US GENIUS Act Opens a New Era for Digital Dollars
The digital asset landscape has entered a new era with the landmark passage and signing of the “Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins” (GENIUS) Act. This legislation marks a pivotal moment, introducing the first-ever comprehensive federal regulatory framework for stablecoins in the United States. The compliance framework it establishes is widely anticipated to become the gold standard, with many institutions seeking the legitimacy and clarity it provides.
Stablecoins are no longer an emerging innovation – they have become foundational to modern institutional finance, with tangible improvements in profitability, liquidity optimization, and 24/7 settlement efficiencies. With the passage of the Genius Act in the U.S. and well-established digital asset regulations across Europe and Asia, the global regulatory landscape now supports the scalable implementation of stablecoin and digital money strategies.
This shift isn’t theoretical – as the financial system shifts toward 24/7 programmable settlement powered by stablecoins, leading institutions across banking, payments, and asset management are integrating stablecoins into their core infrastructure and upgrading their systems to interact with other forms of digital money. These organizations are not only minting digital money, but also launching or participating in integrated payment networks to support real-time, programmable settlement at scale – not as a proof of concept, but as a strategic imperative to remain competitive and unlock new revenue streams in the evolving digital economy.
Oracle Blockchain Platform – Digital Assets edition and the FinTech Data Platform initiative that extends it provide the institutional-grade infrastructure needed to rapidly issue and transact with stablecoins with embedded security, resilience, and enterprise integration capabilities. It enables institutions to build and run interoperable digital money ecosystems, integrate programmable Agentic AI workflows that leverage stablecoins for smarter, faster, and lower-cost operations, and meet compliance, reporting, and embedded supervision requirements of various regulators. Whether your goal is liquidity optimization, 24/7 settlement, or unlocking new business models, Oracle’s digital asset infrastructure helps you execute at scale – with the flexibility and control institutions demand.
With built-in programmability, stablecoins open the door to agentic AI automation, multi-ledger liquidity management, and seamless settlement of both payments and tokenized asset transactions, while meeting stringent compliance and audit standards. In a market where competitors are rapidly deploying stablecoin infrastructure, speed to market becomes essential to meet customer expectations and prevent market share erosion.
This blog post will review several of the key provisions of the GENIUS Act, explaining its significance for the future of payment stablecoins and the broader financial ecosystem.
Background: The Rise of Digital Money and the Case for Stablecoins
The financial world is rapidly digitizing, giving rise to various forms of digital money, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding the differences between these forms, and the specific motivations for adopting stablecoins, helps to see the significance of the GENIUS Act.
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are decentralized and volatile, making them more suitable for speculative investment rather than as a reliable medium of exchange.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are a digital form of a country’s fiat currency, issued and backed by the central bank for interbank transactions (Wholesale CBDCs) or for everyone to use (Retail CBDCs.) While offering stability as a claim on the central bank, they are still in early stages of research and development in many countries.
- Deposit Tokens represent traditional bank deposits on a blockchain, offering a new way to transact with tokenized bank-issued money operating within the existing banking regulatory framework.
- Tokenized Money Market Funds (T-MMFs) represent traditional money market investments on a blockchain, which can also be used as payment instruments for real-time settlement between institutions due to their high quality asset base and high liquidity.
Stablecoins, however, occupy a unique and increasingly critical position. They are digital assets pegged to a stable value, typically the U.S. dollar, combining the speed and efficiency of a blockchain without the volatility of the cryptocurrency. This stable value makes them a highly attractive payment instrument for both retail users and financial institutions.
From a company or individual user perspective, stablecoins offer a modern solution to traditional payment pain points. They enable fast, low-cost, and 24/7 transactions, especially for cross-border payments and remittances, which are often slow and expensive through legacy systems[1]. For users in regions with volatile local currencies, stablecoins provide a stable store of value. A 2024 survey by Castle Island Ventures of 500 adults from each of the following countries: Brazil, Turkey, Nigeria, India, and Indonesia revealed the following common use cases:
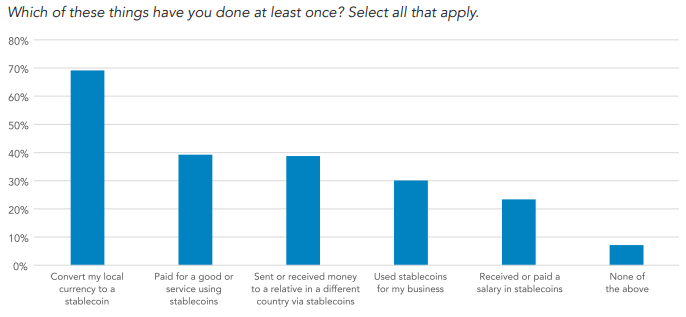
For an issuer (PPSI in GENIUS Act terminology), stablecoins are a strategic imperative. Issuing stablecoins and building the infrastructure to support them opens new business models and revenue streams. It provides an opportunity to offer enhanced services, improve liquidity management, and participate in the shift toward a 24/7, smart, programmable settlement system. The regulatory clarity of the GENIUS Act makes this a viable and scalable path for US institutions seeking to remain competitive in the evolving digital economy. AI can be a key enabler in this new environment, assisting with real-time risk management, fraud detection, and the automation of compliance checks, thus enhancing the security and integrity of stablecoin systems.
