This blog post was originally published on 25 August, 2022.
Oracle APEX running on Autonomous Database (ADB) and APEX Application Development (APEX Service) in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) adds the ability to easily clone your entire APEX environment including the database, app definitions, and app data. This blog post describes how APEX teams can simplify their development, testing, and deployment activities with cloning. It summarizes key things you need to know to take advantage of unique instance cloning capabilities built into ADB and APEX Service. It is part of a larger blog series about APEX on ADB (more).
Use Cases for Cloning
Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery
Cloning an ADB or APEX Service instance provides a copy of the entire APEX environment that can be used by developers, QA testers, and operations teams in support of CI/CD flows. For example, a developer can rebase their dev environment to integrate changes from colleagues using a clone, a tester can create an updated functional testing environment using a clone, and so forth. These clones are all-inclusive, so you do not need to worry about separately exporting and importing various APEX artifacts (e.g. app definitions, static files, UI themes, app data). In addition, clones can be created quickly, refreshed periodically, stopped when not in use, and terminated when no longer needed. In fully automated CI/CD flows, you can script cloning operations using OCI REST APIs, SDKs, and a CLI that are included with your service at no extra cost.
Autonomous APEX Upgrade Testing
Cloning also enables customers to test and verify apps against autonomous APEX upgrades in a non-production environment before applying a given upgrade to production. This procedure uses cloning in combination with other cloud features such as automatic notification emails containing the upgrade date that are sent to customers in advance and an option to defer scheduled upgrades by several weeks. You typically repeat the procedure twice per year for each major upgrade of APEX running on ADB or APEX Service. Below is a summary of how this procedure works. More information is in ADB documentation.
- Upon receiving notification of an upcoming APEX upgrade, open APEX Administration Services on your production ADB or APEX Service instance, and verify the upgrade deferral option is selected.
- In OCI Console, immediately create a clone of your production instance. See further details below.
- On this clone, open APEX Administration Services and select to not defer upgrades.
- Wait for the scheduled autonomous APEX upgrade date to pass, sign into APEX on your clone, and confirm the upgrade was completed successfully by checking the APEX version number.
- Use the upgraded clone to test and verify apps against the new APEX release. Complete testing activities and any necessary app changes before your deferral time expires.
- When you are ready to apply the autonomous upgrade in production, go back to APEX Administration Services on your production instance, and select to apply the upgrade now. Alternatively, wait for your deferral time to expire, at which point APEX will be upgraded automatically.
Available Cloning Options
Three different types of cloning are supported: full, refreshable, and metadata. Refreshable clones are not suitable for running APEX apps because they are read-only, and metadata clones do not include app data – so we will focus on full cloning. This type of clone is available on all ADB workload types including the specialized APEX Service.
You can create a full clone directly from a running or stopped service instance or from a backup of the instance. Full clones are created using a simple dialog that looks similar to the dialog for provisioning new instances. What is different is that you must also pick the type of clone (full in this case), OCI Data Region where the clone will run (geographic location), and origin to clone from (service instance or one of its backups).
How to Create a Full Clone
Before we begin, you must have access to an OCI account and tenancy with privileges to create and manage ADB instances there. You can read more about OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies that provide the required privileges here. You must also have at least one ADB or APEX Service instance with an APEX workspace configured.
Get started by signing into your cloud account and tenancy in OCI Console.

In the Services Menu, navigate to Oracle Database > Autonomous Database.
