Oracle Analytics Cloud provides an AI Assistant that enables users to ask natural language questions and generate insights. It’s built using a generative AI large language model (LLM). While the AI Assistant is commonly accessed within the Oracle Analytics Cloud, it can also be embedded directly into custom HTML page using the supported embedding framework.
This article provides a step-by-step guide to embed the Oracle Analytics AI Assistant, explains the key components involved and outlines token-based embedding considerations for best practices.
Why Embed the AI Assistant?
Embedding the AI Assistant allows you to:
- Bring natural language analytics into custom applications
- Enable business users to explore data without navigating the Oracle Analytics Cloud console
- Combine dashboards and AI insights in a single unified UI
- Build modern analytics experiences for websites, portals, intranets, or demos
- Improve analytics adoption by non-technical users
Required Permissions for Using the Embedded AI Assistant
Access to the embedded AI Assistant is controlled through Roles and Permissions. Before enabling the AI Assistant in a custom HTML page, confirm with your Oracle Analytics administrator that users are assigned an application role that includes the Use Assistant in Workbooks permission.
By default, this permission is included in the DV Content Author application role. However, administrators may choose to create a custom application role and explicitly grant the Use Assistant in Workbooks permission to better align with organizational access and governance requirements.
Setup Guide
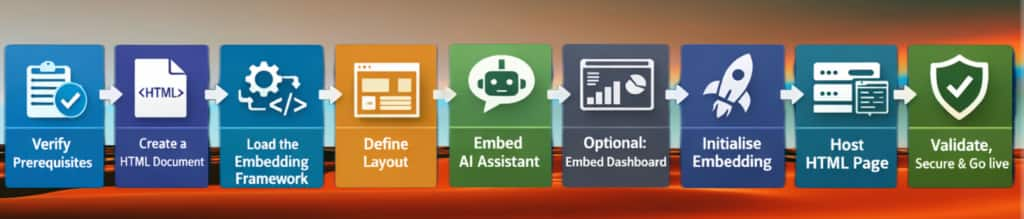
Prerequisites
- Oracle Analytics Cloud instance
- Users should have appropriate permissions to use the AI Assistant
- Access to data source to use with AI Assistant
- Embedding Page is served over HTTPS
- Add the hosting domain to Safe Domains in Oracle Analytics Cloud
Step 1: Create the HTML skeleton
Start with a standard HTML5 document and ensure UTF-8 encoding.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset=utf-8">
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Note:
The global dir attribute controls the layout direction of embedded page. It defines how text and interface elements are rendered within the embedded analytics components. When supporting multiple locales, especially those that require different reading directions, it’s recommended to dynamically set the dir attribute using JavaScript based on the user’s locale. The supported values are:
- ltr – Configures a left-to-right layout. This is the most commonly used option.
- rtl – Configures a right-to-left layout, suitable for languages such as Arabic or Hebrew.
- auto – Not supported for Oracle Analytics embedded content and should not be used.
Step 2: Load the Oracle Analytics embedding framework
Add the following <script> tag, Oracle Analytics embedding JavaScript, from your Oracle Analytics Cloud instance inside the <head> tag in the HTML code. You can find this script under the Embed section of Developer options in your Oracle Analytics Cloud instance.
<script
src="https://<your-oac-host>/public/dv/v2/embedding/auto/embedding.js"
</script>
Step 3: Define a full-height, scroll-free layout
A common issue with embedded analytics is unwanted scrolling caused by fixed heights or absolute positioning. A recommended approach is to use a viewport-based flex layout. This ensures:
- The AI Assistant occupies the full viewport height
- No vertical scrolling is introduced
- The layout adapts to different screen sizes
Include the <style> tag after the </script> tag.
<style>
html, body {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
oracle-analytics-assistant {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: block;
}
</style>
Step 4: Embed the AI Assistant
The AI Assistant is embedded using a custom web component and referenced to the data source to use. <oracle-analytics-assistant> tag is the tag that will embed the AI Assistant. Add the following code within <body> tag.
<oracle-analytics-assistant
id="oaAssistant"
src-data="["XSA('<user-name>'.'<data source name>')"]">
</oracle-analytics-assistant>
Note:
In XSA(‘<user-name>’.'<data source name>’)
- <user-name> represents the Oracle Analytics user under which the data source is accessed.
- <data source name> refers to the name of data source that the AI Assistant uses to interpret user questions.
Step 5: (Optional) Embed the AI Assistant alongside a dashboard
In many enterprise scenarios, AI Assistant is most effective when embedded alongside a dashboard rather than used in isolation. This pattern allows users to combine visual analytics with conversational exploration, enabling deeper insight discovery directly in context.
Why Embed the AI Assistant Next to a Dashboard?
- Ask follow-up questions about what they see in charts and tables
- Explore metrics without navigating away from the dashboard
- Investigate outliers, trends, or variances using natural language
- Reduce dependency on additional dashboard pages or filters
This approach supports a more interactive and exploratory analytics experience. <oracle-dv> tag is the tag that will embed the Dashboard and <oracle-analytics-assistant> tag is the tag that will embed the AI Assistant.
<div class="container">
<div class="analytics">
<oracle-dv
project-path="<project path>"
active-page="insight"
active-tab-id="snapshot!canvas!1"
</oracle-dv>
</div>
<div class="assistant">
<oracle-analytics-assistant
id="oaAssistant"
src-data="["XSA('<user-name>'.'<data source name>')"]">
</oracle-analytics-assistant>
</div>
</div>
Step 6: Initialize the embedded components
Once the page loads, all Oracle Analytics components must be initialized. This script initializes all embedded Oracle Analytics components on the page, including dashboards and the AI Assistant. Place this script after the embedded Oracle Analytics components in the HTML to ensure they are detected and initialized correctly.
<script>
oracle.oa.embedding.ready().then(oApp => oApp.applyBindings());
</script>
Step 7: Host the HTML file
Common options include:
- OCI Object Storage (static website)
- Application servers
- Enterprise web servers
Ensure the page is accessible over HTTPS.
Before embedded Oracle Analytics content (such as the AI Assistant or dashboards) can load inside an external HTML page, the hosting domain must be explicitly allowed in Oracle Analytics Cloud. Oracle Analytics enforces this restriction to prevent unauthorized embedding and to ensure that analytics content is only rendered in trusted web applications.
Steps to add the hosting domain to Safe Domains
To allow embedding, administrators must register the origin of the embedding page in the Safe Domains configuration.
- Sign in to Oracle Analytics Cloud as an administrator.
- Navigate to the Oracle Analytics Cloud Console, click Administration, and then Safe Domains.
- Select Add Domain.
- Enter the origin of the page hosting the embedded AI Assistant.
- Save the configuration.
To test your embedded page on your machine without a web server:
- Open a terminal in the same folder as your HTML file.
- Run: python -m http.server 8000 .
- Open Chrome and go to: http://localhost:8000/yourfilename.html.
- Add http://localhost:8000 to your Oracle Analytics Cloud instance console under Administration, and Safe Domains.
Authentication models for an embedded AI Assistant
Oracle Analytics supports two authentication models for embedded AI Assistant use cases.
Session-based embedding (without tokens)
Session-based embedding uses the existing Oracle Analytics user session. Users must be authenticated to Oracle Analytics Cloud.
Sample script:
<oracle-analytics-assistant
id="oaAssistant"
src-data="["XSA('<user-name>'.'<data source name>')"]">
</oracle-analytics-assistant>
<script>
oracle.oa.embedding.ready().then(oApp => oApp.applyBindings());
</script>
Token-based embedding (recommended)
Token-based embedding allows the AI Assistant to run under a token-defined identity, without requiring users to log in directly to Oracle Analytics.
Sample script:
<oracle-analytics-assistant
id="oaAssistant"
src-data="["XSA('<user-name>'.'<data source name>')"]">
</oracle-analytics-assistant>
<script>
const token = '<access token>';
oracle.oa.embedding.ready().then((oApp) => {
oApp.setEmbeddingConfig({
oSecurityConfig: {
eSecurityType: "token",
oOptions: {
credentials: "",
tokenAuthFunction: new Function("return '" + token + "'")
}
}
});
oApp.applyBindings();
});
</script>
Access token can be securely obtained from Oracle Analytics Cloud. You use an access token and a refresh token to obtain a new access token programmatically before an access token expires.
Conclusion
Embedding the Oracle Analytics AI Assistant into a custom HTML page enables organizations to deliver AI-driven, governed analytics experiences beyond the Oracle Analytics Cloud. By combining the supported embedding framework and secure authentication mechanisms, developers can integrate conversational analytics seamlessly into both internal and external applications—while maintaining security, performance, and governance.
This approach complements advanced enterprise AI architectures by bringing insight discovery directly to end users, exactly where it’s needed.
Call to action
Embedding the Oracle Analytics AI Assistant is available now in the November 2025 update. For a demo, check out this YouTube video.
Get Started Today
- ✅ Connect to your OAC instance
- ✅ Explore the Oracle Analytics AI Assistant
- ✅ Create a html page using the embedded version of Oracle Analytics AI Assistant
Join the Community
Have questions or want to share your journey?
Join the conversation in the Oracle Analytics Community, connect with other practitioners, and get expert insights.
Learn more
To learn more about Oracle Analytics Cloud:
- Visit the Oracle Analytics product page
- Follow twitter@OracleAnalytics
- Read the documentation on Oracle Help Center

