
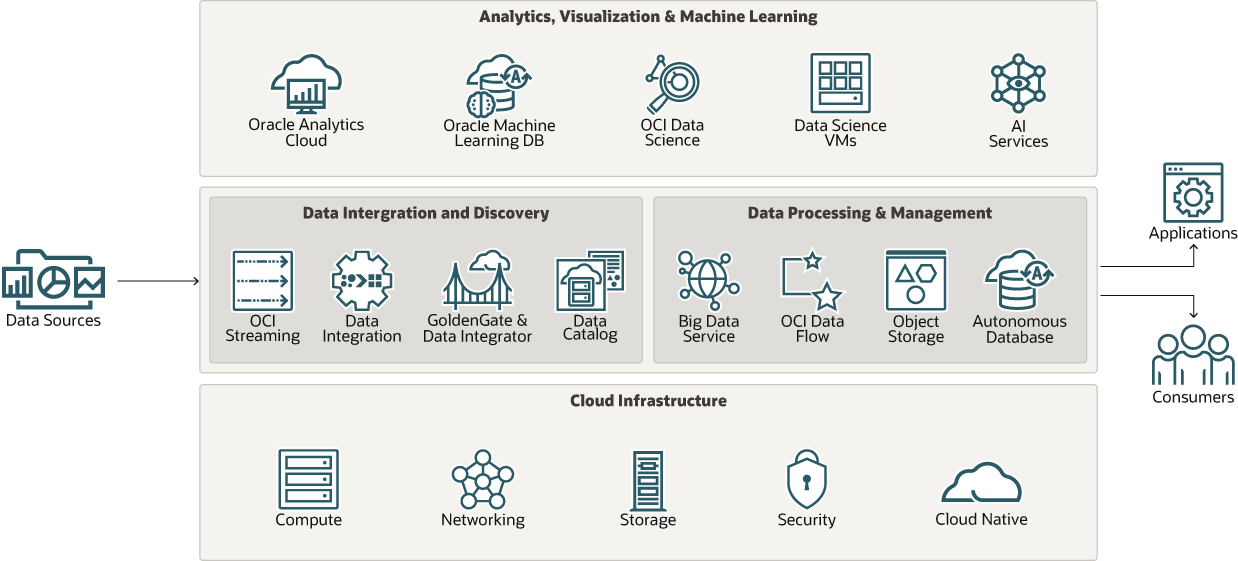
Oracle Data Intelligence Platform in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides a set of data services that help organizations manage, process, and integrate vast amounts of data efficiently. These services, tailored for cloud environments, span data discovery, big data processing, integration, and governance.
- Data lake services: Oracle Big Data Service (BDS), OCI Data Flow (DFS), OCI Data Catalog, Oracle Intelligent Data Lake* (IDL)
- Data motion and integration services: OCI Data Integration (DIS)
* Oracle Intelligent Data Lake (IDL) is a new data lake service in the Oracle Data Intelligence Platform. For a deeper understanding, check the blog Oracle’s Unique 360-degree vision for Data Intelligence.
This article is part of the Securing Oracle Data Intelligence Platform Services using Zero Trust Packet Routing series. The article describes how to prepare Zero Trust Packet Routing (ZPR) components that can secure Oracle Big Data Service (BDS), OCI Data Flow (DFS), OCI Data Integration (DIS).
It includes architectural diagrams, component descriptions, deployment scenarios, and links to other references.
PrerequisitesTo follow this blog you need:
- An existing OCI tenancy.
