This blog was originally published on 11 July, 2017.
More and more Application Express developers are faced with the requirement to integrate REST services or HTTP/JSON data feeds into their applications. Application Express provides great support for SOAP web services, but for REST services using JSON to exchange data, the built-in functionality is limited. For instance, all the JSON parsing has to be done manually by employing PL/SQL code or SQL functions.
During the last weeks, we released a few articles describing how to access a REST service from within Application Express, how to leverage the REST Client Assistant packaged application and how to deal with REST services providing large result sets …
- Generate SQL and PL/SQL code to access REST services using REST Client Assistant
- Work with REST services returning large result sets page-wise
- Configure a database wallet to access HTTPS services
In the previous articles, we always fetched all response data from the REST service – either all at once or page-wise, depending on REST service capabilities. But in practice, it’s often required to get only a subset of the response data – we want to filter the response based on some end user criteria.
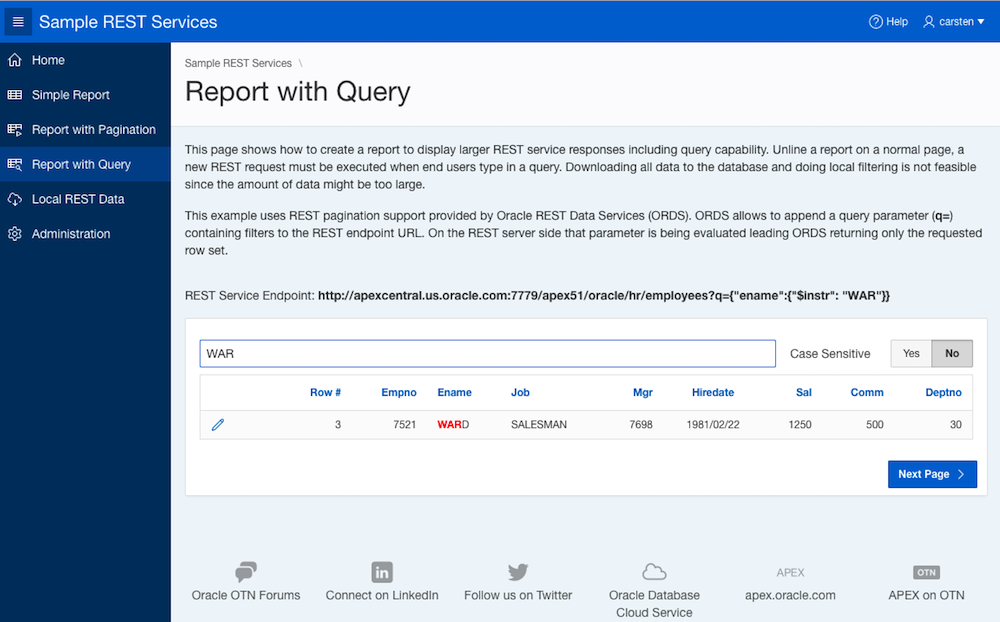
“So that’s easy” might be your first thought – since all JSON parsing is done with SQL functions. In the SQL query, both XMLTABLE and JSON_TABLE act as a row source, so its result can be treated like rows from a table or view. Thus we can simply amend the WHERE clause of the SQL query, which has been generated be the REST Client Assistant packaged application.
But imagine a REST service returning a huge amount of data (thousands or even millions of rows). As learned in the Work with REST services returning large result sets page-wise article, these services return their data page-wise. So, in order to apply a SQL filter, we would first have to fetch all data, walking though all the response pages.
For REST services provided by Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS), a filter syntax is provided: Filter criteria can be passed to ORDS with the REST request and will be executed server-side returning only the final (and limited) amount of rows.
This article shows how the response of a REST service invocation can be filtered either using SQL or a filtering syntax provided by the REST service. Have a read, how this can be used in your own Application Express applications.