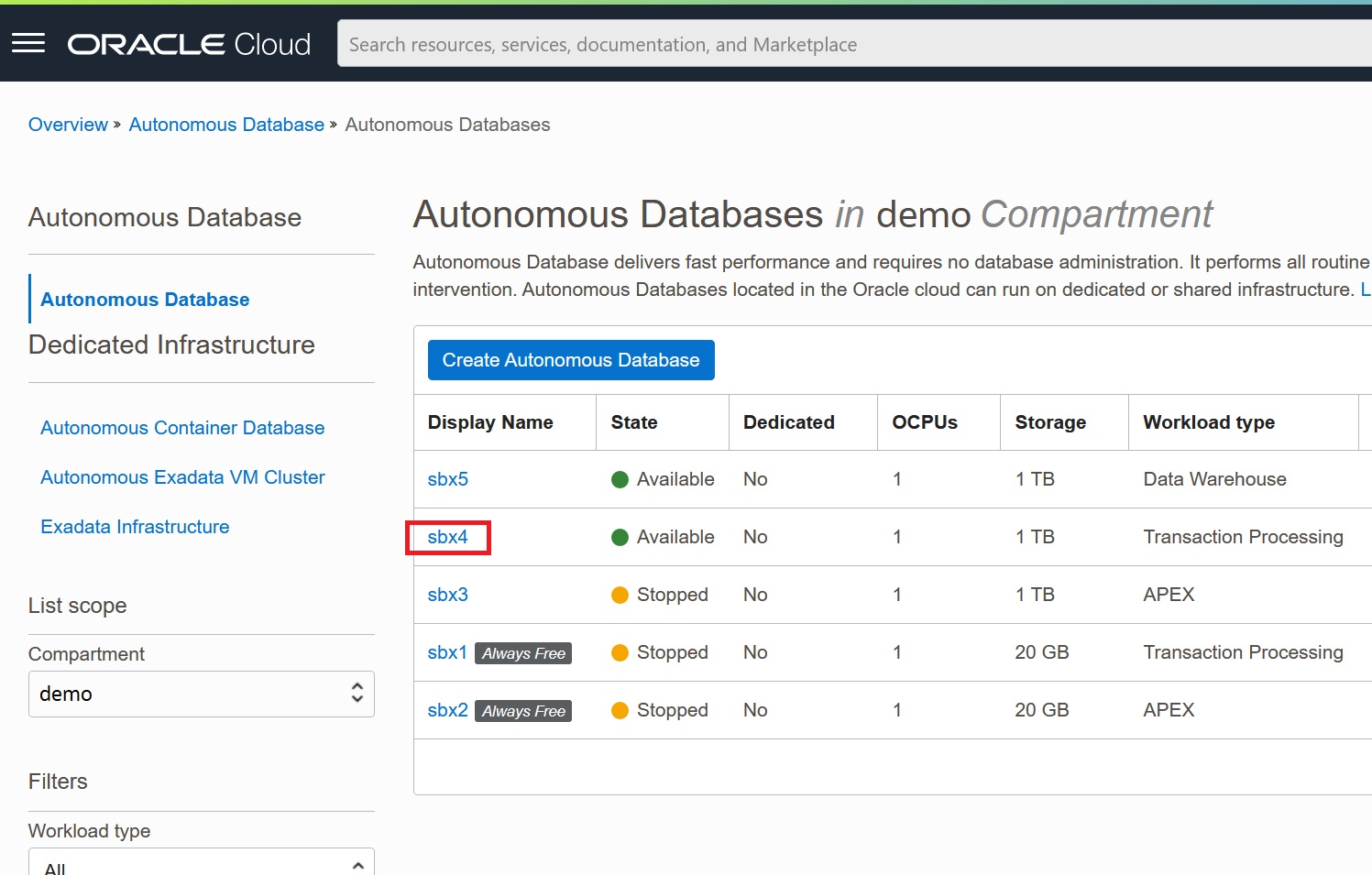
In the instances list, identify an ADB or APEX Service instance that you want to clone from, and click its link.
