Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) has a new suite of artificial intelligence (AI) services in the cloud. Generally available in February 2022, OCI Vision service is a managed service that enables novice data scientists to unlock the power of computer vision.
Vision is a serverless, cloud native service that provides deep learning-based, prebuilt, and custom computer vision models over REST APIs. Vision helps you identify and locate objects, extract text, and identify tables, document types, and key-value pairs from business documents, such as receipts. No data science experience is required to use the prebuilt or custom features of OCI Vision.
In this blog post, we cover a sample manufacturing use case where we detect defects in manufactured auto parts.
Use case
Defects during manufacturing of autoparts are expected, but they can be costly. Among the myriad effects of a defective part on the manufacturing line are a loss of revenue, wasted material, recalls, lawsuits, or potentially delayed product launches. The severity of the defects can also vary from stains or scratches to improper attachments, faulty circuit boards, or even missing or broken parts.
To help solve these issues, you can use OCI Vision.
Solution overview
Vision has several capabilities, but this use case uses object detection. Object detection involves drawing a bounding box around the object of interest in the image and applying a label to identify what object is in the box. When you have a good sample of images containing labeled bounding boxes, Vision creates a custom model that predicts if future images contain the object that it has been trained on.
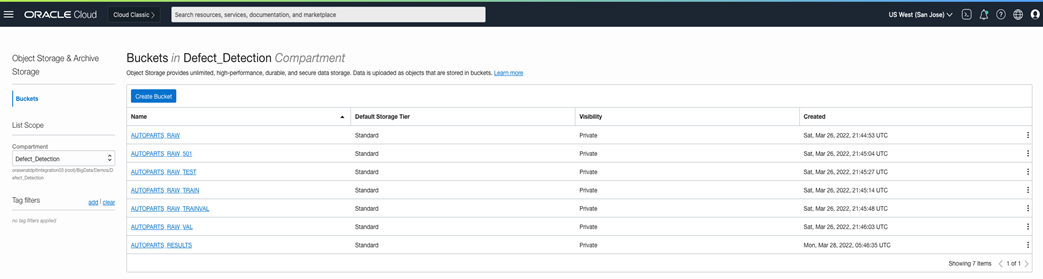
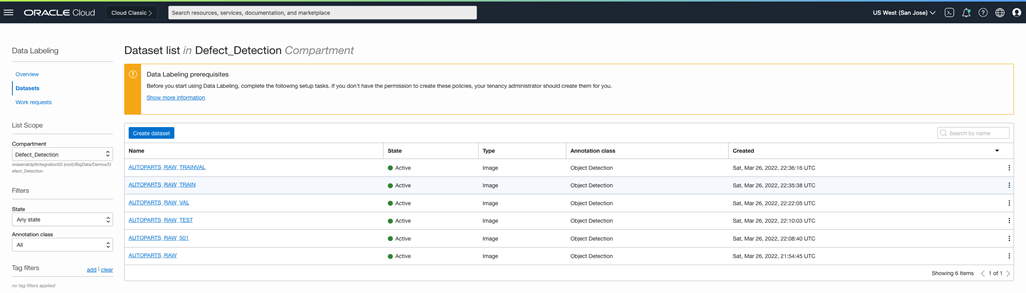
To support the annotation of the autopart images, OCI also includes a Data Labeling service. This service enables the creation of labeled datasets whether it’s for an object detection use case or for a simple image classification use case. The images and results must be stored somewhere, so OCI Object Storage is the obvious, convenient choice.

The sample bounding box in the example image is drawn loosely for illustration, but in practice, the boxes should tightly enclose the object.
The training images are uploaded into Object Storage. Then, Data Labeling annotates the images with boxes bounding the injuries in the image of the autopart. Vision trains a custom model on the data and runs predictions on incoming images. Finally the OCI Data Science platform helps with the process and helps analyze the model. See the following sample architecture.
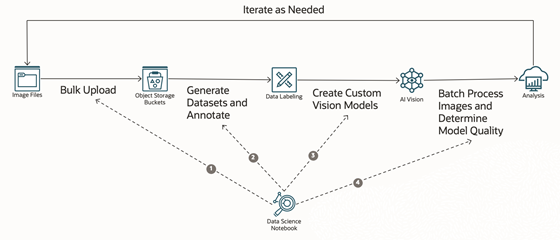
Diving a little deeper
To start, a Jupyter notebook within Data Science uploads all of our images to the designated bucket in Object Storage. I have several different buckets for different training, testing, and validating splits of the data.
Next, another notebook takes care of creating the Data Labeling dataset and applying the prerecorded bounding boxes to the images.
