Introduction
Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) supports the integration of its semantic model with Git. Using a Git repository provides version control and helps with synchronization between multiple developers on the same model.
A semantic model is composed of a set of JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) files. When you create and develop a semantic model locally, the model’s JSON files are stored in the Oracle Cloud. To make the semantic model’s JSON files available for other development team members, the semantic model owner creates a Git repository, initializes it with HTTPS or SSH, and uploads the semantic model JSON files to the repository. Each developer creates a semantic model and uses HTTPS or SSH to connect to and clone the semantic model’s JSON files to their Git repository.
You can use OAC’s Semantic Model Markup Language (SMML) editor to view and change the JSON SMML schema file of an object in your semantic model.
This blog describes how to perform the Git setup using GitHub and integrate it with OAC.
Collaborative Semantic Model Development
Benefits of Git Integration
- A distributed version control system provides each developer with their own data model repository.
- Industry standard branching capability or multiuser development.
- Collaborate among developers to merge one of their branches.
- Familiar version control systems among developers
- The above features facilitate agile development with faster release cycles.
Step 1: Follow this link to GitHub to create an account.
- Create a GitHub repository.
- Decide whether you want to use an HTTPS connection or an SSH connection (see the note below for more information).
- You need to set up a personal access token If you are using GitHub with HTTPS.
- Each Semantic Model can be configured to use a separate GitHub repository.
- Create User profiles for reusing GitHub connections for multiple GitHub repositories.
- It can be configured when cloning a GitHub repository or when initializing a semantic model.
Note: An HTTPS connection uses your GitHub username and password to initialize and upload a semantic model to an empty GitHub repository. An SSH connection uses a key that you generate in OAC and copy into your GitHub account to create an SSH key. This key is used to initialize and connect to a GitHub repository without needing to supply a GitHub username and password.
Step 2: Create a repository to store the files and their versions on GitHub.
All developers who need access to the repository should have a GitHub account, this is mandatory.
Example: WEBINAR_SEMANTICMODEL
- This will generate HTTPS or SSH URLs and a token to identify and access the repository.
- Sample HTTP, https://github.com/Username/WEBINAR_SEMANTICMODEL.git
- Sample of personal access token: lpg_abcdegknklmlljlkouojnasiin012vhtramC
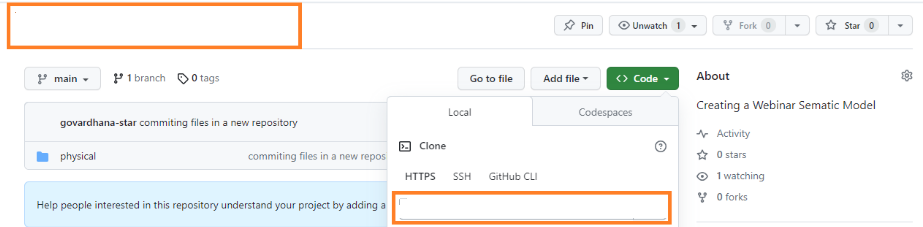
Step 3: Log in to Oracle Analytics Cloud to create a semantic model and map it to repository details using the Clone a Git Repository option.

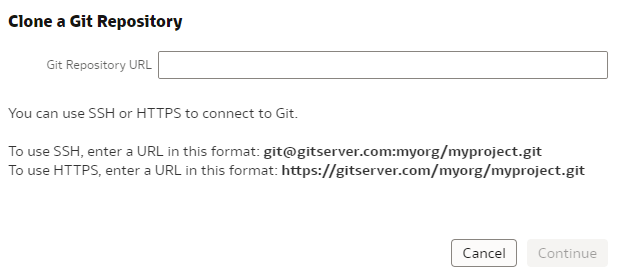
Step 4: Enter the GitHub repository URL as shared above and click Continue.
Step 5: Create a profile name with your user and password details.
Example: Sample Profile
- Git Profile
- Git Username: user ID of GitHub account
- Password: Use the above personal access token shared to uniquely identify and seamlessly access the GitHub repository, and click Initialize Git.
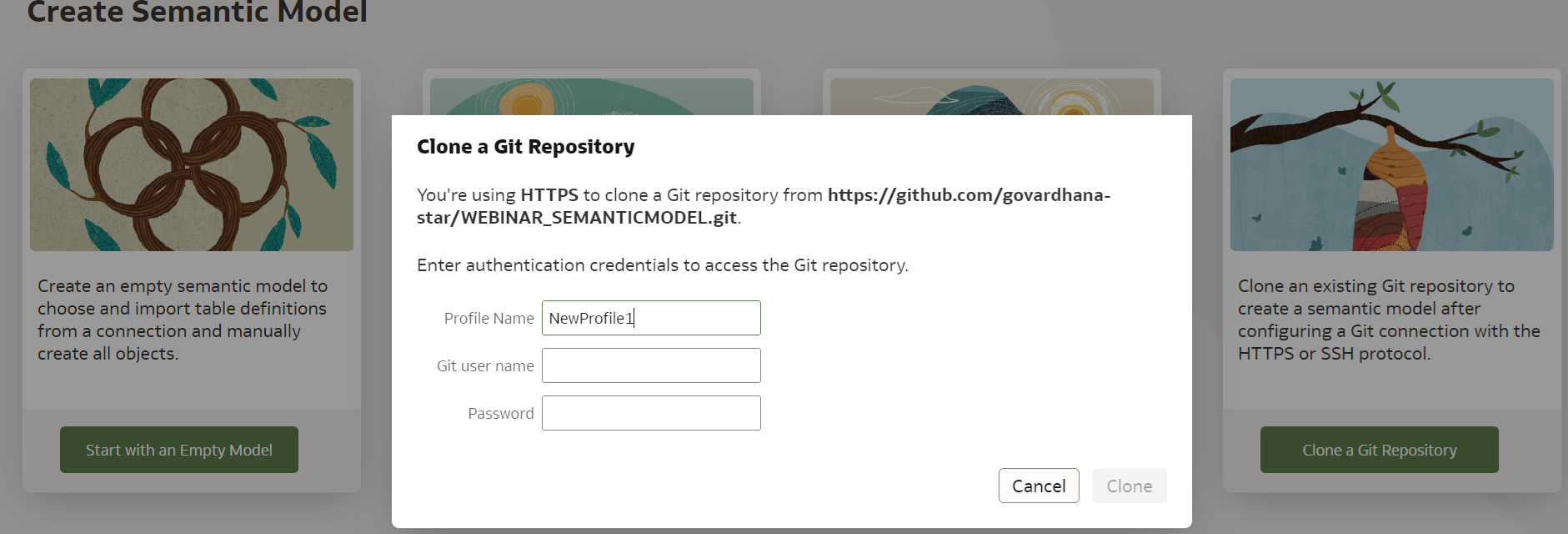
Step 6: After filling in relevant details, click Clone.
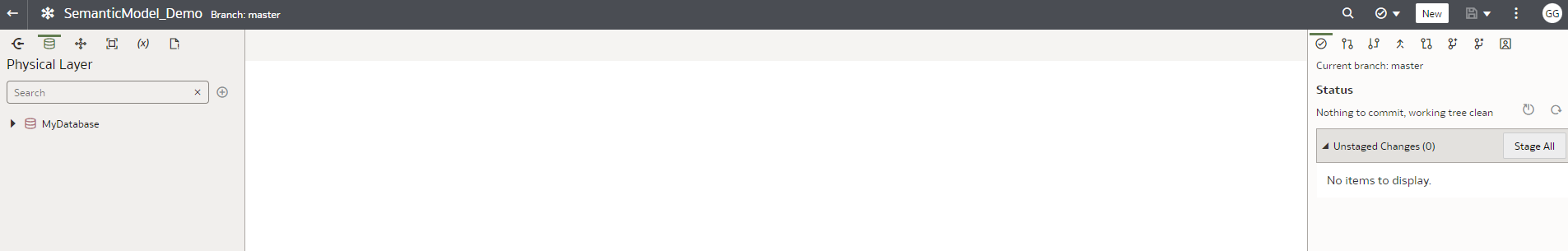
Step 7: You should be able to see the physical, logical, and presentation layers empty.
Step 8: Keep track of the changes in the GitHub Panel.
i.Open the Semantic Model Go to the presentation layer, open any folder or object, and try to edit it. Example: adding a description. Save it.
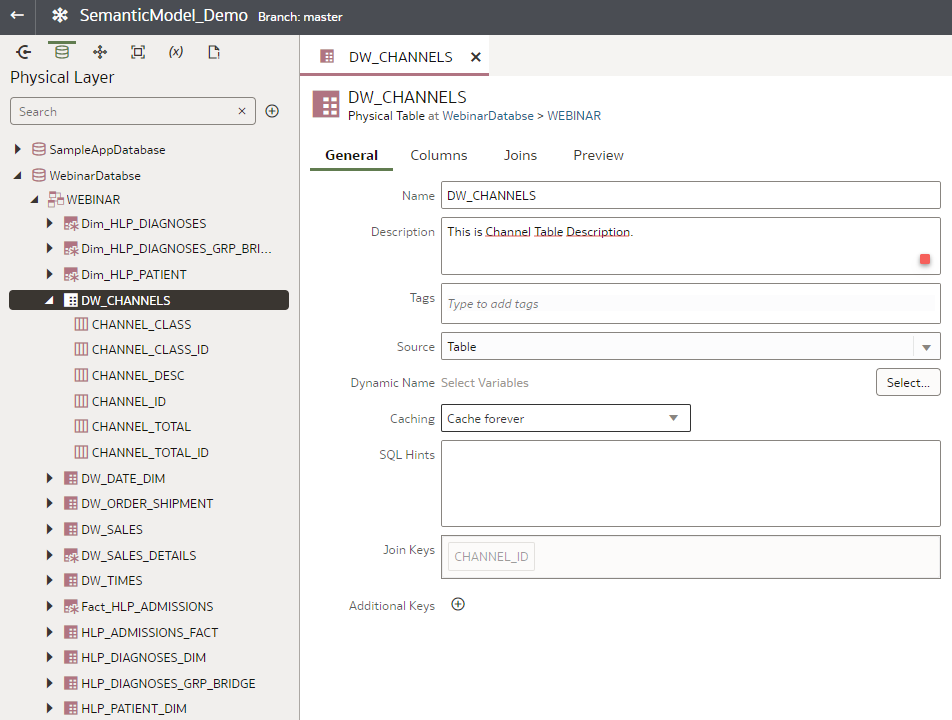
ii.Click Stage All on Status, commit, and push the changes into the semantic model.
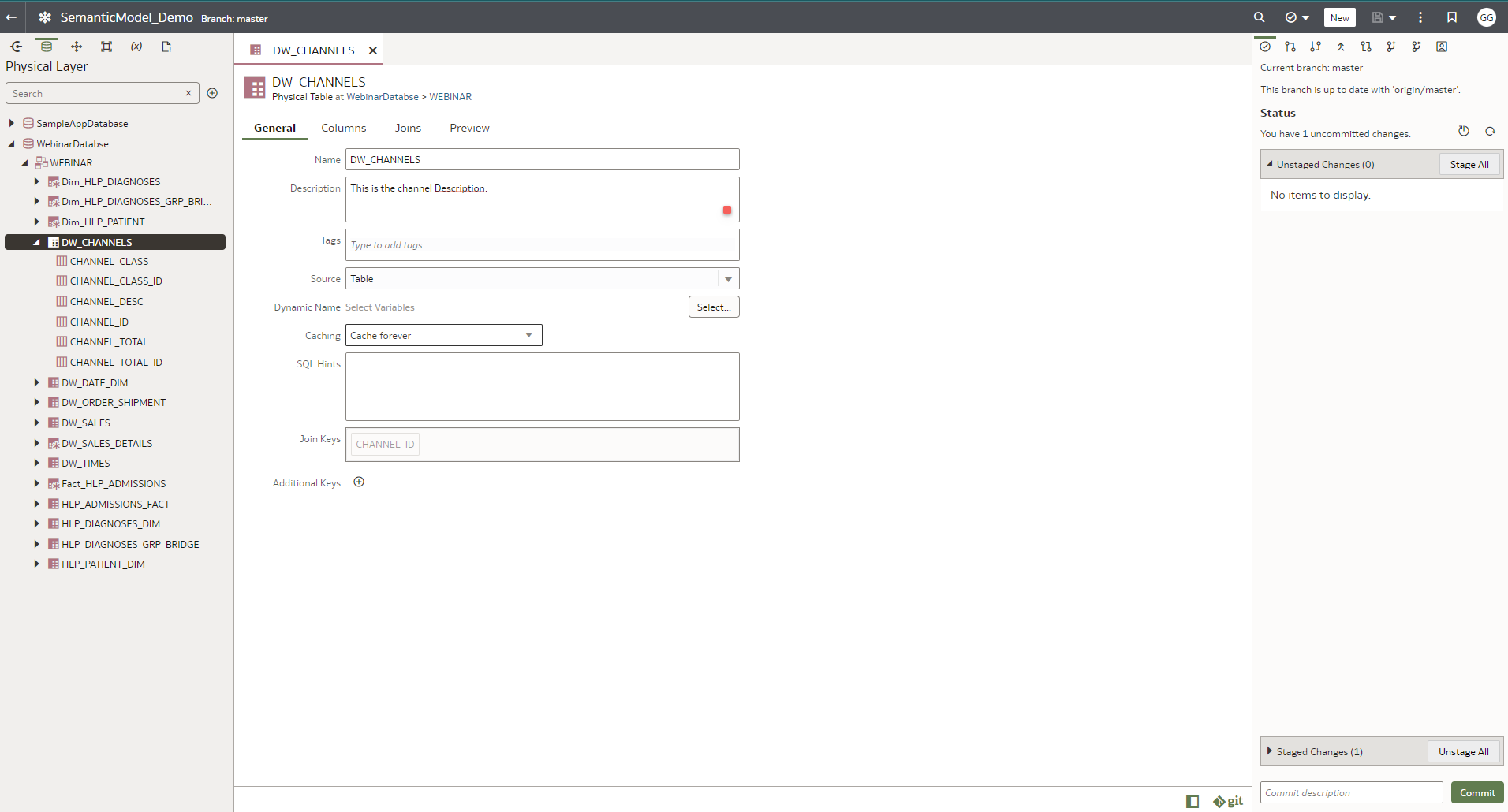
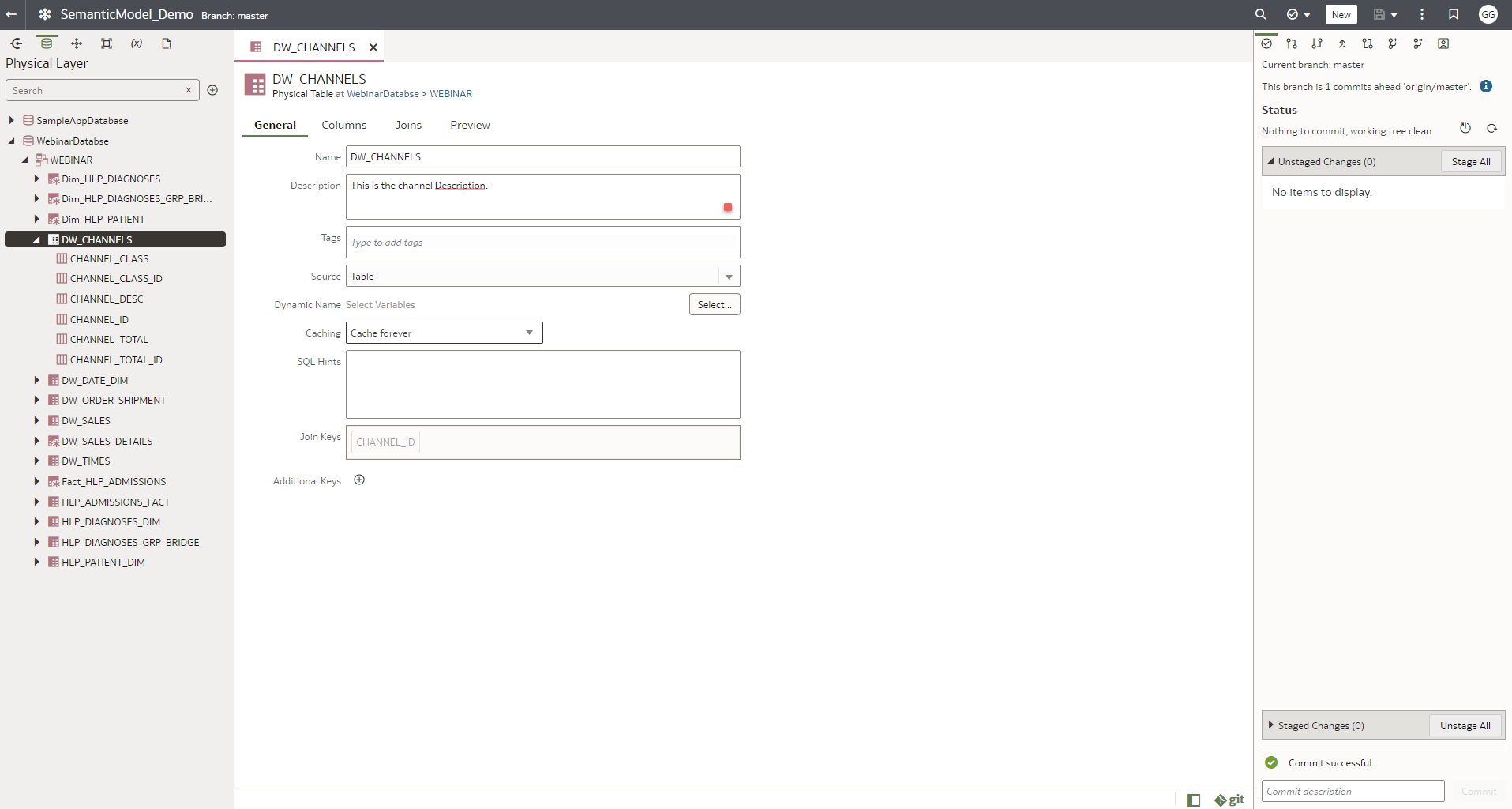
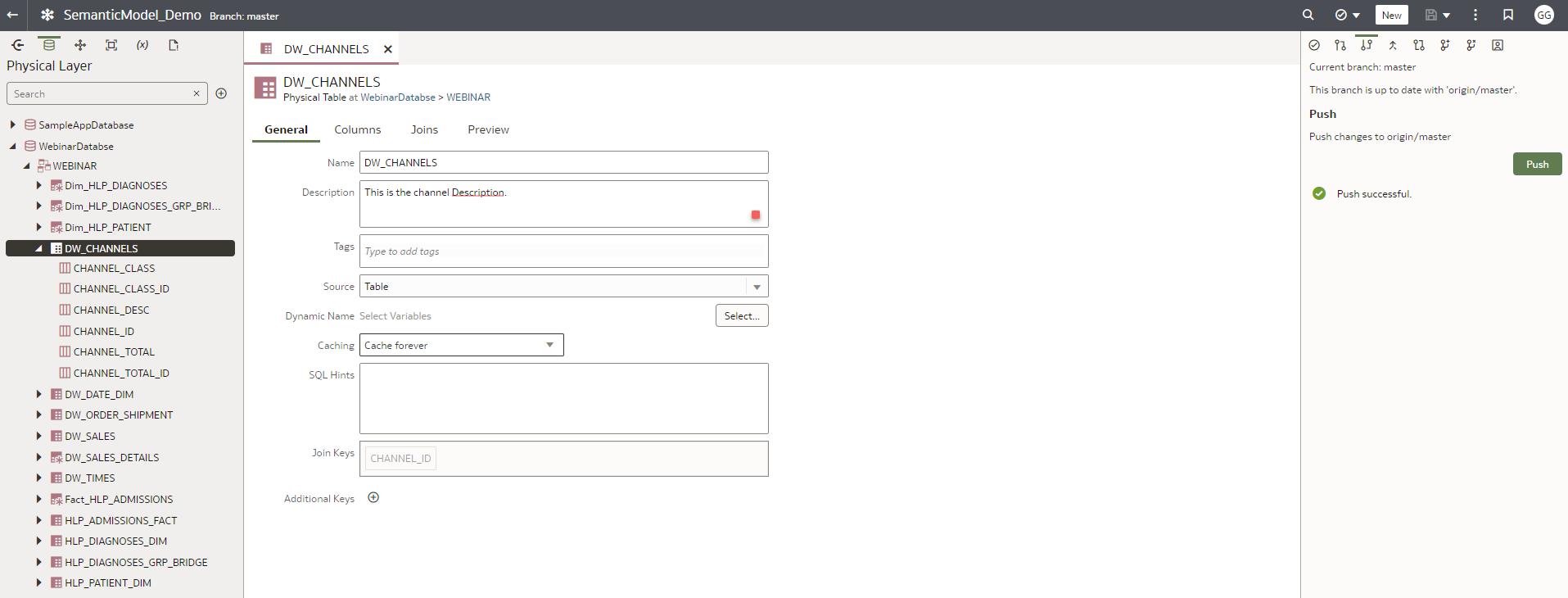
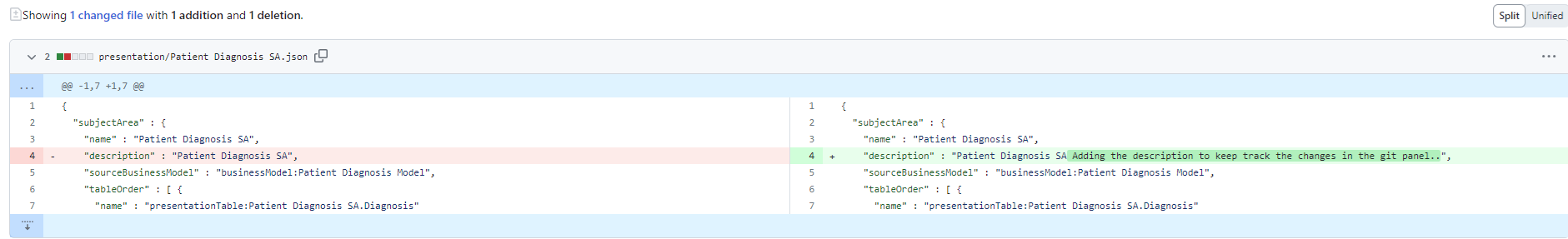
iii. You can track the changes made in the semantic modeler in the GitHub repository, for example, changing the channel table description in the physical layer.
