The Oracle Analytics AI Assistant is an AI-powered tool embedded in Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) that provides a conversational interface to help analysts become more productive. It’s built using a generative AI large language model (LLM) which translates natural language and delivers instant answers to analytical queries. OAC users can build and refine visualizations using the Assistant. You can add any visualizations created with the Assistant to your workbook or a watchlist.
Note: The Assistant is now a default feature and available with all OAC shapes, and there are no minimum CPUs restrictions.
Anatomy of the Assistant
Natural Language – Users can ask questions in any supported language: English, German, French, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Thai. These languages are officially supported by the underlying LLM. The Assistant responds to prompts made in unsupported languages, but responses use English, and may be unreliable.
Author and Consumer – The Assistant is available to workbook authors and consumers.
Datasets and Subject Areas – All types of datasets, such as single-table or multi-table datasets, along with subject areas, are supported.
Incremental – Conversations can be iterative, so a user can ask nested questions.
Smart Modifiers – Users can leverage Smart modifiers to convert visualizations. For example, changing a bart chart to line chart.
Watchlist – For anything you find interesting during the conversation, there’s an option to add in the watchlist.
How to use the Assistant
There are three steps to utilize the Assistant:
- Configure the generative AI
- Enable datasets and subject areas for the Assistant
- Open a workbook and ask questions
Configure the generative AI
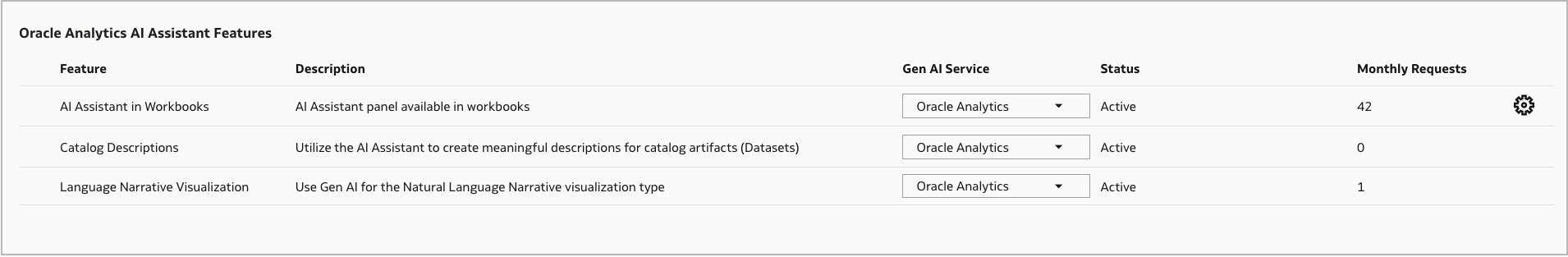
- From the OAC Home page, click Console, and then Generative AI.
- Here’s where you can enable all features for the generative AI:
- AI Assistant in Workbooks
- Catalog Descriptions
- Language Narrative Visualization
- Enable the AI Assistant in Workbooka feature, if it’s disabled.
