Oracle Cloud Guard is a cloud native service to monitor the security posture of an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy and triggering events for remediation of problems. It provides a set of responders with default rules as specific actions to take. No responders are natively offered to rotate Identity and Access Management (IAM) credentials, such as API keys, customer secret keys, and auth tokens.
In this post, we walk you through how to enable automatic rotation of OCI IAM credentials from Cloud Guard events.
Use cases
We recommend rotating your IAM credential every 90 days. Rotating IAM credentials reduces the window of opportunity for an access key associated with a compromised or terminated account to be used.
The following Cloud Guard problems apply to this solution:
- API key is too old.
- IAM auth token is too old.
- IAM customer secret key is too old.
- Password is too old.
Solution Overview
This solution uses OCI Functions, a serverless compute service to read JSON data from OCI Events to rotate IAM credential and store new credentials in an OCI Vault secret.
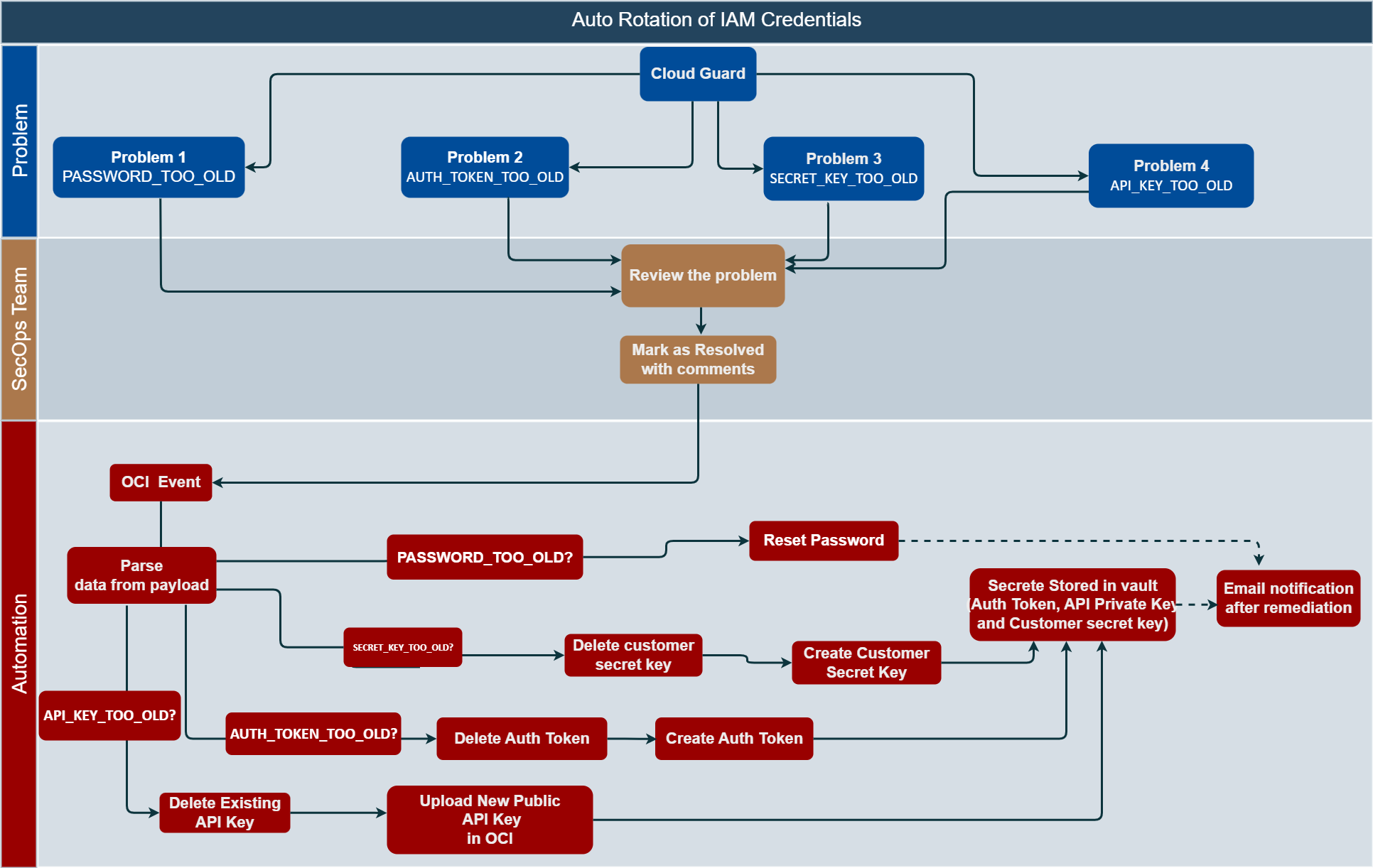
Figure 1. Flow diagram for automatic rotation of IAM credentials
Figure 1 illustrates the cloud native, high-level process flow. Security operations (SecOps) teams review and resolve the problem with comments that trigger an automation.