Defining “Payment Stablecoin” Under the GENIUS Act
The GENIUS Act provides a precise definition for the digital assets it seeks to regulate. A “payment stablecoin” is a digital asset designed primarily for payments, which maintains a stable value pegged to a national currency, such as the U.S. dollar. The act is careful to distinguish this from other digital assets. It explicitly excludes national currencies, securities, and algorithmic stablecoins, which do not have a 1:1 backing with a real-world asset. This narrow definition ensures the framework focuses specifically on the assets most likely to be used for everyday transactions, protecting consumers and promoting financial stability.
Key Pillars of this New Regulatory Framework
The act is built on three core pillars designed to ensure the safety, stability, and integrity of the stablecoin market.
Who Can Issue Stablecoins?
The GENIUS Act introduces a dual-track system for “Permitted Payment Stablecoin Issuers” (PPSI). Issuers can either be federally approved entities—including non-banks and bank subsidiaries—or state-qualified financial institutions. This dual approach provides a clear, regulated path for various types of institutions to enter the market.
Non-banks would be restricted to financial firms unless the Stablecoin Certification Review Committee (SCRC) find they do not pose risks to the banking or financial system and will comply with certain requirements. (“Stablecoin Legislation: An Overview of S. 1582, GENIUS Act of 2025”) Banks and non-banks that opt for the federal regime would be required to apply with the relevant federal banking regulator. The bill also creates a state regulatory option for nonbank issuers with fewer than $10 billion in outstanding stablecoins. The act also includes a safe-harbor and transition period, allowing existing stablecoin projects to come into compliance with the new regulations.
Ensuring Stability: Reserve Requirements
The cornerstone of the act is its strict reserve requirements. All payment stablecoins must be fully backed, mandating a 1:1 ratio of assets to stablecoins in circulation. These reserves must consist of high-quality liquid assets, such as cash and short-term U.S. Treasury bills. Crucially, the act explicitly prohibits the practice of rehypothecation, which is the reuse of reserve assets for other purposes. This ensures that the assets backing the stablecoins are always available for redemption, providing an ironclad guarantee of stability.
Protecting Consumers
Consumer protection is a central theme of the GENIUS Act. It requires PPSIs to establish clear and timely redemption policies, guaranteeing that stablecoin holders can convert their digital assets to fiat currency on demand. Furthermore, institutions must provide monthly public disclosures of their reserve holdings, offering unprecedented transparency. The act also includes restrictions on misleading marketing, ensuring that issuers cannot make false claims about the safety or stability of their products.
Pending CLARITY Act in Congress
A separate piece of digital assets regulations has passed the House on July 17th and is now under consideration in the Senate: Digital Asset Market Clarity (CLARITY) Act of 2025 (H.R. 3633). It’s goal is to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for digital assets by clearly dividing oversight between the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). It’s scope are broader “digital commodities” – defined as blockchain-linked digital assets whose value derives from or is reasonably expected to derive from blockchain usage.
CLARITY Act specifies that digital commodities are not to be treated as securities under federal securities laws. The CFTC would oversee spot markets, trading platforms, brokerage, custody, etc., while the SEC retains authority over investment contracts involving such assets. It also introduces the concept of “tradable assets” to ensure any digital asset not otherwise captured is still subject to CFTC oversight when traded on registered platforms and includes consumer protection measures, such as mandatory public disclosures for issuers of digital commodities and restrictions on insider trading.
This is a structural regulation, which addresses digital assets more broadly, defining asset categories, establishing oversight roles for the SEC and CFTC. The CLARITY Act sets the structural rules and jurisdictional boundaries (who regulates what), and GENIUS Act plugs into that structure when it comes to stablecoins, clearly placing them in a regulated stablecoin-specific framework under banking regulators like the OCC and FDIC. Together, they promise regulatory clarity and consumer safeguards—while promoting innovation and institutional confidence in the U.S. digital assets market.
The Impact on the Broader Financial Landscape
The GENIUS Act will have a profound impact beyond just the issuers themselves, reshaping the entire digital payments ecosystem.
Impact on Financial Institutions
For Permitted Payment Stablecoin Issuers (PPSI), the act unlocks new business models and potential revenue streams. However, this opportunity comes with significant responsibilities, requiring advanced compliance, technology, and security capabilities, as well as subjecting the issuers to direct supervision by federal or state regulators.
