![]()
Introduction
Audit logs play a critical role in ensuring transparency, compliance, and traceability within any cloud infrastructure. In Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), the Audit service emits detailed event logs that can be accessed through the OCI Console Logging Audit page or searched directly from the Search interface alongside other logs.
By default, Oracle allows you to export Audit Logs in JSON format for a custom time range of up to 14 days from the Oracle Cloud Console. While this meets the basic compliance needs, many organizations require extended visibility for periodic reviews, audits, and integration with downstream systems like Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) or Fusion Data Intelligence (FDI).
To support extended auditing, Oracle provides a tutorial for deploying a custom script that can export Audit Logs for periods longer than 14 days in CSV format. This is ideal for historical tracking and reporting.
In this article, we will walk through how to:
- Deploy a modified version of the custom OCI script to extract specific Audit-related fields from JSON logs
- Filter logs for OAC/FDI-specific compartments or user groups
- Convert the logs into a structured and incremental CSV format
- Integrate the output with OAC to enable automated and user-friendly auditing dashboards
Use Case
A common audit requirement in OAC/FDI environments is to track changes related to user group assignments and removals. These changes directly impact access controls, reporting permissions, and overall data security. By default, these logs only cover a maximum of 14 days and are available in JSON format, making them difficult to query, filter, and analyze—especially over longer periods or across large user bases.
This manual process isn’t scalable for enterprise environments where continuous compliance and proactive monitoring are required. Automating the export and transformation of these logs into a more accessible format is not just a convenience — it’s a necessity.
Prerequisites
- OCI Command Line Interface (CLI): You must install and configure OCI CLI on an existing OCI VM (if you have any) or server to deploy and schedule the Python scripts. The server should also have Python installed on it.
- OCI Permissions: Ensure you have necessary permissions in OCI for the user you configured in CLI.
- Deploy and Schedule Python Script: Deploy the script to export group-specific Audit logs and upload them to the OCI Object Storage bucket.
- Integration with Oracle Analytics: Create a connection to the Object Storage bucket in Oracle Analytics and a dataset using the CSV file in the bucket. Create a workbook using this dataset to report on the auditing requirements.
OCI Command Line Interface (CLI)
Follow these instructions to install and configure OCI CLI.
Verify if Python is installed on the VM/server using the following command:
python3 –version
OCI Permissions
The user configured in CLI config file must have appropriate permissions to:
- Read audit logs
- List and filter compartments
- Write to the target Object Storage bucket
Sample IAM Policy Snippets
To enable the CLI-configured user to read audit logs and write to Object Storage, attach the following policy to the appropriate group (in the tenancy or compartment level, as needed):
Allow group <your-group-name> to read audit-events in tenancy Allow group <your-group-name> to inspect compartments in tenancy Allow group <your-group-name> to manage objects in compartment <your-compartment-name> where target.bucket.name='<your-bucket-name>'
Deploy and Schedule the Python Script
Download the custom python script (Audit_Logs.py) to the VM or server where you’re deploying the scripts.
Create and navigate to the directory on the path where you want to deploy the Python script and copy the script to this directory.
mkdir <directory-name> cd <directory-name>
You can test the deployed script by executing it using the following command:
python3 Audit_Logs.py -s <log-start-date> -e <log-end-date> -c <compartment-id> -b <bucket-name> -g <comma separated list of group names>
Refer to the below tips for the parameters in the execution command:
- -s <log-start-date> : Start Date should be in YYYY-MM-DD format >”
- -e <log-end-date> : End Date should be in YYYY-MM-DD format >”
- -c <compartment-id> : OCID of the compartment your IAM domain is in >”
- -b <bucket-name> : Name of the Object Storage bucket you want your output file in >”
- -g <group-names> : This is an optional parameter. If you wish to export audit logs for all groups, you can skip this parameter in the execution command. To pass multiple group names, use a comma separated list of groups names. For example: -g “FAW Service Administrator, FAW Modeler”.
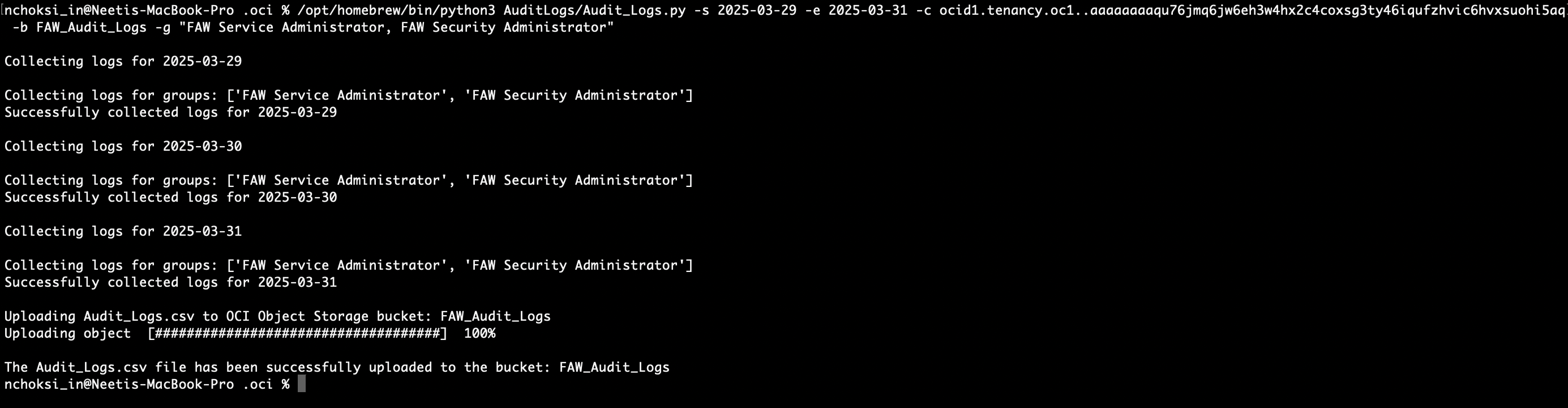
After running the script, the output file “Audit_Logs.csv” is saved in the Object Storage bucket provided in the -b parameter.
To schedule the file to run everyday, create a shell script called run_audit_logs.sh with the following content:
#!/bin/bash python3 /<PATH_TO_PYTHON_SCRIPT>/Audit_Logs.py \ -s $(date -v-1d +%Y-%m-%d) \ -e $(date +%Y-%m-%d) \ -c <Compartment OCID> \ -b <Bucket Name> \ -g "<comma separated group names>" #This line is optional
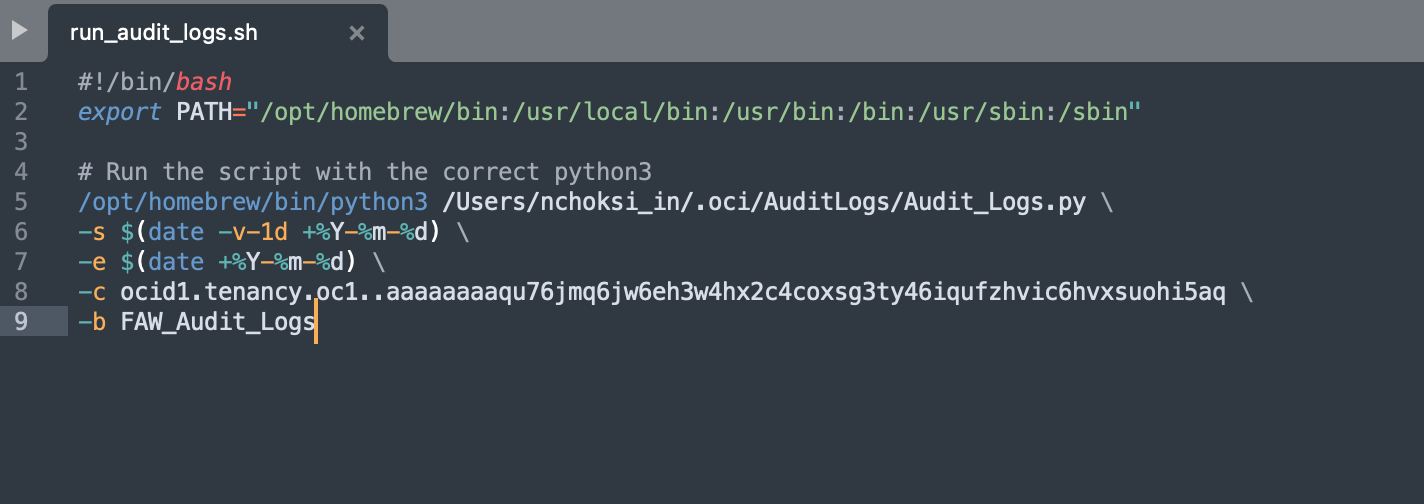
The above script exports and uploads logs for the last one day.
Grant execute permission to run_audit_logs.sh using the following command:
chmod -x run_audit_logs.sh
For Linux or macOS, the script can be scheduled by editing crontab with the execution command and scheduled as follows:
crontab -e 0 0 * * * /<PATH TO SHELL SCRIPT>/run_audit_logs.sh >> /<LOG FILE PATH>/audit_logs.log 2>&1
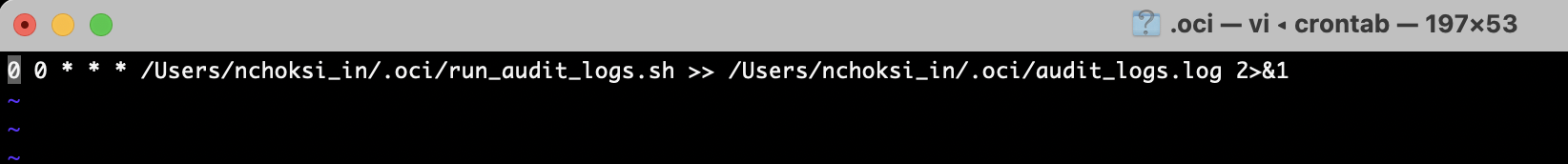
For example, the above job will run at 12:00 a.m. every day.
Save the file and verify the cron job is active using the following command:
crontab -l
For Windows machines, the equivalent batch script can be scheduled using Windows Scheduler.
Integrate with Oracle Analytics
Once the audit logs are exported and uploaded to Oracle Object Storage, the next step is to integrate the output with OAC for analysis and visualization.
Connection and Dataset
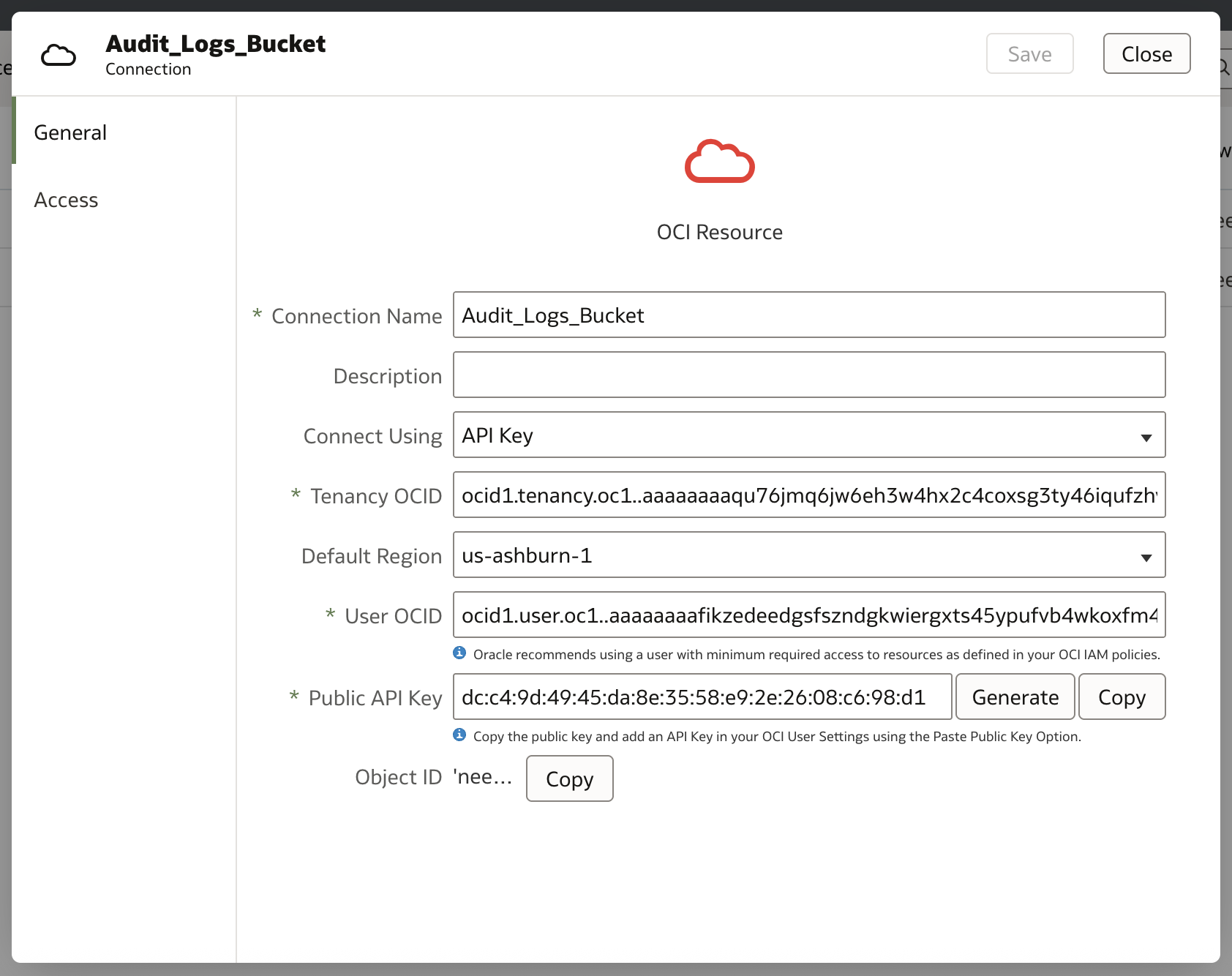
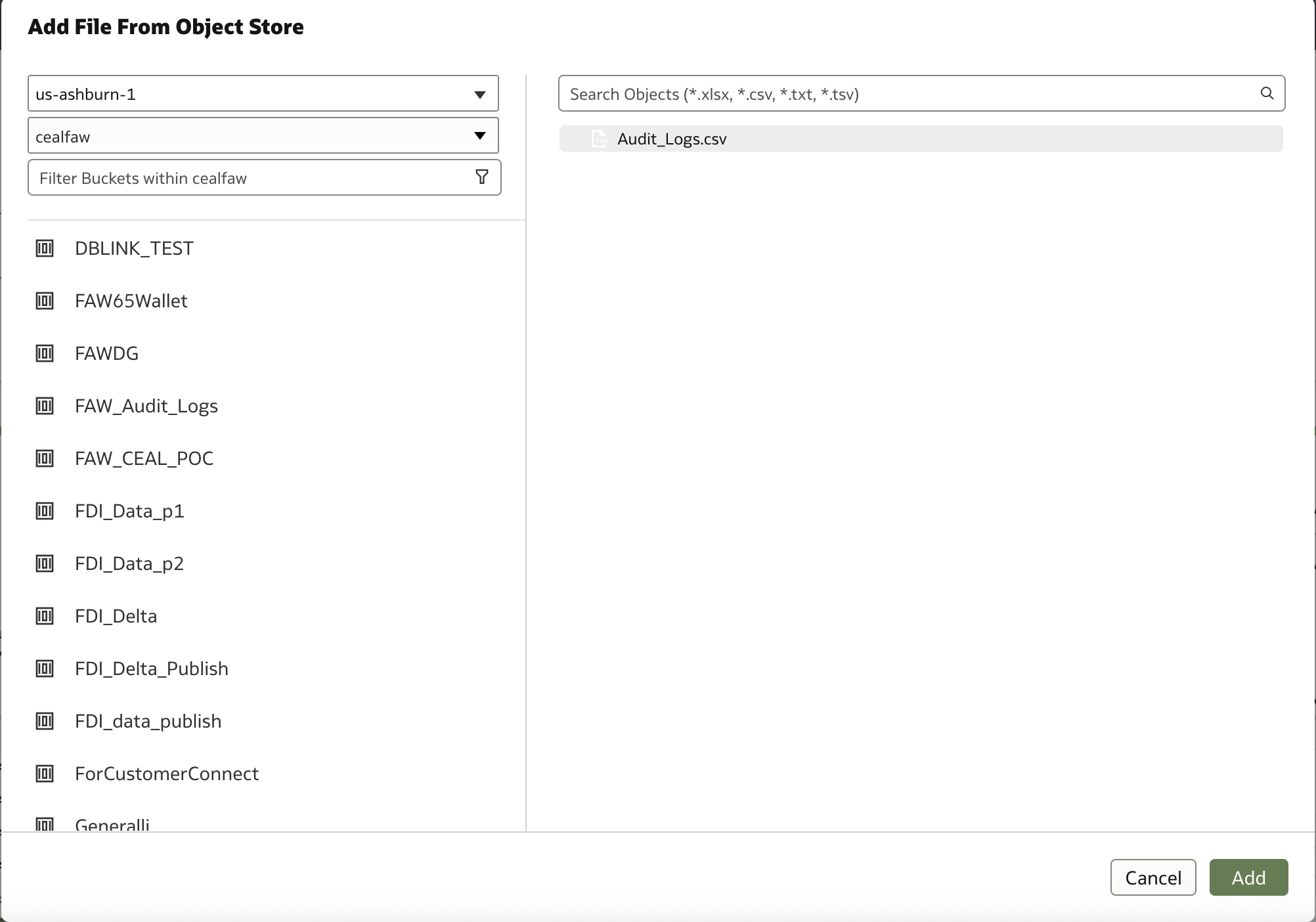
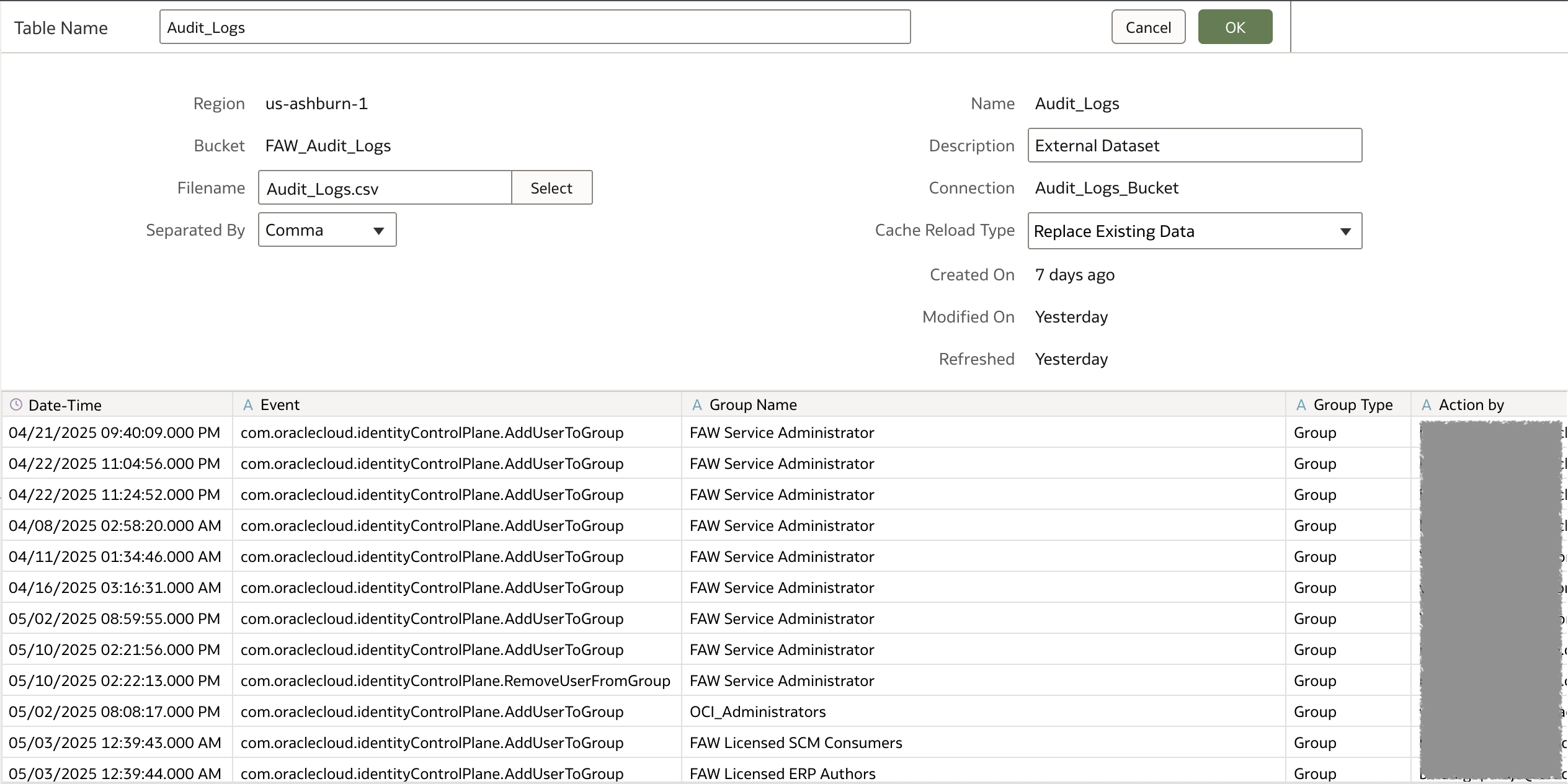
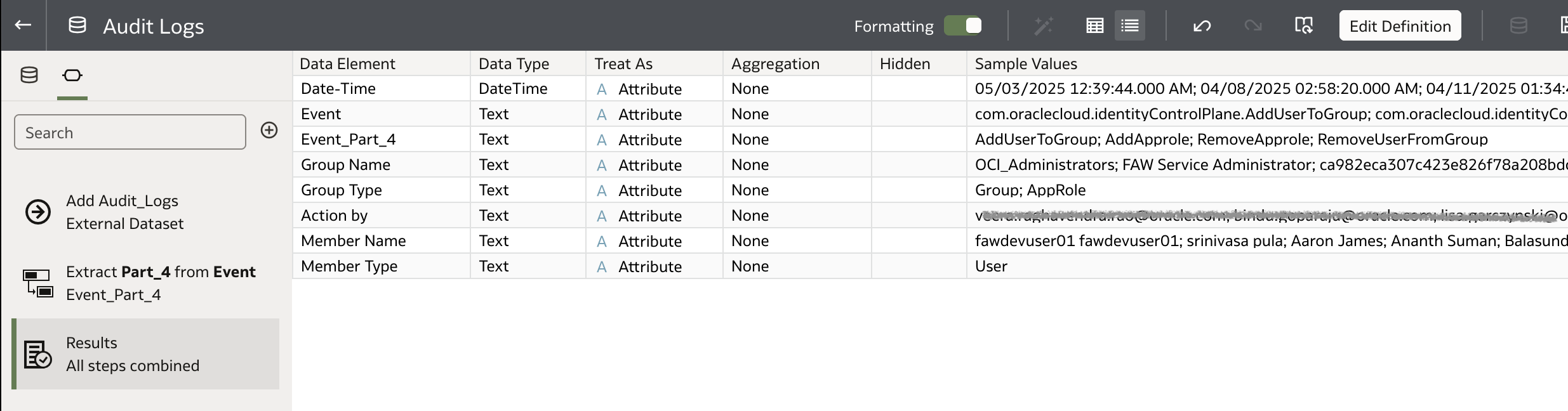
Create a Connection to Object Storage and create a dataset from the CSV file in the bucket. For more information on to the steps to create an Object Storage connection dataset, click here.
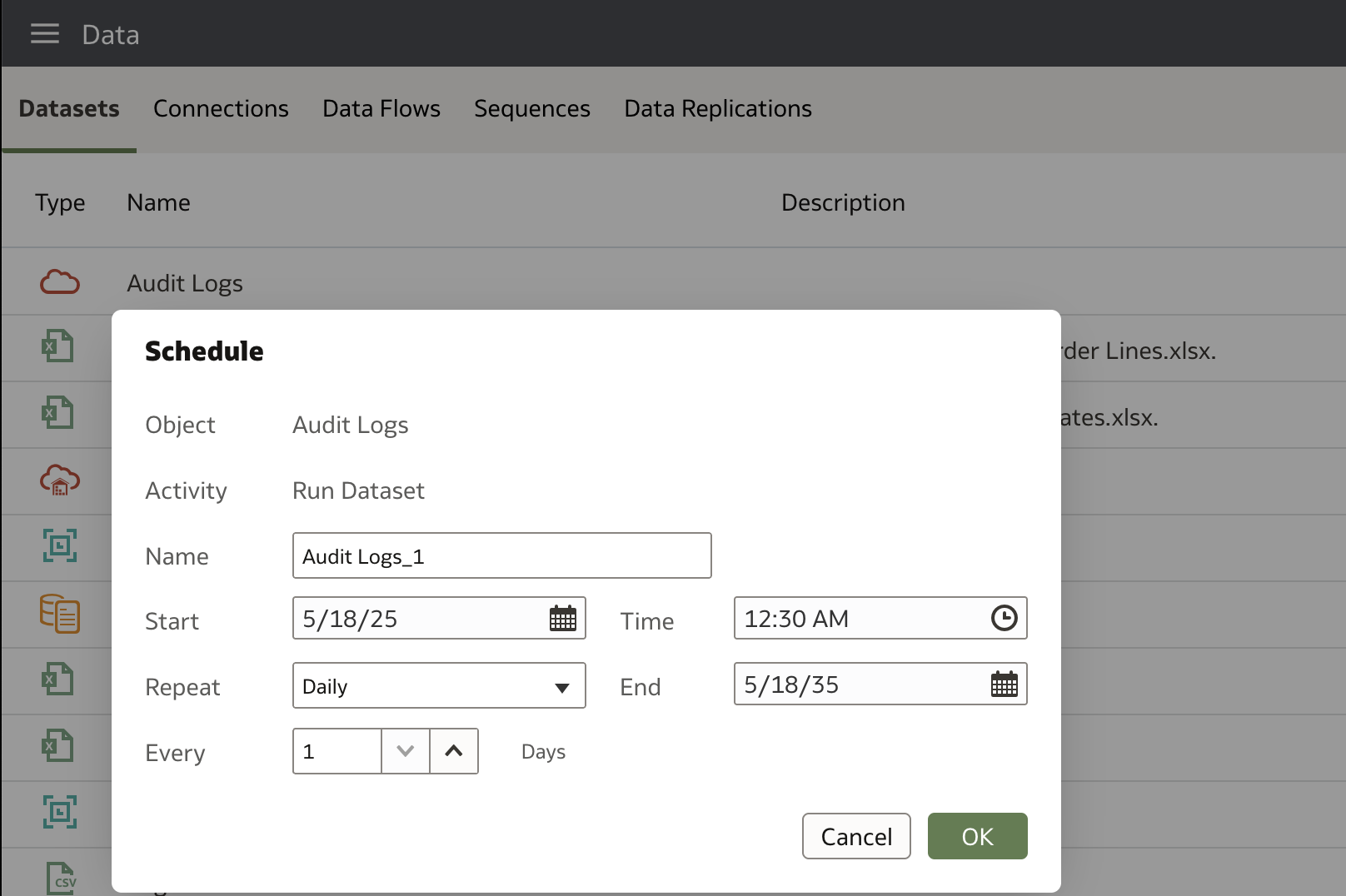
Dataset Refresh Schedule
Set up a refresh schedule to automatically update the dataset as new log exports are added.
Oracle Analytics Workbook
Build a workbook for audit analysis.
You can download a prebuilt sample workbook, along with the dataset and connection settings from here.
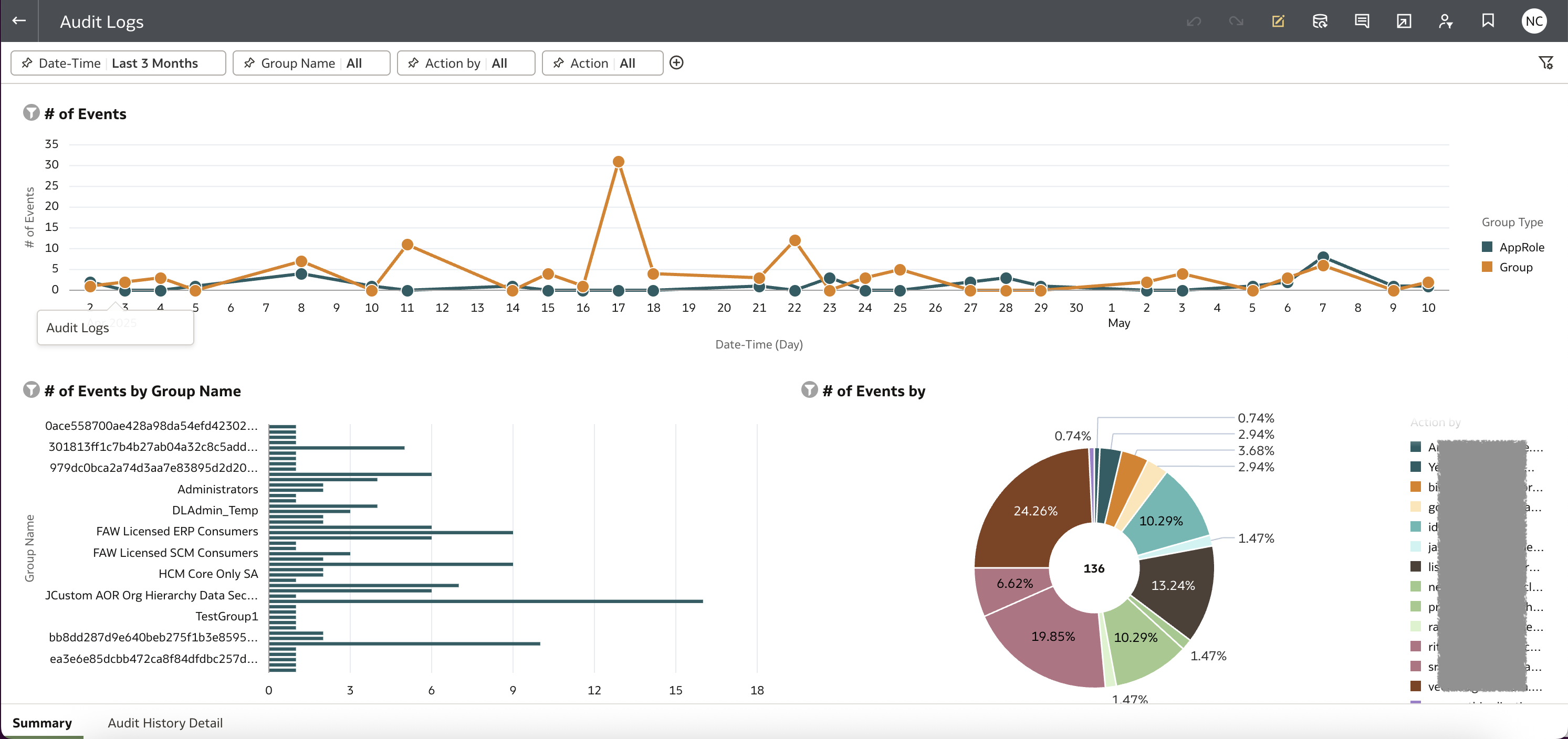
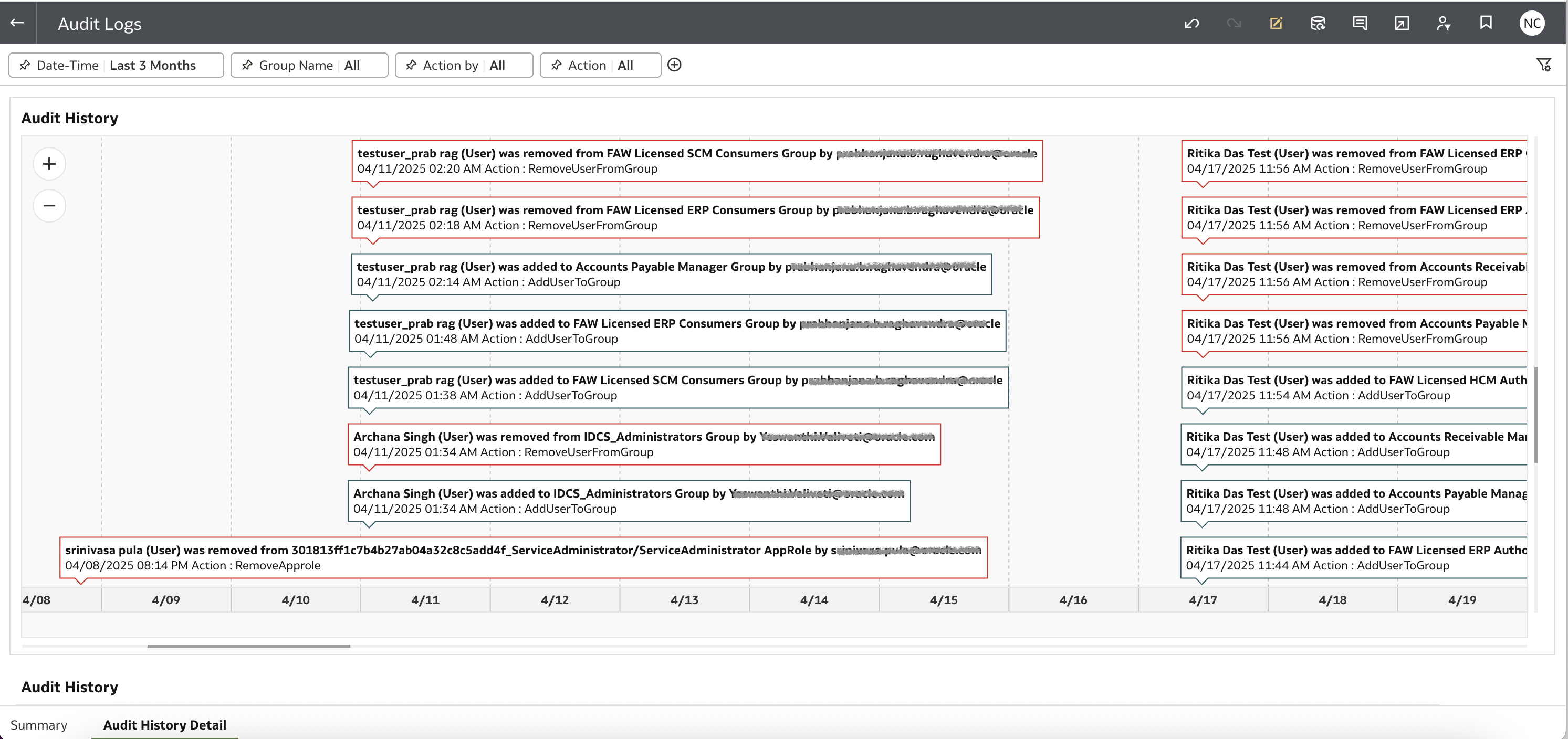
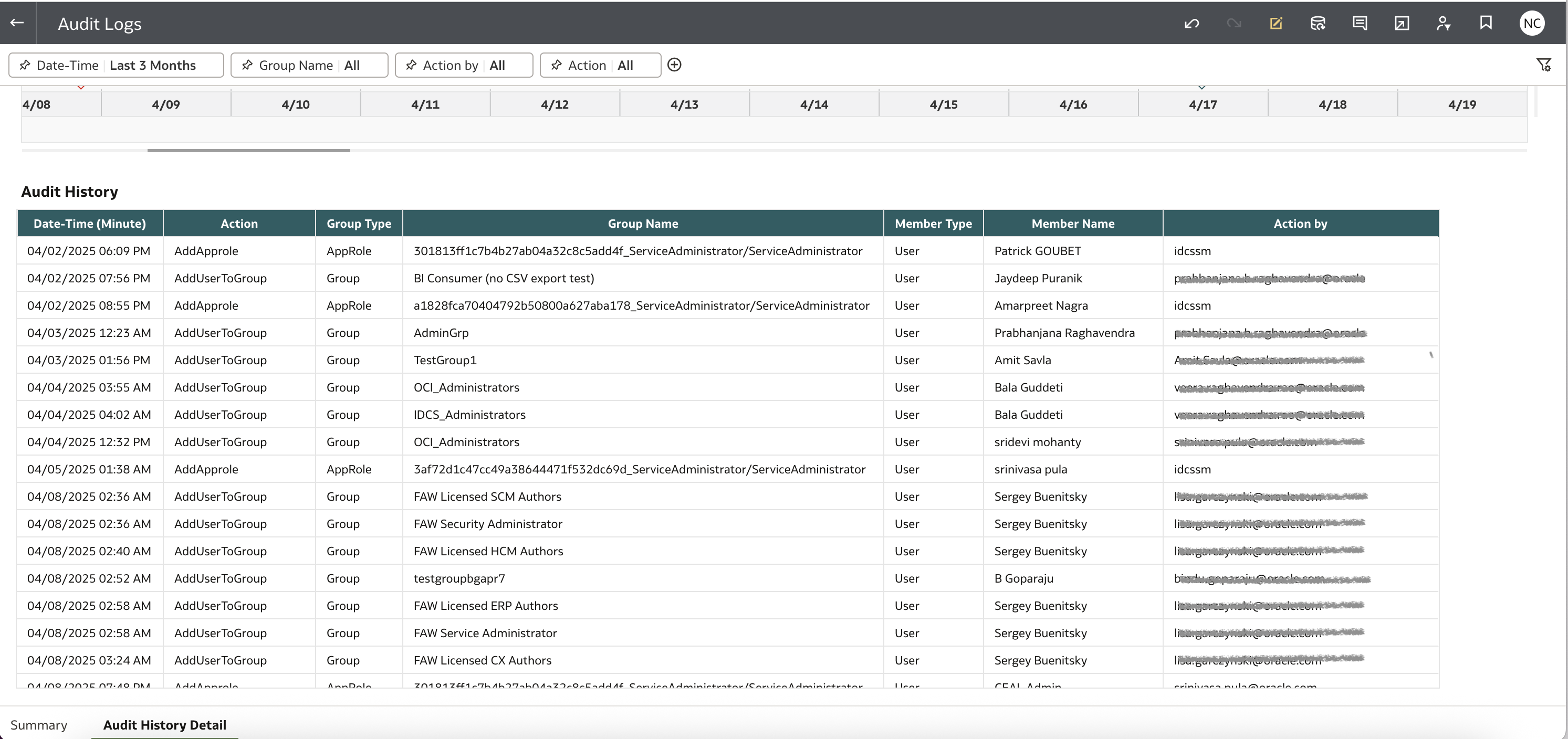
This integration enables your audit logs to become part of a centralized, visual, and continuously updated compliance dashboard — all within Oracle Analytics.
Call to Action
If you have questions, post them in the Oracle Analytics Community and we will follow up with answers.
![]()