When you mark a problem as resolved, you’re telling Cloud Guard that it was in fact a problem, but you’ve taken an action that handled it. If another example of this same problem occurs, it’s detected again.
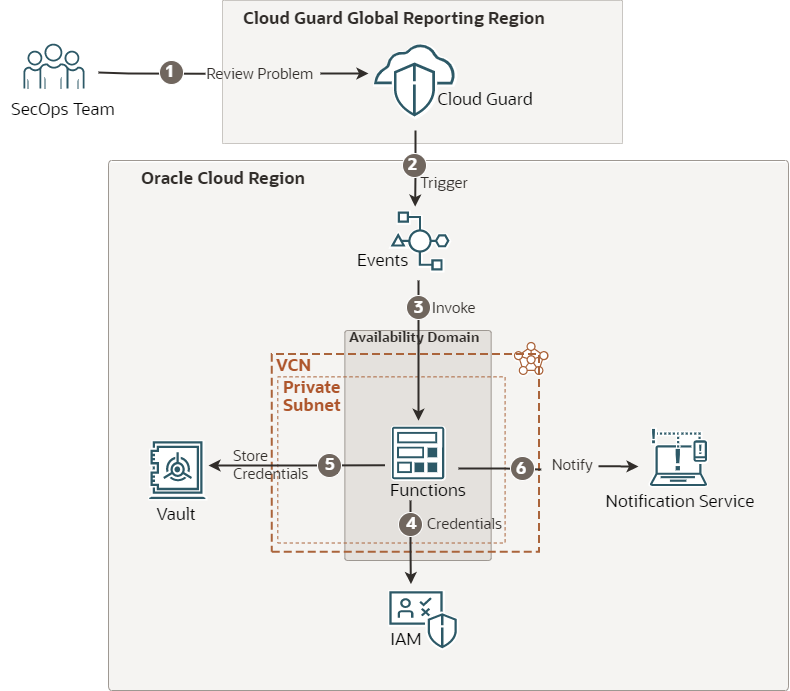
Figure 2. Solution architecture
Figure 2 illustrates the deployment of solution in OCI region.
- The SecOps team reviews the problem in Cloud Guard and follows the change control process to initiate the remediation.
- An event is triggered as soon as the SecOps team resolves the problem with comments.
- The function is invoked and validates the problem information.
- OCI Functions processes the information to rotate the credentials.
- New credentials are stored in an OCI Vault secret.
- The SecOps team are notified.
For detailed steps about automatic rotation of IAM credentials from OCI Cloud Guard events, visit our tutorial on the Learning page.
About the OCI Services in this Solution
OCI Functions is a fully managed, multitenant, highly scalable, on-demand, functions-as-a-service platform. To learn more about Oracle Functions, see the OCI Functions documentation. The OCI Events service produces structured messages that indicate changes in resources. It follows the Cloud Events industry-standard format hosted by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). To learn more about OCI events, see the OCI Events documentation.
Cloud Guard examines your OCI resources for security weakness related to configuration, and your operators and users for risky activities, see the Cloud Guard documentation. OCI Notifications broadcasts messages to distributed components through a publish-subscribe pattern, delivering secure, highly reliable, low-latency, and durable messages for applications hosted on OCI and externally.
Conclusion
In this post, we demonstrated powerful ways to auto rotate OCI IAM credentials from Cloud Guard problem to minimize the risk of compromised credentials.
For more details on Cloud Guard, see our blog posts, How Oracle is helping you maintain a strong security posture in the cloud and Discovering and fixing weak cloud security posture with Oracle Cloud Guard.
Also see Automatic Secret Rotation features in OCI Secret Management, which help manage the secrets rotation. With Automatic Secret Rotation, enable auto rotation of secrets for connected Autonomous Database and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Functions.