- An OCI administrator with the privileges to:
- Manage resources in compartments
- Manage ZPR policies in the tenancy
Topics

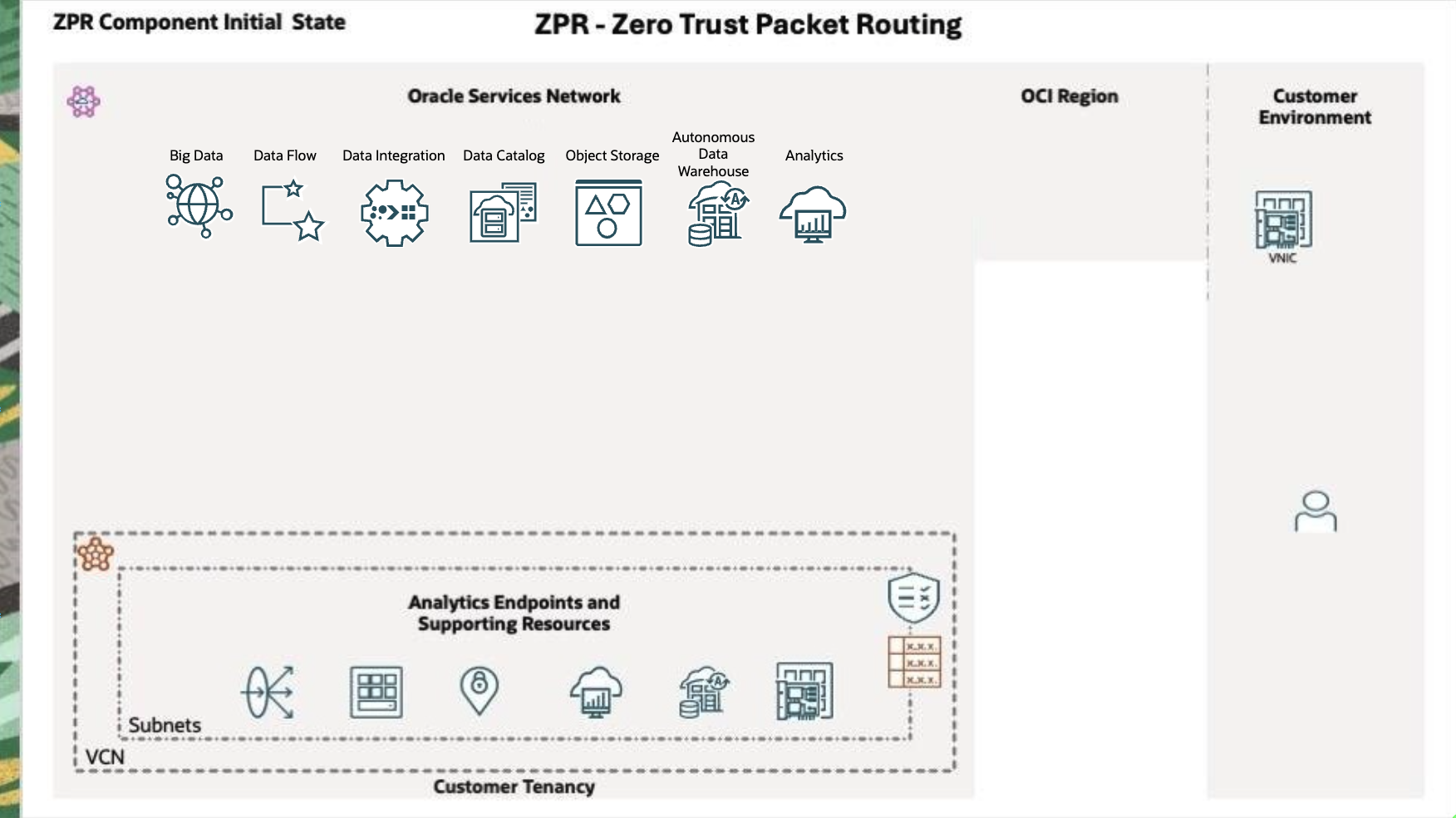
This diagram shows an OCI region in a customer’s cloud account (tenancy) before ZPR is applied. The resources shown include Load Balancers, Compute Instances, BDS Cluster Node’s VNIC, OAC endpoints, Data Flow SQL Endpoint, and ADW (Autonomous Data Warehouse).
Prepared State
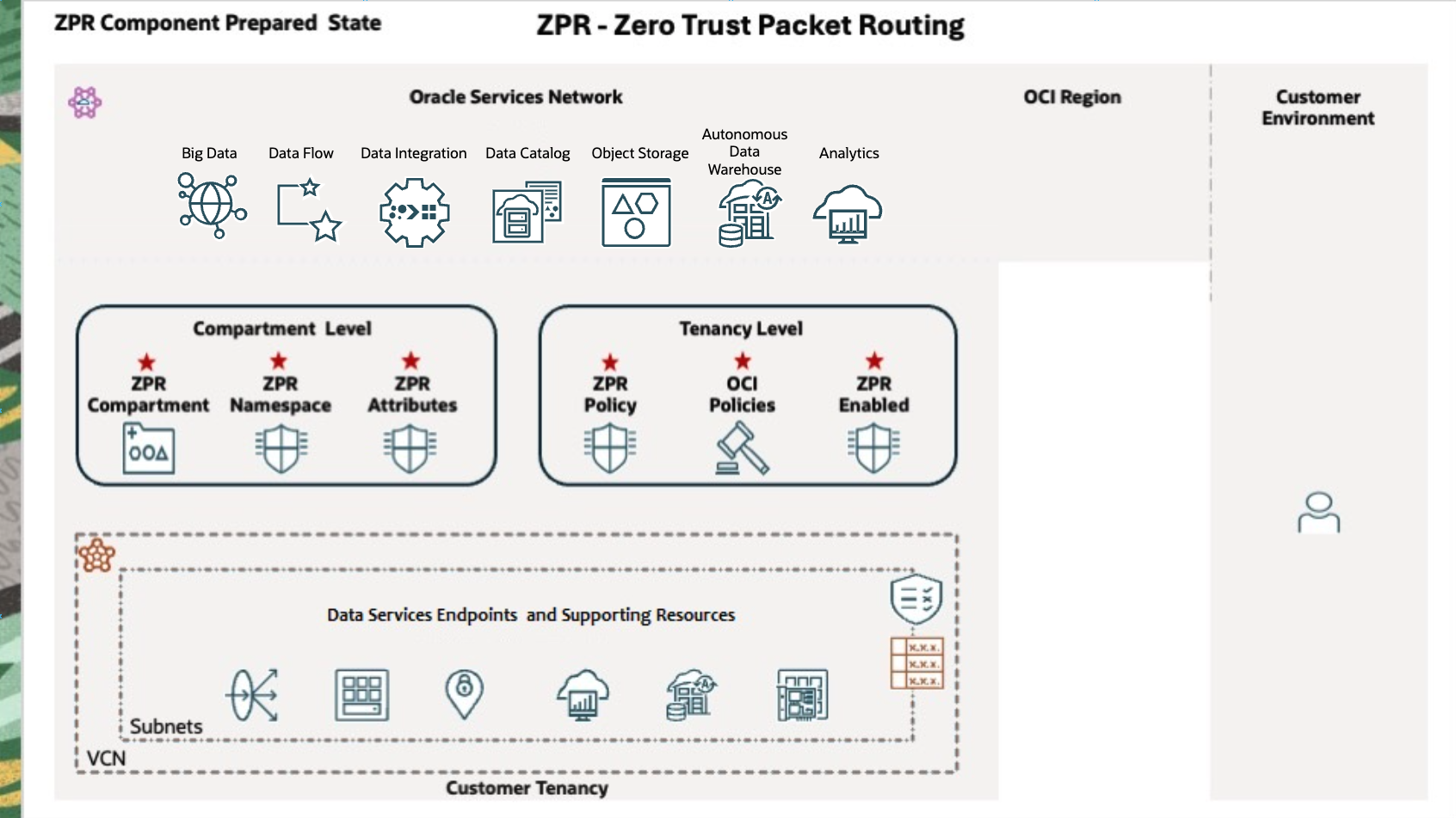
This diagram shows the ZPR components required to secure Oracle Data Intelligence Platform services.
![]()
The prepared architecture requires these additional components:
- OCI ZPR policy rules
- ZPR enablement
- ZPR compartment
- ZPR namespace
- ZPR attributes
- ZPR namespace
- ZPR policy rules
A policy consists of one or more policy rules. A policy rule grants a group, the privileges to interact with resources in a tenancy or compartment.
If you’re an OCI Administrator you have all the required privileges. If not, ZPR administrators require the following privileges:
- Privileges that allow you to manage the resources that ZPR protects.
- Allow group ZPR_Admin to manage zpr-configuration in tenancy
- Allow group ZPR_Admin to manage security-attribute-namespace in tenancy
- Allow group ZPR_Admin to manage zpr-policy in tenancy
- Allow group ZPR_Admin to manage all-resources in compartment ZPR_Compartment
ZPR Enablement
By default, ZPR is disabled in your tenancy. When you enable ZPR in your tenancy, a default Oracle-ZPR security attribute namespace is created that you can use.
ZPR Compartment
Oracle recommends separate compartments for ZPR namespaces to separate duties. For example, a Human Resources ZPR security administrator may not be a Financials ZPR security administrator.