For financial institutions that are not issuers but are “Exposed Financial Institutions” (non-PPSI FSIs), the act presents new opportunities to provide services like custody for reserves or wallet services. The availability of regulated stablecoins will also enable these institutions to leverage faster and more efficient payment rails.
However, in order to engage in this new space, PPSIs and Exposed Financial Institutions will need to implement new risk management and AML capabilities tailored to digital assets. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) would be required to write tailored anti-money-laundering (AML) rules with “novel methods … to detect illicit activity involving digital assets” and the issuers will have to certify that they have implemented AML and sanctions compliance programs.
Rules for Foreign Issuers
To ensure a level playing field and maintain the integrity of the U.S. financial system, the act requires foreign stablecoin providers to register and fully comply with U.S. AML and sanctions laws before operating within the country. This means that not all stablecoins will be covered by this regulation, which can lead to interesting challenges. For example, there might be different degrees of compatibility within non-compliant stablecoins, each with its own set of rules and guidelines defining how (if at all) those can be transacted by a US regulated financial institution.
A Shift in the Digital Payments Ecosystem
By providing regulatory clarity and robust consumer protections, the GENIUS Act is expected to accelerate the adoption of stablecoins by traditional financial institutions and merchants. This could lead to a significant reduction in the cost and time of cross-border payments and remittances, making global transactions more efficient.
The act also serves to enable a clear “sandbox” for innovation, allowing developers and companies to build new applications and services on a foundation of regulated and stable digital assets, all while promoting responsible growth.
How Oracle Can Help Start Your Stablecoin & Digital Asset Journey
Earlier this year Oracle announced the release of Oracle Blockchain Platform – Digital Asset edition (OBP DA), a powerful enterprise-grade solution designed to streamline the development and deployment of digital assets applications, including stablecoins. This platform significantly simplifies digital asset issuance and lifecycle management by providing a comprehensive bank-grade distributed ledger infrastructure combined with pre-packaged smart contracts, rich API capabilities, powerful indexing database integration leveraging Oracle Database, and analytics tools, enabling organizations to bring stablecoins and other innovative digital asset solutions to the market faster and without the need for long and complex development cycles. OBP DA’s pre-packaged application components on a scalable blockchain infrastructure get your business ready to offer stablecoin solutions without having to build from scratch or hire highly specialized blockchain experts.
Built on Linux Foundation open-source permissioned blockchain projects, OBP DA empowers financial institutions and non-bank enterprises to manage the complete lifecycle of Digital Assets from issuance, transfer to tracking and real-time settlement. It reduces time-to-market, cost and complexity by providing a secure, scalable, and production-ready platform with pre-built smart contracts, custodial wallets, sample application and analytics artifacts, rich APIs & events capabilities, low-code development tools, and interoperability with public blockchain and traditional financial systems.
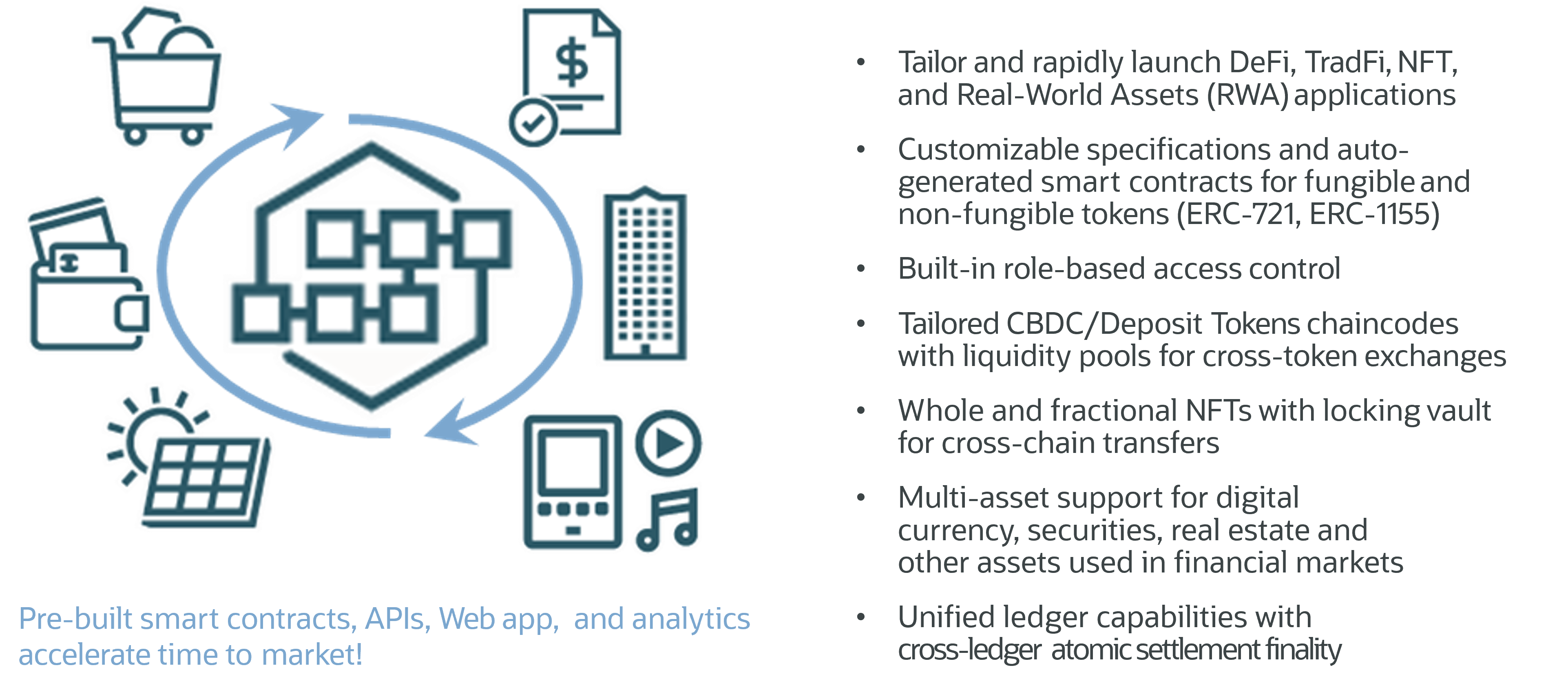