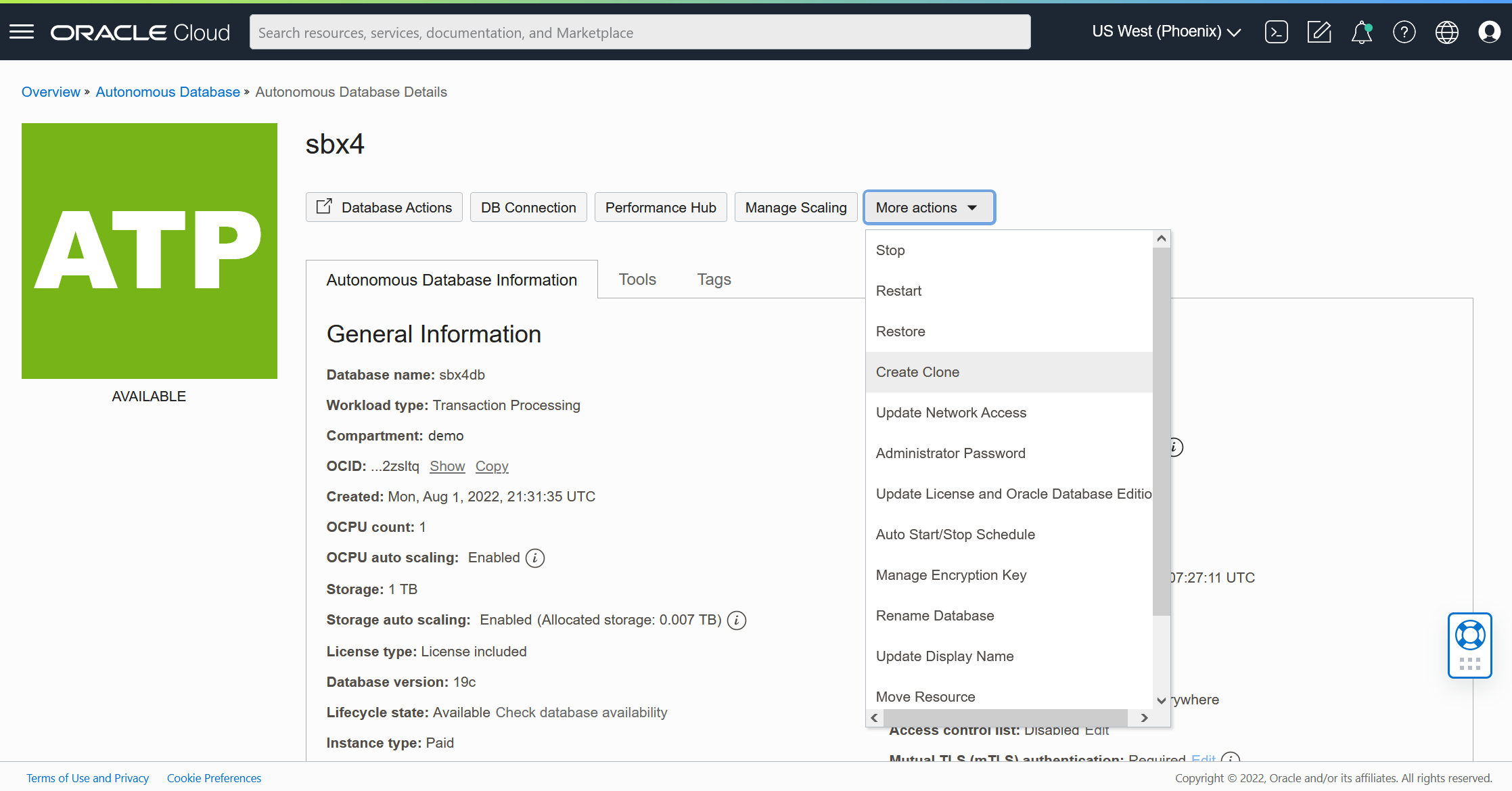
On the instance details page, click More actions, and select Create Clone.