Compartments organize and isolate cloud resources. They span all subscribed regions in the tenancy.
ZPR namespaces are containers for ZPR security attributes.
ZPR Attributes
ZPR security attributes are labels that can be referenced in ZPR policies to control access to supported resources. Attributes are used in conjunction with attribute values when creating ZPR policies. Attributes are used in conjunction with attribute values when creating ZPR policies. The documentation uses application,network, and database as example attributes.
ZPR Policy
A ZPR policy is a container for ZPR policy statements. ZPR policy statements are rules that specify which resources have access to other resources. A ZPR policy is based on an Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) authorization model that evaluates attributes (or characteristics) to determine resource access.
![]()
Several frameworks exist to deploy the ZPR components:
- OCI Terraform – The OCI Terraform provider allows you to use Terraform to interact with OCI resources.
- OCI Console – The OCI Console provides a single interface where you can manage all cloud services.
- OCI APIs – The OCI APIs ((Application Programming Interface) are REST APIs that use HTTPS requests and responses.
- OCI CLI – The OCI CLI (Command Line Interface) is a small footprint tool that you can use on its own or with the OCI Console to complete OCI tasks. The CLI provides the same core functionality as the Console, plus additional commands. Some of these, such as the ability to run scripts, extend the Console functionality.
Deployment Sequence
This section describes a typical provisioning sequence using the OCI Console.
- Create or ensure that ZPR administrators are granted the necessary privileges through OCI policies.