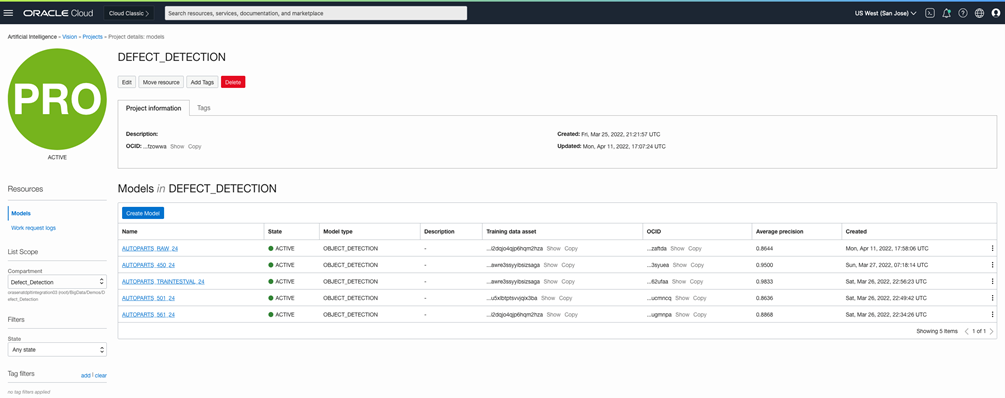
After the dataset is annotated, you can use it to create a custom Vision model! As an alternative to the graphical web-based console, you can use another simple notebook to create the custom model.
When we have our custom model, we can send batches of images to process and make predictions. To give an idea of how the predictions work, the following screenshot shows a prediction being made in the Oracle Cloud Console. You can quickly see where the model predicted a defect, called a bump injury in this example, in the image. A confidence score is provided to show how likely the boxed area on the image contains the defect that we’re looking for.
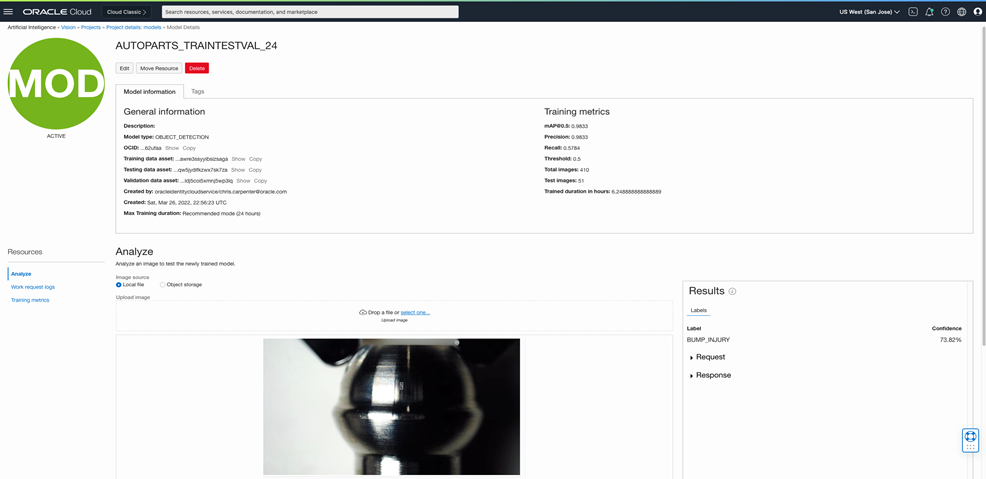
When we can make predictions on the custom model, we can compute various statistics to help determine the quality of the model. Because performing Data Science is an iterative process, we can use the model statistics and human cross-checking to tune the model further.
Other considerations
The methods used in this blog post are one way that you can implement this solution. OCI has a wide variety of services available that enable architectures, from manual processes fully involving the Console to using cloud native services to automate all the steps in the process.
You can also generate advanced statistics with code. For example, as shown in the following notebook running on the OCI Data Science platform, you can compute precision and recall curves for different confidence thresholds and even at different required overlaps of ground truth and predicted bounding boxes. A search for “intersection over union” yields plenty of articles explaining how this process works.
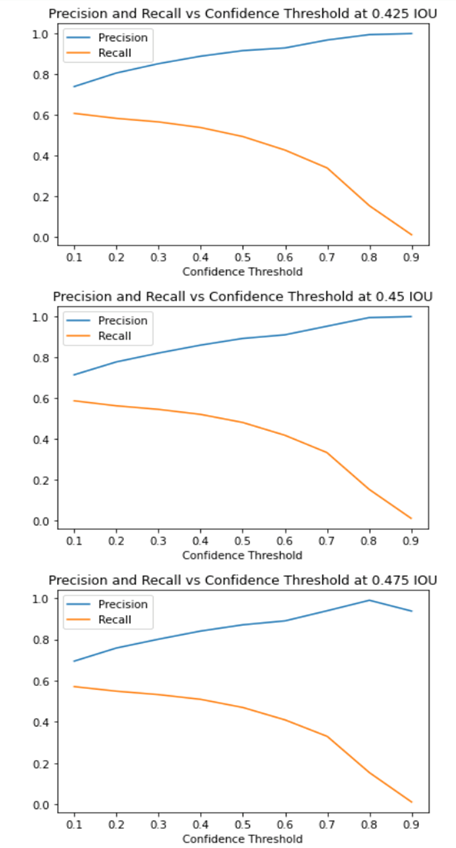
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored the OCI Vision service and a sample use case to which the service can be applied. You can apply the technology to many different use cases, but hopefully this article gives an idea of what’s possible and sparks an innovative mindset to solve tough business problems with the power of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Science and Artificial Intelligence services.
For more information, see the following resources:
