This blog introduces Oracle Big Data Service (BDS) and describes how you can connect to a BDS cluster using Hive and Spark connections from Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC).
Oracle Big Data Service clusters contain a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Hive database which ingests and transforms data from diverse sources and formats (structured, semi-structured, and unstructured). You can access and use the refined data from BDS in Oracle Analytics Cloud to gain deeper insights. Architecture
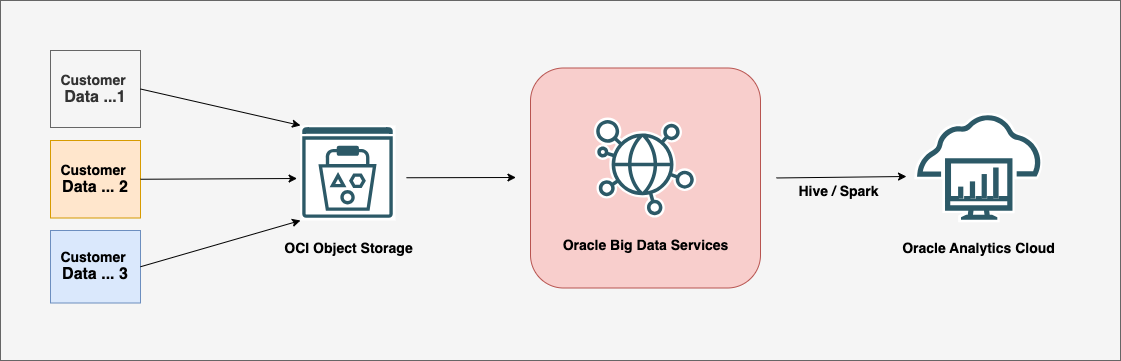
Create a Big Data Service Cluster on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) IAM Policies Required for Big Data Service
For information about OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies required for BDS, see Understanding Big Data Service resources and permissions in IAM policies.
Create a Big Data Service Cluster on OCI
- Sign in to your OCI console.
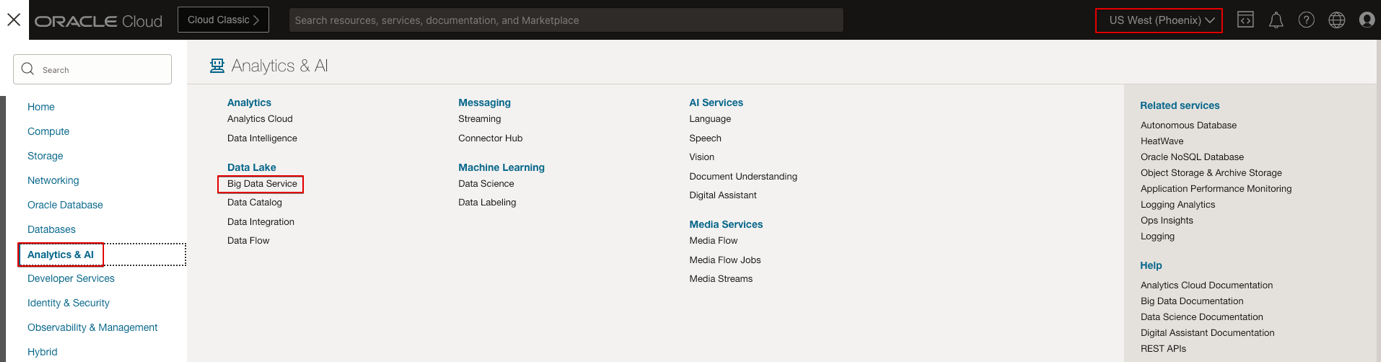
- Navigate to Analytics & AI.
- Under Data Lake, click Big Data Service.
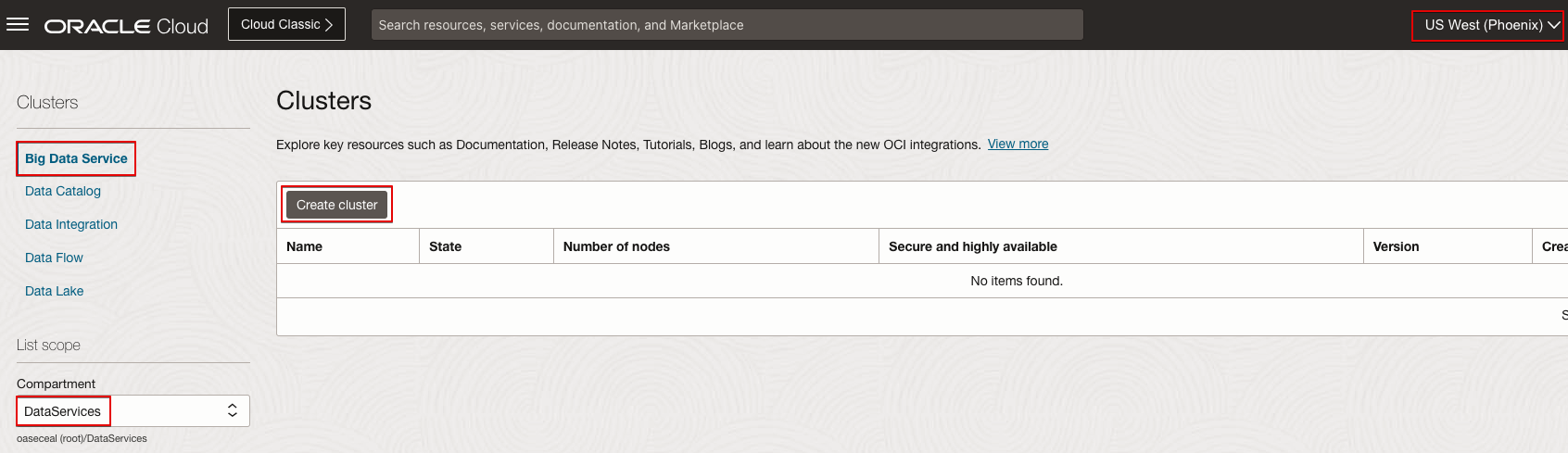
- Select the Compartment where you want to create the BDS cluster.
- Click Create cluster.
- Select the public or private subnets of the Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) where you want to create the BDS cluster.
For information on how to create VCNs and subnets, refer to the OAC disaster recovery technical paper Disaster Recovery Configuration for Oracle Analytics Cloud.
You can create the BDS cluster either as a secure and highly-available (HA) cluster or as a non-HA cluster.
You can create the BDS cluster in the VCN’s public or private subnet.
- If the BDS cluster is created in a public subnet, the public IP address isn’t created by default. You must explicitly create the public IP address.
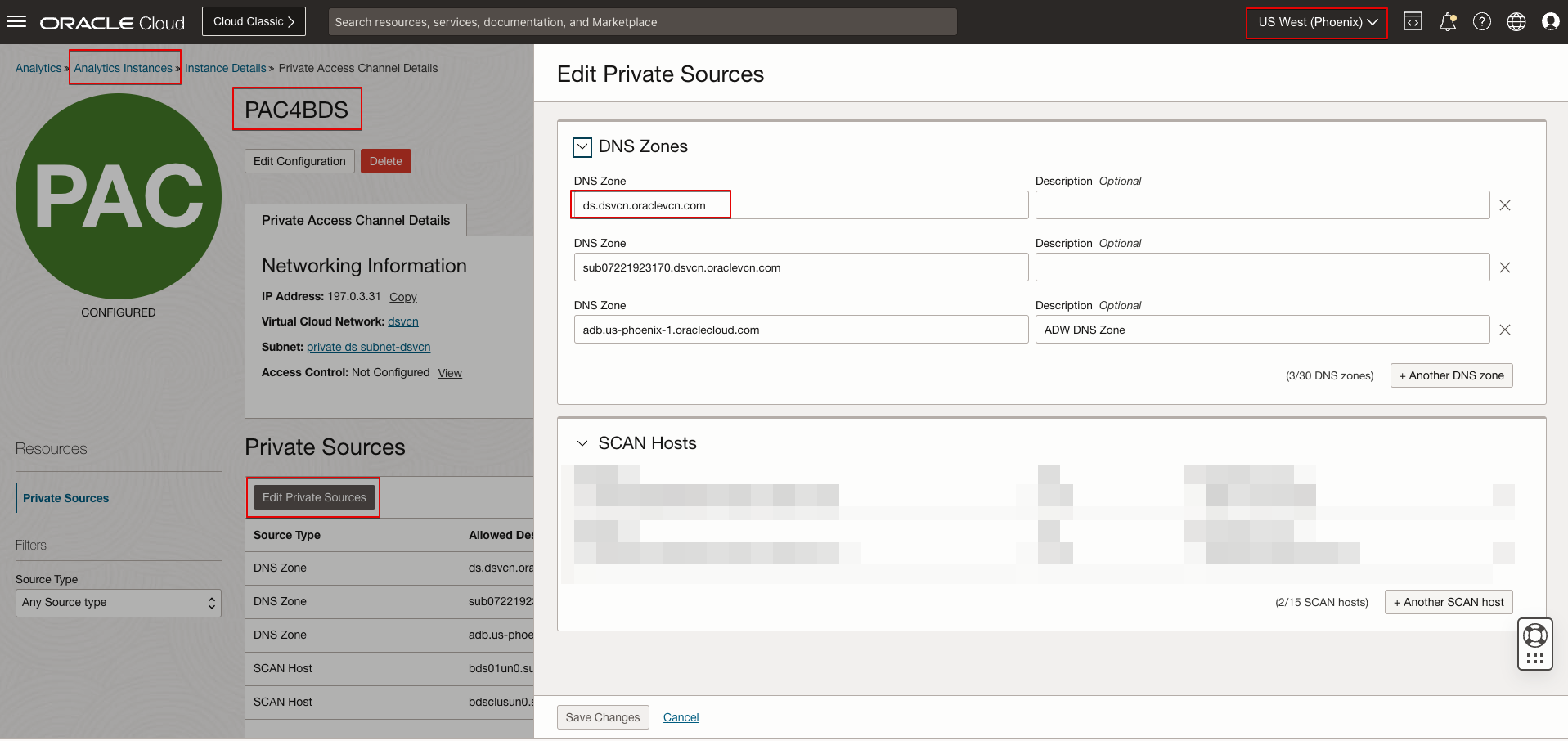
- If the BDS cluster is created in a private subnet, you can’t access it from the Internet. You must create a private access channel (PAC) in Oracle Analytics Cloud to connect to the BDS cluster on the private endpoint.
Network Security for Big Data Service
In OCI, you use Security Lists and Network Security Groups to manage network security.
You must open certain ports on Big Data Service clusters to allow access to services such as Apache Ambari, Cloudera Manager, and Hue.
Use these Ingress Rules Destination Ports for Hive and Spark connections:
- Hive: 10010
- Spark: 10000
Create an OCI Object Storage Bucket
The steps to create OCI Object Storage buckets are described in the document Disaster Recovery Configuration for Oracle Analytics Cloud. After creating a bucket, record the namespace, bucket name, and object storage URL.
Download the Sample Data File
Download the sample date file used in the blog: NYC Taxi Trip Records for Jan19
Upload the Data File to the Object Storage Bucket
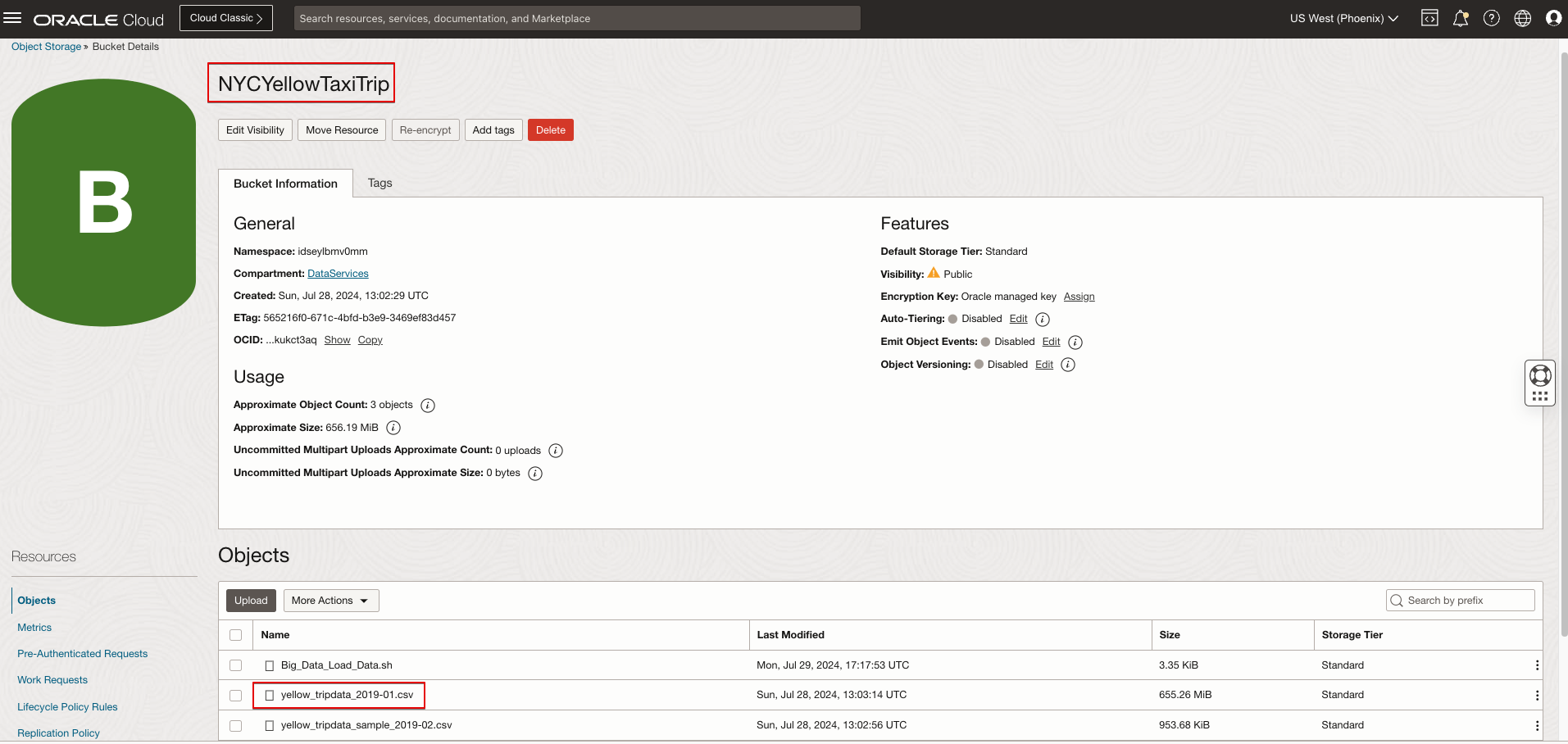
Load the Data File to the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
# Access the first master node (mn0) of the BDS cluster using ssh as the opc user.
# Switch to the Linux user created on the nodes of the cluster (for example, odhadmin).
sudo su odhadmin
# If the BDS cluster is created as a Secure & High Available Cluster, get a Kerberos token for the odhadmin user.
kinit odhadmin
# Create a local download folder
mkdir -p /home/odhadmin/downloads
cd /home/odhadmin/downloads
# Download the data file from the object storage bucket to the local file system.
wget https://{namespace}.objectstorage.{oci-region}.oci.customer-oci.com/n/{namespace}/b/{bucet-name}/o/yellow_tripdata_2019-01.csv
# Remove the header row from the data file.
sed -i 1d yellow_tripdata_2019-01.csv
# Upload the data file to HDFS.
HDFS_ROOT=/data
hadoop fs -mkdir -p /data/YellowTaxiTrip
hadoop fs -chmod 777 /data/YellowTaxiTrip
hadoop fs -put -f /home/odhadmin/downloads/yellow_tripdata_2019-01.csv /data/YellowTaxiTrip/
Create a Hive Database and Tables and Load the Data
Run the following code on the first master node (mn0) of the BDS cluster.
hive -e " create database if not exists yellowtaxi; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS yellowtaxi.trips_ext; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS yellowtaxi.trips; CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE yellowtaxi.trips_ext ( VendorID int, tpep_pickup_datetime timestamp, tpep_dropoff_datetime timestamp, passenger_count int, trip_distance double, RatecodeID int, store_and_fwd_flag string, PULocationID int, DOLocationID int, payment_type int, fare_amount double, extra double, mta_tax double, tip_amount double, tolls_amount double, improvement_surcharge double, total_amount double, congestion_surcharge double ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde' STORED AS TEXTFILE location '/data/YellowTaxiTrip/' ; CREATE TABLE yellowtaxi.trips ( VendorID int, tpep_pickup_datetime timestamp, tpep_dropoff_datetime timestamp, passenger_count int, trip_distance double, RatecodeID int, store_and_fwd_flag string, PULocationID int, DOLocationID int, payment_type int, fare_amount double, extra double, mta_tax double, tip_amount double, tolls_amount double, improvement_surcharge double, total_amount double, congestion_surcharge double ) PARTITIONED BY (p_VendorID int) STORED AS PARQUET ; set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true; set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict; FROM yellowtaxi.trips_ext t INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE yellowtaxi.trips PARTITION(p_VendorID) SELECT VendorID, tpep_pickup_datetime, tpep_dropoff_datetime, passenger_count, trip_distance, RatecodeID, store_and_fwd_flag, PULocationID, DOLocationID, payment_type, fare_amount, extra, mta_tax, tip_amount, tolls_amount, improvement_surcharge, total_amount, congestion_surcharge, VendorID ;"
View the Data Loaded in Hue
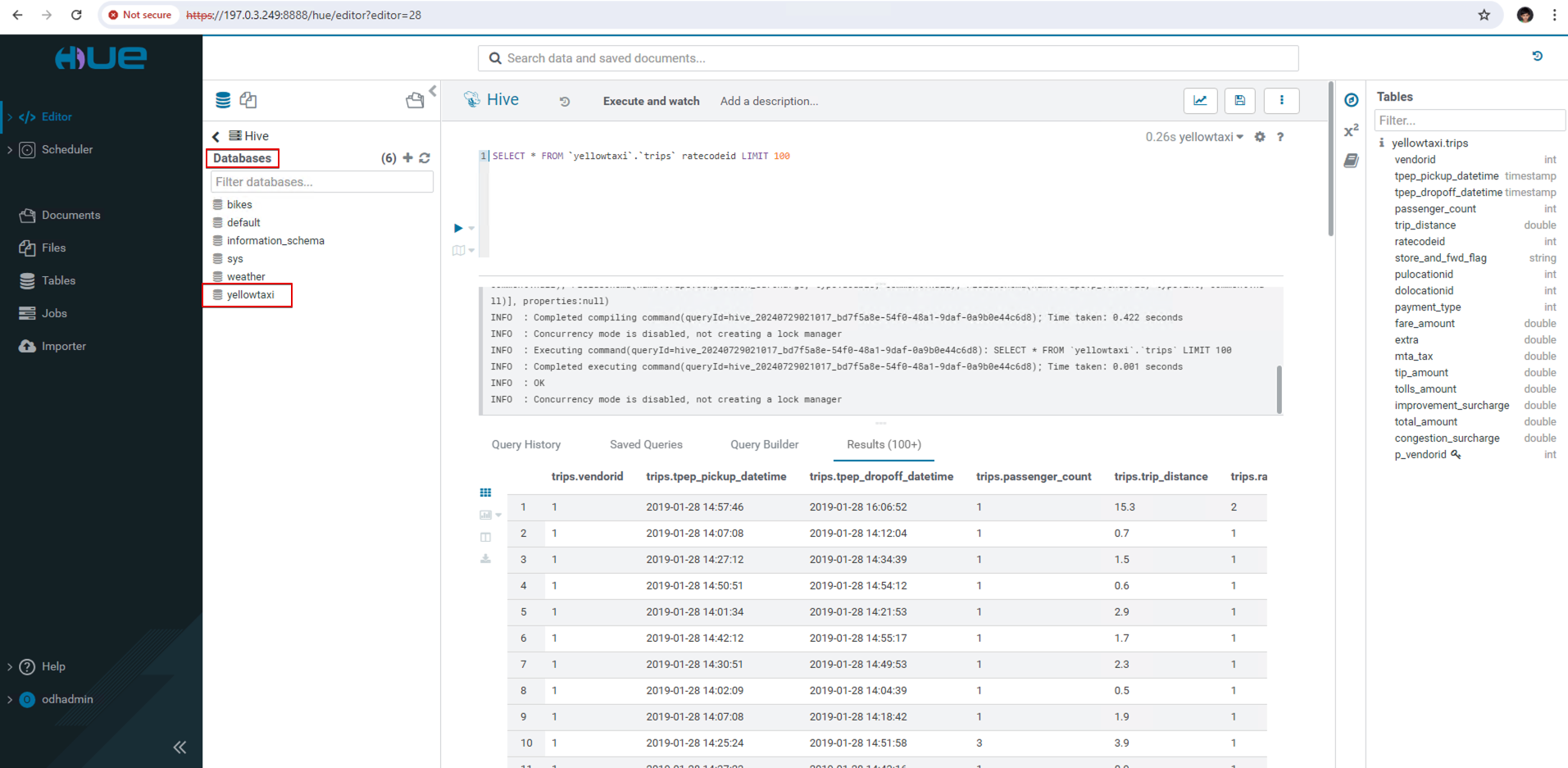
SSL for Certificate Authority Signed Certificates
In Big Data Service clusters version 3.0.7 and later, you can run the Big Data Service certificate utility tool to use Certificate Authority (CA) SSL certificates for your Oracle Distribution including Apache Hadoop (ODH) clusters.
Connect Oracle Analytics Cloud to Big Data Service Clusters
Prerequisites:
- Create an Oracle Analytics Cloud instance in either the same public or private subnet of the same VCN as the BDS cluster, or in a different public or private subnet of the same VCN as the BDS cluster.
- Note: If you create the OAC instance in a different VCN, ensure that the OAC instance can reach the BDS cluster on the other VCN.
- If you created the BDS cluster in a private subnet, create a private access channel (PAC) in OAC.
You can use Apache Hive or Apache Spark to connect Oracle Analytics Cloud to both secure and unsecure BDS clusters.
- Connect to unsecure BDS clusters with no Kerberos or SSL.
- Connect to secure BDS clusters with Kerberos enabled.
- Connect to secure BDS clusters with Kerberos and SSL enabled.
Connect to Unsecure BDS Clusters with no Kerberos or SSL using HiveServer2
In OAC, create an Apache Hive connection to the OCI BDS cluster’s Hive database.
Use Basic authentication with a username and password to connect.
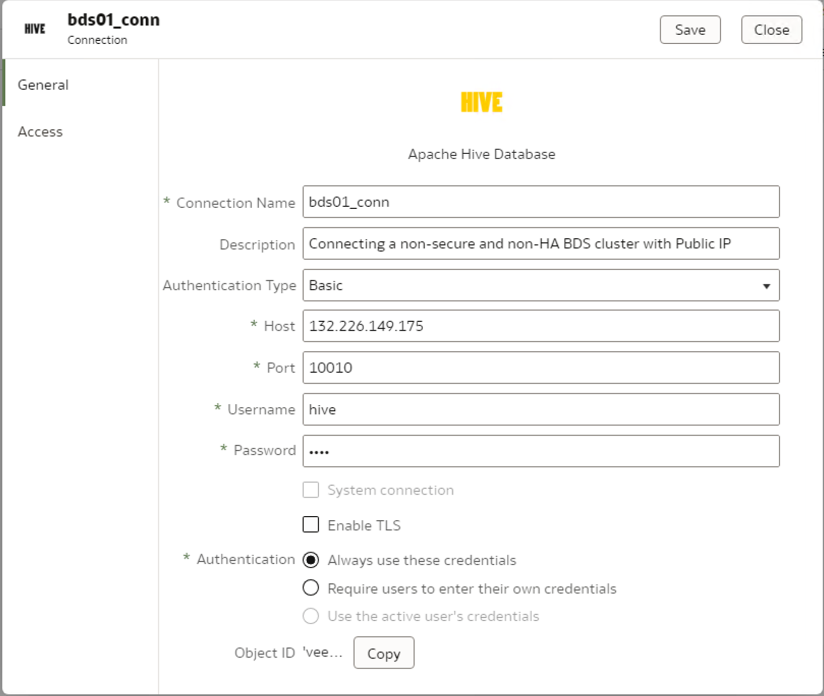
Connect to Secure BDS Clusters with Kerberos Enabled using HiveServer2
Kerberos Authentication
1. Collect the required files for Kerberos authentication.
Before running the cmd to get a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), ensure the Kerberos admin_server and kdc ports 749 and 88 are open for ingress access from the Internet or from the OAC private subnet.
0.0.0.0/0 port 749 TCP
0.0.0.0/0 port 88 TCP
0.0.0.0/0 port 88 UDP
2. Sign in to the un0 node (bdsclusun0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com) of the BDS cluster.
3. Create the folder kerberos under /tmp.
mkdir -p /tmp/kerberos
4. Copy the hive.service.keytab file from /etc/security/keytabs to /tmp/kerberos as oac.keytab.
cp /etc/security/keytabs/hive.service.keytab /tmp/kerberos/oac.keytab
5. Copy the /etc/krb5.conf file to /tmp/kerberos/krb5conf.
cp /etc/krb5.conf /tmp/kerberos/krb5conf
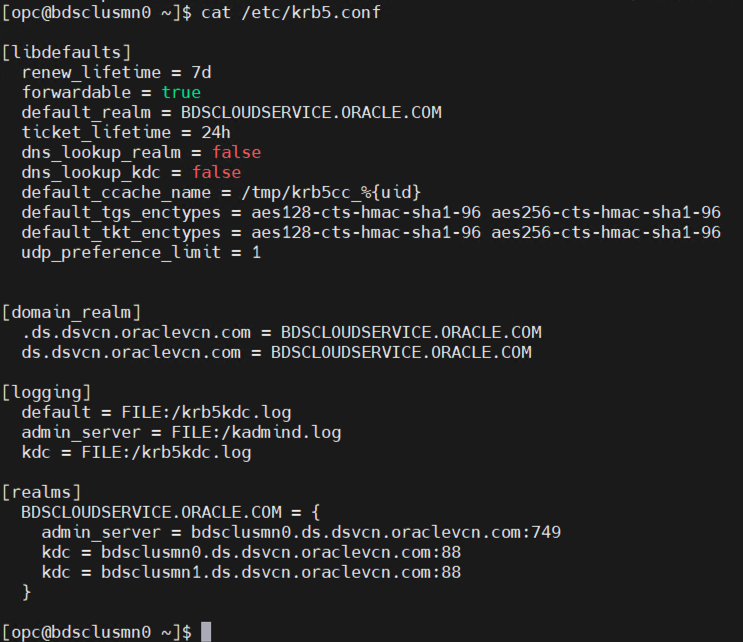
6. If BDS is on a public subnet, update the admin_server and kdc information in the krb5conf file with the public IP address of the cluster’s mn0 node instead of the hostname.
If BDS is on a private subnet, use the same FQDN hostname of the mn0 node of the BDS cluster and configure the PAC in OAC to resolve and reach the BDS cluster mn0 node components.
7. Create a file named service_details.json and save it inside the /tmp/kerberos folder.
{
"Host" : "bdsclusun0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com",
"Port" : "10010",
"ServicePrincipalName" : "hive/bdsclusun0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com@BDSCLOUDSERVICE.ORACLE.COM"
}
If you’re using the BDS public IP address, you must to use the public IP address instead of the hostname in the above json file.
8. Create a ZIP file from the kerberos folder.
cd /tmp
ls -l kerberos
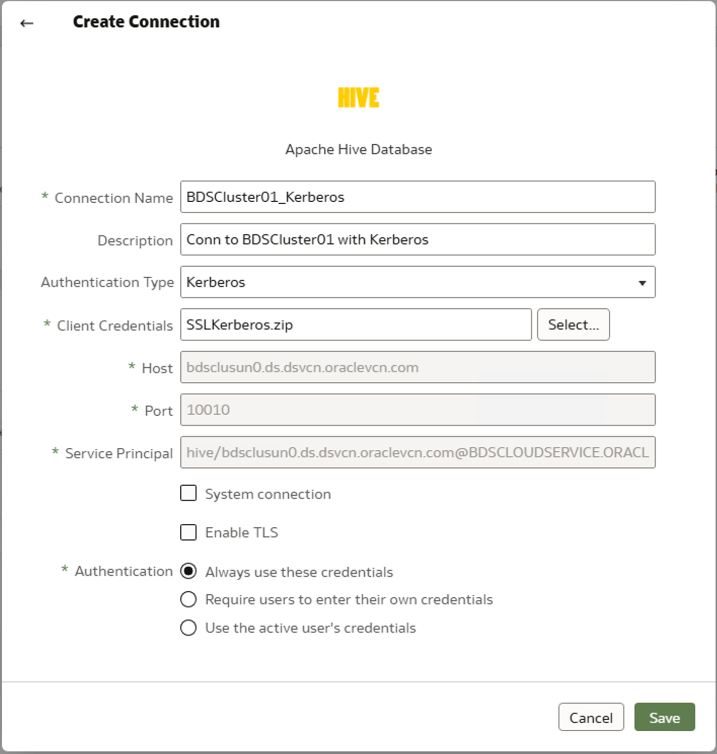
zip -r SSLKerberos.zip kerberos/*
9. Copy the SSLKerberos.zip file to the client machine where you access the OAC URL.
Configure a Private Access Channel for Your Oracle Analytics Cloud Instance
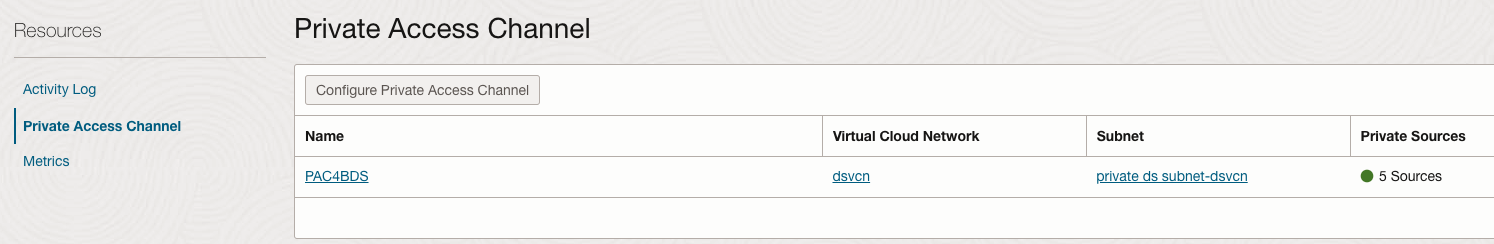
Create a Hive Connection
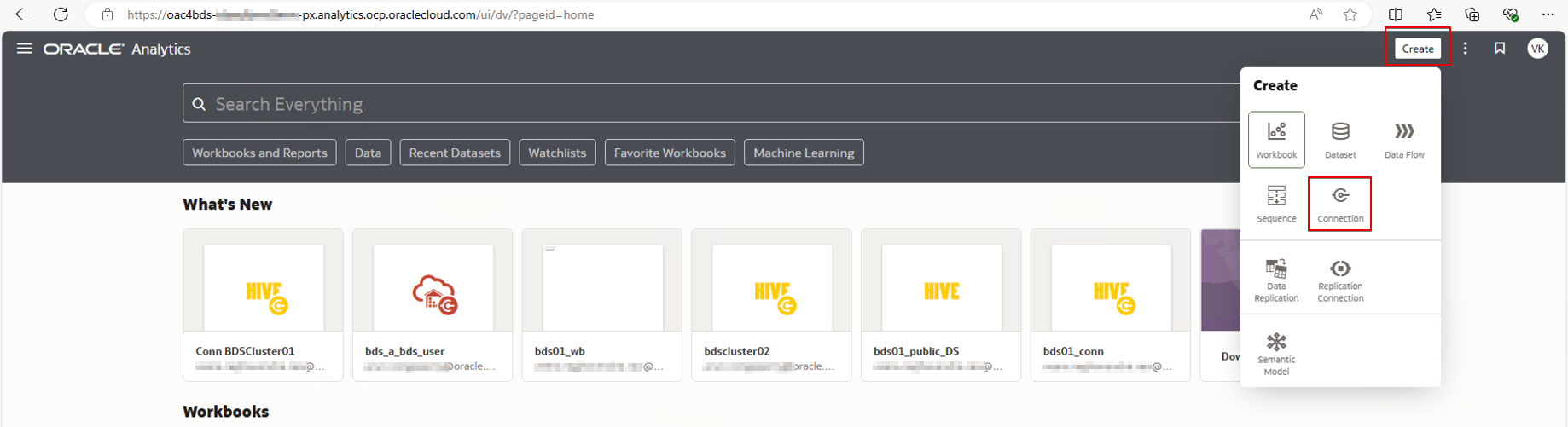
1. Sign in to OAC.
2. Create a connection.
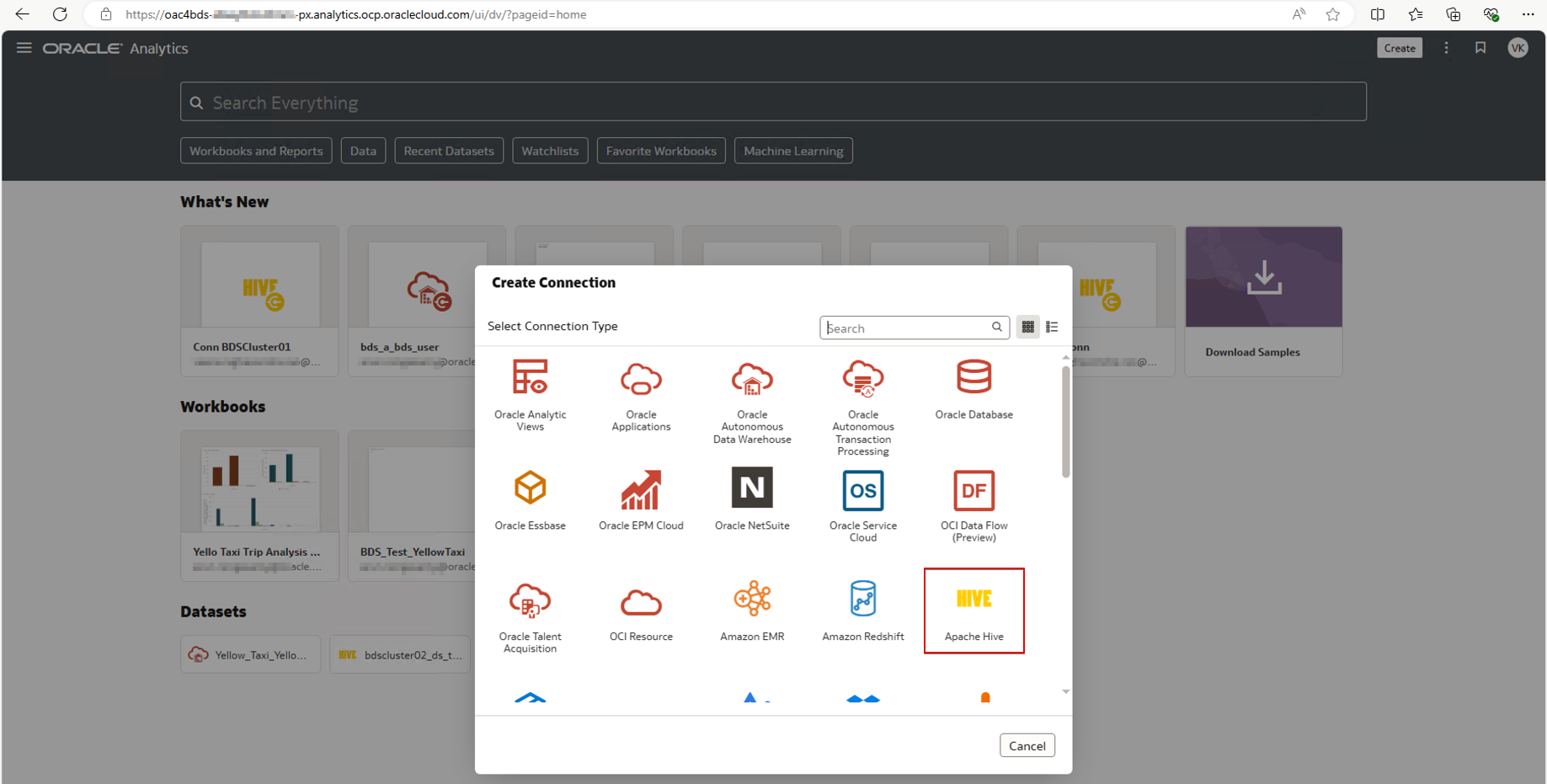
3. Select the connection type Apache Hive.
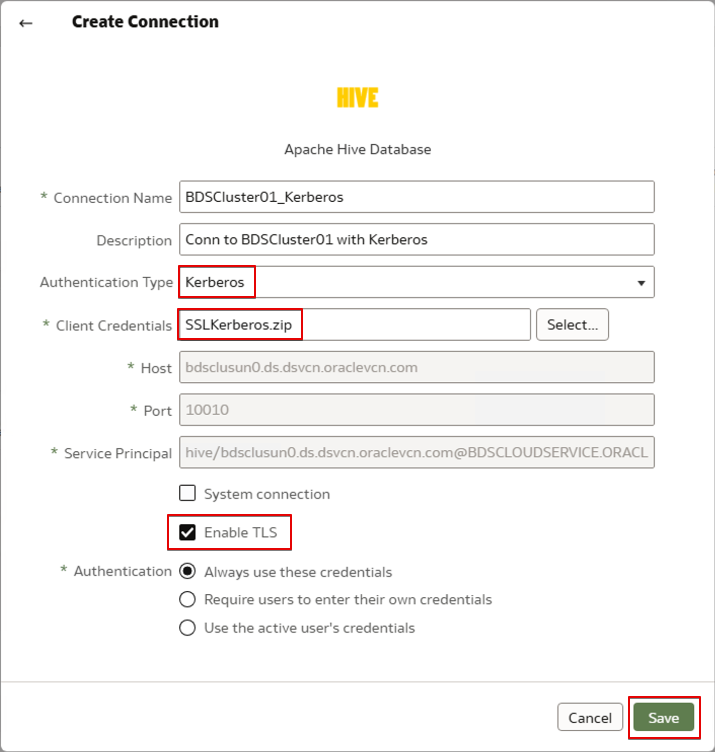
4. Select the authentication type Kerberos and select the Kerberos Credentials ZIP file.
Connect to Secure BDS Clusters with Kerberos and SSL Enabled using HiveServer2
1. If the BDS cluster is SSL-enabled and has a well-known CA-signed SSL Certificate, check the Enable TLS checkbox in the connection dialog.
Note: OAC can trust only well-known CA-signed SSL certificates of the data sources.
2. Similarly, create a Spark connection.
Connecting to Secure BDS Clusters with Kerberos Enabled using Spark3 Thrift Server
Kerberos Authentication
1. Collect the required files for Kerberos authentication.
Before running the cmd to get a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), ensure the Kerberos admin_server and kdc ports 749 and 88 are open for ingress access from the internet or from the OAC private subnet.
0.0.0.0/0 port 749 TCP
0.0.0.0/0 port 88 TCP
0.0.0.0/0 port 88 UDP
2. Sign in to the mn0 node (bdsclusmn0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com) of the BDS cluster.
3. Create a folder kerberos under /tmp.
mkdir -p /tmp/kerberos
4. Copy the spark.service.keytab file from /etc/security/keytabs to /tmp/kerberos as oac.keytab.
cp /etc/security/keytabs/spark.service.keytab /tmp/kerberos/oac.keytab
5. Copy the /etc/krb5.conf file to /tmp/kerberos/krb5conf.
cp /etc/krb5.conf /tmp/kerberos/krb5conf

6. If BDS is on a public subnet, update the admin_server and kdc information in the krb5conf file with the public IP address of the cluster’s mn0 node instead of the hostname.
If BDS is on a private subnet, use the same FQDN hostname of the mn0 node of the BDS cluster and configure the PAC in OAC to resolve and reach the BDS Cluster mn0 node components.
7. Create a file named service_details.json and save it inside the /tmp/kerberos folder.
{
"Host" : "bdsclusmn0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com",
"Port" : "10000",
"ServicePrincipalName" : "spark/bdsclusmn0.ds.dsvcn.oraclevcn.com@BDSCLOUDSERVICE.ORACLE.COM"
}
If you’re using a BDS public IP address, provide the public IP address instead of the hostname in the above JSON file.
8. Create a ZIP file from the kerberos folder.
cd /tmp
ls -l kerberos
zip -r spark3tskerb.zip kerberos/*
9. Copy the spark3tskerb.zip file to the client machine where you access the OAC URL.
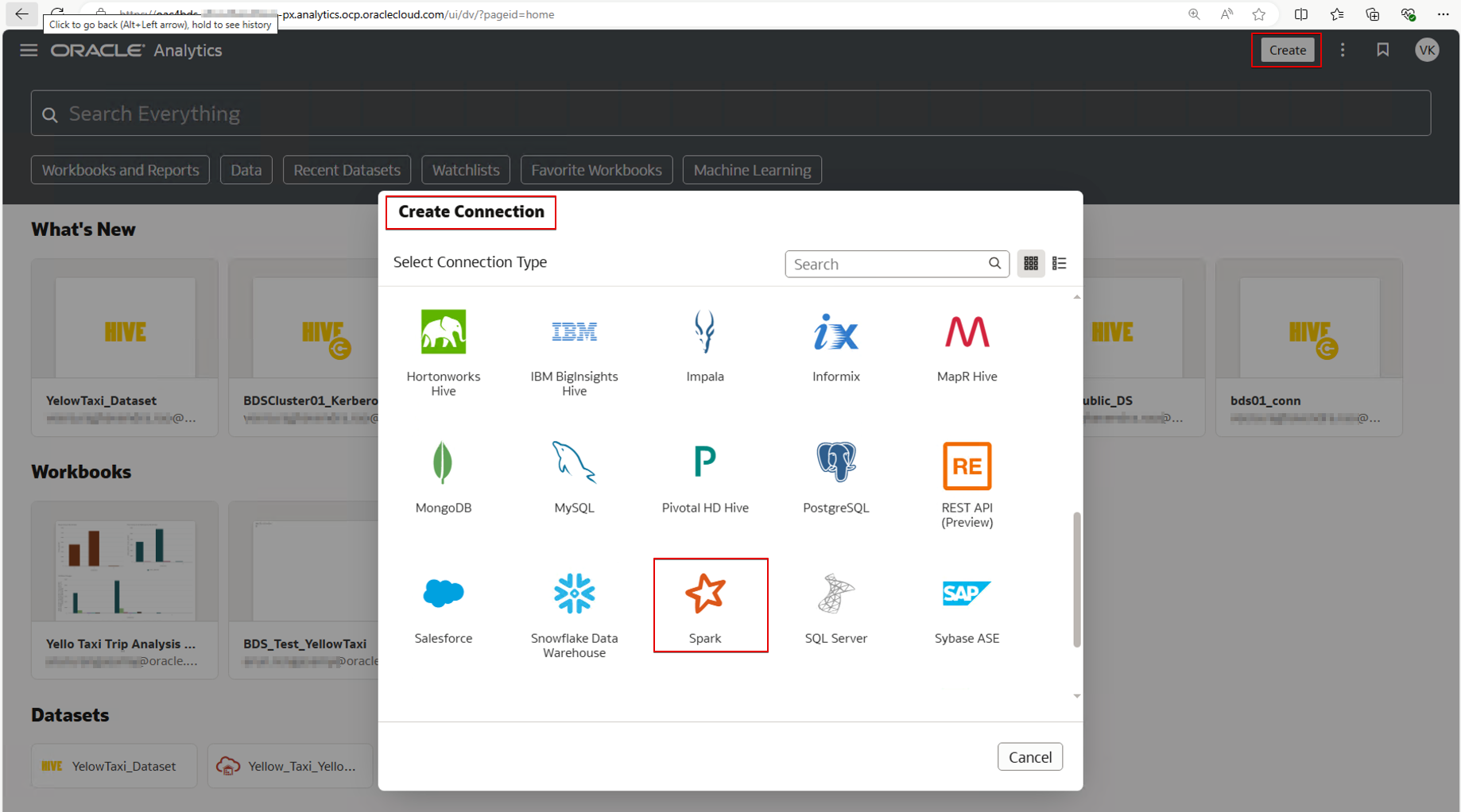
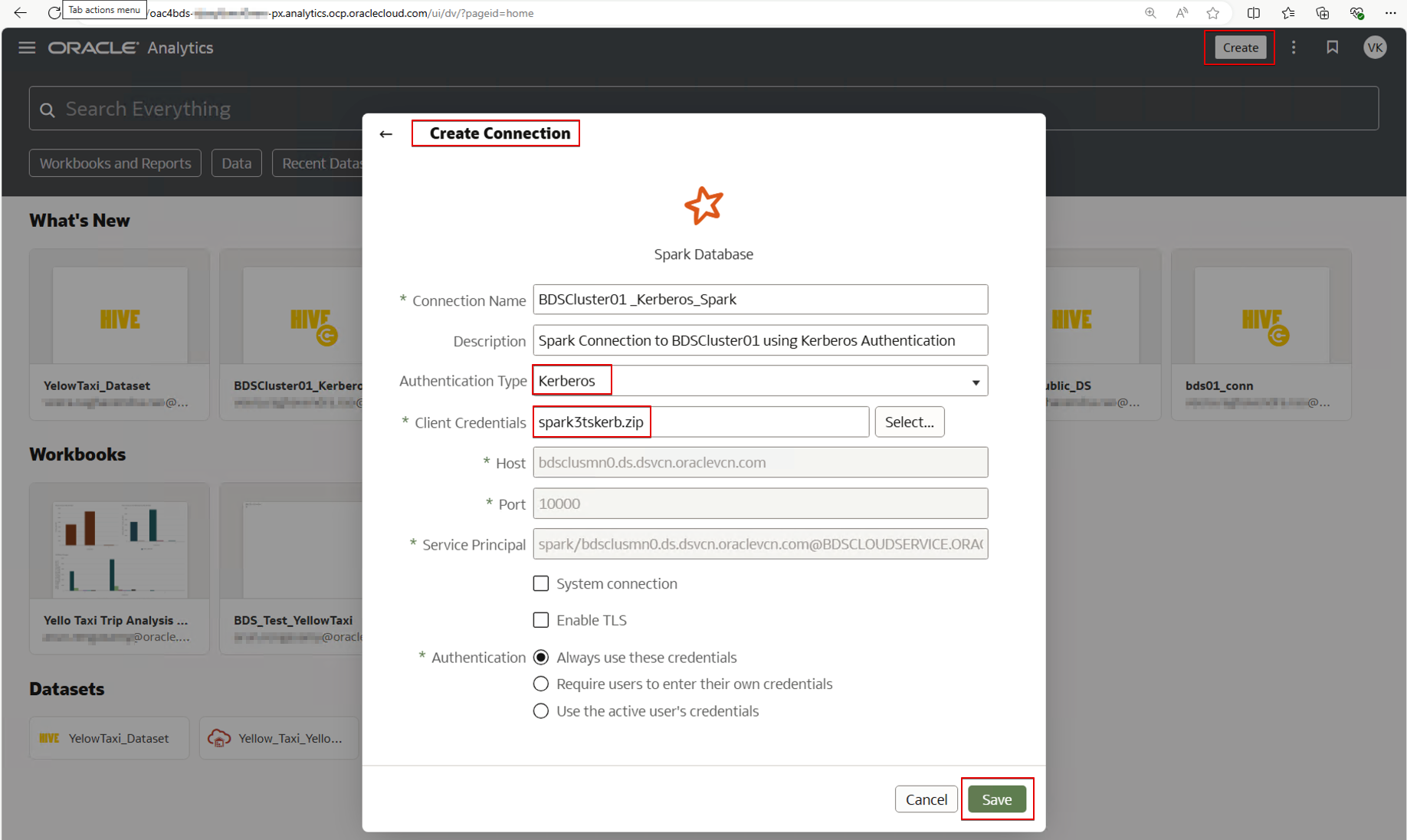
Create a Spark Connection
1. Sign in to OAC.
2. Create a Spark connection.
Create a Dataset from the BDS Connection
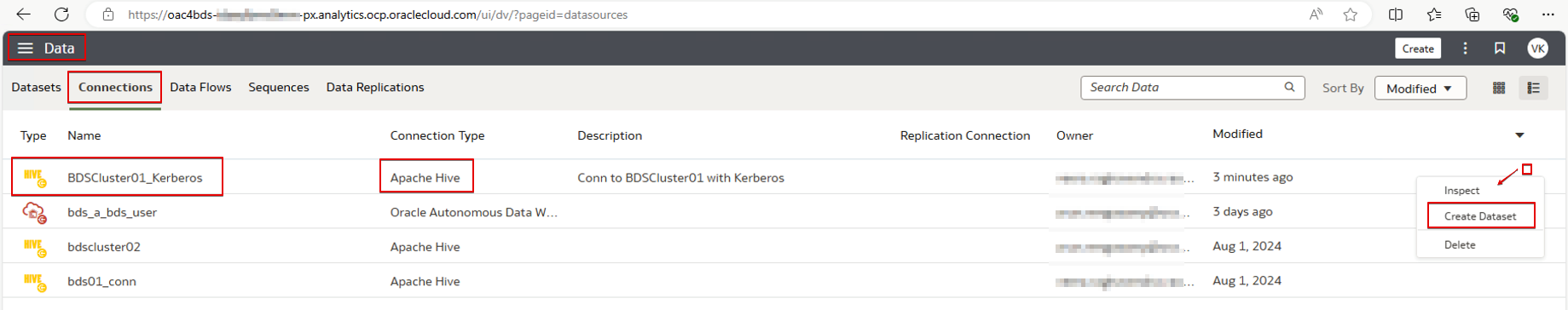
Create a New Dataset
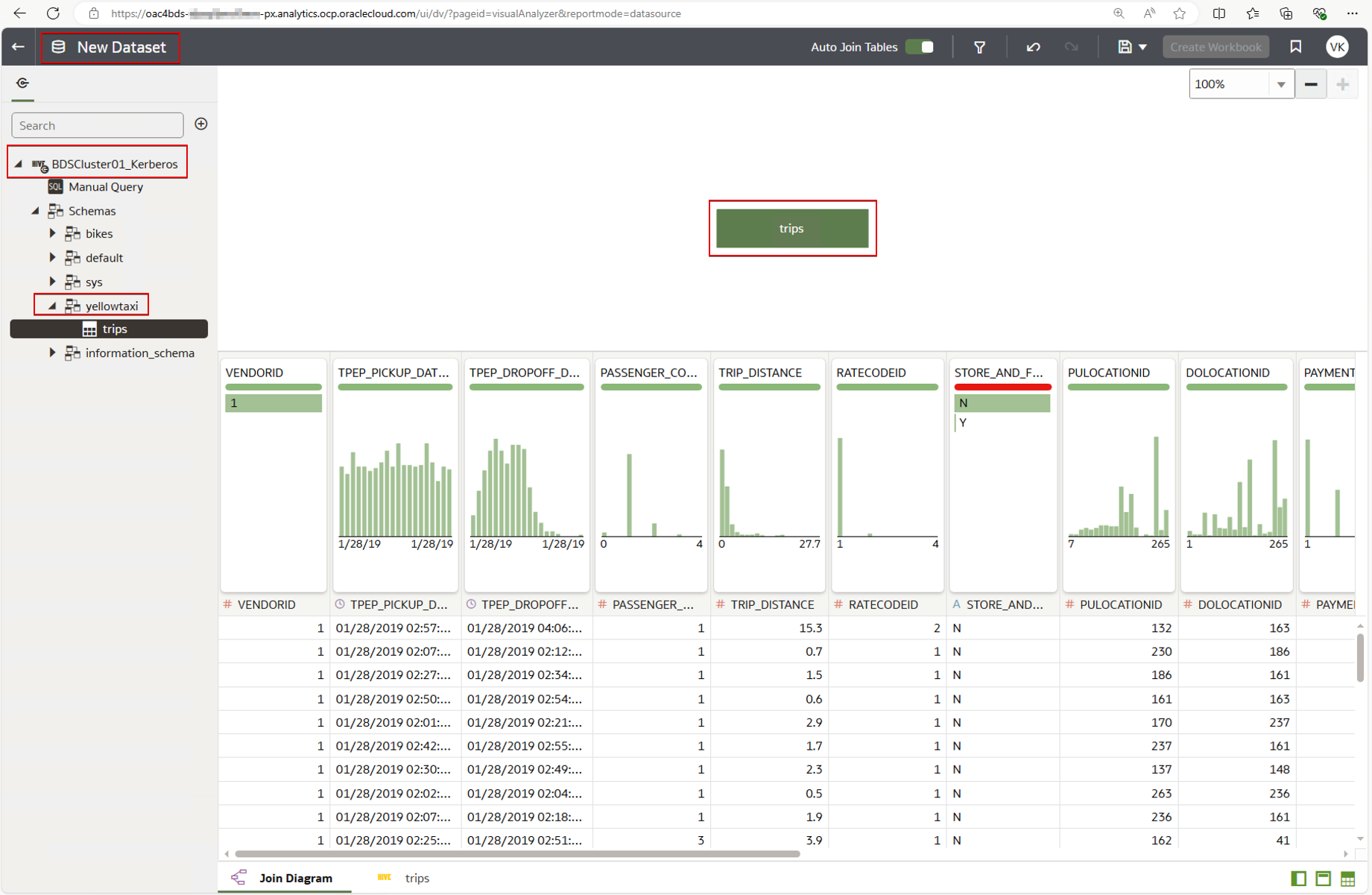
Transform the columns while creating the dataset. For example, you can convert the pickup and drop-off times to Linux timestamp format, and calculate trip duration from the difference between the trip drop-off and pickup time.
Create Workbooks using the Respective Datasets
After creating the dataset, create a workbook from the Hive connection.
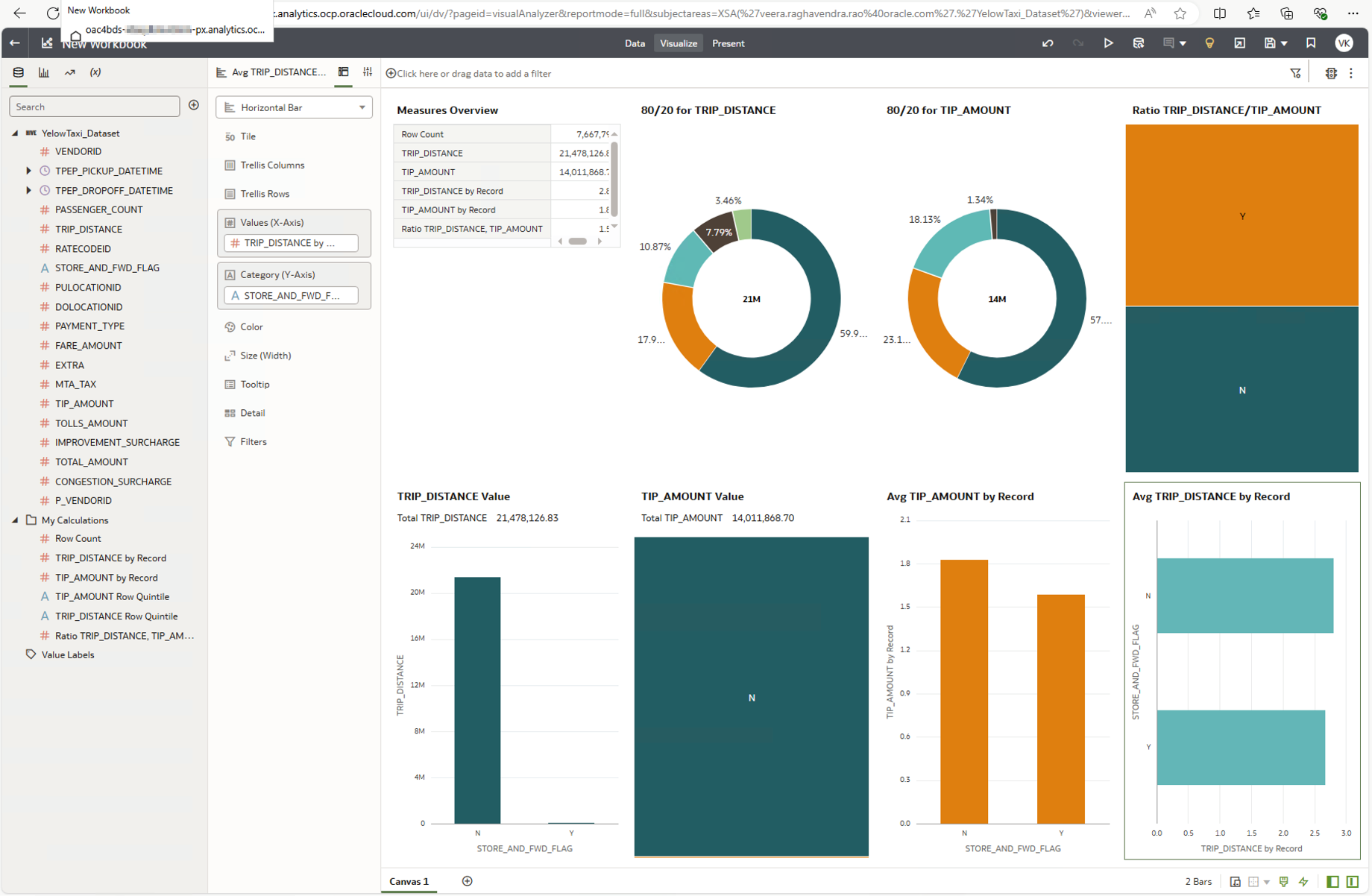
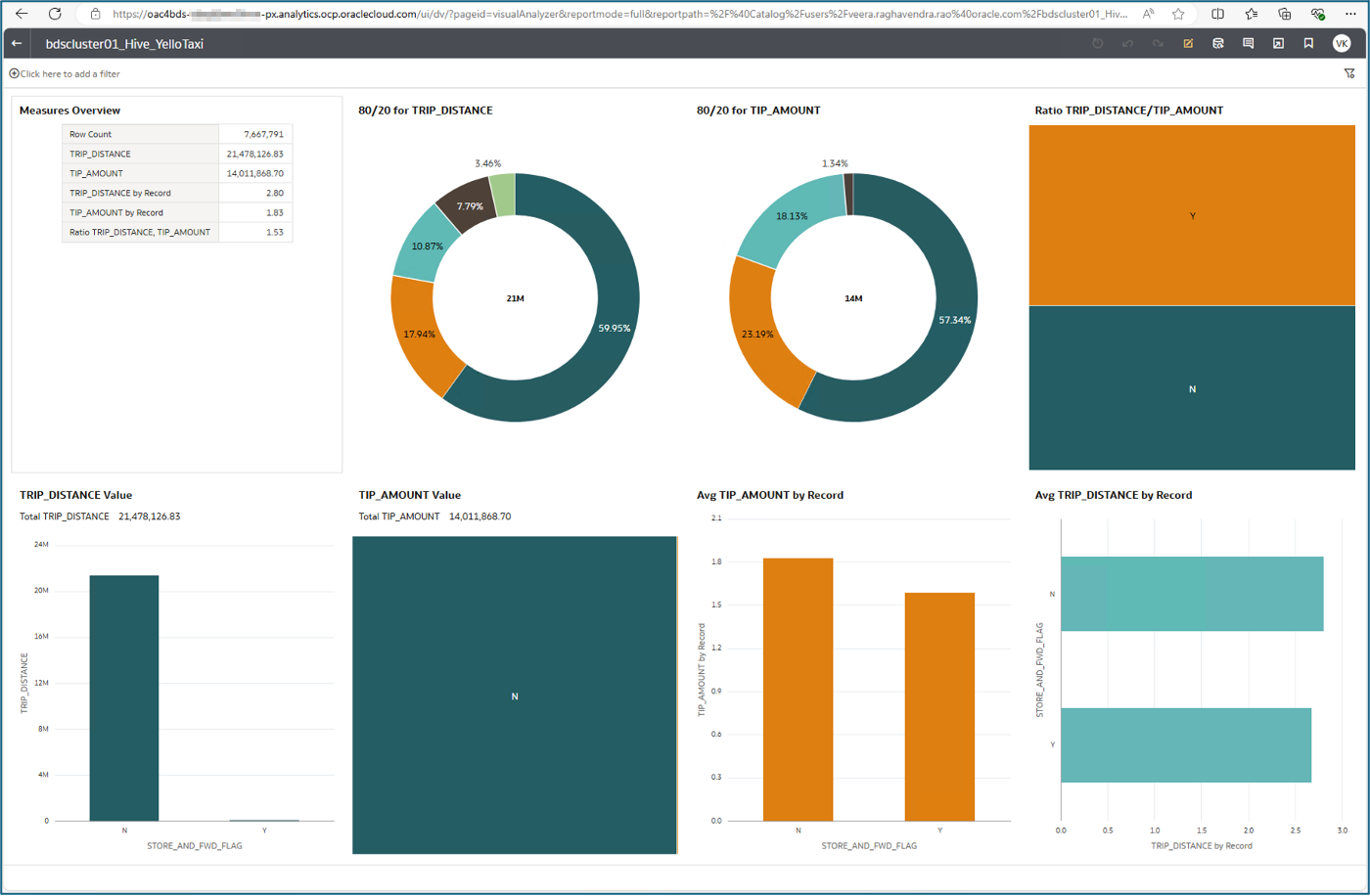
Similarly, create a workbook using the dataset you created from the Spark connection.
Call to Action
Now you’ve learnt how to connect to Oracle Big Data clusters from Oracle Analytics Cloud, try it yourself with your own Oracle Big Data Service clusters. Load your data files (typically extremely large and complex datasets that are difficult or impossible to process using traditional data processing methods) into Oracle Big Data Service clusters and transform the data. Connect Oracle Analytics Cloud to your Oracle BDS clusters and build enhanced data insights in Oracle Analytics Cloud.
If you have questions, post them in the Oracle Analytics Community and we’ll follow up with answers.
![]()