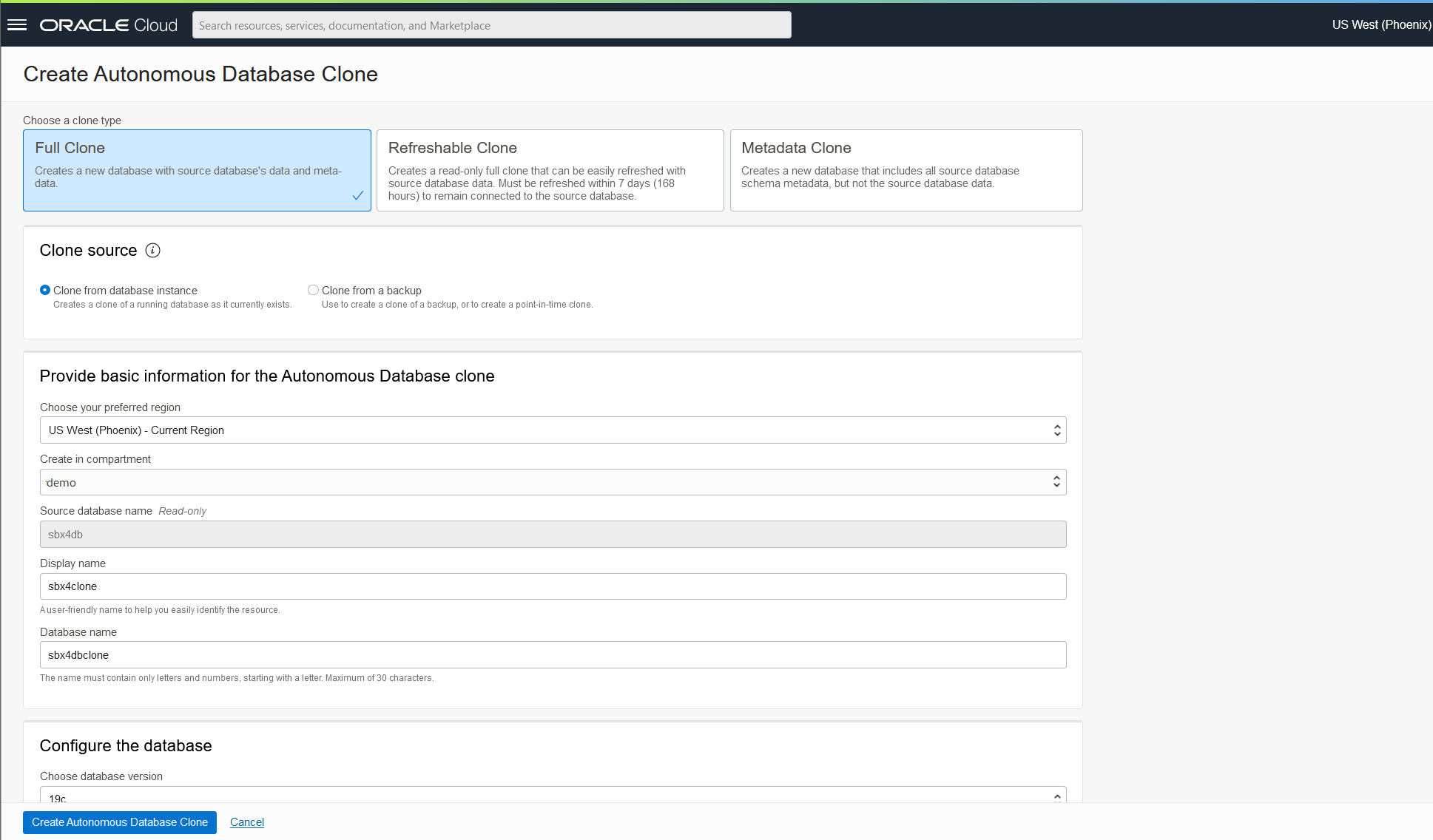
In the cloning dialog, select Full Clone as the clone type. Pick a target OCI Data Region, which in most cases will be the same region where your origin instance resides. If you wish to Clone from backup, select your desired backup timestamp from the dropdown list. Fill in additional details as appropriate. Note that other fields in this dialog are similar to provisioning a new service instance. Click Create Autonomous Database Clone at the bottom to proceed.
You will see a details page for your new clone that initially shows it in Provisioning state. This state should change to Available after a few minutes.