Enable datasets
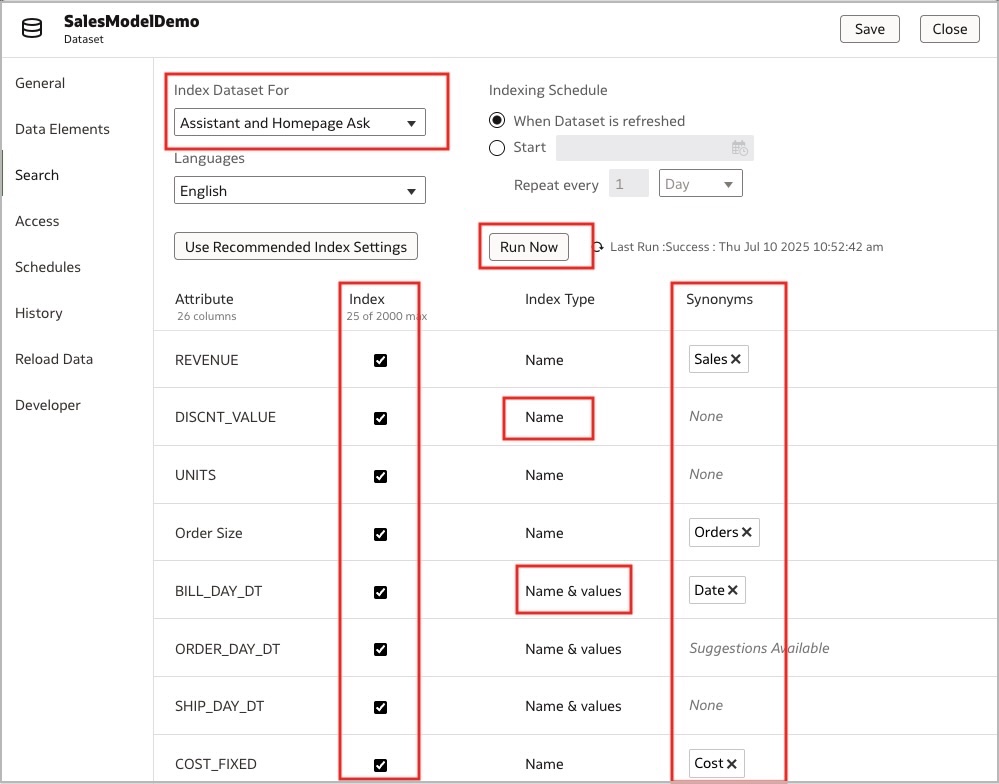
Once you configure the Assistant, the second step is to enable the dataset or subject area to use for queries in the Assistant.
- For the dataset, go to the Datasets tab and inspect the dataset by right-clicking the menu.
- Select Search from the right-hand menu.
- Select Assistant or Assistant and Homepage ask from the Index Dataset for drop-down menu. (The Assistant and Home page ask option enables the dataset for query using the Assistant and OAC Home page search).
- Select the Index option for all attributes you want to enable for the Assistant.
- Under Index Type, select the Name or Name and values.
Note: Select Name and values if the user will also ask a question on the attribute value. For example, “What is the total revenue for the country the United Kingdom?” United Kingdom is the value of the attribute, “country”. - Under Synonyms, provide all synonyms for an attribute. For example, some users may ask, “What is total sales?“ while others may ask, “What is total income?” In this case, use ‘income’ as the synonym for ‘sales’.
- Click Save and then Run Now to train the LLM on all selected attributes.
Enable subject areas
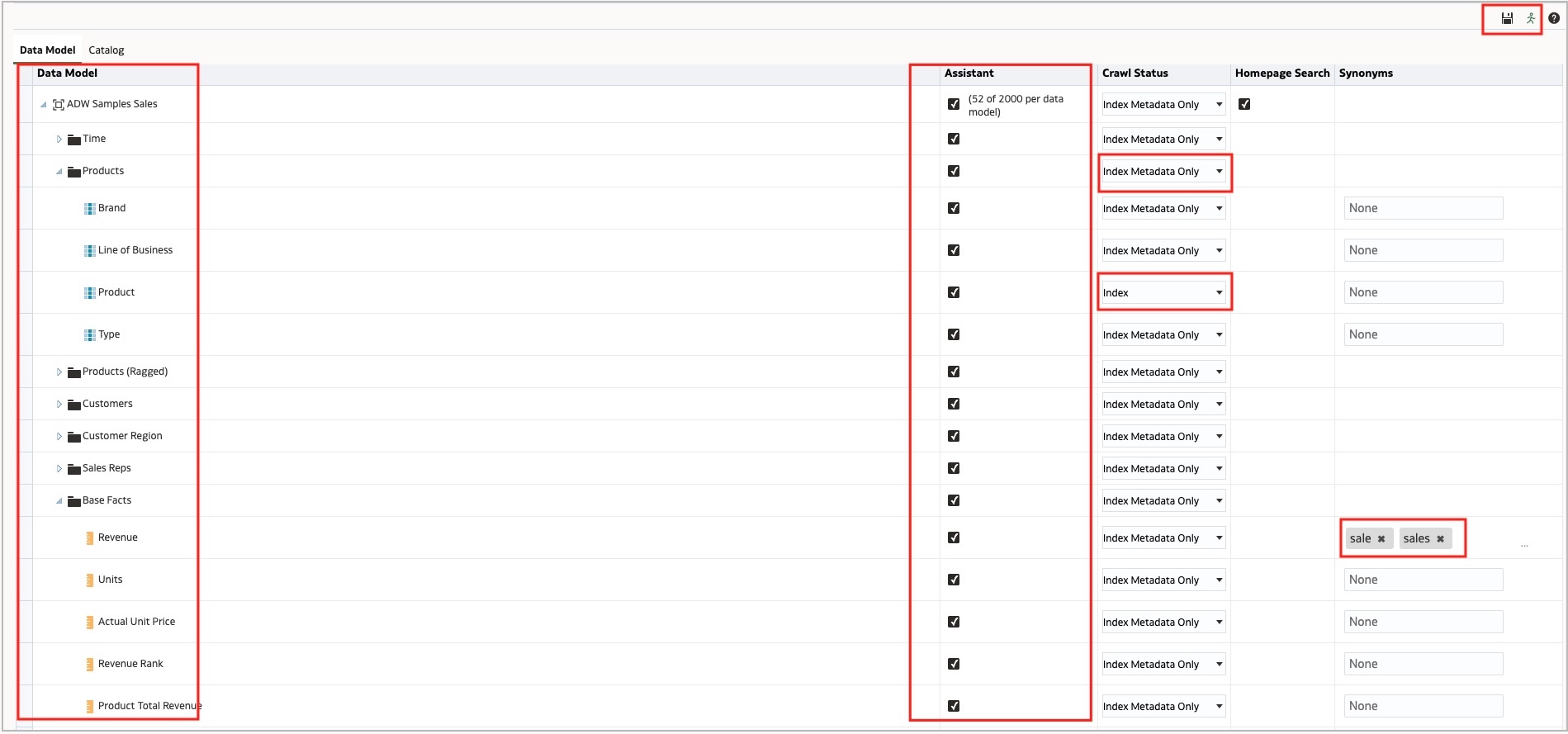
- For a subject area, from the OAC Home page, click Console, and then Search Index.
- Select the Assistant option for all attributes you want to enable for the Assistant.
- Under Crawl Status, select the Index Metadata Only or Index options.
Note: Select Index if the user will also ask a question on attribute value. For example, “What is the total revenue for the country the United Kingdom?” In this case, United Kingdom is the value of the attribute. - Under Synonyms, provide all synonyms for an attribute. For example, some users may ask the question, “What is total sales?, while others may ask, “What is total income?” In this case, use ‘income’ as the synonym for ‘sales’.
- Click Save and then click Run Now to train the LLM on all selected attributes.
Use the Assistant
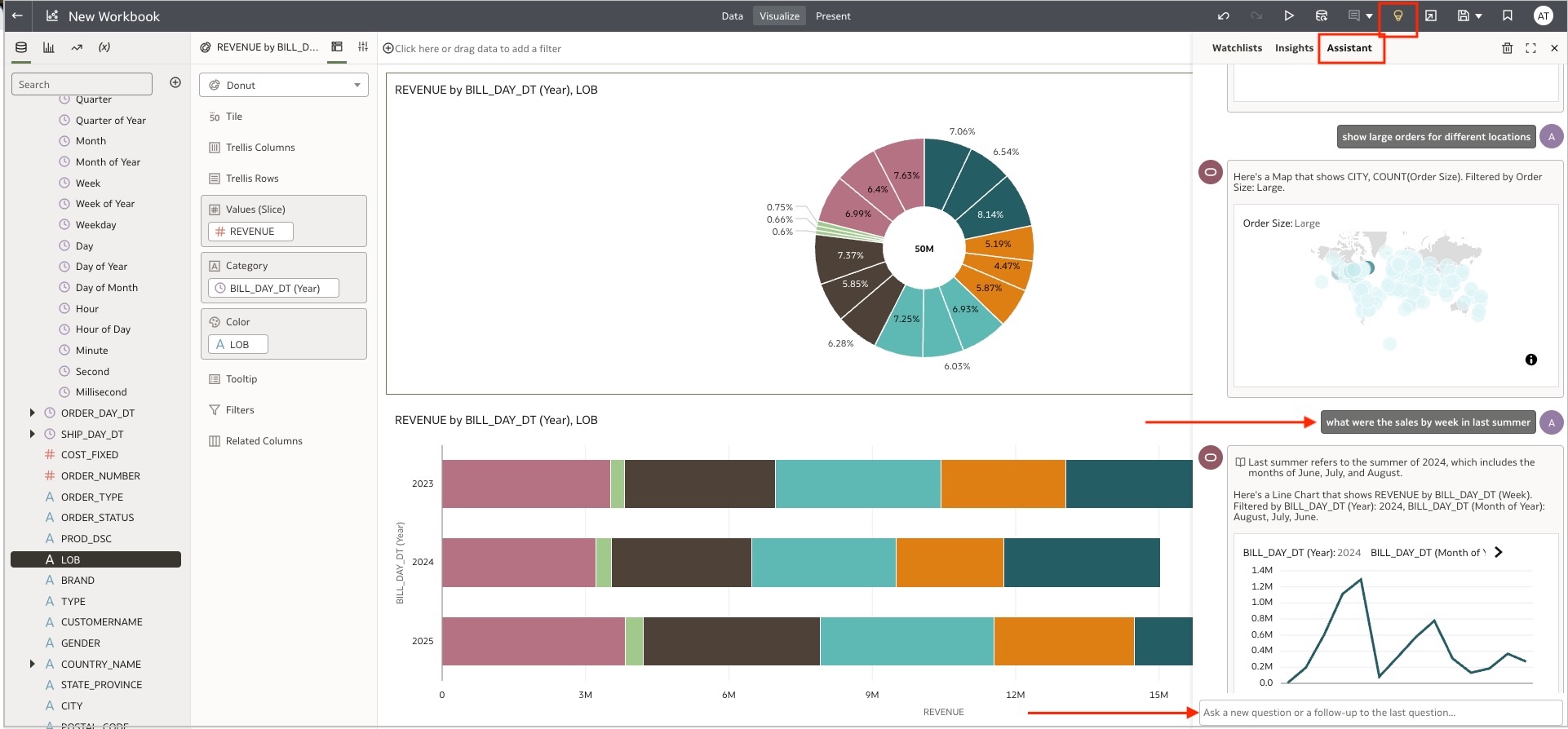
- To use the Assistant, create a workbook on a dataset or subject area.
- Click Auto Insight (lightbulb icon) to display the Assistant tab.
- Click the Assistant tab and start asking questions.