- Enable ZPR in your tenancy.
- Navigate to Identity & Security > Zero Trust Packet Routing.
- Click Enable ZPR.
- Click Enable ZPR again to confirm.
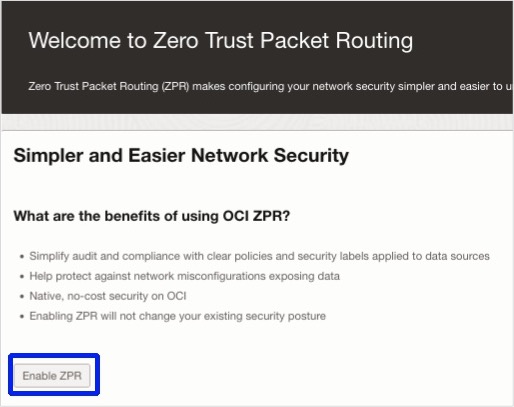
Zero Trust Packet Routing Enablement
- Create a ZPR compartment, namespace, and attributes.
- Create a ZPR compartment for each planned ZPR functional area. For example, HR, ERP, and so on.
- Create a ZPR namespace in the ZPR compartment.
- Navigate to Identity & Security > ZPR Security Attribute Namespace.
- Select the ZPR compartment.
- Click Create Security Attribute Namespace.
- Enter a Name and Description, and click Create.
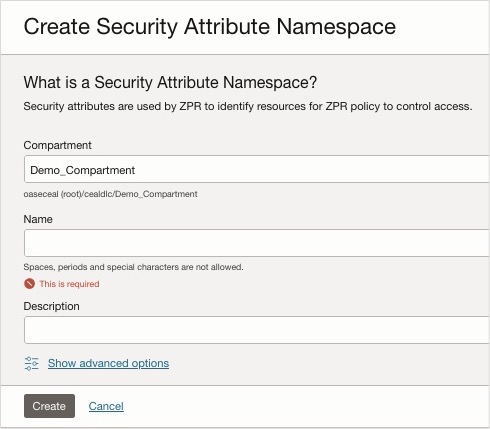
Zero Trust Packet Routing Namespace
- Enter a Name and Description, and click Create.
- Create ZPR attributes in the ZPR namespace. The example policy uses three attributes: app, network, and database.
- Navigate to the ZPR namespace and click on it.
- Click Create Security Attribute.
- Enter a Name and Description, and click Create.
- Repeat for the other attributes.
- Click Create Security Attribute.
- Navigate to the ZPR namespace and click on it.
- Create a ZPR namespace in the ZPR compartment.
- Create a ZPR compartment for each planned ZPR functional area. For example, HR, ERP, and so on.
Caution! The attributes and attribute values assigned to resources such as BDS Cluster node’s VNIC, Data Flow SQL Endpoint VNIC, OAC endpoints, Object Storage private endpoint VNIC, and ADW must first be referenced in a policy statement. If you assign attributes to resources without a corresponding reference, the resources are inaccessible.
Using your ZPR namespace requires the namespace to precede security attributes. An example policy statement that allows OAC to connect to BDS Cluster nodes is:
in ZPR_BD_NS.network:dsvcn-network VCN allow ZPR_BD_NS.app:oac-app endpoints to connect to ZPR_BD_NS.database:bds-cluster endpoints
In the above statement, ZPR_BD_NS is a ZPR namespace, network, app, and database are ZPR attributes, and dsvcn-network, oac-app, and bds-cluster are attribute values.
- Create a ZPR policy.
- Familiarize yourself with ZPR policy basics before you create a policy.
- Navigate to Identity & Security > ZPR Policies, and click Create Policy.
- Enter a Name and Description, and then click Add Policy Statements.
- Add policy statements using the Manual Policy Builder.
- Click Add.
- Click Create Policy.
- Enter a Name and Description, and then click Add Policy Statements.
Next, you must assign ZPR attributes to the Oracle Data Intelligence Platform services and any supporting resources you want to secure with ZPR. The steps differ depending on the use case (for example, Big Data Cluster and Data Flow SQL Endpoint) and are described in the companion posts in this blog series.

Read more about ZPR and OCI:
Zero Trust Packet Routing IAM Policies
Enabling Zero Trust Packet Routing
Managing Security Attribute Namespaces
Managing Security Attributes
ZPR policy basics
Managing Zero Trust Packet Routing Policies
ZPR Policy Syntax
Secure Oracle Data Intelligence Platform Services with Zero Trust Packet Routing – A Series Overview
Secure Oracle Big Data Service using Zero Trust Packet Routing
Secure Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Flow using Zero Trust Packet Routing
Oracle Data Intelligence Platform
Oracle Big Data Service
OCI Data Flow
OCI Data Catalog
OCI Data Integration
Oracle Intelligent Data Lake

