the instance
After the dataset has been loaded, you can delete the temporary instance. When terminated, the instance automatically detached from the block volume, but you can manually detach the volume using OCI CLI, SDK, Console, or Terraform with the following command:
echo y | oci compute volume-attachment detach --volume-attachment-id ocid1.volumeattachment.oc1.phx.anyhqljtpwneysachw44aeehjfbfxvk3mtodtdbxnsufd2434kfdc7yhzmjqAttach the block volume with the training dataset to HPC or GPU accelerated cluster nodes
In this blog, I’m provisioning a two-node GPU cluster with an instance-id of inst-id-1 and inst-id-2.
Attach the block volume to all instances of the cluster
Attach the volume with the access type of “read-only shareable” iSCSI or paravirtualized with an Oracle consistent device path. You can multiattach each volume to up to eight Compute instances at the same time.
In this solution, we use the access type of “read-only shareable” for two reasons. Training datasets are usually read-only (no write) by the artificial intelligence (AI), ML), and deep learning (DL) workloads to build a model. We’re also not using a complex cluster-aware file system (using xfs) to handle concurrent writes to the block device.
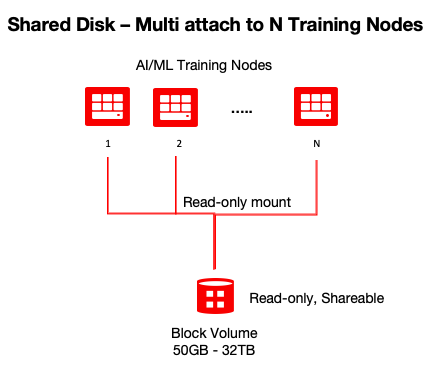
oci compute volume-attachment attach-paravirtualized-volume --instance-id inst-id-1 --volume-id ocid1.volume.oc1.phx.abyhqljtm5jchrbfcrweeni7dinlih3ackrfsqdtqw26o3covvedzjf2em2a --device /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd --display-name attach-training-dataset-volume --is-read-only true --is-shareable trueoci compute volume-attachment attach-paravirtualized-volume --instance-id inst-id-2 --volume-id ocid1.volume.oc1.phx.abyhqljtm5jchrbfcrweeni7dinlih3ackrfsqdtqw26o3covvedzjf2em2a --device /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd --display-name attach-training-dataset-volume --is-read-only true --is-shareable trueMount the block volume on all instances of the cluster
Training datasets are read-only (no write) by the AI, ML, andDL workloads to build a model. So, mount as a read-only file.
sudo mount -o ro /dev/oracleoci/oraclevdd ~/datasets
touch /home/opc/datasets/test-file
touch: cannot touch ‘/home/opc/datasets/test-file’: Read-only file system
Run your workload
When your workload completes, unmount the file system (sudo unmount ~/datasets) and detach the volume from all instances with the following commands:
echo y | oci compute volume-attachment detach --volume-attachment-id ocid1.volumeattachment.oc1.phx.anyhqljtpwneysacp3wimzz4ebmwirhzrvyhxzbtxx6c72jvmj7wkxicnqaa
echo y | oci compute volume-attachment detach --volume-attachment-id ocid1.volumeattachment.oc1.phx.anyhqljtpwneysacdry2xeif4huhmqzhxxgbshk4gouzmxstggadwp6z6e7aLarge clusters: What if my GPU cluster has more than eight instances?
You can attach each volume to eight instances. To support clusters of nine or more instances, you can clone the volume in a few seconds using one command and attach it immediately for use. A cloned volume is a point-in-time direct disk-to-disk deep copy of the source volume, so all the data in the source volume at the clone’s creation is copied to the clone volume.
Using this approach, you can create the cloned volume as part of cluster provisioning, and when the workload finishes, you can delete the cloned volume to save cost. You can use this approach to support large clusters using the building block as shown in the following graphic:
oci bv volume create --availability-domain VXpT:PHX-AD-3 --compartment-id ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaaaaaaacg2kx2vh5y62jvq7bqpgmt7komml6rshkw4hlidt5y2su5gacyja --display-name training-dataset-volume-clone --size-in-gbs 100 --vpus-per-gb 10 --source-volume-id ocid1.volume.oc1.phx.abyhqljtm5jchrbfcrweeni7dinlih3ackrfsqdtqw26o3covvedzjf2em2a 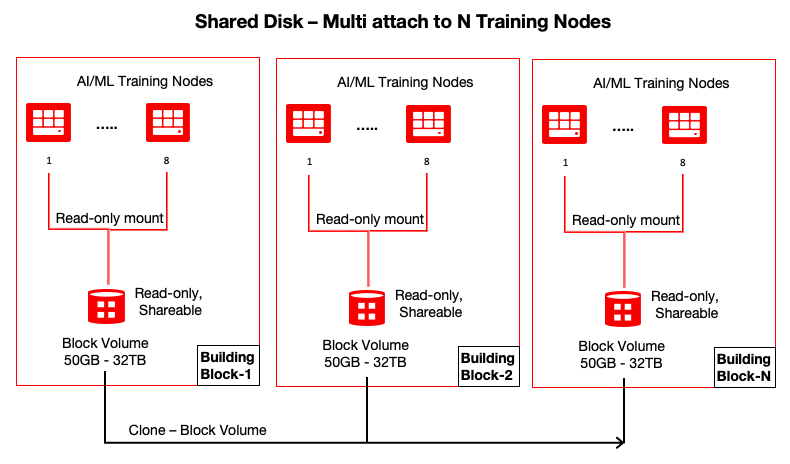
Conclusion
Every use case is different. The only way to know if Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is right for you is to try it. You can select either the Oracle Cloud Free Tier or a 30-day free trial, which includes US$300 in credit to get you started with a range of services, including compute, storage, and networking.