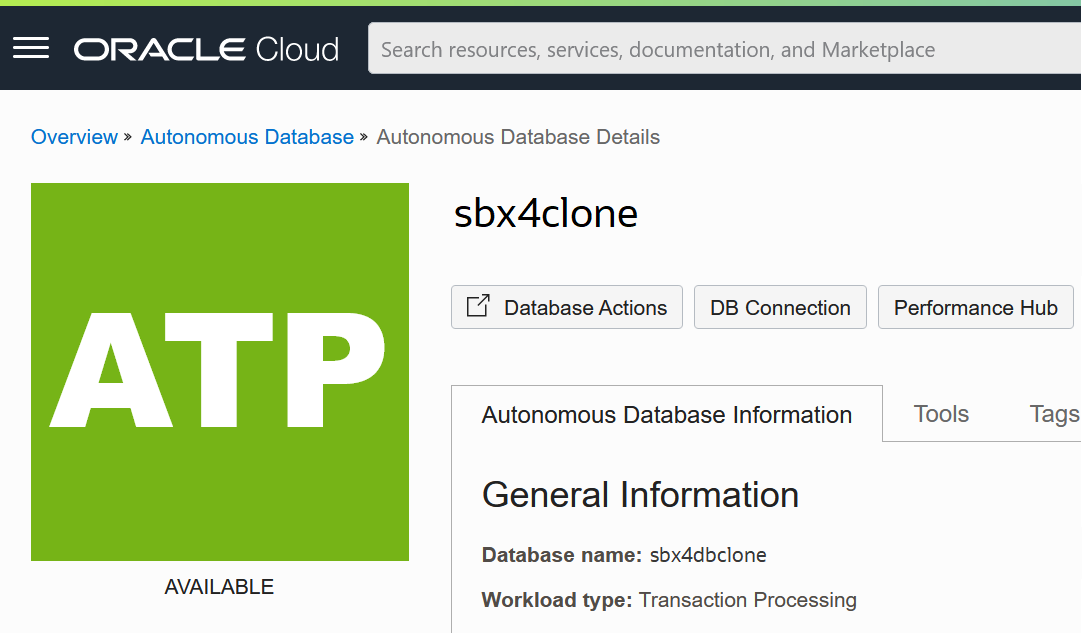
Depending on your specific configuration, you may be able to access APEX on the clone at this point. If you selected to make the clone publicly accessible (it has a public IP address), and APEX developer accounts in your origin instance were database users (the default option), then you can sign into APEX now from the clone’s instance details page under Tools > Open APEX. Because all APEX workspaces and developer accounts from your origin were copied into the clone, you should be able to sign in using an existing workspace, username, and password.
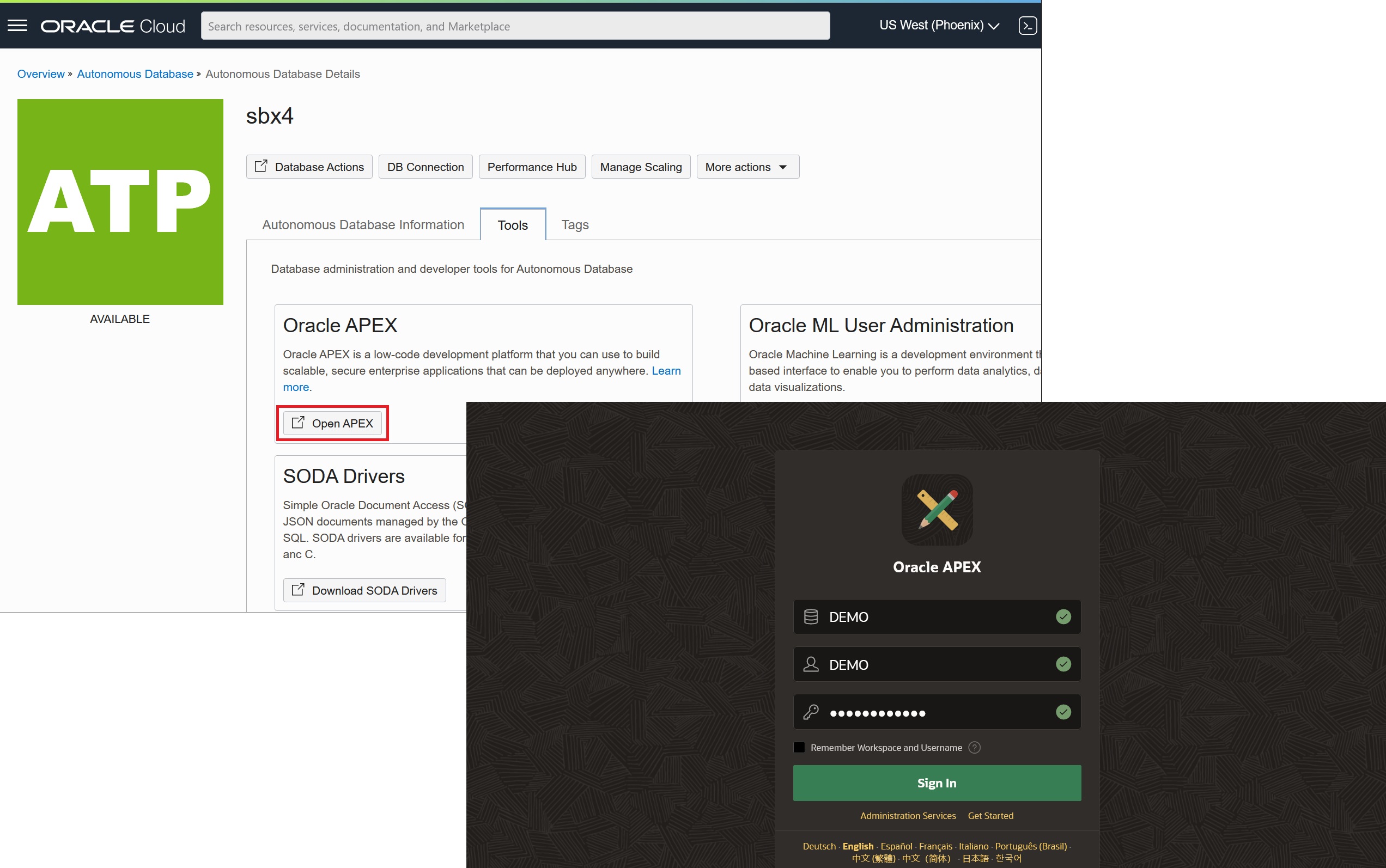
If you selected to make the clone a Private Endpoint (it has a private IP address only) or APEX developer accounts in your origin instance were not database users, then there will be additional steps to complete before you can sign into APEX. This should be a familiar configuration exercise because similar steps were completed on the origin instance.
Tips and Best Practices
Communicate Updated URLs
Usually, the URL for accessing APEX on a new clone will be different than its origin instance. You may notice differences in the subdomain name of URLs that are generated by your included Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS). For example, a database identifier in the generated subdomain will be different if your clone was created in the same OCI Compartment as its origin, and a region identifier in the subdomain will be different if it was created in a different OCI Data Region.
Whatever your clone’s modified APEX URLs look like, they need to be sent to and bookmarked by your APEX administrators, developers, and app users. If these users access APEX via URLs generated by default ORDS, then you should communicate the following:
- APEX Administrators – New APEX Administration Services URL ending in /apex_admin
- APEX Developers – New APEX workspace sign-in URL ending in /apex
- App Users – New app URLs ending in /r/<schema-name>/<app-alias>
Note that ADB Vanity URL configurations are an exception. They expose APEX apps on the public internet at a custom domain name (Vanity URL) determined by the customer. If you set up a Vanity URL architecture for your origin instance and have already switched it to point to your clone, then no further action is necessary. You can read more about ADB Vanity URLs here. General information about ADB and APEX Service URLs is here.