Step 9: To do check-in and check-out operations during repository development
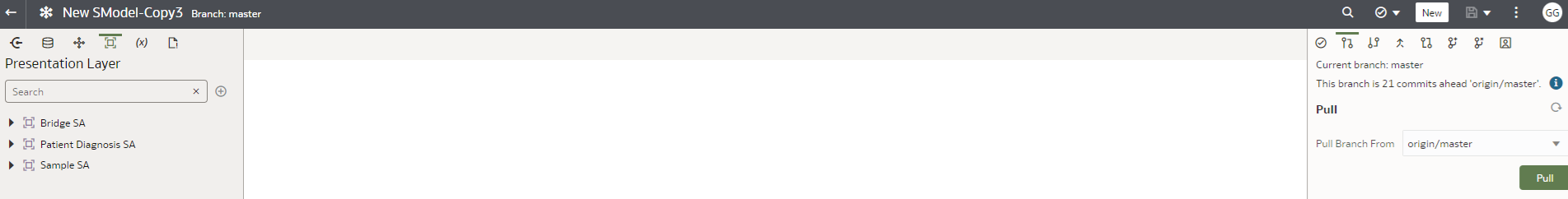
i.Use the Pull option to check out the latest changes committed by other developers on the remote branch to your working branch, e.g., origin/master. Use this option to ensure that you’re working with the latest code.
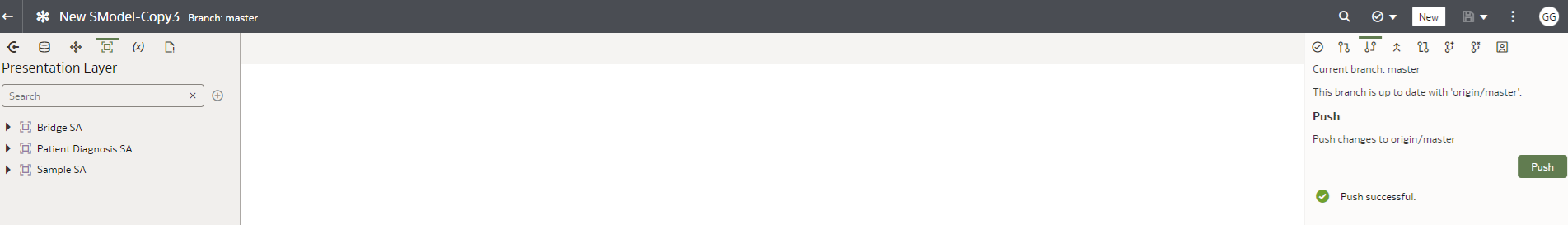
ii.Use this tab to Push your staged and committed changes to the remote branch. The changes you push to the remote branch are available to the other developers using the branch.
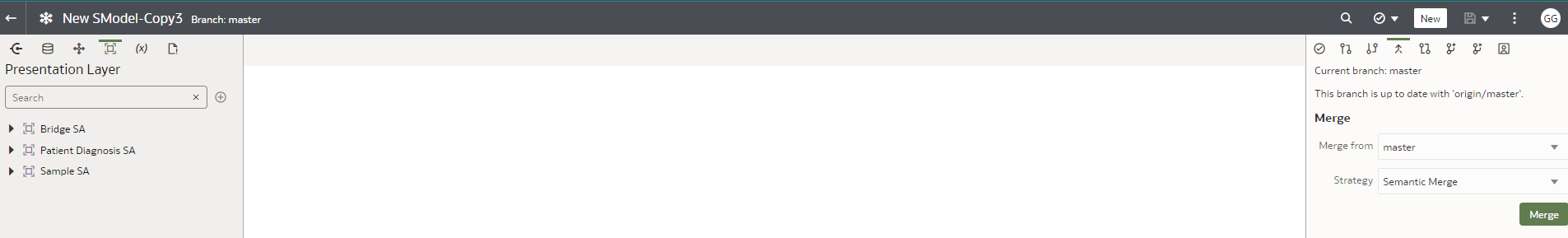
iii. Commit all the files on local computers and then push the commits to the remote repository using the merge option.
Summary
Implement the steps described in this blog to create and set up the integration of semantic models with Oracle Cloud Analytics so that more than one developer can work on and deploy a semantic model. Click here for more information.
Learn more about Oracle Analytics. Follow us on Twitter@OracleAnalytics, and connect with us on LinkedIn. You can also post questions in the Oracle Analytics Community.