- You can use the Chart Type button to change the visualization type. Similarly, use the Add button to add any attribute in visualization, and the Change button to remove and add attributes
- Click the plus (+) to add visualizations to your canvas.
Enable the Assistant for consumers
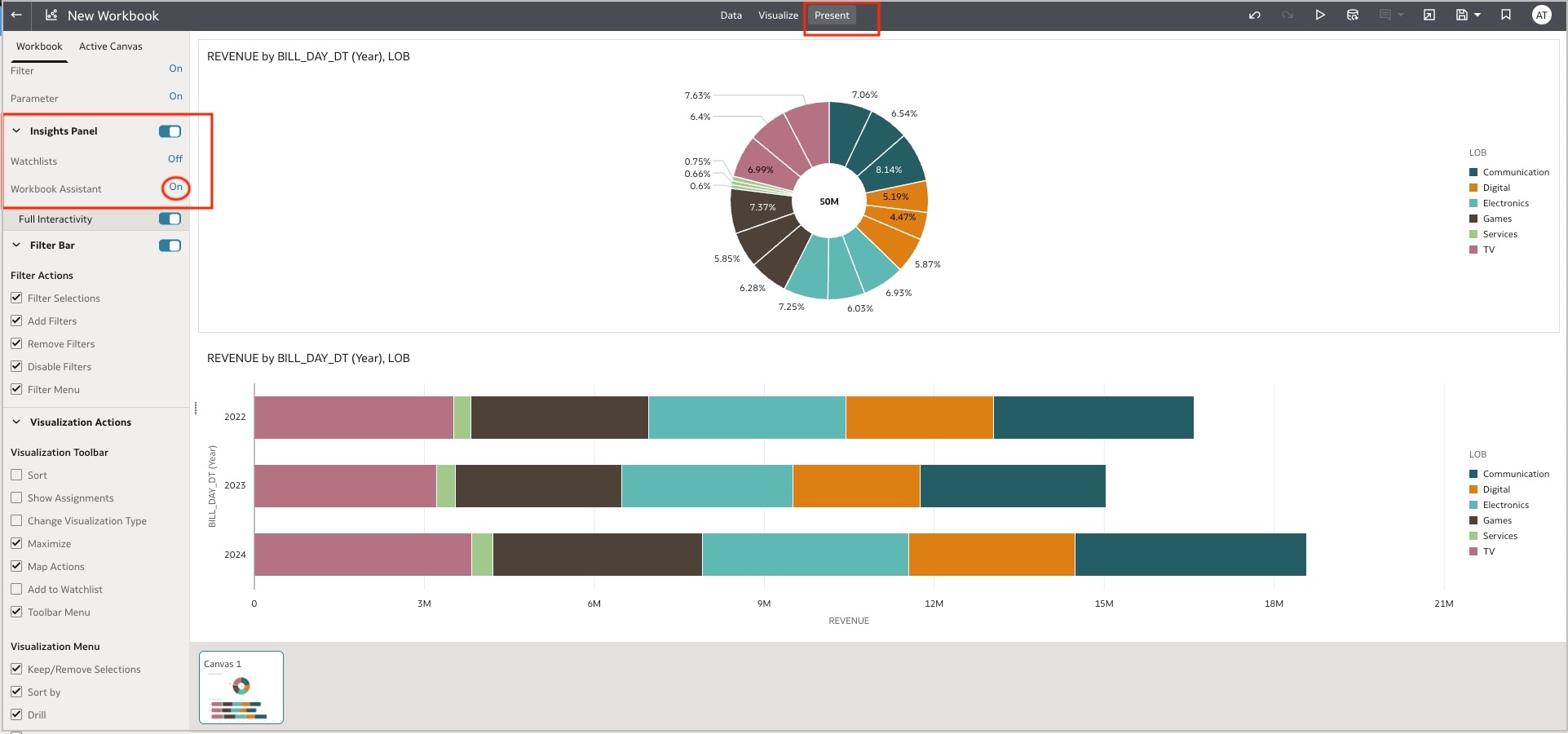
To enable the Assistant for consumers on a workbook, click the Present tab, and on the left-hand menu, under Insights Panel, toggle Workbook Assistant to On.
Basic guidelines for tuning the metadata (attributes) for the Assistant LLM
Here are some of the guidelines to keep in mind before you begin leveraging the Assistant:
- Enabling the indexes in the dataset or subject area allows you to control what users can ask about, so don’t index sensitive attributes.
- The LLM responds better with descriptive names, so always provide the descriptive names of measures and attributes. For example, use ‘Employee name’, not ‘Ename’.
- Identify the attributes that will most often be filtered on and enable them for indexes.
- Use synonyms. For example, some users may use ‘revenue’, where others use ‘profit’. So, use all possible synonyms so that the LLM can understand everyone’s questions and respond.
- Disambiguate similar data columns. For example, if you have multiple dates, such as invoice date, order date, and bill date, enable the index for the base date or default date; otherwise, if someone asks for “sales in the last quarter”, it might pick a random date.
- Use caution when using any special characters and reserved words in attributes such as @, count, total, etc.
- Convert numeric data into defined categories. For example, small, medium, or large orders or silver, gold, or platinum customers. Define what a ‘large order’ means. For example, this could be any order with more than 1,000 order lines. You can use the dataset binning function for this.
- Use the data preparation grouping feature. For instance, group ‘countries’ into ‘continents’.
- Remove null values. LLMs don’t understand nulls—for example, ‘not available’, ‘unknown’, etc.
Want to know more about Oracle Analytics Cloud?
To explore more about OAC, check out the links below, and always feel free to share your experience in the Oracle Analytics Community.