Check Limits and Quotas
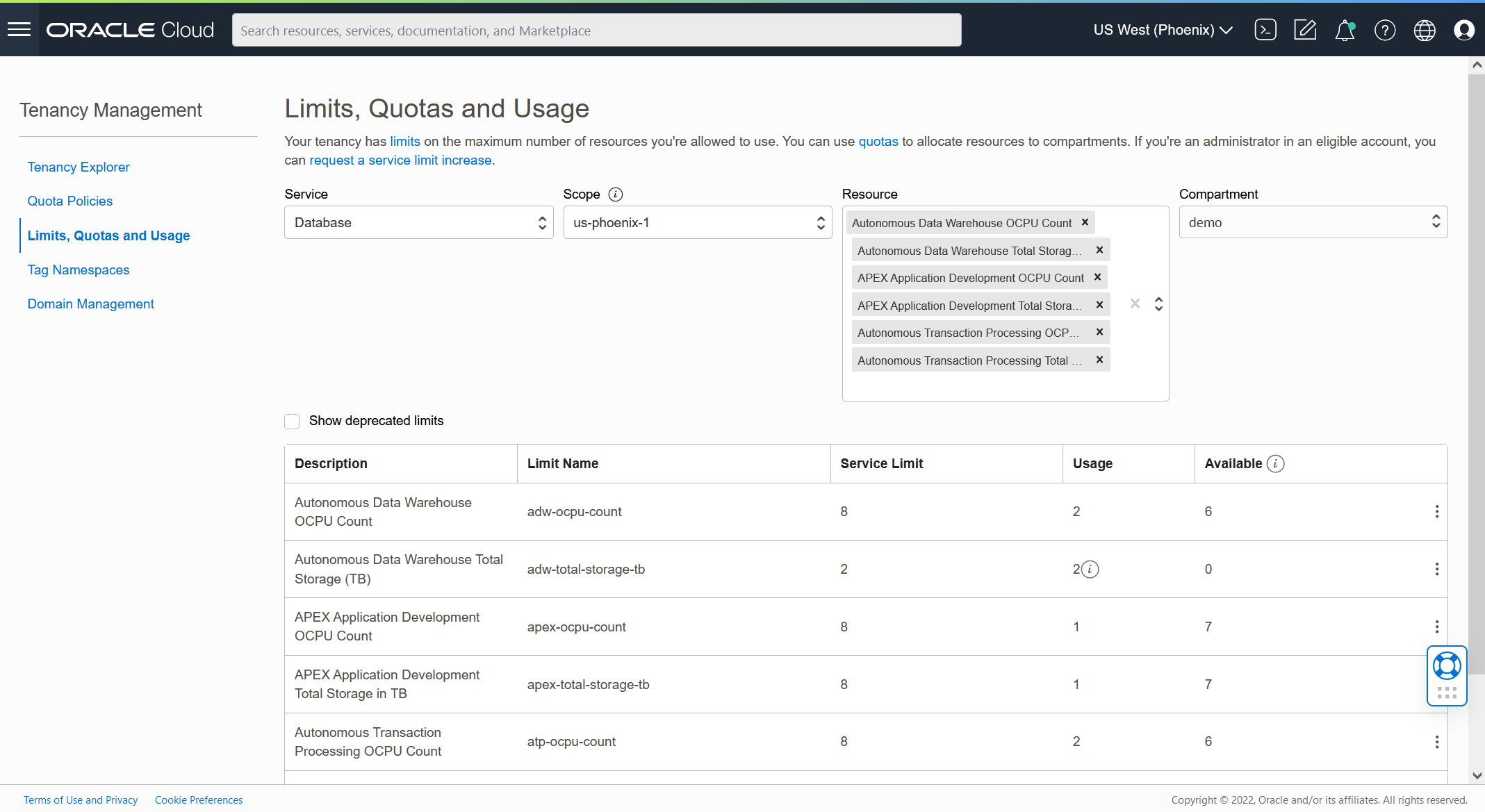
Similar to other software infrastructures that can easily clone virtual machines and containers, the extreme ease with which you can create ADB and APEX Service clones could lead to a proliferation of new instances. OCI avoids this type of uncontrolled sprawl with governance capabilities that enforce Service Limits and Compartment Quotas in your tenancy. However, such limits also can be constraining. You may experience clone failures with an error indicating that Service Limits cannot be exceeded.
For this reason, it is recommended that an OCI tenancy administrator sign into OCI Console to check current Service Limits and Compartment Quotas before any new clones are created. You can find these settings in the Services Menu of OCI Console under Governance & Administration > Tenancy Management. Click on Limits, Quotas and Usage to see the tenancy’s current Service Limits. Here you can increase or decrease limits by submitting a Support Request to Oracle. Also, you can change Compartment Quotas by clicking Quota Policies and authoring a new policy or editing an existing one.
Conclusion
APEX teams can simplify app development in Oracle Cloud with cloning. The unique instance cloning capabilities built into Oracle Autonomous Database (ADB) and APEX Application Development (APEX Service) are easy to use and can help with a range of development, testing, and deployment activities.
Additional Resources
- Read our blog series all about APEX on ADB.
- Learn more about APEX on ADB and APEX Service.
- Build your first low-code app with APEX on ADB or APEX Service for FREE by signing up for Oracle Cloud Free Tier.