This solution not only provides instant expertise, but also enables faster innovation cycles through low-code smart contract, web application, and analytics tools, which enable rapid customization, including auto-generation of smart contracts, APIs, UI elements, dashboards and reports to quickly experiment with various options and respond to the market needs. OBP DA delivers bank-grade security leveraging permissioned blockchain extended with multi-level role-based access controls down to the level of smart contracts, on-chain configuration audit trails with event notifications and reporting, and – crucially – enables privacy protection through confidential transactions.
Integrating stablecoin capabilities with the many internal systems required for meeting all the functional and compliance requirements is a significant challenge for many institutions. OBP DA enables seamless interoperability with rich APIs and event-driven architecture as well as cross-ledger asset portability, which supports the vision of unified financial systems with real-time settlement using atomic transactions & two-phase-commit (2PC) orchestration capabilities with internal systems and other blockchain ledgers. This solution also supports seamless replication of transaction history and account state into Oracle Database and enables real-time insights leveraging integrated analytics and AI to enable better financial decision-making & transparency with dashboards and data visualizations. For integrations across multiple systems, Oracle also enables Agentic AI workflow integration in our MicroTx workflow solution, which integrates with OBP APIs.
OBP DA and related component services can be quickly provisioned in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) as a managed service, which provides easy on-boarding and operations, while Oracle monitors and manages technical services, security, and availability based on built-in high availability architecture with financially-backed 99.95% SLA and continuous ledger replication for cross-region disaster recovery. In addition, it can also be deployed on OBP Enterprise Edition in multicloud or on-premises environments by an individual institution or in a multi-institution network spanning multiple clouds and on-premises nodes.
Conclusion
The GENIUS Act represents a landmark achievement in financial regulation, bringing much-needed clarity and a foundational framework to the stablecoin market. It has set a countdown for implementation, and while compliance is voluntary, its adoption is expected to be widespread. The act’s focus on consumer protection and financial stability—through strict reserve requirements, transparency, and clear redemption policies—is paramount. By providing a clear and comprehensive path for stablecoin regulation, the GENIUS Act solidifies the U.S.’s position as a leader in the global digital asset space, driving innovation while safeguarding the financial system.
Oracle Blockchain Platform – Digital Assets edition can be deployed by bank and non-bank PPSIs to unlock new opportunities and create offerings for the new world of digital money. Oracle Cloud Lift Services are available to provide guidance from cloud engineers on planning, architecting, prototyping and managing OCI deployments, enabling customers to achieve production-readiness in weeks instead of months by leveraging these included services for OCI customer tenancies. Oracle Consulting and our system integration partners can help deploy in multicloud and on-premises environments and develop advanced capabilities for leveraging stablecoins in broader financial services, such as B2B payments, trade finance, settlement of securities transactions and repurchase agreements, and quickly integrate them into customers’ existing applications and IT systems.
In the next blog post, we will delve into the details of stablecoin deployment and explain how the underlying ledger technology and the built-in low-code/no-code tooling can be used to quickly generate, test, deploy and scale a stablecoin offering.
[1] Wholesale cross-border payment processes result in significant transaction costs of $120 billion per annum, per OliverWyman and J.P. Morgan report, “UNLOCKING $120 BILLION VALUE IN CROSS-BORDER PAYMENTS.”


